Deck 11: The Conversion Business Process
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/55
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: The Conversion Business Process
1
Because the conversion cycle usually involves no resource exchanges with external business partners, it usually falls within the enterprise circle of the value system level diagram.
True
2
The economic increment event Production Run in the conversion cycle component of an REA enterprise value chain diagram usually results in a corresponding resource flow of finished goods from the conversion cycle to the revenue cycle.
True
3
The value chain component representing the conversion cycle of a manufacturer usually includes multiple resource inflows.
True
4
For cost assignment purposes, continuous processes include natural starting and ending points, whereas batch processes require the use of artificial starting and ending points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Because most firms produce very different goods and services, and have many different types of production processes, there is no robust conceptual modeling pattern for the conversion cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Conversion cycle is centered on a Transfer duality relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A business process level model of an enterprise's conversion cycle usually includes multiple economic decrement event entities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A Material Issuance is an economic decrement event in the conversion cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Move tickets often document material issuance events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Labor Operations in the Conversion cycle are economic increment events that represent increases of Labor resource types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Job time tickets or time track forms are often used to document labor operations in the conversion cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Stockflow Consume relationships represent decreases of resources that get partially used up in economic decrement events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Production Order is the commitment to an economic increment event that will increase the Finished Goods resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A Raw Materials Requisition in the conversion cycle is a commitment event whereby a designated employee commits to the production supervisor to transfer materials from the materials warehouse to the production floor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
One Reservation relationship in the conversion cycle links a production order to a finished good to indicate which finished goods will be produced in a future production run; another Reservation relationship in the conversion cycle links a material requisition to a raw material to indicate which materials will be used up in a future issuance event.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Linkage relationships are typically included in business process level models of all cycles except the conversion cycle because the conversion cycle does not involve external agents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The average length of all machine operations during a specific time period is an example of a conversion cycle event query.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
To get the information needed to produce a bill of materials, one should focus on the Reservation relationship between Finished Goods and the Production Order event in the conversion cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
To answer the question of how long it took to accomplish a specific type of labor in a labor operation, one should focus on the Fulfillment relationship in the conversion cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
To determine whether any material issuances were not first requisitioned, one should focus on the Fulfillment relationship in the conversion process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
For the following part of a value chain including the conversion cycle, what must be included inside the conversion cycle circle to correspond to the outgoing arrow? 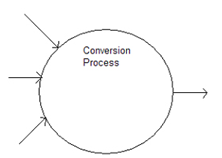
A) A rectangle that represents a resource that is increased by the event the arrow represents.
B) A rectangle that represents a resource that is decreased by the event the arrow represents.
C) A rectangle that represents an event in which the resource the arrow represents is produced.
D) A rectangle that represents an event in which the resource the arrow represents is used up.
E) A rectangle that represents an event in which the resource the arrow represents is consumed.

A) A rectangle that represents a resource that is increased by the event the arrow represents.
B) A rectangle that represents a resource that is decreased by the event the arrow represents.
C) A rectangle that represents an event in which the resource the arrow represents is produced.
D) A rectangle that represents an event in which the resource the arrow represents is used up.
E) A rectangle that represents an event in which the resource the arrow represents is consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Assembling, growing, excavating, harvesting, and cleaning are examples of some of the more general activities in which business process?
A) Sales/Collection
B) Acquisition/Payment
C) Conversion
D) Service Acquisition
E) None of the above
A) Sales/Collection
B) Acquisition/Payment
C) Conversion
D) Service Acquisition
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which economic event typically involves no external agents?
A) Acquisition of products
B) Purchase order
C) Production run
D) Sale or shipment of goods
E) Cash receipt
A) Acquisition of products
B) Purchase order
C) Production run
D) Sale or shipment of goods
E) Cash receipt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In which cycle does duality represent a transformation of one or more resources into another resource, as opposed to a transfer of one or more resources for another resource?
A) Duality represents transformation in the conversion cycle.
B) None; duality always represents transfers rather than transformations.
