Deck 1: The Beginnings of Molecular Biology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/23
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: The Beginnings of Molecular Biology
1
In 1869 Friedrich Miescher isolated a substance called "nuclein" from pus from soiled bandages that was a(n)
A) acidic, phosphorus-rich substance
B) basic, phosphorus-rich substance
C) amino acid-rich substance
D) phospholipid-rich substance
A) acidic, phosphorus-rich substance
B) basic, phosphorus-rich substance
C) amino acid-rich substance
D) phospholipid-rich substance
acidic, phosphorus-rich substance
2
The basic principles of genetics attributed to Gregor Johann Mendel are:
A) the laws of segregation and independent assortment
B) the Punnett square
C) the concept of dominant and recessive traits
D) A and C
E) A, B, and C
A) the laws of segregation and independent assortment
B) the Punnett square
C) the concept of dominant and recessive traits
D) A and C
E) A, B, and C
A and C
3
The Augustinian monk, Gregor Johann Mendel, crossed yellow-seeded and green-seeded pea plants and then allowed the offspring to self-pollinate to produce an F2 generation. The results were as follows: 6018 yellow and 2002 green (8020 total). The allele for green seeds has what relationship to the allele for yellow seeds?
A) semidominant
B) incompletely dominant
C) recessive
D) dominant
A) semidominant
B) incompletely dominant
C) recessive
D) dominant
recessive
4
In 1928 Frederick Griffith discovered that Streptococcus pneumonia caused pneumonia in mice. In his experiments, mice were injected with different strains of treated and untreated bacteria. Which of the following is not likely to have occurred in the series of experiments by Griffith?
A) Mice injected with living S (pathogenic) strain die.
B) Mice injected with living R (nonpathogenic) strain live.
C) Mice injected with living R plus heat-killed S die.
D) Mice injected with living S plus heat-killed R live.
A) Mice injected with living S (pathogenic) strain die.
B) Mice injected with living R (nonpathogenic) strain live.
C) Mice injected with living R plus heat-killed S die.
D) Mice injected with living S plus heat-killed R live.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In 1928, Frederick Griffith injected living S (smooth) Streptococcus pneumonia into mice, and the mice died. When he injected living R (rough) Streptococcus pneumonia into mice, the mice lived. When he injected heat-killed S bacteria into mice, the mice lived. What was the result when he mixed heat-killed S bacteria with live R bacteria and injected this mixture into mice?
A) The mice died, and living bacteria that appeared smooth could be isolated from the dead mice.
B) The mice lived, and living bacteria that appeared smooth could be isolated from the living mice.
C) The mice died, indicating that the heat-killed S bacteria came back to life.
D) The mice lived and neither smooth nor rough-appearing bacteria could be isolated from the living mice.
A) The mice died, and living bacteria that appeared smooth could be isolated from the dead mice.
B) The mice lived, and living bacteria that appeared smooth could be isolated from the living mice.
C) The mice died, indicating that the heat-killed S bacteria came back to life.
D) The mice lived and neither smooth nor rough-appearing bacteria could be isolated from the living mice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In 1944, Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty used an in vitro agglutination assay to demonstrate that purified DNA was sufficient to cause transformation of cells, and that the transforming factor could be destroyed by
A) ribonucleases but not by deoxyribonuclease or protease enzymes.
B) proteases but not by deoxyribonuclease or ribonuclease enzymes.
C) deoxyribonucleases but not by protease or ribonuclease enzymes.
D) both deoxyribonucleases and proteases but not by ribonuclease enzymes.
A) ribonucleases but not by deoxyribonuclease or protease enzymes.
B) proteases but not by deoxyribonuclease or ribonuclease enzymes.
C) deoxyribonucleases but not by protease or ribonuclease enzymes.
D) both deoxyribonucleases and proteases but not by ribonuclease enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to Beadle and Tatum's one-gene, one-enzyme hypothesis, how many different genes are apparently operating in the pathway shown above? 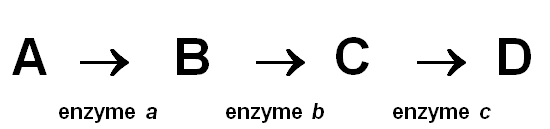
A) It cannot be determined from the pathway.
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
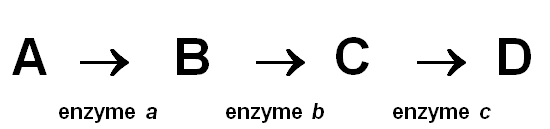
A) It cannot be determined from the pathway.
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Beadle and Tatum's "one gene - one enzyme" hypothesis was later revised to the
A) one gene - one polypeptide hypothesis.
B) one gene - one protein hypothesis.
C) one gene - one DNA molecule hypothesis.
D) one gene - one enzyme, one lipid, one RNA molecule, or one carbohydrate hypothesis.
A) one gene - one polypeptide hypothesis.
B) one gene - one protein hypothesis.
C) one gene - one DNA molecule hypothesis.
