Deck 4: Mechanical Objects, Part 2
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Mechanical Objects, Part 2
1
When sitting still on the ground, a tricycle is in a state of
A) unstable dynamic equilibrium
B) dynamic equilibrium
C) stable static equilibrium
D) unstable static equilibrium
A) unstable dynamic equilibrium
B) dynamic equilibrium
C) stable static equilibrium
D) unstable static equilibrium
stable static equilibrium
2
When moving, a bicycle is in a state of dynamic equilibrium due to
A) gyroscopic effects
B) air resistance
C) the shape of the fork
D) (A) and (C)
A) gyroscopic effects
B) air resistance
C) the shape of the fork
D) (A) and (C)
(A) and (C)
3
A three - wheeler is
A) statically stable and dynamically unstable
B) statically unstable and dynamically stable
C) both statically and dynamically unstable
D) both statically and dynamically stable
A) statically stable and dynamically unstable
B) statically unstable and dynamically stable
C) both statically and dynamically unstable
D) both statically and dynamically stable
statically stable and dynamically unstable
4
A motorcycle is
A) statically stable and dynamically unstable
B) statically unstable and dynamically stable
C) both statically and dynamically unstable
D) both statically and dynamically stable
A) statically stable and dynamically unstable
B) statically unstable and dynamically stable
C) both statically and dynamically unstable
D) both statically and dynamically stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In studying many martial arts, it is necessary to practice efficient and safe postures. One important concept related to how one should stand is that the feet should be reasonably far apart, because
A) the base of support is wider, thus stabilizing the person.
B) the weight on each foot will be less than when standing normally.
C) the weight on each foot will be more than when standing normally.
D) the friction force increases, giving the person more traction.
A) the base of support is wider, thus stabilizing the person.
B) the weight on each foot will be less than when standing normally.
C) the weight on each foot will be more than when standing normally.
D) the friction force increases, giving the person more traction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
At various times in the news it has been reported that certain vehicles are susceptible to rolling over. The physical mechanism that is responsible for rollovers is
A) Frictional torques about the driver only.
B) Frictional torques from the tricycle on the road acting below the road's center of mass.
C) Frictional torques from the road on the tricycle about its center of mass, which is below the rider.
D) Strong air currents simply blowing the system over.
A) Frictional torques about the driver only.
B) Frictional torques from the tricycle on the road acting below the road's center of mass.
C) Frictional torques from the road on the tricycle about its center of mass, which is below the rider.
D) Strong air currents simply blowing the system over.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
It is important for cyclists to lean their bicycles while negotiating sharp turns because
A) the torque created by their leaning balances out the frictional torque from the road which would tend to flip them.
B) the torque created by their leaning balances out their weight and holds them up.
C) their tires flatten out, thus getting better traction on the road.
D) they increase their static stability
A) the torque created by their leaning balances out the frictional torque from the road which would tend to flip them.
B) the torque created by their leaning balances out their weight and holds them up.
C) their tires flatten out, thus getting better traction on the road.
D) they increase their static stability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
You are riding a multi-speed bicycle up a steep hill that's 100 m high and want to do as little work as possible on your way up the hill.
A) You should choose the largest crank sprocket (attached to the pedals) and the smallest freewheel sprocket (attached to the rear wheel).
B) You should choose the smallest crank sprocket (attached to the pedals) and the largest freewheel sprocket (attached to the rear wheel).
C) You should choose the largest crank sprocket (attached to the pedals) and the largest freewheel sprocket (attached to the rear wheel).
D) Your choice of gears doesn't matter because you'll do the same amount of work climbing the hill no matter which gear you choose.
A) You should choose the largest crank sprocket (attached to the pedals) and the smallest freewheel sprocket (attached to the rear wheel).
B) You should choose the smallest crank sprocket (attached to the pedals) and the largest freewheel sprocket (attached to the rear wheel).
C) You should choose the largest crank sprocket (attached to the pedals) and the largest freewheel sprocket (attached to the rear wheel).