C) Duality represents transformation in the acquisition, revenue, and payroll cycles.
D) Duality represents transformation in the conversion and payroll cycles.
E) Duality represents transformation in the acquisition, payroll, and financing cycles because payroll and financing are simply special cases of the acquisition cycle.
A) Duality represents transformation in the conversion cycle.
B) None; duality always represents transfers rather than transformations.
C) Duality represents transformation in the acquisition, revenue, and payroll cycles.
D) Duality represents transformation in the conversion and payroll cycles.
E) Duality represents transformation in the acquisition, payroll, and financing cycles because payroll and financing are simply special cases of the acquisition cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The document in the conversion process that represents the list of all components and their quantities required to produce a finished good (i.e. the document that contains the same data as is captured in the relationship between Raw Material and Finished Good in the REA ontology) is called the
A) Operations list.
B) Move ticket.
C) Master production schedule.
D) Bill of materials.
E) Job time ticket.
A) Operations list.
B) Move ticket.
C) Master production schedule.
D) Bill of materials.
E) Job time ticket.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A Raw Materials Requisition event in a conversion process modeled using the REA enterprise ontology is what kind of event?
A) An economic increment event
B) A commitment event
C) An instigation event
D) An economic decrement event
E) An economic reversal event
A) An economic increment event
B) A commitment event
C) An instigation event
D) An economic decrement event
E) An economic reversal event

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Inputs to the conversion process in a company's value chain are usually made available by
A) The human resource process only.
B) The financing process only.
C) The sales/collection process only.
D) The acquisition/payment process only.
E) Both the acquisition/payment and the human resource process.
A) The human resource process only.
B) The financing process only.
C) The sales/collection process only.
D) The acquisition/payment process only.
E) Both the acquisition/payment and the human resource process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following represents a valid "Linkage" relationship in an enterprise conversion cycle
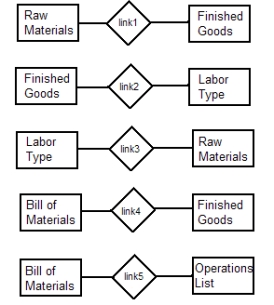
A) Link 1 only
B) Link 3 only
C) Link 4 only
D) Link 5 only
E) Both link1 and link2 represent valid linkage relationships for a conversion cycle

A) Link 1 only
B) Link 3 only
C) Link 4 only
D) Link 5 only
E) Both link1 and link2 represent valid linkage relationships for a conversion cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
You have a conceptual model for the relationship between Production Run and Employee in the conversion cycle as follows. How should this relationship be implemented in relational table format? 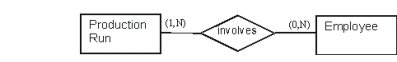
A) Make a table called Production Run, a table called Employee and post the primary key from the Employee table into the Production Run table.
B) Make a table called Involves, a table called Production Run and post the primary key from the Involves table into the Production Run table.
C) Make a table called Production Run, a table called Employee and a table called Involves that has a concatenated primary key.
D) Make a table called Production Run, a table called Employee and post the primary key from the Production Run table into the Employee table.
E) Make a table called Production Run, a table called Employee and post the primary key from the Production Run table into the Supervisors table.

A) Make a table called Production Run, a table called Employee and post the primary key from the Employee table into the Production Run table.
B) Make a table called Involves, a table called Production Run and post the primary key from the Involves table into the Production Run table.
C) Make a table called Production Run, a table called Employee and a table called Involves that has a concatenated primary key.
D) Make a table called Production Run, a table called Employee and post the primary key from the Production Run table into the Employee table.
E) Make a table called Production Run, a table called Employee and post the primary key from the Production Run table into the Supervisors table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following resources is most likely to participate in a conversion cycle Consume relationship for a cake manufacturer?
A) Cash
B) Ingredients
C) Packaging materials
D) Oven
E) Electricity
A) Cash
B) Ingredients
C) Packaging materials
D) Oven
E) Electricity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What documents in the conversion cycle capture the same information as the Linkage relationships?
