Deck 44: Living in Communities
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 44: Living in Communities
1
A community could be defined as
A) a collection of species that happen to live together at the same location.
B) a collection of species that live in the same location and interact strongly with each other.
C) a collection of species that live together and have evolved together.
D) an interacting group of species living together as an ecological unit.
E) Any of the above, depending on which ecological view you subscribe to.
A) a collection of species that happen to live together at the same location.
B) a collection of species that live in the same location and interact strongly with each other.
C) a collection of species that live together and have evolved together.
D) an interacting group of species living together as an ecological unit.
E) Any of the above, depending on which ecological view you subscribe to.
Any of the above, depending on which ecological view you subscribe to.
2
Simpson's Index is one way to measure -diversity. It would be closest to 1 for which of the following communities?
A) Organisms in a harsh desert environment.
B) Grasses living on a well-managed wheat farm.
C) Organisms living in Antarctica.
D) Organisms in a northern Australian rain forest.
E) Organisms in grassy woodlands.
A) Organisms in a harsh desert environment.
B) Grasses living on a well-managed wheat farm.
C) Organisms living in Antarctica.
D) Organisms in a northern Australian rain forest.
E) Organisms in grassy woodlands.
Organisms in a northern Australian rain forest.
3
-diversity and -diversity differ in the following way.
A) One means high-level diversity while the other means low-level diversity.
B) One refers to a community that has many abundant species and the other refers to a community that has many rare species.
C) One refers to diversity within a location and one refers to diversity between locations.
D) One measures the number of different species while the other takes into account the number within each species.
E) One refers to natural diversity and one refers to diversity in communities that have been heavily influenced by humans.
A) One means high-level diversity while the other means low-level diversity.
B) One refers to a community that has many abundant species and the other refers to a community that has many rare species.
C) One refers to diversity within a location and one refers to diversity between locations.
D) One measures the number of different species while the other takes into account the number within each species.
E) One refers to natural diversity and one refers to diversity in communities that have been heavily influenced by humans.
One refers to diversity within a location and one refers to diversity between locations.
4
A commercial plantation of Sydney blue gum (Eucalyptus saligna) would have
A) high structural diversity and low species diversity.
B) high species diversity and low structural diversity.
C) low structural diversity and low species diversity.
D) high species diversity and high structural diversity.
E) high -diversity and low -diversity.
A) high structural diversity and low species diversity.
B) high species diversity and low structural diversity.
C) low structural diversity and low species diversity.
D) high species diversity and high structural diversity.
E) high -diversity and low -diversity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Percentage projective foliage cover is the percentage of the ground surface
A) above which there is foliage.
B) that is predicted to be covered by foliage at a given time in the future.
C) above which tall narrow trees grow.
D) covered with litter from the above trees.
E) above which there is a foliage canopy thick enough to protect small mammals from aerial attack.
A) above which there is foliage.
B) that is predicted to be covered by foliage at a given time in the future.
C) above which tall narrow trees grow.
D) covered with litter from the above trees.
E) above which there is a foliage canopy thick enough to protect small mammals from aerial attack.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A community consists of
A) groups of single species.
B) all sessile organisms such as plants.
C) all organisms living in a particular area.
D) animal species which interact with plant species in an ecological area.
E) the macrofauna and macroflora of a particular area.
A) groups of single species.
B) all sessile organisms such as plants.
C) all organisms living in a particular area.
D) animal species which interact with plant species in an ecological area.
E) the macrofauna and macroflora of a particular area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All of the following match a major vegetation type with its appropriate climate or region EXCEPT
A) high latitude-tundra.
B) high altitude-alpine.
C) mallee-wet, cold climate.
D) grassland-cool, dry climate.
E) temperate wet rainforest-non-tropical coastal regions.
A) high latitude-tundra.
B) high altitude-alpine.
C) mallee-wet, cold climate.
D) grassland-cool, dry climate.
E) temperate wet rainforest-non-tropical coastal regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The relationship between the eastern grey kangaroo and the microbes that live in its foregut is most precisely described as
A) commensalisms.
B) mutualism.
C) parasitism.
D) sessile.
E) symbiosis.
A) commensalisms.
B) mutualism.
C) parasitism.
D) sessile.
E) symbiosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
As wildebeest move through grasslands feeding, their hooves stir up insects. The insects are caught and eaten by small birds that always follow the herd. The interaction between the birds and the wildebeest would be classified as
A) predation.
B) parasitism.
C) commensalism.
D) mutualism.
E) symbiosis.
A) predation.
B) parasitism.
C) commensalism.
D) mutualism.
E) symbiosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A parasitoid is
A) an insect with a parasitic larval stage and a free-living adult stage.