D) Your choice of gears doesn't matter because you'll do the same amount of work climbing the hill no matter which gear you choose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
You buy an older motorcycle and notice that, even in low gear, it is difficult to get the bike going. You should replace the sprocket in the rear wheel with one that is
A) smaller so the motor can do more work at the start
B) smaller so the motor won't have to do so much work at the start.
C) larger so the motor won't have to do so much work at the start.
D) larger so the motor can do more work at the start.
A) smaller so the motor can do more work at the start
B) smaller so the motor won't have to do so much work at the start.
C) larger so the motor won't have to do so much work at the start.
D) larger so the motor can do more work at the start.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
You go to a quick - fix garage to get your brakes worked on. When your tires are re - installed, the mechanic forgets to put the lug nuts on your tires. Although nobody gets hurt, a tire comes off your car when you are traveling fairly rapidly and it is able to roll through a very large distance, even hitting bumps and objects in the way. Please explain why the tire can roll so far without tipping over.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Please explain why tricycles are better at sitting still than bicycles are, but bikes are the vehicles of choice when you want to be moving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why does a skateboarder lean while negotiating a curve?
A) To keep from tipping over by making sure the net force on them is directed towards the skateboard.
B) It saves energy
C) It lowers air resistance
D) To lessen gravitational torque on their center of mass.
A) To keep from tipping over by making sure the net force on them is directed towards the skateboard.
B) It saves energy
C) It lowers air resistance
D) To lessen gravitational torque on their center of mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A top is
A) Statically stable and dynamically unstable.
B) Statically unstable and dynamically stable.
C) Statically unstable and dynamically unstable.
D) Statically stable and dynamically stable.
A) Statically stable and dynamically unstable.
B) Statically unstable and dynamically stable.
C) Statically unstable and dynamically unstable.
D) Statically stable and dynamically stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An object is in stable equilibrium only when
A) Its total potential energy rises whenever it reorients.
B) Its total potential energy lowers whenever it reorients.
C) It is not moving
D) It is moving
A) Its total potential energy rises whenever it reorients.
B) Its total potential energy lowers whenever it reorients.
C) It is not moving
D) It is moving

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
You can make a bicycle lean by
A) briefly steering it in the direction of a turn
B) briefly steering it in the direction opposite the turn
C) Braking
D) Pedaling faster
A) briefly steering it in the direction of a turn
B) briefly steering it in the direction opposite the turn
C) Braking
D) Pedaling faster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is one advantage and one drawback of a very large wheel on a bicycle or tricycle whose operator can pedal the front wheel?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What are three drawbacks to a bicycle or tricycle whose front wheel can be pedaled?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Astronauts in the space shuttle feel weightless because
A) They are so far away from the center of the Earth.
B) they are in a constant state of free - fall.
C) they are moving very rapidly.
D) there is no atmosphere where they are.
A) They are so far away from the center of the Earth.
B) they are in a constant state of free - fall.
C) they are moving very rapidly.
D) there is no atmosphere where they are.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Escape velocity at the surface of the Earth is about
A) 250 mph
B) 11,200 mph
C) 25,000 mph
D) 250,000 mph
A) 250 mph
B) 11,200 mph
C) 25,000 mph
D) 250,000 mph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the gravitational force that two 100 kg persons exert on each other when standing 1m apart?
A) 6.672x10-7 N
B) 1 N
C) 6.672x10-11 N
D) 10,000 N
A) 6.672x10-7 N
B) 1 N
C) 6.672x10-11 N
D) 10,000 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The Earth is about 81 times as massive as the Moon. Suppose the earth and Moon are 10 distance units apart. If you were an astronaut between the Earth and Moon at how many distance units from the Earth will the gravitational attraction on you from the two bodies be equal and opposite?
A) 81 units
B) 9 units
C) 19 units
D) 1 unit
A) 81 units
B) 9 units
C) 19 units
D) 1 unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The Earth is about 81 times as massive as the Moon. Suppose the earth and Moon are 240,000 miles apart. If you were an astronaut between the Earth and Moon at what distance from the Earth will the gravitational attraction on you from the two bodies be equal and opposite?