A) Operations list and Bill of materials
B) Materials requisition and Production order
C) Job time ticket and Production order
D) Bill of materials and Materials requisition
E) Move ticket and Materials requisition
A) Operations list and Bill of materials
B) Materials requisition and Production order
C) Job time ticket and Production order
D) Bill of materials and Materials requisition
E) Move ticket and Materials requisition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the relationship between two conversion cycle commitment events?
A) Custody
B) Duality
C) Reciprocal
D) Fulfillment
E) Reservation
A) Custody
B) Duality
C) Reciprocal
D) Fulfillment
E) Reservation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The resource typically made available to the conversion process by the human resources process is
A) Cash
B) Labor
C) Machinery
D) Raw materials
E) Finished goods
A) Cash
B) Labor
C) Machinery
D) Raw materials
E) Finished goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which business process typically includes an event called Material Issuance?
A) Financing
B) Acquisition/payment
C) Human resources
D) Conversion
E) Revenue
A) Financing
B) Acquisition/payment
C) Human resources
D) Conversion
E) Revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
On which entity or relationship should one focus to answer the question of when the most recent material requisition occurred?
A) Material Requisition event
B) Material Issuance event
C) Fulfillment relationship between Material Requisition and Material Issuance
D) Reservation relationship between Material Requisition and Raw Materials
E) Stockflow relationship between Material Issuance and Raw Materials
A) Material Requisition event
B) Material Issuance event
C) Fulfillment relationship between Material Requisition and Material Issuance
D) Reservation relationship between Material Requisition and Raw Materials
E) Stockflow relationship between Material Issuance and Raw Materials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is a query that could be answered by examining a Fulfillment relationship in the conversion cycle?
A) How long did it take to produce a specific finished good?
B) Which labor operations related to a specific production run?
C) How long did it take to perform a specific type of labor in a certain labor operation?
D) What is the average length of time between a production order and the resulting production run?
E) What finished good type is a production order agreeing to produce?
A) How long did it take to produce a specific finished good?
B) Which labor operations related to a specific production run?
C) How long did it take to perform a specific type of labor in a certain labor operation?
D) What is the average length of time between a production order and the resulting production run?
E) What finished good type is a production order agreeing to produce?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following questions could be answered by examining a Linkage relationship in the conversion cycle for a cookie manufacturer?
A) How many ounces of chocolate chips are used to make a dozen chocolate chip cookies?
B) Which production run produced a specific batch of chocolate chip cookies?
C) Besides chocolate chip cookies, what other types of cookies were produced in a specific production run?
D) How many labor operations were necessary to produce a specific batch of chocolate chip cookies?
E) Which baking order triggered the production run that produced a specific batch of chocolate chip cookies?
A) How many ounces of chocolate chips are used to make a dozen chocolate chip cookies?
B) Which production run produced a specific batch of chocolate chip cookies?
C) Besides chocolate chip cookies, what other types of cookies were produced in a specific production run?
D) How many labor operations were necessary to produce a specific batch of chocolate chip cookies?
E) Which baking order triggered the production run that produced a specific batch of chocolate chip cookies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the conversion business process, what underlying activity does the production run or work-in-process job represent?
A) The act of a production supervisor requesting an inventory clerk to make a set of raw materials available to the production floor.
B) The act of a production employee recording the number of hours he or she worked on each task for a day
C) The act of one or more employees producing finished goods inventory
D) The act of an inventory clerk transferring raw materials from the materials warehouse to the production floor
E) The act of a production supervisor agreeing to produce a certain number of finished goods on a specific future date
A) The act of a production supervisor requesting an inventory clerk to make a set of raw materials available to the production floor.
B) The act of a production employee recording the number of hours he or she worked on each task for a day
C) The act of one or more employees producing finished goods inventory
D) The act of an inventory clerk transferring raw materials from the materials warehouse to the production floor
E) The act of a production supervisor agreeing to produce a certain number of finished goods on a specific future date

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What pair of entities are likely to participate in a conversion cycle Custody relationship?
