Deck 8: Risk, Return, and Portfolio Theory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Risk, Return, and Portfolio Theory
1
The chance or possibility that outcomes may not turn out as expected is best described by:
A) risk
B) variance
C) diversification
D) standard deviation
A) risk
B) variance
C) diversification
D) standard deviation
risk
2
Which of the following would not describe risk?
A) Uncertainty
B) The possibility of incurring harm or the chance of a loss
C) Chance that future outcomes may not turn out as expected
D) Depreciation in the price of an asset from some starting point in time
A) Uncertainty
B) The possibility of incurring harm or the chance of a loss
C) Chance that future outcomes may not turn out as expected
D) Depreciation in the price of an asset from some starting point in time
Depreciation in the price of an asset from some starting point in time
3
A potential investor looks up the historical returns for Capital World Growth and Income Fund. He finds that that as of the November 30, 2012 the 1-year return is 16.14 percent, the 3-year return is 5.65 percent, the 5-year return is -1.14 percent, the 10 year return is 9.80 percent, and the lifetime return is 10.71 percent. These returns are examples of:
A) capital yield.
B) income yield.
C) ex post return.
D) ex ante return.
A) capital yield.
B) income yield.
C) ex post return.
D) ex ante return.
ex post return.
4
Complete the following: Advertisements for mutual funds and other investments show historical or _____________ returns and then have a disclaimer that past returns do not necessarily reflect future or _____________ returns.
A) ex post; ex ante
B) ex ante; ex post
C) ex post; capital yield
D) capital yield; income yield
A) ex post; ex ante
B) ex ante; ex post
C) ex post; capital yield
D) capital yield; income yield

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) Expected return is the estimated future return.
B) Expected return is often estimated using historical averages.
C) Expected return can be calculated using weights to represent the probabilities of possible returns.
D) Using historical averages to calculate expected return is the best method to use for short-term forecasts.
A) Expected return is the estimated future return.
B) Expected return is often estimated using historical averages.
C) Expected return can be calculated using weights to represent the probabilities of possible returns.
D) Using historical averages to calculate expected return is the best method to use for short-term forecasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) Expected return is the estimated future return.
B) Expected return is often estimated using historical averages.
C) Expected return can be calculated using weights to represent the probabilities of possible returns.
D) Using historical averages to calculate expected return is the best method to use for short-term forecasts.
A) Expected return is the estimated future return.
B) Expected return is often estimated using historical averages.
C) Expected return can be calculated using weights to represent the probabilities of possible returns.
D) Using historical averages to calculate expected return is the best method to use for short-term forecasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A member of your investment club tells you they are a day trader. This individual must:
A) follow a value investing philosophy.
B) work on one of the stock exchanges.
C) follow a buy and hold investing philosophy.
D) buy and sell based on intraday price movements.
A) follow a value investing philosophy.
B) work on one of the stock exchanges.
C) follow a buy and hold investing philosophy.
D) buy and sell based on intraday price movements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Total return on your company's stock for 2012 was 9.0%. Income yield was 2.5%. The capital yield is closest to:
A) 6.5%
B) 9.00%
C) 11.5%
A) 6.5%
B) 9.00%
C) 11.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the following probability distribution of possible returns to a project:
 The expected return is closest to:
The expected return is closest to:
A) 0%
B) 4.5%
C) 6.5%
 The expected return is closest to:
The expected return is closest to:A) 0%
B) 4.5%
C) 6.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Consider the following probability distribution of possible returns to a project:
 The expected return is closest to:
The expected return is closest to:
A) -1%
B) 0%
C) 3%
 The expected return is closest to:
The expected return is closest to:A) -1%
B) 0%
C) 3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) Total Return = Income yield + capital gain (or loss) yield.
B) The trend over the past 30 years has been declining dividend yields.
C) Capital gain is the depreciation in the price of an asset from some starting point in time.
D) Dividend yield can change for two reasons - changes in the dividends per share or changes in the stock price.
A) Total Return = Income yield + capital gain (or loss) yield.
B) The trend over the past 30 years has been declining dividend yields.
C) Capital gain is the depreciation in the price of an asset from some starting point in time.