B) an organism that mimics but is not, in fact, a true parasite.
C) an organism that is facultatively parasitic.
D) an bacteria with an requirement for a specific host for development.
E) a parasitic insect that never actually kills its host.
A) an insect with a parasitic larval stage and a free-living adult stage.
B) an organism that mimics but is not, in fact, a true parasite.
C) an organism that is facultatively parasitic.
D) an bacteria with an requirement for a specific host for development.
E) a parasitic insect that never actually kills its host.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Symbiosis is a relationship between two organisms that is
A) beneficial to one.
B) beneficial to both.
C) harmful to one.
D) specific for two organisms.
E) All of the answers are forms of symbiosis.
A) beneficial to one.
B) beneficial to both.
C) harmful to one.
D) specific for two organisms.
E) All of the answers are forms of symbiosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A fig has evolved specialist structures that only allow one type of wasp to pollinate it. The wasp needs the fig, and the wasp and the fig have a relationship that is described as one to one. The wasp is said to
A) be a parasite.
B) be a mutualist.
C) have coevolved.
D) be a predator.
E) be a symbiont.
A) be a parasite.
B) be a mutualist.
C) have coevolved.
D) be a predator.
E) be a symbiont.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In myrmecotrophy (a specialised ant-plant relationship), the plant is thought to benefit from
A) nutrients in ant waste.
B) sap tapping.
C) nectar food rewards.
D) root aeration.
E) construction of domatia.
A) nutrients in ant waste.
B) sap tapping.
C) nectar food rewards.
D) root aeration.
E) construction of domatia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An ectoparasite
A) lives on the outside of its host.
B) lives inside its host.
C) is an insect with a parasitic larval stage.
D) is a predator.
A) lives on the outside of its host.
B) lives inside its host.
C) is an insect with a parasitic larval stage.
D) is a predator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Predator-prey cycles are
A) an almost universal phenomenon resulting from strong interactions between pairs of predator and prey species.
B) usually characterised by simple oscillations of prey and predator abundance.
C) not common in reality.
D) never chaotic.
E) important to the life cycle of many prey.
A) an almost universal phenomenon resulting from strong interactions between pairs of predator and prey species.
B) usually characterised by simple oscillations of prey and predator abundance.
C) not common in reality.
D) never chaotic.
E) important to the life cycle of many prey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which alternative best describes the Monarch butterfly's defence against predators?
A) Batesian mimicry.
B) It sequesters toxic plant compounds in its body making it unpalatable.
C) It copies the coloration pattern of a toxic butterfly.
D) It produces an alkaloid which is toxic.
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) Batesian mimicry.
B) It sequesters toxic plant compounds in its body making it unpalatable.
C) It copies the coloration pattern of a toxic butterfly.
D) It produces an alkaloid which is toxic.
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Predation is
A) a direct interaction between species.
B) an indirect interaction between species.
C) a more specialised form of interaction than parasitism.
D) an interaction between different ecosystems.
E) not an interaction.
A) a direct interaction between species.
B) an indirect interaction between species.
C) a more specialised form of interaction than parasitism.
D) an interaction between different ecosystems.
E) not an interaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Plants often contain chemicals to deter herbivores. These are known as
A) plant primary compounds.
B) plant secondary compounds.
C) terpenoids.
D) alkaloids.
E) physical defences.
A) plant primary compounds.
B) plant secondary compounds.
C) terpenoids.
D) alkaloids.
E) physical defences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Predator-prey cycles in nature
A) are highly predictable.
B) oscillate in a uniform manner.
C) are always tightly coupled.
D) are dependent on the herbivores in the ecosystem.
E) None of the answers are true.
A) are highly predictable.
B) oscillate in a uniform manner.
C) are always tightly coupled.
D) are dependent on the herbivores in the ecosystem.
E) None of the answers are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The introduction of the Cactoblastis moth to eat introduced prickly pear in Australia is an example of
A) symbiosis.
B) mutualism.
C) biological control.
D) parasitism.
E) chemical control.
A) symbiosis.
B) mutualism.
C) biological control.
D) parasitism.
E) chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The rose-crowned fruit pigeon helps disperse seeds in a number of species of rainforest trees. It can best be described as
A) a frugivore.
B) monophagous.
C) an insectivore.
D) a symbiont.
E) an herbivore.
A) a frugivore.
B) monophagous.
C) an insectivore.
D) a symbiont.
E) an herbivore.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
All of the following are defences against predators EXCEPT
A) being physically large.
B) living in groups.
C) containing detoxifying enzymes.
D) speed and agility.
E) using camouflage.
A) being physically large.
B) living in groups.
C) containing detoxifying enzymes.
D) speed and agility.