A) Cash and Cashier
B) Raw Materials Inventory and Inventory Clerk
C) Raw Materials Inventory and Production Run
D) Inventory Clerk and Raw Materials Issuance
E) Raw Materials Inventory and Finished Goods Inventory
A) Cash and Cashier
B) Raw Materials Inventory and Inventory Clerk
C) Raw Materials Inventory and Production Run
D) Inventory Clerk and Raw Materials Issuance
E) Raw Materials Inventory and Finished Goods Inventory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following attributes is LEAST likely to be assigned to the Raw Materials Inventory entity in a conversion cycle business process level REA model?
A) ID-number
B) Description
C) Unit of measure
D) Standard Unit Cost
E) Unit List Selling Price
A) ID-number
B) Description
C) Unit of measure
D) Standard Unit Cost
E) Unit List Selling Price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What two synonyms for conversion are often used to label the conversion business process?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What kind of duality relationship exists in the conversion business process?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What does a conversion process that feeds yarn into a knitting machine to produce blankets have in common with a conversion process that uses automated spray stations to paint cars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the economic increment event in the conversion process called?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which relationship in the conversion cycle contains information that is often captured on operations lists?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which conversion cycle event represents the using up of one or more labor type resources?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which entities typically participate in a duality relationship in the conversion cycle?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What commitment events typically exist in the conversion process, and to what do they commit?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If a person wants to know what kind of finished good a production order is scheduled to produce and when the production is scheduled to occur, what relationship should that person examine? (List the relationship name, the entities that participate in the relationship, and the business process in which the relationship exists.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Is a company that manufactures paperclips and thumbtacks more likely to use job order costing or process costing? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Radio frequency ID tags (RFIDs) may be attached to almost any operating asset or inventory item. Each tag emits a unique signal via radio frequencies, allowing specific items to be tracked electronically as they move from one location to another. Two soup manufacturers, Stout & Chunky and Tureen Filler, produce many different kinds of soup. If Stout & Chunky tags each can of soup produced with RFIDs and Tureen Filler doesn't use any RFIDs, how are the two soup manufacturers' conceptual conversion cycle business process level models likely to differ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
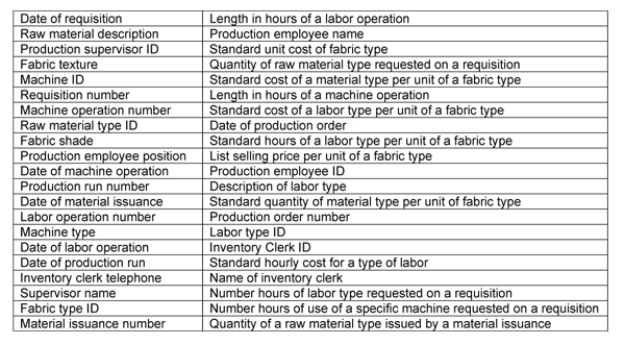
Given the following narrative description for Lydia's Purple Cloth Factory:
a. Create a business process level REA model in either grammar or diagram format, for the following business process. Be sure to include all relevant entities, relationships, attributes, and cardinalities (minimum and maximum).
b. Convert your business process level model into a set of minimal relational database tables. Be sure to identify primary and foreign keys in the relational tables.
Lydia's Purple Cloth Factory (LPCF) produces fabric in many different textures and patterns, all in various shades of purple. Raw materials, employee labor, and machines are used in the production process. Raw materials include various types of threads and dyes, along with assorted chemicals and detergents. Employees are hired to meet the skill requirements of various labor types. Each machine is specifically identified. LPCF uses bills of materials and operations lists to document which raw materials and labor types are needed to produce each type of purple fabric, therefore the database must capture the information needed to produce these documents.
