Deck 8: Compound Interest: Future Value and Present Value
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/155
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Compound Interest: Future Value and Present Value
1
Explain the difference between "compounding period" and "compounding frequency."
The "compound period" is the time interval between successive conversions of interest to principal. The "compounding frequency" is not a time interval. Rather, it indicates how frequently (that is, the number time per year) we convert interest to principal.
2
Explain the difference between "nominal rate of interest" and "periodic rate of interest."
The "periodic rate of interest" is the percent interest earned in a single compounding period. The "nominal rate of interest" is the annual interest rate you obtain if you extend the periodic rate to a full year. This is done by multiplying the periodic rate of interest by the number of compounding periods in a year.
3
Calculate the periodic rate of interest if the nominal interest rate is 6% compounded:
a. monthly.
b. quarterly.
c. semiannually.
a. monthly.
b. quarterly.
c. semiannually.
a) 0.5% per month
b) 1.5% per quarter
c) 3.0% per half-year
b) 1.5% per quarter
c) 3.0% per half-year
4
Determine the periodic interest rate for a nominal interest rate of 4.8% compounded:
a. semiannually.
b. quarterly.
c. monthly.
a. semiannually.
b. quarterly.
c. monthly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the periodic rate of interest corresponding to:
a. 5.4% compounded quarterly?
b. 5.4% compounded monthly?
a. 5.4% compounded quarterly?
b. 5.4% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Calculate the nominal interest rate if the periodic rate is:
a. 3.6%% per half year.
b. 1.8% per quarter.
c. 0.6% per month.
a. 3.6%% per half year.
b. 1.8% per quarter.
c. 0.6% per month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Determine the nominal rate of interest if the periodic rate is:
a. 1.5% per month?.
b. 1.5% per quarter?
c. 1.5% per half year.
a. 1.5% per month?.
b. 1.5% per quarter?
c. 1.5% per half year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Determine the nominal interest rate if the periodic rate is:
a) 1.25% per quarter.
b)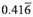 % per month.
% per month.
a) 1.25% per quarter.
b)
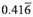 % per month.
% per month.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the nominal rate of interest if the periodic rate is:
a)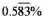 per month?
per month?
b) 5.8% per year?
a)
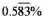 per month?
per month?b) 5.8% per year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Calculate the compounding frequency for a nominal rate of 6.6% if the periodic rate of interest is:
a. 1.65%.
b. 3.3%.
c. 0.55%.
a. 1.65%.
b. 3.3%.
c. 0.55%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For a nominal rate of 5.9%, determine the compounding frequency if the periodic interest rate is:
a. 2.95%.
b.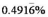
c. 1.475%.
a. 2.95%.
b.
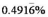
c. 1.475%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the compounding frequency for a nominal rate of 4.7% if the periodic interest rate is:
a) 1.175%?
b) %?
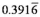
a) 1.175%?
b) %?
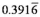

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For a given nominal interest rate (say 10%) on a loan, would the borrower prefer it to be compounded annually or compounded monthly? Which compounding frequency would the lender prefer? Give a brief explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
From a simple inspection, it is possible for an investor to rank the four rates of return in each of parts (a) and (b)? If so, state the ranking. Give a brief explanation to justify your answer.
a) 9.0% compounded monthly, 9.1% compounded quarterly, 9.2% compounded semiannually, 9.3% compounded annually.
b) 9.0% compounded annually, 9.1% compounded semiannually, 9.2% compounded quarterly, 9.3% compounded monthly.
a) 9.0% compounded monthly, 9.1% compounded quarterly, 9.2% compounded semiannually, 9.3% compounded annually.
b) 9.0% compounded annually, 9.1% compounded semiannually, 9.2% compounded quarterly, 9.3% compounded monthly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Suppose it took x years for an investment to grow from $100 to $200 at a fixed compound rate of return. How many more years will it take to earn an additional:
a) $100?
b) $200?
c) $300? In each case, pick an answer from: (i) more than x years, (ii) less than x years, (iii) exactly x years.