D) one gene - one enzyme, one lipid, one RNA molecule, or one carbohydrate hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the 1950s, Hershey and Chase conducted a now famous experiment to determine whether DNA or protein carried the hereditary information in bacteriophage T2. What method did they used to selectively label the DNA and protein components of bacteriophage T2?
A) 35S to label the DNA and 32P to label the protein
B) 35S to label the protein and 32P to label the DNA
C) 35P to label the protein and 32S to label the DNA
D) none of the above
A) 35S to label the DNA and 32P to label the protein
B) 35S to label the protein and 32P to label the DNA
C) 35P to label the protein and 32S to label the DNA
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The classic experiment performed by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase revealed:
A) RNA was not the hereditary material.
B) Microbes could exchange genetic information.
C) In a bacteriophage infection, protein was transferred into the infected bacterial cell.
D) In a bacteriophage infection, DNA was transferred into the infected bacterial cell.
A) RNA was not the hereditary material.
B) Microbes could exchange genetic information.
C) In a bacteriophage infection, protein was transferred into the infected bacterial cell.
D) In a bacteriophage infection, DNA was transferred into the infected bacterial cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick proposed
A) the tetranucleotide structure of DNA.
B) the one gene - one enzyme hypothesis.
C) the double helix as a model for the structure of DNA.
D) that Griffith's transforming principle was DNA.
A) the tetranucleotide structure of DNA.
B) the one gene - one enzyme hypothesis.
C) the double helix as a model for the structure of DNA.
D) that Griffith's transforming principle was DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The primary principle of the "neutral" theory of natural selection is that
A) evolution is primarily driven by purifying selection against deleterious mutations.
B) advantageous and deleterious mutations play an equal role in evolution.
C) genetic drift by random allele fixation plays a dominant role in evolution.
D) it is impossible to deduce whether observed allele frequencies are caused by positive or negative selection.
A) evolution is primarily driven by purifying selection against deleterious mutations.
B) advantageous and deleterious mutations play an equal role in evolution.
C) genetic drift by random allele fixation plays a dominant role in evolution.
D) it is impossible to deduce whether observed allele frequencies are caused by positive or negative selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Neo-Darwinism did not recognize a significant role of _________________ variation in evolution.
A) advantageous
B) deleterious
C) adaptive
D) neutral
A) advantageous
B) deleterious
C) adaptive
D) neutral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following theories suggests that mutations create a pool of genetic diversity that may undergo selection at a later time when conditions change?
A) Darwinism
B) Neo-Darwinism
C) Neutral Theory
D) Nearly Neutral Theory
A) Darwinism
B) Neo-Darwinism
C) Neutral Theory
D) Nearly Neutral Theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Darwin's original theory of evolution recognized ________________ variations.
A) advantageous, deleterious, and neutral
B) advantageous, deleterious, and dominant
C) dominant, recessive, and advantageous
D) neutral, dominant, and recessive
A) advantageous, deleterious, and neutral
B) advantageous, deleterious, and dominant
C) dominant, recessive, and advantageous
D) neutral, dominant, and recessive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Define the terms "in vivo" and "in vitro."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The discovery by Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty that Griffith's transforming principle was DNA came as a surprise to scientists at the time. Provide an explanation for why their finding was unexpected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Explain how technological advances allowed Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase to carry out their classic experiment in 1952.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Discuss scientific findings at the time that provided the necessary context for the proposed structure of DNA by Watson and Crick in 1953.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Sodium hydroxide denatures both proteins and nucleic acids, while phenol denatures proteins but not nucleic acids. In the transformation experiments performed by Griffith with Streptococcus pnemoniae, what result would be expected if an extract of S-strain bacteria was treated with phenol? What would be expected if it was treated with sodium hydroxide?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When Hershey and Chase infected bacterial cells that had been grown in the presence of radioactive phosphorus with bacteriophage T2, both the phage RNA and DNA must also have incorporated the labeled phosphorus and yet the experimental results were not affected. Why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Four independent methionine auxotrophs of Neurospora were studied to determine which related compounds might substitute for their methionine requirement. In the table below "+" indicates growth on minimal medium supplemented with the indicated compound, and "-" indicates no growth.
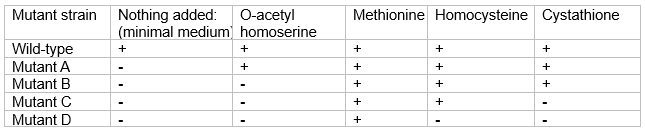 Based on the results, give the order of these four compounds in the biosynthetic pathway of methionine.
Based on the results, give the order of these four compounds in the biosynthetic pathway of methionine.
 Based on the results, give the order of these four compounds in the biosynthetic pathway of methionine.
Based on the results, give the order of these four compounds in the biosynthetic pathway of methionine.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Explain how Tomoko Ohta's "nearly neutral" theory of molecular evolution reconciled the differences between neutral evolutionary theory and selection evolutionary theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



