Deck 3: The Balance of Payments and Effective Exchange Rate
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: The Balance of Payments and Effective Exchange Rate
1
Which of the following is NOT an international economic transaction?
A) Exporting Australian beef to Japan
B) Selling Japanese yen bonds by BHP Billiton to Australian investors
C) Selling Telstra shares to foreign investors
D) Importing crude oil
A) Exporting Australian beef to Japan
B) Selling Japanese yen bonds by BHP Billiton to Australian investors
C) Selling Telstra shares to foreign investors
D) Importing crude oil
Selling Japanese yen bonds by BHP Billiton to Australian investors
2
Which of the following items is NOT a stock?
A) Foreign assets held by Australian investors
B) Debt owed by the government of Victoria
C) Exports of live sheep to Saudi Arabia
D) Australian dollar bonds held by Japanese investors
A) Foreign assets held by Australian investors
B) Debt owed by the government of Victoria
C) Exports of live sheep to Saudi Arabia
D) Australian dollar bonds held by Japanese investors
Exports of live sheep to Saudi Arabia
3
Which of the following items is NOT a flow?
A) Unilateral transfers
B) The increase in foreign assets held by Australian investors over a period of six months
C) Foreign exchange reserves lost by the Reserve Bank as a result of intervention in the foreign exchange market
D) The foreign currency and gold reserves of the Reserve Bank
A) Unilateral transfers
B) The increase in foreign assets held by Australian investors over a period of six months
C) Foreign exchange reserves lost by the Reserve Bank as a result of intervention in the foreign exchange market
D) The foreign currency and gold reserves of the Reserve Bank
The foreign currency and gold reserves of the Reserve Bank
4
Seasonally-adjusted balance of payments figures can be obtained by
A) removing seasonal variation from the actual, seasonally-unadjusted data
B) taking account of the seasonal effects on agriculture
C) measuring the balance of payments items at the end of each quarter
D) adjusting the figures for the effect of rainfall
A) removing seasonal variation from the actual, seasonally-unadjusted data
B) taking account of the seasonal effects on agriculture
C) measuring the balance of payments items at the end of each quarter
D) adjusting the figures for the effect of rainfall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The quality of the reported balance of payments data has deteriorated because:
A) international trade has become complex
B) international investment has become more diversified
C) the level of financial disclosure is inadequate
D) capital account statistical systems have failed to keep pace with important developments in international capital markets
A) international trade has become complex
B) international investment has become more diversified
C) the level of financial disclosure is inadequate
D) capital account statistical systems have failed to keep pace with important developments in international capital markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The ABS defines the concept of 'resident' to encompass:
A) all persons living in Australia for 12 months or more, except for foreign diplomatic, consular, military or government personnel as well as foreign students
B) all persons living in Australia for 12 months or more, except for foreign diplomatic, consular, military or government personnel
C) all persons living in Australia for 12 months or more
D) all persons living in Australia
A) all persons living in Australia for 12 months or more, except for foreign diplomatic, consular, military or government personnel as well as foreign students
B) all persons living in Australia for 12 months or more, except for foreign diplomatic, consular, military or government personnel
C) all persons living in Australia for 12 months or more
D) all persons living in Australia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The balance of payments is an accounting identity in which:
A) all accounts must show a surplus
B) a surplus on the capital account is offset by a deficit on the financial and current accounts, assuming the balancing item equals zero
C) a surplus on the current account is offset by a deficit on the financial and capital accounts, assuming the balancing item equals zero
D) all accounts must show a deficit
A) all accounts must show a surplus
B) a surplus on the capital account is offset by a deficit on the financial and current accounts, assuming the balancing item equals zero
C) a surplus on the current account is offset by a deficit on the financial and capital accounts, assuming the balancing item equals zero
D) all accounts must show a deficit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The balancing item appears on the balance of payments to:
A) account for errors and omissions in the data
B) equate the trade and services accounts
C) account for changes in official reserves
D) balance the current account
A) account for errors and omissions in the data
B) equate the trade and services accounts
C) account for changes in official reserves
D) balance the current account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Australian current account, since 1972, has been:
A) in surplus
B) at times in surplus and at times in deficit
C) in deficit
D) constant
A) in surplus
B) at times in surplus and at times in deficit
C) in deficit
D) constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The Australian financial account, since 1972, has been:
A) in surplus
B) at times in surplus and at times in deficit
C) in deficit
D) constant
A) in surplus
B) at times in surplus and at times in deficit
C) in deficit
D) constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The sale of foreign bonds by a foreign corporation leads to:
A) an increase in the supply of the foreign currency
B) an increase in the demand for the foreign currency
C) a decrease in the supply of the domestic currency
D) both an increase in the demand for the foreign currency and a decrease in the supply of the domestic currency
A) an increase in the supply of the foreign currency
B) an increase in the demand for the foreign currency
