Deck 7: International Banking Regulation and Basel Accords
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: International Banking Regulation and Basel Accords
1
Under the Glass-Steagall Act what distinguished commercial banks from investment banks?
A) Commercial banks were deposit taking and lending institutions and were precluded from activities such as underwriting securities.
B) Commercial banks were involved in raising debt and equity capital.
C) Investment banks were involved in lending and securities underwriting.
D) None of the given answers.
A) Commercial banks were deposit taking and lending institutions and were precluded from activities such as underwriting securities.
B) Commercial banks were involved in raising debt and equity capital.
C) Investment banks were involved in lending and securities underwriting.
D) None of the given answers.
Commercial banks were deposit taking and lending institutions and were precluded from activities such as underwriting securities.
2
Why are banks considered different from non-financial firms?
A) Banks face an asymmetric loss function.
B) Banks assets and liabilities are highly liquid.
C) Banks create the medium of exchange via their credit creation ability.
D) All of the given answers.
A) Banks face an asymmetric loss function.
B) Banks assets and liabilities are highly liquid.
C) Banks create the medium of exchange via their credit creation ability.
D) All of the given answers.
All of the given answers.
3
Why are banks considered different from non-financial firms?
A) The failure of a bank has more significant flow-on effects on other firms and the economy at large.
B) Banks rely on the confidence of their depositors and investors.
C) The commodity of banks, money, is more likely to attract criminal activity.
D) All of the given answers.
A) The failure of a bank has more significant flow-on effects on other firms and the economy at large.
B) Banks rely on the confidence of their depositors and investors.
C) The commodity of banks, money, is more likely to attract criminal activity.
D) All of the given answers.
All of the given answers.
4
Financial risk includes:
A) liquidity risk.
B) credit risk.
C) market risk.
D) credit risk and market risk.
A) liquidity risk.
B) credit risk.
C) market risk.
D) credit risk and market risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Non-financial risk includes:
A) liquidity risk.
B) credit risk.
C) market risk.
D) credit risk and market risk.
A) liquidity risk.
B) credit risk.
C) market risk.
D) credit risk and market risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Non-financial risk includes:
A) Hersttat risk
B) liquidity risk
C) credit risk
D) Herstatt risk and liquidity risk
A) Hersttat risk
B) liquidity risk
C) credit risk
D) Herstatt risk and liquidity risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Losses not associated with operational risk include those arising from:
A) internal fraud.
B) damage to physical assets by a natural disaster.
C) an act of default by a counter party.
D) failed transaction processing with counterparties.
A) internal fraud.
B) damage to physical assets by a natural disaster.
C) an act of default by a counter party.
D) failed transaction processing with counterparties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Major factors which will continue to affect operational risk in the foreign exchange market include:
A) growing trade in emerging market currencies.
B) new types of customers.
C) new technology.
D) all of the given answers.
A) growing trade in emerging market currencies.
B) new types of customers.
C) new technology.
D) all of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Banking regulation cannot be justified on the basis of:
A) market failure.
B) market power.
C) symmetry of information flows between buyers and sellers.
D) market failure and market power.
A) market failure.
B) market power.
C) symmetry of information flows between buyers and sellers.
D) market failure and market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Negative externalities may flow from a banking failure as a result of:
A) the short-term nature of their assets and the long-term nature of their liabilities.
B) the long-term nature of their assets and the long-term nature of their liabilities.
C) the short-term nature of their assets and the short-term nature of their liabilities.
D) the long-term nature of their assets and the short-term nature of their liabilities.
A) the short-term nature of their assets and the long-term nature of their liabilities.
B) the long-term nature of their assets and the long-term nature of their liabilities.
C) the short-term nature of their assets and the short-term nature of their liabilities.
D) the long-term nature of their assets and the short-term nature of their liabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Regulatory functions include:
A) macroprudential supervision.
B) microprudential supervision.
C) macroprudential supervision and microprudential supervision.
D) none of the given answers.
A) macroprudential supervision.
B) microprudential supervision.
C) macroprudential supervision and microprudential supervision.
D) none of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Macroprudential supervision is intended to limit financial system distress that might damage the economy.
B) Microprudential supervision monitors the compliance of individual institutions with prudential regulation.
C) Conduct of business regulation aims to safeguard customers from unfair practices.
D) All of the given answers.
A) Macroprudential supervision is intended to limit financial system distress that might damage the economy.
B) Microprudential supervision monitors the compliance of individual institutions with prudential regulation.
C) Conduct of business regulation aims to safeguard customers from unfair practices.
D) All of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The problem with deposit insurance is that:
A) it may encourage banks to take more risk.
B) it may encourage customers to deposit their funds in well run banks.
C) it may encourage banks to take less risk.
D) it may discourage customers from using banks.
A) it may encourage banks to take more risk.
B) it may encourage customers to deposit their funds in well run banks.
C) it may encourage banks to take less risk.
D) it may discourage customers from using banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Forms of banking regulation include:
A) deposit insurance regulation.
B) securities services regulation such as the Glass-Steagall Act.
C) capital adequacy regulation.
D) all of the given answers.
A) deposit insurance regulation.
B) securities services regulation such as the Glass-Steagall Act.
C) capital adequacy regulation.
D) all of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The functions of capital exclude:
A) providing a buffer against unexpected losses.
B) providing a cushion to protect banks against insolvency.
C) providing funds out of which to pay dividends to shareholders.
D) providing a signal that the bank's lenders will not be taken advantage of.
A) providing a buffer against unexpected losses.
B) providing a cushion to protect banks against insolvency.
C) providing funds out of which to pay dividends to shareholders.
D) providing a signal that the bank's lenders will not be taken advantage of.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Calculate how much capital the bank must hold using the risk-adjusted value of assets. A bank has four categories of assets classified by the level of risk embodied in them. The capital adequacy ratio is 10%. You are given the following asset categories and associated values in AUD million: 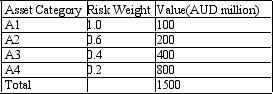
A) 245.45
B) 24.54
C) 54.00
D) 540.00