a) $100?
b) $200?
c) $300? In each case, pick an answer from: (i) more than x years, (ii) less than x years, (iii) exactly x years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the maturity value of $5000 invested at 6.0% compounded semiannually for seven years?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the future value of $8500 after 5½ years if it earns 9.5% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
To what amount did $12,100 grow after 3¼ years if it earned 7.5% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What was a $4400 investment worth after 6¾ years if it earned 5.4% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Assume that a $10,000 investment can earn 8% compounded quarterly. What will be its future value: a. After 15 years? b. After 20 years? c. After 25 years? d. After 30 years?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How much will $10,000 be worth after 25 years if it earns:
a. 6% compounded semiannually?
b. 7% compounded semiannually?
c. 8% compounded semiannually?
a. 6% compounded semiannually?
b. 7% compounded semiannually?
c. 8% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
To what amount will $10,000 grow after 25 years if it earns:
a. 9% compounded annually?
b. 9% compounded semiannually?
c. 9% compounded quarterly? d. 9% compounded monthly?
a. 9% compounded annually?
b. 9% compounded semiannually?
c. 9% compounded quarterly? d. 9% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
$10,000 is invested at 7% compounded annually. Over the next years, how much of the investment's increase in value represents:
a. Earnings strictly on the original $10,000 principal?
b. Earnings on re-invested earnings? (This amount reflects the cumulative effect of compounding.)
a. Earnings strictly on the original $10,000 principal?
b. Earnings on re-invested earnings? (This amount reflects the cumulative effect of compounding.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the maturity value of a $12,000 loan for 18 months at 7.2% compounded quarterly? How much interest is charged on the loan?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How much more will an investment of $10,000 be worth after 25 years if it earns 9% compounded annually instead of 8% compounded annually? Calculate the difference in dollars and as a percentage of the smaller maturity value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A $1000 investment is made today. Calculate its maturity values for the six combinations of terms and annually compounded interest rates in the following table.
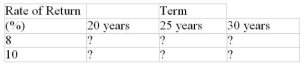
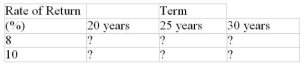

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A $5000 payment due 1½ years ago has not been paid. If money can earn 8.25% compounded annually, what amount paid 2½ years from now would be the economic equivalent of the missed payment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What amount three years from now is equivalent to $3000 due five months from now? Assume that money can earn 7.5% compounded monthly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What amount two years from will be equivalent to $2300 1½ years ago, if money earns 6.25% compounded semiannually during the intervening time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Payments of $1300 due today and $1800 due in 1¾ years are to be replaced by a single payment 4 years from now. What is the amount of that payment if money is worth 6% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Bjorn defaulted on payments of $2000 due 3 years ago and $1000 due 1½ years ago. What would a fair settlement to the payee be 1½ years from now if the money could have been invested in low-risk government bonds to earn 4.2% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Interest rates were at historical highs in the early 1980s. In August of 1981, you could earn 17.5% compounded annually on a five-year term deposit with a Canadian bank. Since then, the interest rate offered on five-year term deposits dropped to a low of 2.0% compounded annually in August of 2009. On a $10,000 deposit for a term of five years, how much more would you have earned at the historical high interest rate than at the more recent low rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Nelson borrowed $5000 for years. For the first years, the interest rate on the loan was 8.4% compounded monthly. Then the rate became 7.5% compounded semiannually. What total amount was required to pay off the loan if no payments were made before the expiry of the -year term?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Roger has just invested $60,000 in a five-year Guaranteed Investment Certificate (GIC) earning 6% compounded semiannually. When the GIC matures, he will reinvest its entire maturity value in a new five-year GIC. What will be the maturity value of the second GIC if it yields:
a) The same rate as the current GIC?
b) 7% compounded semiannually?
c) 5% compounded semiannually?
a) The same rate as the current GIC?
b) 7% compounded semiannually?