As a need for a fabric type is identified, a production supervisor orders production and issues a signle requisition for the necessary raw materials, labor types, and machinery. LPCF never combines multiple fabric types on the same production order or production run; however, multiple materials, labor types, and machines are often needed to produce a single fabric type. When all requisitioned inputs are available, the raw materials are issued and the labor operations and machine operations are completed in a production run. Production employees perform the labor operations (one employee and one labor type per operation) under the watchful eye of a production supervisor; the machine operations are fully automated with one machine per operation, so they require only a production supervisor's attention. Raw material issuances are accomplished by inventory clerks and are authorized by production supervisors (one clerk and one supervisor per issuance). LPCF does not directly assign production supervisors to production employees; the supervisor position simply designates responsibility for all events and other activities associated with a production run.
The following attributes must be accounted for in your model.
a. Create a business process level REA model in either grammar or diagram format, for the following business process. Be sure to include all relevant entities, relationships, attributes, and cardinalities (minimum and maximum).
b. Convert your business process level model into a set of minimal relational database tables. Be sure to identify primary and foreign keys in the relational tables.
Lydia's Purple Cloth Factory (LPCF) produces fabric in many different textures and patterns, all in various shades of purple. Raw materials, employee labor, and machines are used in the production process. Raw materials include various types of threads and dyes, along with assorted chemicals and detergents. Employees are hired to meet the skill requirements of various labor types. Each machine is specifically identified. LPCF uses bills of materials and operations lists to document which raw materials and labor types are needed to produce each type of purple fabric, therefore the database must capture the information needed to produce these documents.
As a need for a fabric type is identified, a production supervisor orders production and issues a signle requisition for the necessary raw materials, labor types, and machinery. LPCF never combines multiple fabric types on the same production order or production run; however, multiple materials, labor types, and machines are often needed to produce a single fabric type. When all requisitioned inputs are available, the raw materials are issued and the labor operations and machine operations are completed in a production run. Production employees perform the labor operations (one employee and one labor type per operation) under the watchful eye of a production supervisor; the machine operations are fully automated with one machine per operation, so they require only a production supervisor's attention. Raw material issuances are accomplished by inventory clerks and are authorized by production supervisors (one clerk and one supervisor per issuance). LPCF does not directly assign production supervisors to production employees; the supervisor position simply designates responsibility for all events and other activities associated with a production run.
The following attributes must be accounted for in your model.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Create a "generic" REA business process level model (without cardinalities) in either grammar or diagram format to represent the conversion business process for a manufacturer of high volume, low cost inventory items identified at the type level, whose manufacturing process includes both labor and machine operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Given the following narrative description for Seminole Computer Experts (SCE):
a. Create a business process level REA model in either grammar or diagram format, for the following business processes. Be sure to include all relevant entities, relationships, attributes, and cardinalities (minimum and maximum).
b. Convert your business process level model into a set of minimal relational database tables. Be sure to identify primary and foreign keys in the relational tables.
Seminole Computer Experts (SCE) is an enterprise that buys used computers for low prices, restores the computers, and then sells them at high prices. Each individual computer is assigned a unique identification number, and is categorized into a certain type (e.g. Notebook Pentium II, Notebook Pentium III, Desktop Pentium II, and so forth). Categories can be entered into the database before any computers in the categories are actually purchased. The unrestored computers are purchased from wholesalers as well as from individuals. One of SCE's purchasing agents submits a bid to the supplier that has listed a given computer (or computers) for sale. These unrestored computers are assigned unique identification numbers and are entered into the database upon making the bid. Sometimes it may be weeks before SCE is notified that its bid has been accepted or rejected. If the bid is accepted, one of SCE's inventory clerks will receive the item(s). Multiple bids accepted by the same supplier may be consolidated into one purchase. Bids are accepted in their entirety or not at all. For example, if SCE's bid on three different computers is accepted, SCE will receive all three of those items on the resulting purchase. If the supplier only accepts the bid as two of the three computers, that is considered a rejection of the bid. SCE may then submit a new bid that includes the two computers at the prices the supplier found acceptable. Slightly less than half of all SCE's bids are accepted. Suppliers and employees can be entered into the database before any transactions involving them occur.
