Deck 5: Time Value of Money
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/107
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Time Value of Money
1
The concept that a unit of currency today is not worth the same as a unit of currency in another time period is best described as the:
A) rate of money.
B) capital use rate.
C) time value of money.
D) economic measure of money.
A) rate of money.
B) capital use rate.
C) time value of money.
D) economic measure of money.
capital use rate.
2
If we convert a future value into a present value, this process is best described as:
A) discounting.
B) compounding.
A) discounting.
B) compounding.
discounting.
3
Suppose you invest $1,000 today in an account that pays 3% interest, compounded annually. The balance in the account at the end of ten years, if you make no withdrawals, is closest to:
A) $744
B) $1,000
C) $1,300
D) $1,344
A) $744
B) $1,000
C) $1,300
D) $1,344
$1,344
4
If you invest $10,000 today in an account that pays 4% interest, compounded quarterly, the balance in the account at the end of ten years, if you make no withdrawals, is closest to:
A) $14,000.00
B) $14,802.44
C) $14,888.64
D) $14,918.25
A) $14,000.00
B) $14,802.44
C) $14,888.64
D) $14,918.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose you invest $1,000 today in an account that pays 5% interest, compounded annually. The balance in the account at the end of five years, if you make no withdrawals, is closest to:
A) $784
B) $1,000
C) $1,250
D) $1,276
A) $784
B) $1,000
C) $1,250
D) $1,276

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Calculating the present value of a future value, considering the time value of money is best described as:
A) annuitizing.
B) discounting.
C) compounding.
A) annuitizing.
B) discounting.
C) compounding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Consider a deposit of $4,000 in an account that promises 6% interest, compounded annually. By the end of five years, the interest on interest is closest to:
A) $152.90
B) $240.00
C) $352.90
A) $152.90
B) $240.00
C) $352.90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Consider a deposit of $10,000 in an account that promises 5% interest, compounded continuously. By the end of five years, the interest on interest is closest to:
A) $340.25
B) $250.00
C) $840.25
A) $340.25
B) $250.00
C) $840.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider a deposit of $2,000 in an account that promises 4% interest, compounded annually. By the end of five years, the interest on interest is closest to:
A) $33.31
B) $80.00
C) $93.51
D) $433.31
A) $33.31
B) $80.00
C) $93.51
D) $433.31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Consider a deposit of $1,000 in an account that promises 6% interest, compounded annually. By the end of five years, the interest on interest is closest to:
A) $38.23
B) $60.00
C) $75.75
D) $300.00
A) $38.23
B) $60.00
C) $75.75
D) $300.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A retired person has been earning 4.5% on a tax-free bond, which is called. He has the opportunity to invest in a new tax-free bond earning 50 basis points less. The rate on the new bond offering is closest to:
A) 4.00%
B) 4.50%
C) 5.00%
A) 4.00%
B) 4.50%
C) 5.00%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If you invest $1,000 in a security that provides a return of 4% the first year, 0% the second year, and 6% the third year, the value of your investment at the end of the third years is closest to:
A) $0
B) $1,102.40
C) $1,157.63
D) $1,092.73
A) $0
B) $1,102.40
C) $1,157.63
D) $1,092.73

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If you invest $1,000 in a security that provides a return of 3% the first year, 4% the second year, and 5% the third year, the value of your investment at the end of the third years is closest to:
A) $0
B) $1,000.00
C) $1,124.76
D) $1,200.00
A) $0
B) $1,000.00
C) $1,124.76
D) $1,200.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose an account promises interest at the rate of 5% the first two years and then 3% thereafter. If $2,000 is deposited in the account today, the balance in the account at the end of 10 years from today if you make no withdrawals is closest to:
A) $2,000.00
B) $2,793.23
C) $2,794.06
D) $3,257.79
A) $2,000.00
B) $2,793.23
C) $2,794.06
D) $3,257.79

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Suppose an account promises interest at the rate of 8% the first five years and then 10% thereafter. If $3,000 is deposited in the account today, the balance in the account at the end of 10 years from today if you make no withdrawals is closest to:
A) $3,000.00
B) $6,476.77
C) $7,099.10
D) $7,781.23
A) $3,000.00
B) $6,476.77
C) $7,099.10
D) $7,781.23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose an account promises interest at the rate of 5% the first two years and then increases 100 basis points thereafter. If $1,000 is deposited in the account today, the balance in the account at the end of 10 years from today if you make no withdrawals is closest to:
A) $1,000.00
B) $1,628.89
C) $1,757.22
D) $1,790.85
A) $1,000.00
B) $1,628.89
C) $1,757.22
D) $1,790.85