c) 5% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Follow the instructions in the NET @ssets box earlier in this section to access the interactive chart named "Future Value of $100"
in the student textbook's OLC. Use the chart to help you answer these questions. What is the percentage increase in an investment's future value every five years if the investment earns:
a) 7% compounded annually?
b) 9% compounded annually?
c) 11% compounded annually?
in the student textbook's OLC. Use the chart to help you answer these questions. What is the percentage increase in an investment's future value every five years if the investment earns:
a) 7% compounded annually?
b) 9% compounded annually?
c) 11% compounded annually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Follow the instructions in the NET @ssets box earlier in this section to access the interactive chart named "Future Value of $100" in the student textbook's OLC. Use the chart to help you answer:
a) Problem 13.
b) Problem 15
a) Problem 13.
b) Problem 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Follow the instructions in the NET @ssets box earlier in this section to access the interactive chart named "Future Value of $100" in the student textbook's OLC. Use the chart to help you answer these questions. Over a 25-year period, how much more (expressed as a percentage) will an investment be worth if it earns:
a) 6% compounded monthly instead of 6% compounded annually?
b) 9% compounded monthly instead of 9% compounded annually?
c) 12% compounded monthly instead of 12% compounded annually?
a) 6% compounded monthly instead of 6% compounded annually?
b) 9% compounded monthly instead of 9% compounded annually?
c) 12% compounded monthly instead of 12% compounded annually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the present value of $100 due eight years from now is $50, what is the present value of $100 due 16 years from now? Answer without using formula (8-2).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If money can be invested to earn 6.5% compounded annually, how much would have to be invested today to grow to $10,000 after:
a. 10 years?
b. 20 years?
c. 30 years?
a. 10 years?
b. 20 years?
c. 30 years?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What amount would have to be invested today for the future value to be $10,000 after 20 years if the rate of return is:
a. 5% compounded quarterly?
b. 7% compounded quarterly?
c. 9% compounded quarterly?
a. 5% compounded quarterly?
b. 7% compounded quarterly?
c. 9% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What amount invested today would grow to $10,000 after 25 years if the investment earns: a. 8% compounded annually? b. 8% compounded semiannually?
c. 8% compounded quarterly?
d. 8% compounded monthly?
c. 8% compounded quarterly?
d. 8% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If money is worth 6% compounded annually, what amount today is equivalent to $10,000 paid
a. 12 years from now?
b. 24 years from now?
c. 36 years from now?
a. 12 years from now?
b. 24 years from now?
c. 36 years from now?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the present value of $10,000 discounted at 4.5% compounded annually over ten years?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What principal amount will have a maturity value of $5437.52 after 27 months if it earns 8.5% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The maturity value of an investment after 42 months is $9704.61. What was the original investment if it earned 7.5% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What amount today is economically equivalent to $8000 paid 18 months from now if money is worth 5% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
You owe $6000 payable three years from now. What alternative amount should your creditor be willing to accept today if she can earn 4.2% compounded monthly on a low-risk investment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What amount, 1½ years from now, is equivalent to $7000 due in 8 years if money can earn 6.2% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A payment of $1300 is scheduled for a date 3½ years from now. What would be an equivalent payment 9 months from now if money is worth 5.5% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What single amount, paid three years from now, would be economically equivalent to the combination of $1400 due today and $1800 due in five years if funds can be invested to earn 6% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Ramon wishes to replace payments of $900 due today and $500 due in 22 months by a single equivalent payment 18 months from now? If money is worth 5% compounded monthly, what should that payment be?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Mohinder has financial obligations of $1000 due in 3½ years and $2000 due in 5½ years. He wishes to settle the obligations sooner with a single payment one year from now. If money is worth 7.75% compounded semiannually, what amount should the payee be willing to accept?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What payment 2¼ years from now would be a fair substitute for the combination of $1500 due (but not paid) 9 months ago and $2500 due in 4½ years, if money can earn 9% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A scheduled payment stream consisted of three payments: $2100 due (but not paid) 1½ years ago, $1300 due today, and $800 due in 2 years. What single payment, 6 months from now, would be economically equivalent to the payment stream?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A debtor owing payments of $750 due today, $1000 due in 2 years, and $1250 due in 4 years requests a payout figure to settle all three obligations by means of a single economically-equivalent payment 18 months from now. What is that amount if the payee can earn 9.5% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A bond pays $1000 interest at the end of every year for the next 30 years. What is the current economic value of each of the 15th and 30th payments if we discount the payments at:
a) 5% compounded semiannually?