D) Dividend yield can change for two reasons - changes in the dividends per share or changes in the stock price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When evaluating your portfolio at year end, you notice that the mutual fund you bought a year ago for $14 is now trading for $17. The mutual fund has recently paid a $1.00 dividend. Your total return is closest to:
A) 7.14%
B) 21.43%
C) 23.53%
D) 28.57%
A) 7.14%
B) 21.43%
C) 23.53%
D) 28.57%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When evaluating your portfolio at year end, you notice that the mutual fund you bought a year ago for $18 is now trading for $16. The mutual fund has recently paid a $.50 dividend. The total return is closest to:
A) -8.33%
B) 2.78%
C) 8.33%
D) 15.63%
A) -8.33%
B) 2.78%
C) 8.33%
D) 15.63%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When interested in the rate of return performance of an investment over time it is best to use:
A) the arithmetic mean.
B) the geometric mean.
C) either the arithmetic mean or the geometric mean.
D) neither the arithmetic mean nor the geometric mean.
A) the arithmetic mean.
B) the geometric mean.
C) either the arithmetic mean or the geometric mean.
D) neither the arithmetic mean nor the geometric mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider a project that provides a return of 2 percent in the first year, 10 percent in the second year, 15 percent in the third year, and 3 percent in the fourth year. The geometric mean return over these four years is closest to:
A) 1.07%
B) 7.37%
C) 7.50%
D) 32.90%
A) 1.07%
B) 7.37%
C) 7.50%
D) 32.90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider a project that provides a return of -2 percent in the first year, 10 percent in the second year, 15 percent in the third year, and -3 percent in the fourth year. The geometric mean return over these four years is closest to:
A) 4.72%
B) 5.00%
C) 7.37%
A) 4.72%
B) 5.00%
C) 7.37%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When evaluating your portfolio at last year's end, you notice that the value of your portfolio was $100,000. The value of your portfolio at this year's end is $112,000, and you received cash dividends of $1,000 at the end of the first six months of this year and $1,200 in cash dividends at year end. The total return and the holding period yield (i.e., internal rate of return) are closest to:
A) 13.2 percent and 13.73 percent, respectively
B) 13.2 percent and 13.79 percent, respectively
C) 14.2 percent and 13.73 percent, respectively
D) 14.2 percent and 13.79 percent, respectively
A) 13.2 percent and 13.73 percent, respectively
B) 13.2 percent and 13.79 percent, respectively
C) 14.2 percent and 13.73 percent, respectively
D) 14.2 percent and 13.79 percent, respectively

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The measure of dispersion calculated as the difference between the maximum and minimum values is best described as the:
A) range.
B) variance.
C) standard deviation.
D) ex post standard deviation.
A) range.
B) variance.
C) standard deviation.
D) ex post standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is not a measure of dispersion?
A) range.
B) variance.
C) weighted mean.
D) standard deviation.
A) range.
B) variance.
C) weighted mean.
D) standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) The range is a measure of dispersion.
B) The standard deviation is a more common measure of risk than range.
C) The range is calculated as the difference between the maximum and minimum values.
D) The range is a good measure of risk because it captures the variability of returns between the maximum and minimum values.
A) The range is a measure of dispersion.
B) The standard deviation is a more common measure of risk than range.
C) The range is calculated as the difference between the maximum and minimum values.
D) The range is a good measure of risk because it captures the variability of returns between the maximum and minimum values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A statistical measure of the degree to which two or more series move together or co-vary is best described as:
A) variance.
B) covariance.
C) diversification.
D) standard deviation.
A) variance.
B) covariance.
C) diversification.
D) standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is not a statistical measure of the degree to which two or more series move together or co-vary?
A) covariance.
B) correlation.
C) standard deviation.
A) covariance.
B) correlation.
C) standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements is true?
A) A correlation of -2 is a perfect negative correlation.
B) The correlation coefficient may be greater than +1.
C) A correlation equal to +1 is a perfect positive correlation.
D) A zero correlation indicates a strong relation between the returns on the two assets.
A) A correlation of -2 is a perfect negative correlation.
B) The correlation coefficient may be greater than +1.
C) A correlation equal to +1 is a perfect positive correlation.
D) A zero correlation indicates a strong relation between the returns on the two assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Stocks in the same industry can be expected to have a correlation coefficient of zero.
