Deck 5: Chemical Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/83
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Chemical Reactions
1
The minimum energy that reactants need in order for the molecules to be in the correct orientation is called:
A)collision energy
B)dissociation energy
C)activation energy
D)orientation energy
A)collision energy
B)dissociation energy
C)activation energy
D)orientation energy
activation energy
2
For a reaction to be exothermic or endothermic it is determined by:
A)the activation energy
B)the states of the reactants
C)the overall loss or gain of energy when the bonds break and reform
D)collision orientation of molecules
A)the activation energy
B)the states of the reactants
C)the overall loss or gain of energy when the bonds break and reform
D)collision orientation of molecules
the overall loss or gain of energy when the bonds break and reform
3
What type of nutrient has the highest energy content per gram?
A)Carbohydrate
B)Fat
C)Protein
D)They all have the same energy content.
A)Carbohydrate
B)Fat
C)Protein
D)They all have the same energy content.
Fat
4
A food sample contains 10 g fat, 12 g carbohydrate, and 8 g protein. The energy content is:
A)120 Cal
B)160 Cal
C)170 Cal
D)180 Cal
A)120 Cal
B)160 Cal
C)170 Cal
D)180 Cal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following factors influence the rate of a reaction?
A)Temperature
B)Reactant concentration
C)A catalyst
D)All of the above
A)Temperature
B)Reactant concentration
C)A catalyst
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A fast reaction rate for a chemical reaction is dependent on:
A)having a large activation energy
B)having a small activation energy
C)being exothermic
D)being endothermic
A)having a large activation energy
B)having a small activation energy
C)being exothermic
D)being endothermic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following processes is nonspontaneous?
A)An antacid tablet reacting with stomach acid to produce carbon dioxide
B)A hot pan cooling on the counter
C)Water turning to ice below 0°C
D)A battery being recharged
A)An antacid tablet reacting with stomach acid to produce carbon dioxide
B)A hot pan cooling on the counter
C)Water turning to ice below 0°C
D)A battery being recharged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Determine which of the statements is incorrect regarding this figure: 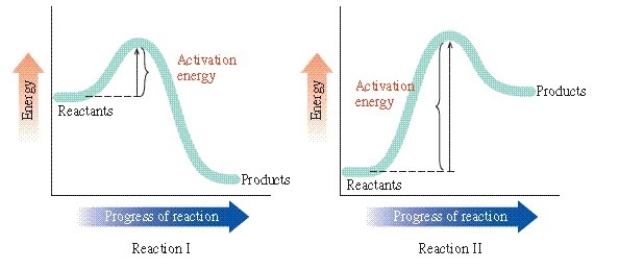
A)Reaction I is exergonic.
B)Reaction II occurs faster than reaction I.
C)Reaction II is endergonic.
D)The activation energy for reaction I is smaller than that of reaction II.

A)Reaction I is exergonic.
B)Reaction II occurs faster than reaction I.
C)Reaction II is endergonic.
D)The activation energy for reaction I is smaller than that of reaction II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following actions would not increase the rate of a reaction?
A)Diluting the reactants by a factor of 2
B)Increasing the temperature by 10°C
C)Adding a catalyst
D)Increasing the concentration of the reactants by a factor of 2
A)Diluting the reactants by a factor of 2
B)Increasing the temperature by 10°C
C)Adding a catalyst
D)Increasing the concentration of the reactants by a factor of 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An enzyme increases the rate of a biological process in what way?
A)Increases the concentration of reactants
B)Increases the temperature of the reactants
C)Lowers the activation energy of the process
D)Makes the reaction more exergonic
A)Increases the concentration of reactants
B)Increases the temperature of the reactants
C)Lowers the activation energy of the process
D)Makes the reaction more exergonic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following are enzyme-based diseases?
A)Gout
B)Lactose intolerance
C)Phenylketonuria
D)All of the above
A)Gout
B)Lactose intolerance
C)Phenylketonuria
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In what type of reaction are there more reactant substances than product substances?
A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement
A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In what type of reaction are there more product substances than reactant substances?
A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement
A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What type of reaction is illustrated in this diagram? 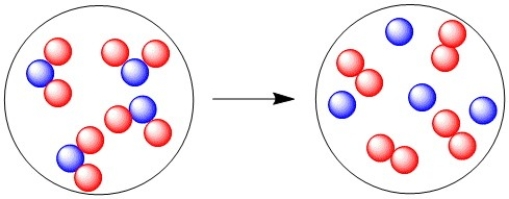
A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement

