Deck 16: Maxwells Equations: Magnetism of Matter
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Maxwells Equations: Magnetism of Matter
1
The statement that magnetic field lines form closed loops is a direct consequence of:
A) Faraday's law
B) Ampere's law
C) Gauss' law for electricity
D) Gauss' law for magnetism
E) the Lorentz force
A) Faraday's law
B) Ampere's law
C) Gauss' law for electricity
D) Gauss' law for magnetism
E) the Lorentz force
Gauss' law for magnetism
2
A magnetic field exists between the plates of a capacitor:
A) always
B) never
C) when the capacitor is fully charged
D) while the capacitor is being charged
E) only when the capacitor is starting to be charged
A) always
B) never
C) when the capacitor is fully charged
D) while the capacitor is being charged
E) only when the capacitor is starting to be charged
while the capacitor is being charged
3
Displacement current exists wherever there is:
A) a magnetic field
B) moving charge
C) a changing magnetic field
D) an electric field
E) a changing electric field
A) a magnetic field
B) moving charge
C) a changing magnetic field
D) an electric field
E) a changing electric field
a changing electric field
4
One of the Maxwell equations begins with 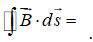 .... The symbol "
.... The symbol " 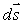 " means:
" means:
A) an infinitesimal displacement of a charge
B) an infinitesimal displacement of a magnetic pole
C) an infinitesimal inductance
D) an infinitesimal surface area
E) none of the above
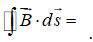 .... The symbol "
.... The symbol " 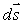 " means:
" means:A) an infinitesimal displacement of a charge
B) an infinitesimal displacement of a magnetic pole
C) an infinitesimal inductance
D) an infinitesimal surface area
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Two of Maxwell's equations contain a path integral on the left side and an area integral on the right. The directions of the infinitesimal path element 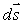 and infinitesimal area element
and infinitesimal area element  are:
are:
A) always in the same direction
B) always in opposite directions
C) always perpendicular to each other
D) never perpendicular to each other
E) none of the above
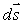 and infinitesimal area element
and infinitesimal area element  are:
are:A) always in the same direction
B) always in opposite directions
C) always perpendicular to each other
D) never perpendicular to each other
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following equations can be used, along with a symmetry argument, to calculate the electric field of a point charge?
A)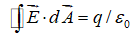
B)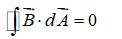
C)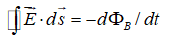
D)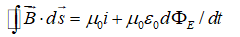
E) none of these
A)
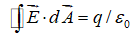
B)
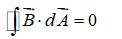
C)
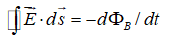
D)
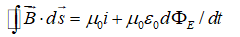
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following equations can be used, along with a symmetry argument, to calculate the magnetic field of a long straight wire carrying current?
A)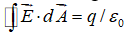
B)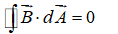
C)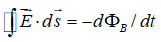
D)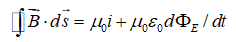
E) none of these
A)
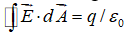
B)
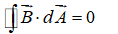
C)
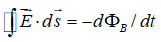
D)
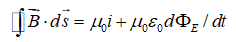
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following equations can be used to show that magnetic field lines form closed loops?
A)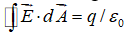
B)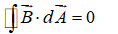
C)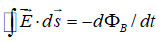
D)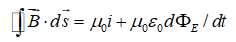
E) none of these
A)
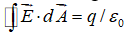
B)
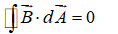
C)
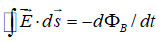
D)
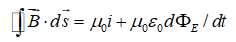
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The magnetic field of Earth is roughly the same as that of a magnetic dipole with a dipole moment of about:
A) 1017 J/T
B) 1019 J/T
C) 1021 J/T
D) 1023 J/T
E) 1025 J/T
A) 1017 J/T
B) 1019 J/T
C) 1021 J/T
D) 1023 J/T
E) 1025 J/T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Of the following places one would expect that the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field to be largest in:
A) Maine
B) Florida
C) Maryland
D) New York
E) Iowa
A) Maine
B) Florida
C) Maryland
D) New York
E) Iowa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The polarity of an unmarked magnet can be determined using:
A) a charged glass rod
B) a compass
C) an electroscope
D) another unmarked magnet
E) iron filings
A) a charged glass rod
B) a compass
C) an electroscope
D) another unmarked magnet
E) iron filings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If  is the orbital angular momentum of an electron, the magnetic dipole moment associated with its orbital motion:
is the orbital angular momentum of an electron, the magnetic dipole moment associated with its orbital motion:
A) is in the direction of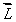 and has magnitude proportional to L
and has magnitude proportional to L
B) is opposite to the direction of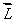 and has magnitude proportional to L
and has magnitude proportional to L
C) is in the direction of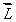 and has magnitude proportional to L2
and has magnitude proportional to L2
D) is opposite to the direction of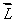 and has magnitude proportional to L2
and has magnitude proportional to L2
E) does not depend on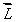
 is the orbital angular momentum of an electron, the magnetic dipole moment associated with its orbital motion:
is the orbital angular momentum of an electron, the magnetic dipole moment associated with its orbital motion:A) is in the direction of
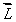 and has magnitude proportional to L
and has magnitude proportional to LB) is opposite to the direction of
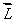 and has magnitude proportional to L
and has magnitude proportional to LC) is in the direction of
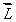 and has magnitude proportional to L2
and has magnitude proportional to L2D) is opposite to the direction of
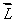 and has magnitude proportional to L2
and has magnitude proportional to L2E) does not depend on
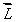