b) 8% compounded semiannually?
a) 5% compounded semiannually?
b) 8% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A $15,000 loan at 11.5% compounded semiannually is advanced today. Two payments of $4000 are to be made 1 year and 3 years from now. The balance is to be paid in 5 years. What will the third payment be?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A $4000 loan at 10% compounded monthly is to be repaid by three equal payments due 5, 10, and 15 months from the date of the loan. What is the size of the payments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A $6000 loan at 9% compounded quarterly is to be settled by two payments. The first payment is due after 9 months and the second payment, half the amount of the first payment, is due after 1½ years. Determine the size of each payment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Teresita has three financial obligations to the same person: $2700 due in 1 year, $1900 due in 1½ years, and $1100 due in 3 years. She wishes to settle the obligations with a single payment in 2¼ years, when her inheritance will be released from her mother's estate. What amount should the creditor accept if money can earn 9% compounded monthly from the date nine months ago when the obligations were incurred?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Mrs. Sandhu placed $11,500 in a 4-year compound-interest GIC earning 6.75% compounded monthly. What is the GIC's maturity value?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
For a given term of compound-interest GIC, the nominal interest rate with annual compounding is typically 0.125% higher than the rate with semiannual compounding and 0.25% higher than the rate with monthly compounding. Suppose that the rates for 5-year GICs are 5.00%, 4.875%, and 4.75% for annual, semiannual, and monthly compounding, respectively. How much more will an investor earn over 5 years on a $10,000 GIC at the most favourable rate than at the least favourable rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Sun Life Financial offers a five-year compound-interest GIC earning rates of 2.5%, 3%, 3.5%, 4.25%, and 5% in successive years. Manulife offers a similar GIC paying rates of 2.75%, 3.25%, 3.5%, 4%, and 4.25% in successive years. For a $10,000 investment, which GIC will have the greater maturity value after five years? How much greater?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Sun Life Financial offers a five-year compound-interest GIC earning rates of 2.5%, 3%, 3.5%, 4.25%, and 5% in successive years. Manulife offers a similar GIC paying rates of 2.75%, 3.25%, 3.5%, 4%, and 4.25% in successive years. For a $10,000 investment, calculate the interest earned in the third year in each GIC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Stan purchased a $15,000 compound-interest Series103 Canada Savings Bond on December 1, 2008. The interest rate in the first year was 2.5% and in the second year was 3.00%. What interest did he receive when he redeemed the CSB on May 1, 2010?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What amount did the owner of a $5000 face value compound-interest series S96 Canada Savings Bond receive when she redeemed the bond on:
a) November 1, 2009?
b) August 21, 2010?
a) November 1, 2009?
b) August 21, 2010?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What amount did the owner of a $10,000 face value compound-interest series S102 CSB receive when he redeemed the bond on:
a) November 1, 2009?
b) May 19, 2010?
a) November 1, 2009?