E) using camouflage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The competitive exclusion principle does not usually apply in the real world because
A) its conception was based on a complex experimental environment and the real world is much more simple.
B) it is only applicable to grain beetles.
C) in the real world predation is much more important.
D) in the real world competitive interactions are modified by a range of other interactions.
E) equilibrium is reached in ecosystems before the extreme conditions are reached.
A) its conception was based on a complex experimental environment and the real world is much more simple.
B) it is only applicable to grain beetles.
C) in the real world predation is much more important.
D) in the real world competitive interactions are modified by a range of other interactions.
E) equilibrium is reached in ecosystems before the extreme conditions are reached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Two species of birds eat the seeds of the same rainforest plant. Hence they are
A) interspecific competitors.
B) intraspecific competitors.
C) partitioning resources.
D) likely to become extinct.
E) exploitative competitors.
A) interspecific competitors.
B) intraspecific competitors.
C) partitioning resources.
D) likely to become extinct.
E) exploitative competitors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Two species of weevil are placed in a closed bottle of flour. At the end of a month, only one species is found in the bottle. This demonstrates
A) intraspecific competition.
B) the competitive exclusion principle.
C) the need for a minimum viable population.
D) partitioning of resources.
A) intraspecific competition.
B) the competitive exclusion principle.
C) the need for a minimum viable population.
D) partitioning of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Limpets and urchins are both algal grazers. If limpets tend to eat smaller algae, while sea urchins eat both large and small sizes, we say that
A) limpets have a smaller realised niche.
B) limpets and urchins are aggressively interfering with each other.
C) limpets and urchins are not competing.
D) urchins have a greater niche breadth.
E) limpets and urchins co-habitat.
A) limpets have a smaller realised niche.
B) limpets and urchins are aggressively interfering with each other.
C) limpets and urchins are not competing.
D) urchins have a greater niche breadth.
E) limpets and urchins co-habitat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An example of primary succession would be when the first
A) barnacle larvae settle and metamorphose on a new boat mooring.
B) eucalypt seeds of the season germinate in a eucalypt woodland.
C) seed germinates after a fire.
D) herbaceous plants begin to grow on a recent larva flow that had previously only been colonised by lichens.
E) individual of a new pest species arrives in a previously uninfested region.
A) barnacle larvae settle and metamorphose on a new boat mooring.
B) eucalypt seeds of the season germinate in a eucalypt woodland.
C) seed germinates after a fire.
D) herbaceous plants begin to grow on a recent larva flow that had previously only been colonised by lichens.
E) individual of a new pest species arrives in a previously uninfested region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When does disturbance usually promote maximum diversity in a community?
A) When it is rare
B) When it is common
C) When it occurs with intermediate frequency
D) When it is extreme and causes a sudden change
E) Never, disturbance always reduces the overall diversity of a community
A) When it is rare
B) When it is common
C) When it occurs with intermediate frequency
D) When it is extreme and causes a sudden change
E) Never, disturbance always reduces the overall diversity of a community

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following best describes the effect of bushfires on an ecosystem?
A) They promote species richness.
B) They promote species diversity.
C) They add structure to communities.
D) They promote habitat variability.
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) They promote species richness.
B) They promote species diversity.
C) They add structure to communities.
D) They promote habitat variability.
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
There is often an abrupt transition between a patch of grassland and a patch of woodland. The boundary between two such different communities is known as
A) a cline.
B) a gradient.
C) a succession.
D) an ecotone.
E) a disturbance.
A) a cline.
B) a gradient.
C) a succession.
D) an ecotone.
E) a disturbance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A community may be described in many ways which include
A) the types of species present.
B) the change of the species with time.
C) the interactions between the species.
D) the abundance of different species.
E) All of the answers are required to describe a community.
A) the types of species present.
B) the change of the species with time.
C) the interactions between the species.
D) the abundance of different species.
E) All of the answers are required to describe a community.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Species' richness
A) is a measure of diversity within an ecological group.
B) is the number of species in an ecological group.
C) includes the relative abundance of the species.
D) is diversity between communities.
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) is a measure of diversity within an ecological group.
B) is the number of species in an ecological group.
C) includes the relative abundance of the species.
D) is diversity between communities.
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Predation is the feeding of one organism on the fruit of a plant.
B) Predators have little effect on the abundance of their prey in an ecosystem.
C) Some organisms avoid predators by mimicking the behaviour of an unpalatable animal.
D) An ectoparasite of cattle is a predator.
E) Predators are an excellent means for biological control of organisms.
A) Predation is the feeding of one organism on the fruit of a plant.
B) Predators have little effect on the abundance of their prey in an ecosystem.
C) Some organisms avoid predators by mimicking the behaviour of an unpalatable animal.