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An apartment lease where the payments are due at the beginning of each month would be an example of a(n):
A) perpetuity.
B) annuity due.
C) ordinary annuity.
D) deferred annuity.
A) perpetuity.
B) annuity due.
C) ordinary annuity.
D) deferred annuity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which financial math approach would you use to analyze equipment lease payments, made at the end of each month for five years?
A) Present Value of a Lump Sum
B) Present Value of an Annuity Due
C) Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity
A) Present Value of a Lump Sum
B) Present Value of an Annuity Due
C) Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which financial math approach would you use to analyze a gym membership of $45 per month, paid at the beginning of each month for one year?
A) Present Value of a Lump Sum
B) Present Value of an Annuity Due
C) Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity
A) Present Value of a Lump Sum
B) Present Value of an Annuity Due
C) Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which financial math approach would you use to analyze a legal settlement's value in the future? The settlement is paid in twenty-five annual installments, beginning today, settlement date?
A) Future Value of a Lump Sum
B) Future Value of an Annuity Due
C) Future Value of an Ordinary Annuity
A) Future Value of a Lump Sum
B) Future Value of an Annuity Due
C) Future Value of an Ordinary Annuity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The Powerball Lottery pays out winnings in twenty payments, with the first payment immediate, and the rest following once per year. This is an example of a(n):
A) lump-sum.
B) annuity due.
C) ordinary annuity.
D) deferred annuity.
A) lump-sum.
B) annuity due.
C) ordinary annuity.
D) deferred annuity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The present value of a perpetuity with an annual year-end payment of $12,000 and expected annual rate of return equal to 7% is closest to:
A) $144,000.00.
B) $148,908.49.
C) $171,428.57.
A) $144,000.00.
B) $148,908.49.
C) $171,428.57.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The present value of a perpetuity with an annual year-end payment of : $2,000 and expected annual rate of return equal to 7% is closest to:
A) $24,000.00
B) $24,818.08
C) $28,571.43
A) $24,000.00
B) $24,818.08
C) $28,571.43

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The present value of a perpetuity with an annual year-end payment of $1,000 and expected annual rate of return equal to 0.5% is closest to:
A) $20,000
B) $100,000
C) $200,000
A) $20,000
B) $100,000
C) $200,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The value today of a perpetuity with an annual, year-end payments of $500 each and an expected annual rate of return equal to 1% is closest to:
A) $5
B) $500
C) $5,000
D) $50,000
A) $5
B) $500
C) $5,000
D) $50,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Consider an investment that promises $1,000 at the end of each of the next four years, and $2,000 per year thereafter, forever. If the discount rate is 5%, the present value of this investment is closest to:
A) $32,908.10
B) $36.454.05
C) $40,000.00
D) $43,545.95
A) $32,908.10
B) $36.454.05
C) $40,000.00
D) $43,545.95

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider an investment that promises $2,000 at the end of each of the next four years, and $3,000 per year thereafter for four years. If the discount rate is 5%, the present value of this investment is closest to:
A) $10,737.85
B) $15,843.69
C) $17,729.75
A) $10,737.85
B) $15,843.69
C) $17,729.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A borrower is offered a loan of $10,000 for three years. She is given a choice on how the interest is to be calculated. Which method of interest calculation would be most beneficial to the borrower?
A) Simple interest
B) Interest compounded annually
C) Interest compounded monthly
A) Simple interest
B) Interest compounded annually
C) Interest compounded monthly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Hunter wants to borrow money from the mortgage company with the lowest effective annual rate (EAR). Which of the following loan offers will meet his objectives:
A) 10% compounded daily
B) 10% compounded monthly
C) 10% compounded annually
D) 10% compounded continuously
A) 10% compounded daily
B) 10% compounded monthly
C) 10% compounded annually
D) 10% compounded continuously

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Under which circumstance is EAR equal to APR?
A) If interest is compounded daily
B) If interest is compounded annually
C) If interest is compounded quarterly
D) If interest is compounded continuously
A) If interest is compounded daily
B) If interest is compounded annually
C) If interest is compounded quarterly
D) If interest is compounded continuously