B) A correlation coefficient of zero indicates there is no relationship between the returns on the two assets.
C) The closer the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is to 1, the stronger the relationship between the returns on the two assets.
D) Generally, security returns display positive correlations with one another, but these correlations are less than one because most stocks tend to follow the movements of the overall market.
A) Stocks in the same industry can be expected to have a correlation coefficient of zero.
B) A correlation coefficient of zero indicates there is no relationship between the returns on the two assets.
C) The closer the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is to 1, the stronger the relationship between the returns on the two assets.
D) Generally, security returns display positive correlations with one another, but these correlations are less than one because most stocks tend to follow the movements of the overall market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Following is a chart of the correlation between the returns of stock C and stock D. 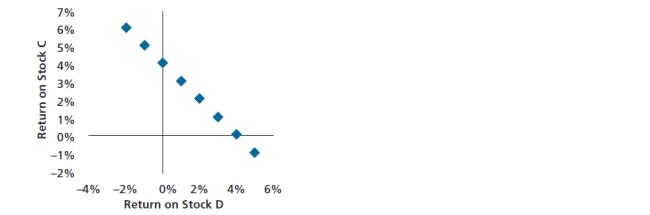 The correlation between the two returns is best described as:
The correlation between the two returns is best described as:
A) no correlation.
B) positive correlation.
C) negative correlation.
D) perfect negative correlation.
 The correlation between the two returns is best described as:
The correlation between the two returns is best described as:A) no correlation.
B) positive correlation.
C) negative correlation.
D) perfect negative correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Following is a chart of the correlation between the returns of stock E and stock F. The correlation between the returns on these two stocks is best described as:
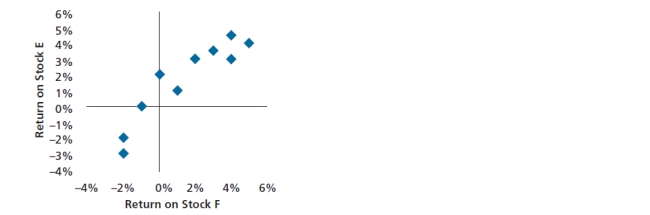
A) no correlation.
B) positive correlation.
C) negative correlation.
D) perfect negative correlation.

A) no correlation.
B) positive correlation.
C) negative correlation.
D) perfect negative correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Stock returns are typically:
A) positively correlated with the returns of other stocks.
B) negatively correlated with the returns of other stocks.
C) perfectly, positively correlated with the returns of other stocks.
D) perfectly, negatively correlated with the returns of other stocks.
A) positively correlated with the returns of other stocks.
B) negatively correlated with the returns of other stocks.
C) perfectly, positively correlated with the returns of other stocks.
D) perfectly, negatively correlated with the returns of other stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Diversification is most effective when the returns on assets are:
A) positively correlated with the returns of other assets.
B) negatively correlated with the returns of other assets.
C) perfectly, positively correlated with the returns of other assets.
D) perfectly, negatively correlated with the returns of other assets.
A) positively correlated with the returns of other assets.
B) negatively correlated with the returns of other assets.
C) perfectly, positively correlated with the returns of other assets.
D) perfectly, negatively correlated with the returns of other assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Using the given correlation matrix, which of the following statements is incorrect? 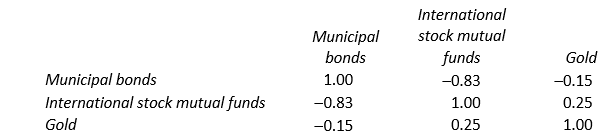
A) Gold and municipal bonds are perfectly, negatively correlated.
B) Gold and international stock mutual funds are positively correlated.
C) There is a negative correlation between the returns on international stock mutual funds and municipal bonds.
D) If one owned lots of municipal bonds, a good diversification strategy would be to purchase international stock mutual funds.

A) Gold and municipal bonds are perfectly, negatively correlated.
B) Gold and international stock mutual funds are positively correlated.
C) There is a negative correlation between the returns on international stock mutual funds and municipal bonds.