A) 245.45
B) 24.54
C) 54.00
D) 540.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Calculate the risk-adjusted capital ratio. A bank has four categories of assets classified by the level of risk embodied in them. The bank's capital is AUD100. You are given the following asset categories and associated values in AUD million: 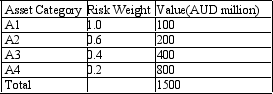
A) 6.67%
B) 18.52%
C) 40.74%
D) 245.45%

A) 6.67%
B) 18.52%
C) 40.74%
D) 245.45%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Calculate how much capital the bank must hold using the risk-adjusted value of assets. A bank has four categories of assets classified by the level of risk embodied in them. The capital adequacy ratio is 10%. You are given the following asset categories and associated values in AUD million: 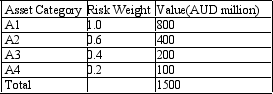
A) 150.00
B) 518.18
C) 51.82
D) 540.00

A) 150.00
B) 518.18
C) 51.82
D) 540.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Calculate the risk-adjusted capital ratio. A bank has four categories of assets classified by the level of risk embodied in them. The bank's capital is AUD100. You are given the following asset categories and associated values in AUD million: 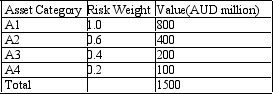
A) 19.30%
B) 6.67%
C) 8.77%
D) 518.18%

A) 19.30%
B) 6.67%
C) 8.77%
D) 518.18%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
RAROC is:
A) the risk-adjusted rate of return on capital.
B) the economic profit of the firm divided by the firm's economic capital.
C) none of the given answers.
D) the risk-adjusted rate of return on capital as measured by the economic profit of the firm divided by the firm's economic capital.
A) the risk-adjusted rate of return on capital.
B) the economic profit of the firm divided by the firm's economic capital.
C) none of the given answers.
D) the risk-adjusted rate of return on capital as measured by the economic profit of the firm divided by the firm's economic capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Calculate the bank's RAROC. A bank has four categories of assets classified by the level of risk embodied in them. The bank's capital is AUD100. The capital adequacy ratio is 10%. The bank's economic profit for the most recent period was AUD15 million. You are given the following asset categories and associated values in AUD million: 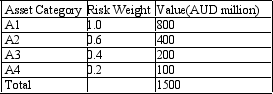
A) 28.95%
B) 15.00%
C) 1.00%
D) 2.89%

A) 28.95%
B) 15.00%
C) 1.00%
D) 2.89%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Calculate the risk-adjusted capital ratio. A bank has four categories of assets classified by the level of risk embodied in them. The bank's capital is AUD100. You are given the following asset categories and associated values in AUD million: 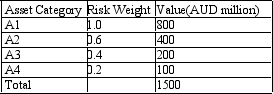
A) 250.00%
B) 20.16%
C) 16.67%
D) 302.42%