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If an electron has an orbital angular momentum with magnitude L the magnitude of the orbital contribution to its magnetic dipole moment is given by:
A) eL/m
B) eL/2m
C) 2eL/m
D) mL/e
E) mL/2
A) eL/m
B) eL/2m
C) 2eL/m
D) mL/e
E) mL/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If an electron has zero orbital angular momentum, the magnitude of its magnetic dipole moment equals:
A) zero
B) half the Bohr magneton
C) a Bohr magneton
D) twice a Bohr magneton
E) none of these
A) zero
B) half the Bohr magneton
C) a Bohr magneton
D) twice a Bohr magneton
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The magnetic properties of materials stem chiefly from:
A) particles with north poles
B) particles with south poles
C) motions of protons within nuclei
D) proton spin angular momentum
E) electron magnetic dipole moments
A) particles with north poles
B) particles with south poles
C) motions of protons within nuclei
D) proton spin angular momentum
E) electron magnetic dipole moments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A magnetic field 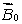 is applied to a diamagnetic substance. In the interior the magnetic field produced by the magnetic dipoles of the substance is:
is applied to a diamagnetic substance. In the interior the magnetic field produced by the magnetic dipoles of the substance is:
A) greater than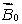 and in the opposite direction
and in the opposite direction
B) less than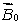 and in the opposite direction
and in the opposite direction
C) greater than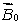 and in the same direction
and in the same direction
D) less than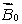 and in the same direction
and in the same direction
E) the same as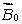
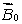 is applied to a diamagnetic substance. In the interior the magnetic field produced by the magnetic dipoles of the substance is:
is applied to a diamagnetic substance. In the interior the magnetic field produced by the magnetic dipoles of the substance is:A) greater than
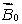 and in the opposite direction
and in the opposite directionB) less than
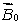 and in the opposite direction
and in the opposite directionC) greater than
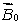 and in the same direction
and in the same directionD) less than
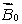 and in the same direction
and in the same directionE) the same as
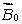

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Lenz' law can explain:
A) paramagnetism only
B) diamagnetism only
C) ferromagnetism only
D) only two of the three types of magnetism
E) all three of the types of magnetism
A) paramagnetism only
B) diamagnetism only
C) ferromagnetism only
D) only two of the three types of magnetism
E) all three of the types of magnetism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A magnetic field 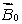 is applied to a paramagnetic substance. In the interior the magnetic field produced by the magnetic dipoles of the substance is:
is applied to a paramagnetic substance. In the interior the magnetic field produced by the magnetic dipoles of the substance is:
A) greater than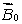 and in the opposite direction
and in the opposite direction
B) less than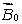 and in the opposite direction
and in the opposite direction
C) greater than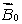 and in the same direction
and in the same direction
D) less than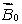 and in the same direction
and in the same direction
E) the same as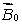
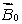 is applied to a paramagnetic substance. In the interior the magnetic field produced by the magnetic dipoles of the substance is:
is applied to a paramagnetic substance. In the interior the magnetic field produced by the magnetic dipoles of the substance is:A) greater than
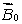 and in the opposite direction
and in the opposite directionB) less than
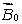 and in the opposite direction
and in the opposite directionC) greater than
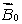 and in the same direction
and in the same directionD) less than
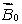 and in the same direction
and in the same directionE) the same as
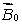

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When a permanent magnet is strongly heated:
A) nothing happens
B) it becomes an induced magnet
C) it loses its magnetism
D) its magnetism increases
E) its polarity reverses
A) nothing happens
B) it becomes an induced magnet
C) it loses its magnetism
D) its magnetism increases
E) its polarity reverses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The behavior of ferromagnetic domains in an applied magnetic field gives rise to:
A) hysteresis
B) ferromagnetism
C) the Curie law
D) a lowering of the Curie temperature
E) Gauss' law for magnetism
A) hysteresis
B) ferromagnetism
C) the Curie law
D) a lowering of the Curie temperature
E) Gauss' law for magnetism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