D) If one owned lots of municipal bonds, a good diversification strategy would be to purchase international stock mutual funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Using the given correlation matrix of these product lines, which of the following statements is correct? 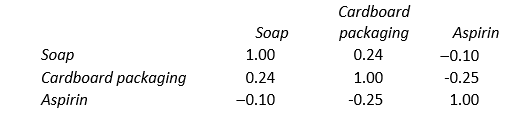
A) Aspirin and Soap are positively correlated.
B) Soap and packaging are positively correlated.
C) Soap and Aspirin are perfectly negatively correlated.
D) A company with these three lines of business has perfectly, positively correlated line of business.
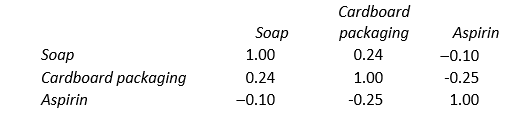
A) Aspirin and Soap are positively correlated.
B) Soap and packaging are positively correlated.
C) Soap and Aspirin are perfectly negatively correlated.
D) A company with these three lines of business has perfectly, positively correlated line of business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is the basis for hedging?
A) No correlation
B) Negative correlation
C) Perfect positive correlation
D) Perfect negative correlation
A) No correlation
B) Negative correlation
C) Perfect positive correlation
D) Perfect negative correlation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the likely correlation between milk, bread, and rice?
A) Zero
B) Positive
C) Negative
D) Perfect negative
A) Zero
B) Positive
C) Negative
D) Perfect negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the likely correlation between gold and speculative internet stocks?
A) Zero
B) Positive
C) Negative
D) Perfect negative
A) Zero
B) Positive
C) Negative
D) Perfect negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose that you read that the stock prices of drug companies do not vary with gross domestic product (GDP). This would mean that the correlation between the drug company stock prices and GDP is:
A) Zero
B) Positive
C) Negative
D) Perfect negative
A) Zero
B) Positive
C) Negative
D) Perfect negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the following time series:
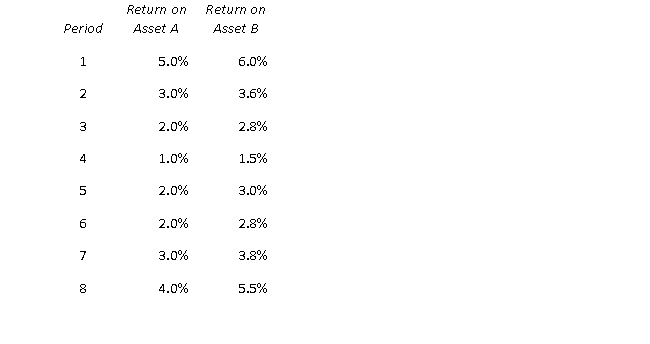 The correlation between these two series is best described as:
The correlation between these two series is best described as:
A) Zero
B) Positive
C) Negative
D) Perfectly positive
 The correlation between these two series is best described as:
The correlation between these two series is best described as:A) Zero
B) Positive
C) Negative
D) Perfectly positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The collection of investments that offers the highest expected return for a given level of risk, or offers the lowest risk for a given expected return is best described as a(n):
A) hedged portfolio.
B) efficient portfolio.
C) diversified portfolio.
D) maximized portfolio.
A) hedged portfolio.
B) efficient portfolio.
C) diversified portfolio.
D) maximized portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Complete the following: Modern Portfolio ______ is a set of theories that explain how _________investors, who are risk ________, can select a set of investments that ____________ the expected return for a given level of _______.
A) Theory; some; seekers; maximize; risk
B) Theory; rational; averse; maximize; risk
C) Theory; rational; seekers; maximize; investment
D) Construction; many; averse; maximize; investment
A) Theory; some; seekers; maximize; risk
B) Theory; rational; averse; maximize; risk
C) Theory; rational; seekers; maximize; investment
D) Construction; many; averse; maximize; investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is not an assumption of Modern Portfolio Theory?
A) Investors are risk averse.
B) Investors are rational decision makers.
C) Risk comes from not knowing what you are doing.
D) Investors' preferences are based on a portfolio's expected return and risk.
A) Investors are risk averse.
B) Investors are rational decision makers.
C) Risk comes from not knowing what you are doing.