A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What type of reaction is illustrated in this diagram? 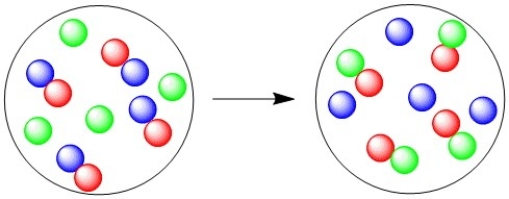
A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement

A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The following reaction is an example of which of the following?
Na2CO3(aq)+ Pb(NO3)2(aq)? 2NaNO3(aq)+ PbCO3(s)
A)Synthesis
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement
Na2CO3(aq)+ Pb(NO3)2(aq)? 2NaNO3(aq)+ PbCO3(s)
A)Synthesis
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A piece of zinc placed in hydrochloric acid results in a fierce effervescence and the zinc eventually dissolves, yielding a solution of zinc chloride. A glowing splint gives a "popping" sound, indicating the presence of hydrogen gas. What type of reaction is it?
A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement
A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A solution of sodium chloride when added to a solution of silver nitrate produces a white precipitate of silver chloride. What type of reaction is it?
A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement
A)Combination
B)Decomposition
C)Single displacement
D)Double displacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the coefficient for O2 when the equation for the combustion of C5H12 to CO2 and H2O is balanced?
A)6
B)7
C)8
D)9
A)6
B)7
C)8
D)9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the coefficient for O2 when the equation for the combustion of C4H10 to CO2 and H2O is balanced?
A)6
B)7
C)12
D)13
A)6
B)7
C)12
D)13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of these reactions is a double displacement reaction?
A)K(s)+ H2O(l)? H2(g)+ KOH(aq)
B)Mg(s)+ HClO4(aq)? Mg(ClO4)2(aq)+ H2(g)
C)BaO(s)+ H2O(l)? Ba(OH)2(aq)
D)CH3COOH(aq)+ K2CO3(aq)? H2O(l)+ CO2(g)+ KCH3COO(aq)
A)K(s)+ H2O(l)? H2(g)+ KOH(aq)
B)Mg(s)+ HClO4(aq)? Mg(ClO4)2(aq)+ H2(g)
C)BaO(s)+ H2O(l)? Ba(OH)2(aq)
D)CH3COOH(aq)+ K2CO3(aq)? H2O(l)+ CO2(g)+ KCH3COO(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What statement is incorrect about this oxidation-reduction reaction?
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)? 2 SO3(g)
A)O2 is the oxidizing agent.
B)SO2 is the reducing agent.
C)O2 is reduced.
D)SO2 gains electrons.
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)? 2 SO3(g)
A)O2 is the oxidizing agent.
B)SO2 is the reducing agent.
C)O2 is reduced.
D)SO2 gains electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When an organic molecule loses hydrogens it is said to be:
A)reduced
B)oxidized
C)both oxidized and reduced
D)neither oxidized or reduced
A)reduced
B)oxidized
C)both oxidized and reduced
D)neither oxidized or reduced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When an organic molecule gains hydrogens it is said to be:
A)reduced
B)oxidized
C)both oxidized and reduced
D)neither oxidized or reduced
A)reduced
B)oxidized
C)both oxidized and reduced
D)neither oxidized or reduced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When a substance is oxidized it is called a(n):
A)oxidizing agent
B)reducing agent
C)both
D)neither
A)oxidizing agent
B)reducing agent
C)both
D)neither

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When a substance is reduced it is called a(n):
A)oxidizing agent
B)reducing agent
C)both
D)neither
A)oxidizing agent
B)reducing agent
C)both
D)neither

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If this is the reduced form of NADH which of the following is the oxidized form of this important biomolecule?
A)NADH2
B)NAD+
C)NAD
D)NAD+2
A)NADH2
B)NAD+
C)NAD
D)NAD+2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Identify the correct sequence of substances in degree of oxidation.
A)Alcohol ? aldehyde ? carboxylic acid
B)Carboxylic acid ? aldehyde ? alcohol
C)Alcohol ? carboxylic acid ? aldehyde
D)Carboxylic acid ? alcohol ? aldehyde
A)Alcohol ? aldehyde ? carboxylic acid
B)Carboxylic acid ? aldehyde ? alcohol
C)Alcohol ? carboxylic acid ? aldehyde
D)Carboxylic acid ? alcohol ? aldehyde

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Hydrogenation of an alkene is an example of what kind of reaction?
A)Addition
B)Oxidation
C)Hydrolysis
D)Hydration
A)Addition
B)Oxidation
C)Hydrolysis
D)Hydration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the most likely product of hydration of CH3CH=CH2?
A)CH3CH2CH2OH
B)CH3CH2CH3
C)CH3CHOHCH3
D)CH3CHOHCH2OH
A)CH3CH2CH2OH
B)CH3CH2CH3
C)CH3CHOHCH3
D)CH3CHOHCH2OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following molecules would yield this product when hydrated? 
A)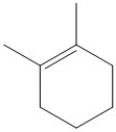
B)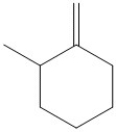
C)
D)All of the above could yield this product.