SCE only purchases computers that need some work done on them, because that allows SCE to significantly increase their value by restoring them. Therefore when a computer is purchased, it is similar to raw material, although it is called unrestored computer inventory. When one or more restoration employees are available to begin restoring a computer, an inventory clerk issues the unrestored computer to a restoration job (and it never goes back into unrestored inventory). Each issuance and each job involve just one computer. The restoration of the computer is assigned a unique job number, and the start date and completion dates are recorded. Although SCE wants to keep track of each employee's position, SCE only wants to include one employee table in its database. SCE tracks which employees participate in each restoration job and also tracks what types of labor are used up; however, SCE does not track details of the specific labor operations that use up the labor. For each restoration job, one specific restoration employee serves as the restoration supervisor. The supervisor designation is not a permanent employee position; instead, any given employee may serve as the supervisor on one job and may serve as a subordinate on another restoration job. Each completed restoration job results in a computer that becomes part of "restored computer inventory."
In very rare instances, it is possible for the same computer to be bid on and purchased more than once. For example, SCE could buy a computer, sell it, and then a few months later buy it back again. However, SCE only buys computers that have needs for new restorations. Therefore, if SCE bids on and/or purchases the same computer again, the computer is assigned a different ID number than what it was assigned the previous time. SCE never returns computers to suppliers.
When payment is due for a purchase, SCE's cashier issues one check for payment in full for the item(s) on that purchase. Sometimes if multiple purchases have been made from the same supplier within a short period of time, SCE will pay for those purchases with just one check. One of SCE's managers is required to authorize all bids greater than $5,000 and is also required to sign all checks (including checks written for expenditures other than purchases of unrestored computers). Most of SCE's checks are written for purchases of unrestored computers. SCE needs to keep track of the managers' participation in these events as well as the participation of other employees in these events.
The following attributes are of interest to SCE and must be included in your solution. You may not add any attributes. You may abbreviate the attributes using the abbreviations given in bold in parentheses next to the attributes in the list.
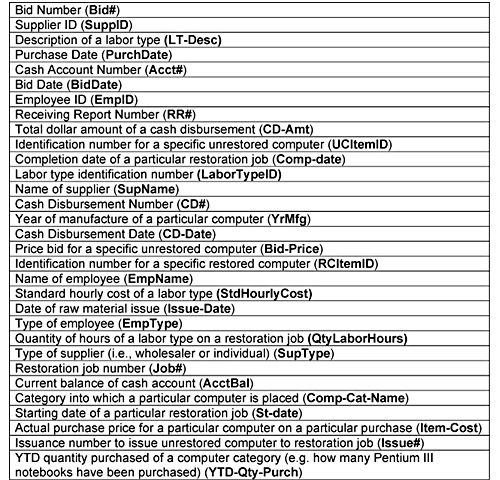
a. Create a business process level REA model in either grammar or diagram format, for the following business processes. Be sure to include all relevant entities, relationships, attributes, and cardinalities (minimum and maximum).
b. Convert your business process level model into a set of minimal relational database tables. Be sure to identify primary and foreign keys in the relational tables.
Seminole Computer Experts (SCE) is an enterprise that buys used computers for low prices, restores the computers, and then sells them at high prices. Each individual computer is assigned a unique identification number, and is categorized into a certain type (e.g. Notebook Pentium II, Notebook Pentium III, Desktop Pentium II, and so forth). Categories can be entered into the database before any computers in the categories are actually purchased. The unrestored computers are purchased from wholesalers as well as from individuals. One of SCE's purchasing agents submits a bid to the supplier that has listed a given computer (or computers) for sale. These unrestored computers are assigned unique identification numbers and are entered into the database upon making the bid. Sometimes it may be weeks before SCE is notified that its bid has been accepted or rejected. If the bid is accepted, one of SCE's inventory clerks will receive the item(s). Multiple bids accepted by the same supplier may be consolidated into one purchase. Bids are accepted in their entirety or not at all. For example, if SCE's bid on three different computers is accepted, SCE will receive all three of those items on the resulting purchase. If the supplier only accepts the bid as two of the three computers, that is considered a rejection of the bid. SCE may then submit a new bid that includes the two computers at the prices the supplier found acceptable. Slightly less than half of all SCE's bids are accepted. Suppliers and employees can be entered into the database before any transactions involving them occur.