A) 216,000 mi
B) 2963 mi
C) 24,000 km
D) 24,000 miles
A) 216,000 mi
B) 2963 mi
C) 24,000 km
D) 24,000 miles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose you are spending your weekend on roller skates trying to get momentum from somewhere. Which of the following will give you momentum in the north direction?
A) Throwing your keys southward.
B) Throwing your keys northward.
C) Bending down and throwing your keys straight up.
D) (B) or (C).
A) Throwing your keys southward.
B) Throwing your keys northward.
C) Bending down and throwing your keys straight up.
D) (B) or (C).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
You are substitute teaching for your spouse and are using balloons to demonstrate how rockets work. The balloons are blown up and released so that the air can leave them rapidly. Why do the balloons fly all around, even though the balloon does not have a surface to push against?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose your instructor staggers into class the morning after an all-night excellence in classroom humor workshop. He proceeds to do a demonstration in class where he measures a 6.67 N gravitational force of repulsion between two particles each having a mass of 1 kg and separated by 1m. Moreover he cuts the distance to 0.1 of what it originally was and then claims the force changes to a new value of 0.667 N. Specific to the scientific content of his demonstration please briefly describe three important concepts he incorrectly illustrated (there's more than three, trust me). One of your three points must be quantitative - involving a force calculation of some sort.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose you have two identical particles that attract each other with a certain gravitational force. Now you move them so they are three times as far apart as they were originally, but the force between them stays the same. What is one way in which the masses might change so the force could remain constant?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider astronauts orbiting the earth in the space shuttle.
-The acceleration of gravity in the orbiting space shuttle is over 90% that on the surface of the earth but the astronauts still feel weightless (no apparent weight) please explain. You may assume the orbit is perfectly circular.
-The acceleration of gravity in the orbiting space shuttle is over 90% that on the surface of the earth but the astronauts still feel weightless (no apparent weight) please explain. You may assume the orbit is perfectly circular.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider astronauts orbiting the earth in the space shuttle.
-Suppose that the astronauts are traveling at a speed of 1000 m/sec. What must the radius of their circular orbit be if their acceleration is 8.5 m/sec2?
-Suppose that the astronauts are traveling at a speed of 1000 m/sec. What must the radius of their circular orbit be if their acceleration is 8.5 m/sec2?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
You and a friend are on roller skates. You are in a room and have a basketball and are standing in between two parallel walls. By touching only the ball, describe how you would make yourselves come together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Compared to planets close to the sun, and based upon Kepler's third law of planetary motion, the length of the year of planets farther out from the sun are
A) the same
B) less
C) larger
D) more information is necessary.
A) the same
B) less
C) larger
D) more information is necessary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Comets have very eccentric orbits around the sun. Please explain why it is that they spend so little time near the earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The rest energy of a 60 kg person is
A) 8.4x1018 J
B) 5.4x1018 J
C) 1.8x1010 J
D) 9x1016 J
A) 8.4x1018 J
B) 5.4x1018 J
C) 1.8x1010 J
D) 9x1016 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What mass has a rest energy of 100J?