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The more frequent the compounding within a year:
A) It makes no difference on EAR and APR.
B) The lesser the difference between the EAR and APR.
C) The greater the difference between the EAR and APR.
A) It makes no difference on EAR and APR.
B) The lesser the difference between the EAR and APR.
C) The greater the difference between the EAR and APR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Marie needs to take out a loan for her new business and has decided to go with the loan that has the lowest effective annual rate. Which of the following would meet her stated objective?
A) 8.00% compounded daily
B) 8.00% compounded monthly
C) 8.00% compounded continuously
A) 8.00% compounded daily
B) 8.00% compounded monthly
C) 8.00% compounded continuously

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An equipment lease where the payments are due at the end of each month would be an example of a(n):
A) perpetuity.
B) annuity due.
C) ordinary annuity.
D) deferred annuity.
A) perpetuity.
B) annuity due.
C) ordinary annuity.
D) deferred annuity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The consumer finance office wants its' loan officers to make loans at the highest effective annual rate. Which of the following credit terms will have the highest effective annual rate?
A) 17.00% compounded daily
B) 17.00% compounded monthly
C) 17.00% compounded continuously
A) 17.00% compounded daily
B) 17.00% compounded monthly
C) 17.00% compounded continuously

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A family member is considering an annuity with either cash flows of 30 years or cash flows forever. Both options have cash flows of $5,000 occurring at the end of each period and an interest rate of 7%. The difference in the present values of the annuities is closest to:
A) $9,383.37
B) $62,045.21
C) $71,428.58
D) $133,473.78
A) $9,383.37
B) $62,045.21
C) $71,428.58
D) $133,473.78

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The present value of an annuity with cash flows forever of $12,000 at the end of each year and an interest rate of 10% is closest to what amount? What is the present value if the annuity is instead for 25 years?
A) $11,075.52
B) $108,924.48
C) $120,000.00
D) $228,924.48
A) $11,075.52
B) $108,924.48
C) $120,000.00
D) $228,924.48

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
With a discount rate of .25% per month, which investment would have the highest present value today - Investment A: Beginning today, has a cash flow of $1,500 per month for 60 months or Investment B: Beginning one month from today, has a cash flow of $1,540 per month for 59 months?
A) Investment A
B) Investment B
C) Investment A and B have the same present value
A) Investment A
B) Investment B
C) Investment A and B have the same present value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
With a discount rate of .25% per month, which investment would have the highest present value today -
Investment A: Beginning today, has a cash flow of $1,500 per month for 60 months, or
Investment B: Beginning one month from today, has a cash flow of $1,525 per month for 59 months?
A) Investment A
B) Investment B
C) Investment A and B have the same present value
Investment A: Beginning today, has a cash flow of $1,500 per month for 60 months, or
Investment B: Beginning one month from today, has a cash flow of $1,525 per month for 59 months?
A) Investment A
B) Investment B
C) Investment A and B have the same present value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider a deposit of $100,000 that can be made into one of four banks. Which of the following provides the largest balance by the end of five years?
A) Bank A: 4.7% compounded continuously
B) Bank B: 4.8% compounded monthly
C) Bank C: 5% compounded annually
D) Bank D: 5.1% simple interest
A) Bank A: 4.7% compounded continuously
B) Bank B: 4.8% compounded monthly
C) Bank C: 5% compounded annually
D) Bank D: 5.1% simple interest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider a deposit of $100,000 that can be made into one of four banks. Which of the following provides the largest balance by the end of five years?
A) Bank A: 5.0% compounded continuously
B) Bank B: 5.2% compounded monthly
C) Bank C: 6.0% simple interest
D) Bank D: 5.4% compounded annually
A) Bank A: 5.0% compounded continuously
B) Bank B: 5.2% compounded monthly
C) Bank C: 6.0% simple interest
D) Bank D: 5.4% compounded annually