D) Investors' preferences are based on a portfolio's expected return and risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following portfolios could not lie on the efficient frontier? 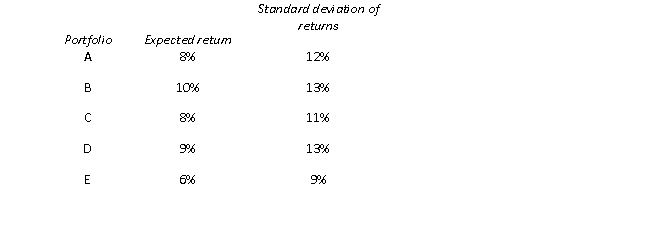
A) Portfolio E
B) Portfolio A and Portfolio D
C) Portfolio A, Portfolio C and Portfolio E
D) Portfolios A, B, C, D and

A) Portfolio E
B) Portfolio A and Portfolio D
C) Portfolio A, Portfolio C and Portfolio E
D) Portfolios A, B, C, D and

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following portfolios could not lie on the efficient frontier? 
A) Portfolio A
B) Portfolio B
C) Portfolio A and Portfolio B
D) All of these portfolios could lie on the efficient frontier

A) Portfolio A
B) Portfolio B
C) Portfolio A and Portfolio B
D) All of these portfolios could lie on the efficient frontier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following portfolios could not lie on the efficient frontier? 
A) Portfolio A
B) Portfolio E
C) Portfolio A and Portfolio D
D) Portfolio A, Portfolio B and Portfolio C

A) Portfolio A
B) Portfolio E
C) Portfolio A and Portfolio D
D) Portfolio A, Portfolio B and Portfolio C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An investor throwing darts at the NYSE stock listings in the newspaper to select stocks to invest in is an example of:
A) unique risk.
B) efficient portfolio
C) portfolio management
D) random diversification.
A) unique risk.
B) efficient portfolio
C) portfolio management
D) random diversification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Total risk is equal to market risk plus:
A) beta risk.
B) unique risk.
C) systematic risk.
D) nondiversifiable risk.
A) beta risk.
B) unique risk.
C) systematic risk.
D) nondiversifiable risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following would not be an example of random diversification?
A) Throwing darts at the stock listings to select a portfolio of stocks.
B) Purchasing whichever stocks were recommended by the expert on a financial program.
C) Stocks selected from asking all of your friends their favorite stock and then putting together a portfolio from them.
D) A portfolio recommended by your financial planner, which includes a variety of different investments and stocks from various industries, countries, and company sizes.
A) Throwing darts at the stock listings to select a portfolio of stocks.
B) Purchasing whichever stocks were recommended by the expert on a financial program.
C) Stocks selected from asking all of your friends their favorite stock and then putting together a portfolio from them.
D) A portfolio recommended by your financial planner, which includes a variety of different investments and stocks from various industries, countries, and company sizes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) Risk can be totally eliminated by diversification.
B) "Not putting all our eggs in the same basket" is an example of diversification.
C) Diversification is the reduction of risk by investing funds across several assets.
D) As long as the correlation between two assets returns is not perfect, positive, there is a benefit to combining assets into portfolios.
A) Risk can be totally eliminated by diversification.
B) "Not putting all our eggs in the same basket" is an example of diversification.
C) Diversification is the reduction of risk by investing funds across several assets.