A) 1.1x10-15 kg
B) 3x10-8 kg
C) 3.3x10-7 kg
D) 0.01 kg
A) 1.1x10-15 kg
B) 3x10-8 kg
C) 3.3x10-7 kg
D) 0.01 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The relativistic energy of a 1000 kg car moving at 0.95 times the speed of light is
A) 1000 J
B) 2.8x1017 J
C) 2.9x1020J
D) 9.3x1011 J
A) 1000 J
B) 2.8x1017 J
C) 2.9x1020J
D) 9.3x1011 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The relativistic momentum of a 1000 kg car moving at 0.95 times the speed of light is
A) 9.13x108 kg m/s
B) 9.13x1011 kg m/s
C) 3200 kg m/s
D) 2.85x1011 kg m/s
A) 9.13x108 kg m/s
B) 9.13x1011 kg m/s
C) 3200 kg m/s
D) 2.85x1011 kg m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The speed at which a car must move so that its relativistic momentum is twice its nonrelativistic momentum is
A) 0.9 times the speed of light
B) ½ the speed of light
C) ¾ times the speed of light
D)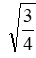 times the speed of light
times the speed of light
A) 0.9 times the speed of light
B) ½ the speed of light
C) ¾ times the speed of light
D)
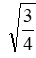 times the speed of light
times the speed of light
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The speed at which a car must move so that its relativistic energy is three times its rest energy is
A) 1/9 times the sped of light
B) 1/3 times the speed of light
C)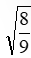 times the speed of light
times the speed of light
D) 8/9 times the speed of light
A) 1/9 times the sped of light
B) 1/3 times the speed of light
C)
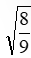 times the speed of light
times the speed of lightD) 8/9 times the speed of light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The maximum speed a rocket can achieve is
A) the speed of light
B) the speed of sound.
C) equal to the speed of its exhaust plume.
D) less than the speed of its exhaust plume.
E) greater than the speed of its exhaust plume but less than the speed of light.
A) the speed of light
B) the speed of sound.
C) equal to the speed of its exhaust plume.
D) less than the speed of its exhaust plume.
E) greater than the speed of its exhaust plume but less than the speed of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
All current rockets eject stages or booster rockets as they climb from the earth's surface up to orbit. A rocket that did not eject any stages or booster rockets while climbing from the ground to orbit would
A) experience too much drag while in orbit and would be unable to remain in orbit for more than a day or two.
B) not have anything beneath the rocket on which to push and would be unable to propel itself upward after it left the launch pad area.
C) clutter the space around the earth with orbiting debris.
D) have to have a launch weight that was about 90% rocket fuel.
A) experience too much drag while in orbit and would be unable to remain in orbit for more than a day or two.
B) not have anything beneath the rocket on which to push and would be unable to propel itself upward after it left the launch pad area.
C) clutter the space around the earth with orbiting debris.
D) have to have a launch weight that was about 90% rocket fuel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Astronauts in a space shuttle accelerating uniformly in a straight line far away from any planet or star would
A) feel weightless.
B) feel just like there is local gravity
C) feel like they are moving very rapidly.
D) feel nothing
A) feel weightless.
B) feel just like there is local gravity
C) feel like they are moving very rapidly.
D) feel nothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Rockets receive their forward propulsion through
A) pushing against the ground and objects in space
B) mass conservation of the rocket and fuel
C) pushing against the exhaust
D) small aerodynamic forces
A) pushing against the ground and objects in space
B) mass conservation of the rocket and fuel
C) pushing against the exhaust
D) small aerodynamic forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
How far apart would two 100 kg persons need to be so that the force they exert on each other is equal to 1N? You can assume they are point masses, having mass but no size.
A) 1m
B) 6.672x10-7 m
C) 8.17x10-4 m
D) 100 m
A) 1m
B) 6.672x10-7 m
C) 8.17x10-4 m
D) 100 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Suppose you have two identical particles that attract each other with a certain gravitational force. Now you move them so they are one quarter as far apart as they were originally, but the force between them stays the same. What is one way in which the masses might change so the force could remain constant?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Ideal physics theory would tell you that, if you climb into a basket at a store you cannot go from one side of the store to the other. In fact you can do this, and physicists often take breaks from late night test writing to do such things. Please explain why ideally we should not be able to do this but in reality we can.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Consider the Moon orbiting the Earth. _______ is the centripetal force for the orbit, and one could therefore measure the mass of the ________ by studying the Moon's orbit.
A) Drag; Earth
B) Tension; Moon
C) Gravity; Moon
D) Gravity; Earth
A) Drag; Earth
B) Tension; Moon
C) Gravity; Moon
D) Gravity; Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