SCE only purchases computers that need some work done on them, because that allows SCE to significantly increase their value by restoring them. Therefore when a computer is purchased, it is similar to raw material, although it is called unrestored computer inventory. When one or more restoration employees are available to begin restoring a computer, an inventory clerk issues the unrestored computer to a restoration job (and it never goes back into unrestored inventory). Each issuance and each job involve just one computer. The restoration of the computer is assigned a unique job number, and the start date and completion dates are recorded. Although SCE wants to keep track of each employee's position, SCE only wants to include one employee table in its database. SCE tracks which employees participate in each restoration job and also tracks what types of labor are used up; however, SCE does not track details of the specific labor operations that use up the labor. For each restoration job, one specific restoration employee serves as the restoration supervisor. The supervisor designation is not a permanent employee position; instead, any given employee may serve as the supervisor on one job and may serve as a subordinate on another restoration job. Each completed restoration job results in a computer that becomes part of "restored computer inventory."
In very rare instances, it is possible for the same computer to be bid on and purchased more than once. For example, SCE could buy a computer, sell it, and then a few months later buy it back again. However, SCE only buys computers that have needs for new restorations. Therefore, if SCE bids on and/or purchases the same computer again, the computer is assigned a different ID number than what it was assigned the previous time. SCE never returns computers to suppliers.
When payment is due for a purchase, SCE's cashier issues one check for payment in full for the item(s) on that purchase. Sometimes if multiple purchases have been made from the same supplier within a short period of time, SCE will pay for those purchases with just one check. One of SCE's managers is required to authorize all bids greater than $5,000 and is also required to sign all checks (including checks written for expenditures other than purchases of unrestored computers). Most of SCE's checks are written for purchases of unrestored computers. SCE needs to keep track of the managers' participation in these events as well as the participation of other employees in these events.
The following attributes are of interest to SCE and must be included in your solution. You may not add any attributes. You may abbreviate the attributes using the abbreviations given in bold in parentheses next to the attributes in the list.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Bentley Balloons is an enterprise that specializes in providing helium filled balloons for customers' special occasions. They only sell balloons in large quantities; for example they provide balloons to large corporations who are having celebrations, or to department stores that want to advertise a special sale with the help of some balloons (they even have some balloons that say "Clearance Sale" on them); or to circuses or carnivals that intend to re-sell the balloons. Bentley acquires the balloons, or helium tanks, ribbons, and weights in bulk from various suppliers. Bentley's inventory clerks identify the need for those items and request the purchasing department to get them, and often the inventory clerks identify a particular vendor from whom they want purchasing to place the order (this does not obligate the purchasing department to do so, but they will need to track the information). Some requisitions are rejected by purchasing agents and are never filled. Others are approved and purchase orders are prepared and sent to vendors for the requested goods. Some purchase orders are rejected by vendors and are never filled. Others are accepted and the goods are sent by the vendors and received by Bentley's receiving clerks. Once goods are received, one of Bentley's accounting clerks issues an electronic payment to the corresponding vendor from one of its checking accounts. To meet demand, Bentley's production supervisors perform the scheduling of production jobs, the scheduling consists of ordering production (documented by production orders) and requisitioning materials (documented by materials requisitions). No equipment is needed, when new helium tanks are delivered by vendors, they take back the empty helium tanks. Production supervisors receive materials into production and oversee the production employees who perform the work in the production jobs. Bentley sees no need to track specific labor operations with respect to the production of the helium-filled balloons, as it is a very simple process.
On the next page is a cycle-level REA diagram that is intended to represent the materials acquisition and conversion (manufacturing) cycles. Your task is to identify errors in this diagram. The types of errors you should consider include missing entities, missing relationships, extra entities, and extra relationships (i.e., entities or relationships that are either nonsense or don't belong to the represented cycles). List the errors on the following page. Do NOT worry about cardinalities or attributes for this problem!