A) 250.00%
B) 20.16%
C) 16.67%
D) 302.42%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Calculate the bank's RAROC. A bank has four categories of assets classified by the level of risk embodied in them. The bank's capital is AUD100. The capital adequacy ratio is 10%. The bank's economic profit for the most recent period was AUD15 million. You are given the following asset categories and associated values in AUD million: 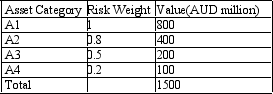
A) 1.0%
B) 15.00%
C) 3.02%
D) 30.24%

A) 1.0%
B) 15.00%
C) 3.02%
D) 30.24%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Assume that the bank securitises asset A1. Calculate the risk-adjusted regulatory capital both before and after the securitization. The table below presents the distribution of assets held by a bank with the associated probabilities of default and rates of return. The regulatory capital ratio is 10%. 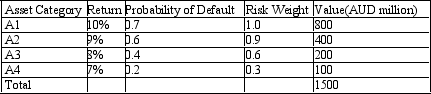
A) Before 467.86, After 182.14
B) 46.79, 18.21
C) 46.79, 28.33
D) 467.86, 283.33

A) Before 467.86, After 182.14
B) 46.79, 18.21
C) 46.79, 28.33
D) 467.86, 283.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Assume that the bank securitises asset A1. Calculate the risk-adjusted regulatory capital both before and after the securitisation. The table below presents the distribution of assets held by a bank with the associated probabilities of default and rates of return. The regulatory capital ratio is 10%. 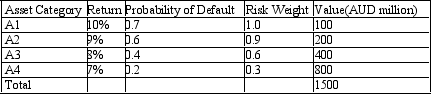
A) Before 271.43, After 235.71
B) 27.14, 36.67
C) 271.43, 366.67
D) 27.14, 23.57

A) Before 271.43, After 235.71
B) 27.14, 36.67
C) 271.43, 366.67
D) 27.14, 23.57

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Assume that the bank securitises asset A1. Calculate the risk-adjusted regulatory capital both before and after the securitisation. The table below presents the distribution of assets held by a bank with the associated probabilities of default and rates of return. The regulatory capital ratio is 10%. 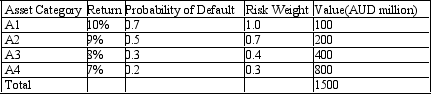
A) Before 26.67, After 22.50
B) 266.67, 225
C) 266.67, 385.71
D) 26.67, 38.57

A) Before 26.67, After 22.50
B) 266.67, 225
C) 266.67, 385.71
D) 26.67, 38.57

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Calculate the maximum possible loss. The table below presents the distribution of assets held by a bank with the associated probabilities of default and rates of return. The regulatory capital ratio is 10%. 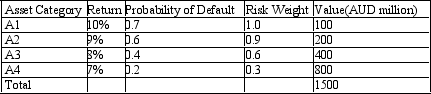
A) 510
B) 760
C) 1500
D) 150

A) 510
B) 760
C) 1500
D) 150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Calculate the maximum possible loss. The table below presents the distribution of assets held by a bank with the associated probabilities of default and rates of return. The regulatory capital ratio is 10%.
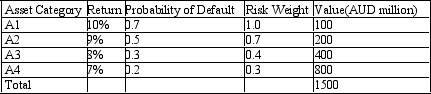
A) 640
B) 1500
C) 450
D) 150