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider a deposit of $50,000 that can be made into one of four banks. Which of the following provides the largest balance by the end of five years?
A) Bank A: 8.0% compounded continuously
B) Bank B: 8.0% compounded monthly
C) Bank C: 8.2% compounded annually
D) Bank D: 8.2% simple interest
A) Bank A: 8.0% compounded continuously
B) Bank B: 8.0% compounded monthly
C) Bank C: 8.2% compounded annually
D) Bank D: 8.2% simple interest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A twenty year-old college student decides to forgo coffee at Starbucks and instead invest the saved $600 per year into a mutual fund earning 6% compounding annually. The amount he would have in the fund by age 65 is closest to:
A) $30,696.07
B) $315,515.24
C) $1,798,973.08
A) $30,696.07
B) $315,515.24
C) $1,798,973.08

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A couple nearing retirement plans to increase their retirement savings by investing an equal amount of $20,000 in Roth IRAs each year end, beginning this year. The expected return on the IRAs is 7%. They plan to invest for 10 years. The amount the couple expects to have at the end of ten years is closest to:
A) $39,343.03.
B) $189,743.42.
C) $276,328.96.
A) $39,343.03.
B) $189,743.42.
C) $276,328.96.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Caroline's roof is aging. To plan for the eventual roof replacement, she puts $1,000 at the end of each year, starting with this year, into a certificate of deposit (CD) paying 4%. Caroline plans to do this for seven years. The amount Caroline should have at the end of seven years for roof replacement is closest to:
A) $1,315.93
B) $6,002.05
C) $7,898.29
A) $1,315.93
B) $6,002.05
C) $7,898.29