C) a decrease in the supply of the domestic currency
D) both an increase in the demand for the foreign currency and a decrease in the supply of the domestic currency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The demand for foreign exchange rises as the exchange rate (S) falls because:
A) the demand for imports rises
B) the domestic currency price of imports falls
C) the demand for exports rises
D) both the domestic currency price of imports falls AND the demand for imports rises
A) the demand for imports rises
B) the domestic currency price of imports falls
C) the demand for exports rises
D) both the domestic currency price of imports falls AND the demand for imports rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A change in the exchange rate (S) affects:
A) the domestic currency price of exports
B) the foreign currency price of imports
C) the foreign currency price of exports
D) all of the given answers
A) the domestic currency price of exports
B) the foreign currency price of imports
C) the foreign currency price of exports
D) all of the given answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A rise in the exchange rate (S) leads to:
A) a rise in the supply of foreign exchange
B) a fall in the supply of foreign exchange
C) no change in the supply of foreign exchange
D) any of the given answers
A) a rise in the supply of foreign exchange
B) a fall in the supply of foreign exchange
C) no change in the supply of foreign exchange
D) any of the given answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A fall in the exchange rate (S) may lead to:
A) a rise in the foreign currency price of exports and a fall in the quantity of exports demanded
B) a fall in the foreign currency price of exports and a rise in the quantity of exports demanded
C) no change in the foreign currency price of exports and a rise in the quantity of exports demanded
D) a rise in the foreign currency price of exports and a rise in the quantity of exports demanded
A) a rise in the foreign currency price of exports and a fall in the quantity of exports demanded
B) a fall in the foreign currency price of exports and a rise in the quantity of exports demanded
C) no change in the foreign currency price of exports and a rise in the quantity of exports demanded
D) a rise in the foreign currency price of exports and a rise in the quantity of exports demanded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An increase in domestic economic growth rate, greater than that of trading partners, leads to a deterioration in the current account because it leads to:
A) an increase in imports and a decrease in exports
B) an increase in imports without a corresponding change in exports
C) an increase in unilateral transfers
D) an increase in the demand for foreign services
A) an increase in imports and a decrease in exports
B) an increase in imports without a corresponding change in exports
C) an increase in unilateral transfers
D) an increase in the demand for foreign services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The J-curve effect describes:
A) the inverse relationship between the current account and the growth rate
B) the tendency for the current account to deteriorate immediately after the depreciation of the domestic currency
C) the tendency for exporters to reduce the foreign price of exports following the appreciation of the domestic currency
D) the depreciation of the domestic currency immediately after a fall in the domestic inflation rate
A) the inverse relationship between the current account and the growth rate
B) the tendency for the current account to deteriorate immediately after the depreciation of the domestic currency
C) the tendency for exporters to reduce the foreign price of exports following the appreciation of the domestic currency
D) the depreciation of the domestic currency immediately after a fall in the domestic inflation rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to the elasticities approach to the balance of payments, a devaluation of the domestic currency leads to an improvement in the balance of payments if:
A) the demand for exports is elastic while the demand for imports is inelastic
B) the demand for exports is inelastic while the demand for imports is elastic
C) the sum of elasticities of the demand for exports and imports is greater than one
D) the individual elasticities of the demand for exports and imports are greater than one
A) the demand for exports is elastic while the demand for imports is inelastic
B) the demand for exports is inelastic while the demand for imports is elastic
C) the sum of elasticities of the demand for exports and imports is greater than one
D) the individual elasticities of the demand for exports and imports are greater than one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A rise in the exchange rate (S) leads to:
A) an increase in the current account
B) a decrease in the current account
C) no change in the current account
D) an indeterminate effect on the current account, which will ultimately depend on the relative . elasticities of demand for imports and exports
A) an increase in the current account
B) a decrease in the current account
C) no change in the current account
D) an indeterminate effect on the current account, which will ultimately depend on the relative . elasticities of demand for imports and exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A fall in the exchange rate (S) leads to:
A) an increase in the current account
B) a decrease in the current account
C) no change in the current account
D) an indeterminate effect on the current account, which will ultimately depend on the relative . elasticities of demand for imports and exports
A) an increase in the current account
B) a decrease in the current account
C) no change in the current account
D) an indeterminate effect on the current account, which will ultimately depend on the relative . elasticities of demand for imports and exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Calculate the balance on current account in Australian dollar terms. You are given the following information: 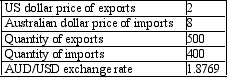
A) -AUD2 200
B) -AUD1 323
C) +AUD5 077
D) -USD705