A)

B)

C)

D)All of the above could yield this product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A hotpack is an example of an endothermic reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An exothermic reaction requires heat energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The free energy of the products in an endergonic reaction is higher than that of the reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In a solid, the particles are arranged in the most random way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A spontaneous reaction proceeds without requiring additional energy from the surroundings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The Gibbs free energy change includes contributions from both heat and randomness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Diamond will convert spontaneously into graphite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An exergonic reaction is always spontaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The following energy diagram represents an exergonic reaction:
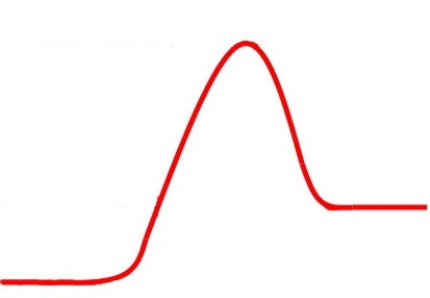


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Carbohydrates have the highest energy content per gram among carbohydrates, fats and proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A spontaneous reaction always occurs rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A catalyst increases the reaction rate by reducing the free energy change for the process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A catalyst increases the reaction rate by reducing the activation energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An enzyme is a biological catalyst.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An enzyme is a carbohydrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The conversion of ATP to ADP provides energy used to drive other biological reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A reducing agent gains electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Reduction is associated with gain of hydrogen atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Oxidation is associated with loss of oxygen atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
NAD+ is an oxidizing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Conversion of an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid involves reduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Conversion of an alcohol to a ketone involves oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In condensation reactions one molecule is split into two molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In condensation reactions water molecules are produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Hydrogenation of an alkene is a reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The energy required for a reaction to occur is called the ________ energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Energy is defined as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Energy comes in different forms that can be interchanged. One major form is potential energy. The other is ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The amount of energy in molecules available to do work is called the ________ energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The symbol for free energy change is ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A reaction where the free energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants is called an ________ reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An endergonic reaction is one in which the free energy of the products is ________ than that of the reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In an exergonic reaction, the sign of ΔG is ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The following energy diagram represents an ________ reaction.
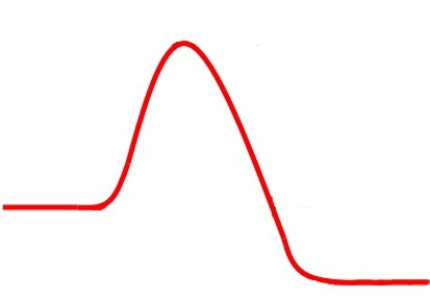


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Calculate the energy content of a snack bar that contains 25 g carbohydrate, 8 g fat and 5 g protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A catalyst speeds up a reaction rate by ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A protein that acts as a biological catalyst is called a/an ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Why does increasing the temperature increase the reaction rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When heated in air, copper metal develops a black appearance over time. Analysis shows that copper(II)oxide is formed. What type of reaction is this?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A solution of potassium (K2CrO4)when added to a solution of lead(II)acetate (Pb(CH3COO)2 produces a yellow precipitate of lead(II)chromate. What type of reaction is it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What substance is indicated by the name under the arrow in this equation?
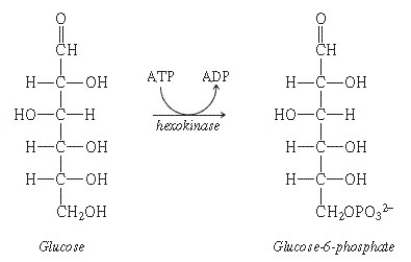


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What do the initials ATP stand for?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Oxidation always involves ________ of electrons and maybe involve ________ of oxygen atoms or ________ of hydrogen atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Is benzoic acid oxidized or reduced in this reaction?
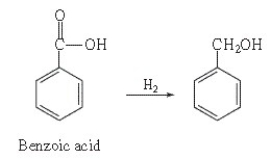


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the oxidized form of FADH?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What is the reduced form of NAD+?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The formation of ATP from ADP is an example of a ________ reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The reaction of ATP to produce ADP and energy involves ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Esterification is an example of a ________ reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