D) As long as the correlation between two assets returns is not perfect, positive, there is a benefit to combining assets into portfolios.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Ex ante means "after the fact."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
CF1/P0 is the formula for total return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A paper loss is taxable to the owner of the security.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Carrying securities at the current market value regardless of whether they are sold is called mark to market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The sum of all returns divided by the number of observations is called geometric mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Geometric mean return is a better estimate of long-run investment performance than the arithmetic mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In financial decision analysis, ex post returns are used when we look forward into the future, ex ante returns are used when we look back at what has happened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Assets offering higher expected rates of return tend to be riskier than those offering a lower rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Ex ante standard deviation is a forward-looking measure of risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Expected return on a portfolio is always a weighted average of the expected return on each individual asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
By combining assets into portfolios we can reduce risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Perfect positive correlation is the basis for hedging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The correlation coefficient between returns on a portfolio and a potential investment of the portfolio that most likely will provide the greatest diversification benefits for a given portfolio is 1.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The correlation coefficient between returns on a portfolio and a potential investment of the portfolio that most likely will provide the greatest diversification benefits for a given portfolio is 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Risk tolerators dislike risk and require compensation to assume additional risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The father of Modern Portfolio Theory is Warren Buffet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An attainable portfolio is one that lies along the minimum variance frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Rational, risk-averse investors are only interested in holding portfolios that are on the efficient frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The new frontier is the set of portfolios that offers the highest expected return for their given level of risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Total Risk = Market Risk + Beta Risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The part of risk that is not eliminated by diversification is market risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Diversification in a company requires selecting products or projects whose cash flows are not highly correlated with one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Diversification can only exist when the assets' returns are negatively correlated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Benefits to diversification are constant, meaning adding one more stock to a two stock portfolio has the same effect as adding one more stock to a thousand-stock portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the arithmetic mean return for Generic Company stock given the following information:



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
There is much uncertainty regarding projected cash flows for your firm's newest location. Analysts provide you with the following possible scenarios and probabilities:
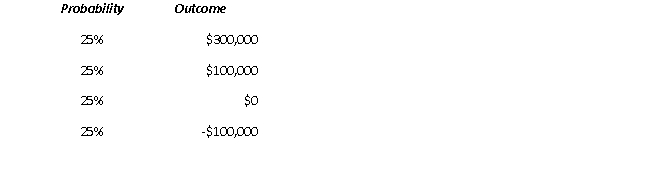 What is the expected cash flow of the new location?
What is the expected cash flow of the new location?
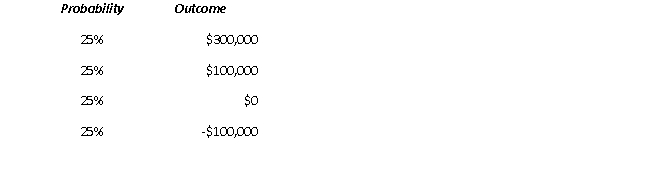 What is the expected cash flow of the new location?
What is the expected cash flow of the new location?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
You are evaluating job possibilities. After a good deal of research, you feel there is a 10% chance of landing a job that pays $75,000, a 20% chance of paying $60,000, a 50% chance of paying $55,000, and a 20% chance of paying $40,000. What is your expected salary?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A college student has three assets: $10,000 in a 529 college plan, which is expected to return 8%, $2,000 in savings bonds, which are expected to return 2%, and $500 of baseball cards, which are expected to return 40%. What is the weighted expected return of the college student's assets?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is an efficient frontier?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose an analyst gathers data to calculate sixty monthly stock returns for a particular stock. These returns are best described as:
A) ex ante returns.
B) ex post returns.
A) ex ante returns.
B) ex post returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Consider a stock that had a price of $40 per share at the beginning of the year, paid $2 of dividends at the end of the year, and traded for $45 at the end of the year. This stock's return for the year is closest to:
A) 7.5 percent.
B) 11.1 percent.
C) 12.5 percent.
D) 15.6 percent.
A) 7.5 percent.
B) 11.1 percent.
C) 12.5 percent.
D) 15.6 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Consider a stock that has a 40 percent chance of a return of 5 percent, and a 60 percent change of a return of 10 percent. The expected return, based on this probability distribution, is closest to:
A) 7 percent.
B) 7.5 percent.
C) 8 percent.
A) 7 percent.
B) 7.5 percent.
C) 8 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When we calculate the expected return by weighted possible returns by the likelihood of the return, we are calculating:
A) ex ante returns.
B) ex post returns.
A) ex ante returns.
B) ex post returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider a stock that has a 40 percent chance of a return of 5 percent, and a 60 percent change of a return of 10 percent. The standard deviation of this probability distribution is closest to:
A) 0.6 percent.
B) 2.5 percent.
C) 3.6 percent.
A) 0.6 percent.
B) 2.5 percent.
C) 3.6 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Suppose you have a portfolio consisting of three stocks, and are considering the addition of a fourth stock. The possible stocks are Stock A, which has a correlation of 0.2 with the existing portfolio, and Stock B, which has a correlation of 0.4 with the existing portfolio. Which stock offers the greater diversification potential?
A) Stock A
B) Stock B
A) Stock A
B) Stock B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