A) -AUD2 200
B) -AUD1 323
C) +AUD5 077
D) -USD705

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the exchange rate changes to 2.0000, what is the percentage change in the US dollar price of exports from that when the exchange rate was 1.8769? You are given the following information: 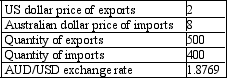
A) -6.16%
B) +6.56%
C) +6.16%
D) -6.56%

A) -6.16%
B) +6.56%
C) +6.16%
D) -6.56%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the quantity of exports at the end of one year? You are given the following information: ? 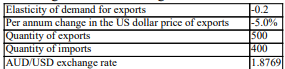
A) 475
B) 525
C) 505
D) 495

A) 475
B) 525
C) 505
D) 495

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The quantity of imports is equal to: 40-(2.1*domestic price of imports). Based on the following information, calculate the demand for foreign exchange. 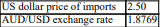
A) 30.15
B) 75.37
C) 86.87
D) 93.01
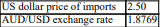
A) 30.15
B) 75.37
C) 86.87
D) 93.01

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A higher rate of inflation, relative to trading partners, has an adverse effect on the balance of payments because:
A) it leads to higher interest rates
B) it leads to a lower growth rate
C) it reduces the competitiveness of the domestic economy
D) all of the given answers
A) it leads to higher interest rates
B) it leads to a lower growth rate
C) it reduces the competitiveness of the domestic economy
D) all of the given answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Studies examining the effect of currency appreciation and depreciation on the trade balance should be based on:
A) the nominal effective exchange rate
B) the real effective exchange rate
C) the nominal bilateral exchange rate of the country's largest trading partner
D) the real bilateral index of the currency of the country's largest trading partner
A) the nominal effective exchange rate
B) the real effective exchange rate
C) the nominal bilateral exchange rate of the country's largest trading partner
D) the real bilateral index of the currency of the country's largest trading partner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Tariffs and quotas:
A) reduce the current account
B) improve the capital account
C) are intended to improve the current account but in fact if they cause trading partners to retaliate may . have an indeterminate affect of the current account
D) reduce the capital account
A) reduce the current account
B) improve the capital account
C) are intended to improve the current account but in fact if they cause trading partners to retaliate may . have an indeterminate affect of the current account
D) reduce the capital account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Taxes imposed on capital gains and dividend income:
A) may adversely affect the financial account
B) may adversely affect the current account
C) may positively affect the current account
D) may positively affect the financial account
A) may adversely affect the financial account
B) may adversely affect the current account
C) may positively affect the current account
D) may positively affect the financial account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the exchange rate is expected to appreciate:
A) the current account is expected to be unaffected
B) the financial account is expected to deteriorate
C) the current account is expected to improve
D) the financial account is expected to improve
A) the current account is expected to be unaffected
B) the financial account is expected to deteriorate
C) the current account is expected to improve
D) the financial account is expected to improve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The effective exchange rate measures the:
A) exchange rate adjusted for inflation
B) exchange rate adjusted for taxes
C) value of a currency against the currencies of major trading partners