b) May 19, 2010?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What was the redemption value of a $300 face value compound-interest series S90 CSB on March 8, 2010?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
On February 1, 2007, Selma purchased a $50,000 compound-interest CSB. The interest rate on the CSB was 1.55% for each of the first two years and 2.675% for the third year. What was the total interest earned on the CSB by the time Selma redeemed the bond on April 1, 2009? (Taken from CIFP course materials.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Calculate the maturity value of $2000 invested in a five-year compound-interest GIC earning 4.1% compounded annually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A compound-interest GIC will earn 5% compounded annually for the first two years and 6% compounded annually for the last three years of its five-year term. What will be the maturity value of $3000 invested in this GIC?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
$8000 is invested in a five-year compound-interest GIC earning interest rates of 4%, 4.5%, 5%, 5.5%, and 6% in successive years. What amount will the investor receive at maturity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Western Life's "Move-Up" compound-interest GIC earns 4.125%, 4.25%, 4.5%, 4.875%, and 5% in successive years. What will be the maturity value of $7500 invested in this GIC?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
On the same date that the CIBC advertised rates of 2%, 2.5%, 3%, 3.25%, and 7% in successive years of its five-year compound-interest Escalating Rate GIC, it offered 2.75% compounded annually on its five-year fixed-rate GIC. Calculate the interest earned in the fourth year from a $10,000 investment in each GIC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
On the same date that the CIBC advertised rates of 2%, 2.5%, 3%, 3.25%, and 7% in successive years of its five-year compound-interest Escalating Rate GIC, it offered 2.75% compounded annually on its five-year fixed-rate GIC. How much would have to be initially invested in each GIC to have a maturity value of $20,000?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Zimbabwe's descent into economic chaos during the late 1990s and early 2000s resulted in hyperinflation. By August of 2008, the monthly inflation rate stood at 839%! Retailers were increasing their prices more than once each day. The government had to issue currency in ever rising denominations-the highest denomination note circulating in August 2008 was for $100 billion ($100,000,000,000) Zimbabwean dollars!
a. Consider a loaf of bread with a price of $4 at the beginning of a month. With an inflation rate of 839% per month, what would the loaf's price be at the end of a month in order to "keep pace" with inflation?
b. In the scenario in part (a), what percentage of its purchasing power did a fixed nominal amount of currency retain at the end of the month?
c. What daily per cent price increase, compounded over a 30-day month, would result in an 839% overall price increase during the month?
d. Consider a piece of candy priced at just one cent ($0.01) at the beginning of a year. If inflation continued at the rate of 839% per month for an entire year, what would be the inflation-adjusted price of the candy at the end of the year?
a. Consider a loaf of bread with a price of $4 at the beginning of a month. With an inflation rate of 839% per month, what would the loaf's price be at the end of a month in order to "keep pace" with inflation?
b. In the scenario in part (a), what percentage of its purchasing power did a fixed nominal amount of currency retain at the end of the month?
c. What daily per cent price increase, compounded over a 30-day month, would result in an 839% overall price increase during the month?
d. Consider a piece of candy priced at just one cent ($0.01) at the beginning of a year. If inflation continued at the rate of 839% per month for an entire year, what would be the inflation-adjusted price of the candy at the end of the year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In 2002 the number of workers in the forest industry was forecast to decline by 3% per year, reaching 80,000 in 2012. How many were employed in the industry in 1992?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What price should be paid for a $5000 face value strip bond with 19.5 years remaining to maturity if it is to yield the buyer 6.1% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider a $5000 face value Province of Ontario strip bond from the issue in Table 8.3 that matures on
December 1, 2018. If the yield does not change as years go by, what will be the bond's value on:
a) December 1, 2012?
b) December 1, 2014?
c) December 1, 2016?
December 1, 2018. If the yield does not change as years go by, what will be the bond's value on:
a) December 1, 2012?
b) December 1, 2014?
c) December 1, 2016?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Consider a $10,000 face value Government of Canada strip bond from the issue in Table 8.3 that matures on June 1, 2025. Assume the yield does not change as years go by.
a) What will be the bond's value on December 1, 2016?
b) What will be the bond's value on December 1, 2020?
c) Suppose you invest an amount equal to the answer from Part (a) at 4.08% compounded semiannually for four years. What will its maturity value be?
d) To three-figure accuracy, why do you get the same answers for Parts (b) and (c)?
a) What will be the bond's value on December 1, 2016?
b) What will be the bond's value on December 1, 2020?
c) Suppose you invest an amount equal to the answer from Part (a) at 4.08% compounded semiannually for four years. What will its maturity value be?
d) To three-figure accuracy, why do you get the same answers for Parts (b) and (c)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