A) 640
B) 1500
C) 450
D) 150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision is a supranational authority which is able to make. regulatory banking standards which have international legal force.
B) The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision is concerned with defining the role of regulators in cross-jurisdictional situations
C) The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision ensures that international banks do not escape . comprehensive supervision by domestic authorities
D) The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision promotes uniform capital requirements.
A) The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision is a supranational authority which is able to make. regulatory banking standards which have international legal force.
B) The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision is concerned with defining the role of regulators in cross-jurisdictional situations
C) The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision ensures that international banks do not escape . comprehensive supervision by domestic authorities
D) The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision promotes uniform capital requirements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The most important feature of the Basel I Accord was:
A) the provision that a bank must hold capital that varies according to the perceived operational risk of the bank.
B) the provision that a bank must hold capital that varies according to the perceived market risk of the bank's investment portfolio.
C) the provision that a bank must hold capital that varies according to the perceived credit risk of the bank's loan portfolio.
D) none of the given answers.
A) the provision that a bank must hold capital that varies according to the perceived operational risk of the bank.
B) the provision that a bank must hold capital that varies according to the perceived market risk of the bank's investment portfolio.
C) the provision that a bank must hold capital that varies according to the perceived credit risk of the bank's loan portfolio.
D) none of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Under Basel I, banks are required to hold an amount of capital equal to 8% of their risk-weighted assets.
B) Under Basel I, banks are required to hold an amount of capital equal to 10% of their risk-weighted assets.
C) Under Basel I, banks are required to hold an amount of capital equal to 8% of their assets.
D) None of the given answers.
A) Under Basel I, banks are required to hold an amount of capital equal to 8% of their risk-weighted assets.
B) Under Basel I, banks are required to hold an amount of capital equal to 10% of their risk-weighted assets.
C) Under Basel I, banks are required to hold an amount of capital equal to 8% of their assets.
D) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Under Basel I, banks are required to hold an amount of capital equal to 8% of their risk-weighted assets.
B) Under Basel I, the individual assets of banks are divided into four basic credit risk categories, . according to the creditworthiness of the counterparty.
C) Under Basel I, each credit risk category is assigned a weight ranging from 0 - 100%.
D) None of the given answers.
A) Under Basel I, banks are required to hold an amount of capital equal to 8% of their risk-weighted assets.
B) Under Basel I, the individual assets of banks are divided into four basic credit risk categories, . according to the creditworthiness of the counterparty.
C) Under Basel I, each credit risk category is assigned a weight ranging from 0 - 100%.
D) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The amendment to Basel I, which occurred in 1996:
A) incorporated market risk arising from open foreign exchange positions, traded debt securities, equities, commodities and options.
B) incorporated operational risk.
C) replaced credit risk with operational risk.
D) None of the given answers.
A) incorporated market risk arising from open foreign exchange positions, traded debt securities, equities, commodities and options.
B) incorporated operational risk.
C) replaced credit risk with operational risk.
D) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Basel I has been subject to the following criticisms:
A) it allowed a gap to arise between regulatory and economic capital.
B) it was conducive to regulatory capital arbitrage.
C) it ignores the risk reduction that may result from diversification of credit exposures.
D) All of the given answers.
A) it allowed a gap to arise between regulatory and economic capital.
B) it was conducive to regulatory capital arbitrage.
C) it ignores the risk reduction that may result from diversification of credit exposures.
D) All of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The Basel II Accord only considers credit, market and operational risk.
B) The Basel II Accord only considers credit and operational risk.
C) The Basel II Accord only considers market and operational risk.
D) The Basel II Accord only considers credit, market and liquidity risk.
A) The Basel II Accord only considers credit, market and operational risk.
B) The Basel II Accord only considers credit and operational risk.
C) The Basel II Accord only considers market and operational risk.
D) The Basel II Accord only considers credit, market and liquidity risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The Basel II Accord measures operational risk as the operational value at risk with a 99.9% confidence level.
B) The Basel II Accord maintains the regulatory capital ratio at a minimum of 8% or risk adjusted assets.
C) The Basel II Accord allows for a greater use of a bank's internal models for risk assessment and the calculation of regulatory capital.
D) The Basel II Accord only considers credit and operational risk.
A) The Basel II Accord measures operational risk as the operational value at risk with a 99.9% confidence level.
B) The Basel II Accord maintains the regulatory capital ratio at a minimum of 8% or risk adjusted assets.
C) The Basel II Accord allows for a greater use of a bank's internal models for risk assessment and the calculation of regulatory capital.
D) The Basel II Accord only considers credit and operational risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The objectives of Basel II include:
A) promoting a sound financial system.
B) enhancing competitive equality.
C) establishing a more comprehensive approach to risk.
D) all of the given answers.
A) promoting a sound financial system.
B) enhancing competitive equality.
C) establishing a more comprehensive approach to risk.
D) all of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The expected loss is calculated under Basel II as being equal to:
A) the product of the probability of default, the loss given default and the exposure at default.
B) the sum of the probability of default, the loss given default and the exposure at default.
C) the product of the probability of default and the exposure at default.
D) the sum of the probability of default and the exposure at default.
A) the product of the probability of default, the loss given default and the exposure at default.
B) the sum of the probability of default, the loss given default and the exposure at default.
C) the product of the probability of default and the exposure at default.
D) the sum of the probability of default and the exposure at default.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Operational risk under the Basel II Accord is measured by:
A) the indicators approach.
B) the standardised approach.
C) the advanced measurement approach.
D) any one of the given answers.
A) the indicators approach.
B) the standardised approach.
C) the advanced measurement approach.
D) any one of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements is (are) true?
A) Basel II has no provisions for liquidity.
B) Basel II has been criticised for aligning regulatory capital with economic capital.
C) Basel II is not only concerned with capital adequacy but also with the risk management process within banks.
D) All of the given answers.
A) Basel II has no provisions for liquidity.
B) Basel II has been criticised for aligning regulatory capital with economic capital.
C) Basel II is not only concerned with capital adequacy but also with the risk management process within banks.
D) All of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