D) value of a currency against the currency of a major trading partner
A) exchange rate adjusted for inflation
B) exchange rate adjusted for taxes
C) value of a currency against the currencies of major trading partners
D) value of a currency against the currency of a major trading partner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The real exchange rate measures:
A) the exchange rate adjusted for inflation
B) the exchange rate adjusted for taxes
C) the exchange rate adjusted for the interest rate differential
D) the value of a currency against the currency of the major trading partner
A) the exchange rate adjusted for inflation
B) the exchange rate adjusted for taxes
C) the exchange rate adjusted for the interest rate differential
D) the value of a currency against the currency of the major trading partner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An exchange rate relative is:
A) a measure of the appreciation or depreciation of a currency relative to the currencies of the major trading partners
B) a measure of the appreciation or depreciation of a currency relative to its value in the previous day
C) the value of an exchange rate relative to a base value
D) a measure of the relative movements of a currency against several currencies
A) a measure of the appreciation or depreciation of a currency relative to the currencies of the major trading partners
B) a measure of the appreciation or depreciation of a currency relative to its value in the previous day
C) the value of an exchange rate relative to a base value
D) a measure of the relative movements of a currency against several currencies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Calculate the real effective AUD/USD exchange rate index at end of 2001. You are given the following information: 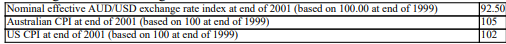
A) 95.22
B) 97.13
C) 100.00
D) 89.86
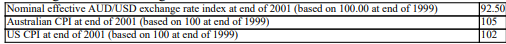
A) 95.22
B) 97.13
C) 100.00
D) 89.86

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Calculate the AUD/USD exchange rate index for 2001, where 1999 AUD/USD exchange rate index equals 100. You are given the following exchange rates: 
A) 1.0135
B) 101.35
C) 0.9867
D) 98.67

A) 1.0135
B) 101.35
C) 0.9867
D) 98.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Calculate the normalised trade weight for the UK's share of Australia's two-way merchandise trade. You are given the following information 
A) 14.00%
B) 35.71%
C) 5.00%
D) 26.32%

A) 14.00%
B) 35.71%
C) 5.00%
D) 26.32%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Calculate the geometric trade-weighted effective exchange rate as at 31/12/02. You are given the following information: 
A) 98.63
B) 96.87
C) 100.35
D) 100.30

A) 98.63
B) 96.87
C) 100.35
D) 100.30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Calculate the real geometric trade-weighted effective exchange rate as at 31/12/02. You are given the following information: 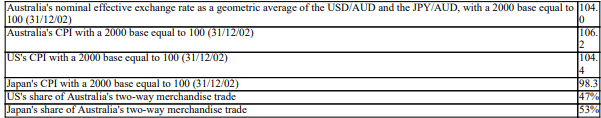
A) 109.2
B) 99.0
C) 109.0
D) 99.2

A) 109.2
B) 99.0
C) 109.0
D) 99.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The TWI is:
A) a nominal effective exchange rate calculated for the AUD by the RBA
B) the currency unit of the Tiwi Islands
C) a real effective exchange rate calculated for the AUD by the RBA
D) a real exchange rate calculated for the AUD by the RBA
A) a nominal effective exchange rate calculated for the AUD by the RBA
B) the currency unit of the Tiwi Islands
C) a real effective exchange rate calculated for the AUD by the RBA
D) a real exchange rate calculated for the AUD by the RBA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The TWI post October 1988 is calculated as:
A) an arithmetic weighted average
B) a geometric weighted average
C) a simple average
D) none of the given answers
A) an arithmetic weighted average
B) a geometric weighted average
C) a simple average
D) none of the given answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