REA model for Bentley's Balloons
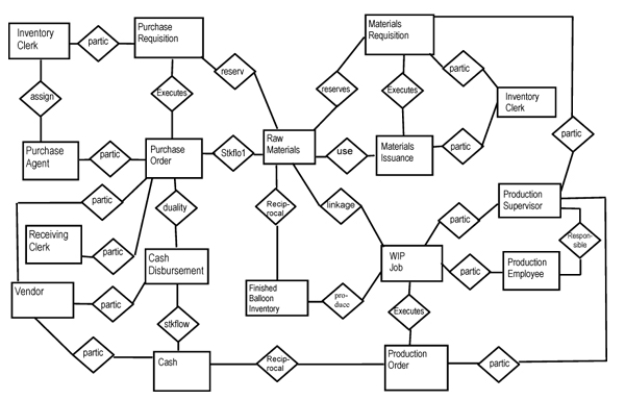 List the errors you identified from Bentley Balloons' materials acquisition and conversion cycle model below. The number of blanks available does not correspond to the number of actual errors. Use only as many as you need to use, and add blanks if necessary.
List the errors you identified from Bentley Balloons' materials acquisition and conversion cycle model below. The number of blanks available does not correspond to the number of actual errors. Use only as many as you need to use, and add blanks if necessary.
1. ________________________________________________________________
2. ________________________________________________________________
3. ________________________________________________________________
4. ________________________________________________________________
5. ________________________________________________________________
6. ________________________________________________________________
7. ________________________________________________________________
8. ________________________________________________________________
9. ________________________________________________________________
10. ________________________________________________________________
11. ________________________________________________________________
12. ________________________________________________________________
13. ________________________________________________________________
14. ________________________________________________________________
15. ________________________________________________________________
16. ________________________________________________________________
17. ________________________________________________________________
18. ________________________________________________________________
19. ________________________________________________________________
20. ________________________________________________________________
21. ________________________________________________________________
22. ________________________________________________________________
23. ________________________________________________________________
24. ________________________________________________________________
25. ________________________________________________________________
26. ________________________________________________________________
27. ________________________________________________________________
28. ________________________________________________________________
On the next page is a cycle-level REA diagram that is intended to represent the materials acquisition and conversion (manufacturing) cycles. Your task is to identify errors in this diagram. The types of errors you should consider include missing entities, missing relationships, extra entities, and extra relationships (i.e., entities or relationships that are either nonsense or don't belong to the represented cycles). List the errors on the following page. Do NOT worry about cardinalities or attributes for this problem!
REA model for Bentley's Balloons
 List the errors you identified from Bentley Balloons' materials acquisition and conversion cycle model below. The number of blanks available does not correspond to the number of actual errors. Use only as many as you need to use, and add blanks if necessary.
List the errors you identified from Bentley Balloons' materials acquisition and conversion cycle model below. The number of blanks available does not correspond to the number of actual errors. Use only as many as you need to use, and add blanks if necessary.1. ________________________________________________________________
2. ________________________________________________________________
3. ________________________________________________________________
4. ________________________________________________________________
5. ________________________________________________________________
6. ________________________________________________________________
7. ________________________________________________________________
8. ________________________________________________________________
9. ________________________________________________________________
10. ________________________________________________________________
11. ________________________________________________________________
12. ________________________________________________________________
13. ________________________________________________________________
14. ________________________________________________________________
15. ________________________________________________________________
16. ________________________________________________________________
17. ________________________________________________________________
18. ________________________________________________________________
19. ________________________________________________________________
20. ________________________________________________________________
21. ________________________________________________________________
22. ________________________________________________________________
23. ________________________________________________________________
24. ________________________________________________________________
25. ________________________________________________________________
26. ________________________________________________________________
27. ________________________________________________________________
28. ________________________________________________________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