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Javier starts a college savings account for his child and places $500 into it every year end, beginning this year. His expected annual return on the account is 2%. He plans to invest for twelve years and then turn over the money to the child for college. The amount he expects to have at the end of the twelve years is closest to:
A) $6,000.00.
B) $6,120.00.
C) $6,706.04.
A) $6,000.00.
B) $6,120.00.
C) $6,706.04.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The process of determining how much of each payment is interest and principal repayment best describes the following:
A) mortgage.
B) amortization.
C) present value.
D) balloon payment.
A) mortgage.
B) amortization.
C) present value.
D) balloon payment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
After making their mortgage payment, the Browns wonder how much their loan balance was reduced by the payment they just made. They should consult a(n):
A) mortgage.
B) amortization schedule.
C) balloon payment schedule.
D) lump sum payment schedule.
A) mortgage.
B) amortization schedule.
C) balloon payment schedule.
D) lump sum payment schedule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Consider a 5% loan of $150,000 for thirty years, with monthly payments and a balloon payment of $50,000 at the end of thirty years. The monthly payment on this loan is closest to:
A) $599.55
B) $849.55
C) $899.33
D) $1,149.33
A) $599.55
B) $849.55
C) $899.33
D) $1,149.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider an 8% loan of $300,000 for twenty years, with monthly payments and a balloon payment of $100,000 at the end of twenty years. The monthly payment on this loan is closest to:
A) $10,714.72
B) $11,381.39
C) $16,072.09
D) $16,738.75
A) $10,714.72
B) $11,381.39
C) $16,072.09
D) $16,738.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider a mortgage of $175,000 that is to be repaid over 360 months. If the annual percentage rate on this mortgage is 4%, the monthly mortgage payments are closest to:
A) $252.14
B) $583.33
C) $835.48
D) $7,000.00
A) $252.14
B) $583.33
C) $835.48
D) $7,000.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Consider a mortgage loan of $300,000, to be amortized over thirty years with monthly payments. If the annual percentage rate on this mortgage is 4%, the amount of principal and interest in the second month's mortgage payment is closest to:
A) Principal repayment is $1,000.00, and interest paid is $432.25.
B) Principal repayment is $432.25, and interest paid is $1,000.00.
C) Principal repayment is $998.56, and interest paid is $433.69.
D) Principal repayment is $433.69, and interest paid is $998.56.
A) Principal repayment is $1,000.00, and interest paid is $432.25.
B) Principal repayment is $432.25, and interest paid is $1,000.00.
C) Principal repayment is $998.56, and interest paid is $433.69.
D) Principal repayment is $433.69, and interest paid is $998.56.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Vincent would like to have $50,000 per year to live off in his retirement. He expects to retire on his 65th birthday, make his first retirement withdrawal on his 66th birthday, and to live until his 85th birthday. He is celebrating his 30th birthday today and will make his first savings deposit one year from today. If he can earn 4% per year on his savings, the amount he must save each year to meet his goal, with the last savings deposit on his 65th birthday, is closest to:
A) $7,257.59.
B) $7,547.90.
C) $7,849.81.
A) $7,257.59.
B) $7,547.90.
C) $7,849.81.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Discounting is the mathematical conversion of a present value into a future value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the interest rate is equal to 0%, the present value of an amount is equal to the future value of that amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The difference between future value with compound interest and future value with simple interest is interest-on -interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If you know the present value of an investment is $5,000 and the interest rate is 5%, you can calculate future value?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A seasoned investor wants to triple her investment in twenty years. To accomplish her objectives, she will have to earn 3.526% on her investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Future values represent a special type of cash flow stream that involve equal payments at the same interval, with the same interest rate being applied throughout the period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An annuity that provides periodic payments forever would best be described as a perpetuity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If each periodic cash flow is the same amount, occurring at the same intervals of time, the present value of a perpetuity will be greater than the present value of a 100-year ordinary annuity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If interest is compounded more than once a year, the annual percentage rate is also the effective interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The nominal rate or stated rate is also referred to as annual percentage rate (APR).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The nominal rate or stated rate is also referred to as effective annual rate (EAR).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Continuous compounding is going to lead to the smallest difference between the effective annual rate (EAR) and annual percentage rate (APR).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The effective annual rate on an account that pays 5% interest, compounded quarterly, is greater than the effective annual rate on an account that pays 4.8% interest, compounded continuously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The effective annual rate on an account that pays 10% interest, compounded semiannually, is greater than the effective annual rate on an account that pays 9.9% interest, compounded continuously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A loan, usually for real estate, that involves level, periodic payments consisting of interest and principal repayment over a specified payment period is best described as a mortgage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A monthly payment is the payment that represents repayment of some amount of the principal of the loan above and beyond what is paid as part of the amortized loan payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose a homeowner is evaluating two mortgages, both of which are arrangements for repaying a loan of $200,000. Mortgage A requires quarterly payments at the end of each quarter for 15 years at a stated annual rate of 5%. Mortgage B has quarterly payments, paid at the beginning of each quarter for 18 years, at a stated annual rate of 5.5%. Mortgage A has a higher periodic payment than Mortgage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose a homeowner is evaluating two mortgages, both of which are arrangements for repaying a loan of $200,000. Mortgage C requires monthly payments at the end of each month for 15 years at a stated annual rate of 6%. Mortgage D has monthly payments, paid at the beginning of each month for 18 years, at a stated annual rate of 5.5%. Mortgage C has a higher periodic payment than Mortgage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose a company borrows $1 million and pays off this 10-year, 5% interest loan in end-of-year payments of $113,603.66 each. This loan is fully amortized at the end of the ten years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A company that borrows $10 million and pays this off with a 10-year, 5% interest loan in end-of-year payments of $1,295,045.75 each has a zero balance remaining on this loan at the end of 10 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If you deposit $5,000 in an account that pays 3% interest, compounded annually, what balance would you have at the end of four year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the future value of $3,000 five years from now if interest is earned at a rate of 4% per year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is the present value of $5,000 to be received five years from now if the discount rate is 6% per year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An investor invests $25,000 today for a five-year term and receives 4% annual compound interest.
A. How much would the investor have after five years?
B. How much interest-on-interest would the investor earn during the five years?
A. How much would the investor have after five years?
B. How much interest-on-interest would the investor earn during the five years?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An investor invests $10,000 today for a four-year term and receives 5% annual compound interest.
A. How much would the investor have after four years?
B. How much interest-on-interest would the investor earn during the four years?
A. How much would the investor have after four years?
B. How much interest-on-interest would the investor earn during the four years?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Suppose you are considering an investment that promises $25,000 in five years. If you determine that the appropriate discount rate for this investment, considering its risk, is 8%, what is this investment worth to you today?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A friend's broker promises that they will double their money in five years with Investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Complete the following table:
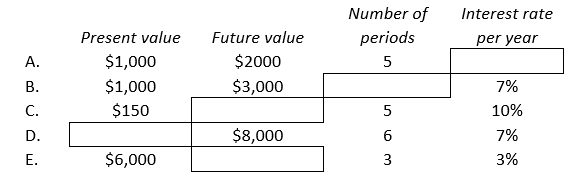


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