D) An ectoparasite of cattle is a predator.
E) Predators are an excellent means for biological control of organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
All animals have requirements without which they would not survive and reproduce. These include
A) light for plants.
B) fruit for fruit-bats.
C) flowers for some insects.
D) prey for predators.
E) All of these are requirements for specific organisms.
A) light for plants.
B) fruit for fruit-bats.
C) flowers for some insects.
D) prey for predators.
E) All of these are requirements for specific organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Simpson's index is
A) the probably of randomly picking two individuals that are different species within a community.
B) zero when there is a single species in a community.
C) nearly one when there are many species in equal numbers in a community.
D) relates the number of species in a community to their relative abundance.
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) the probably of randomly picking two individuals that are different species within a community.
B) zero when there is a single species in a community.
C) nearly one when there are many species in equal numbers in a community.
D) relates the number of species in a community to their relative abundance.
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Coral bleaching occurs when
A) zooxanthellae undergo photosynthesis and provide waste products for the coral to grow.
B) zooxanthellae grow on coral and change their colour.
C) the symbiotic algae which cover corals and are white.
D) corals are stressed and expel their zooxanthellae leading to death by starvation.
E) coral reefs sink and are unable to photosynthesise in the deep water.
A) zooxanthellae undergo photosynthesis and provide waste products for the coral to grow.
B) zooxanthellae grow on coral and change their colour.
C) the symbiotic algae which cover corals and are white.
D) corals are stressed and expel their zooxanthellae leading to death by starvation.
E) coral reefs sink and are unable to photosynthesise in the deep water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An ecologist is studying the diversity of grasshopper species in different forest types. This would be an example of
A) -diversity.
B) -diversity.
C) -diversity.
D) -diversity.
E)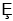 -diversity.
-diversity.
A) -diversity.
B) -diversity.
C) -diversity.
D) -diversity.
E)
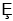 -diversity.
-diversity.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A community in which the growth form of the tallest stratum consists of low trees (<10m) and in which the foliage cover is 45% would be classified as
A) open forest.
B) None of the options listed are correct.
C) closed heath.
D) low woodland.
E) open woodland.
A) open forest.
B) None of the options listed are correct.
C) closed heath.
D) low woodland.
E) open woodland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Ryegrass is an important pasture plant in Australia and is often found with a fungal symbiont called Neotyphodium. The fungus produces a toxin that accumulates in the leaves of ryegrass that can deter insect pests and herbivory without affecting the plant. The fungus can also increase seedling vigour and plant productivity, while the fungus is protected by the plant as it grows inside the leaves, stem and seeds of the host. This relationship would be described as
A) mutualistic.
B) parasitic.
C) commensal.
D) exophytic.
E) All of the answers are incorrect.
A) mutualistic.
B) parasitic.
C) commensal.
D) exophytic.
E) All of the answers are incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A big-cat species hunts across a significant area within which it preys upon a large and varied array of other animals. In so doing, it helps maintain the balance of the ecosystem in which it lives and hunts. As such, it can be considered to be a
A) keystone predator.
B) aggressive species.
C) Yautja.
D) alpha micophagist.
E) ambush predator.
A) keystone predator.
B) aggressive species.
C) Yautja.
D) alpha micophagist.
E) ambush predator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A banana farmer in northern Australia is trying to deal with an outbreak of an extremely virulent fungal pathogen that is destroying his plantation. In desperation, he sprays a large section of his farm with a new product that consists of a number of bacterial and yeast species in a growth medium. To his surprise he finds that although the pathogenic fungus is still evident on his plants, its virulence is greatly decreased such that his plantation is once again financially viable. The application of the product containing microorganisms would be an example of a
A) chemical fungicide.
B) bio-fertiliser.
C) hormonal application.
D) bacterial symbiont.
E) biological control.
A) chemical fungicide.
B) bio-fertiliser.
C) hormonal application.
D) bacterial symbiont.
E) biological control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A species of ant wards off predators by secreting a pungent aroma to alert predators that the ant is toxic and extremely unpalatable. An unrelated species of ant that is palatable secretes a compound that is almost identical. Many predators are fooled into thinking this is also a toxic ant, thus it avoids predation. This is an example of
A) thespianism.
B) mummer.
C) mimicry.
D) trouper.
E) camouflage.
A) thespianism.
B) mummer.
C) mimicry.
D) trouper.
E) camouflage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Many plants produce tannins to reduce herbivory, but tannins are not toxic when ingested. In what way do tannins make plants unpalatable to herbivores?
A) Tannins bind to the gut walls of herbivores, inhibiting nutrient uptake.
B) Tannins disrupt the osmotic gradient in the digestive tract, causing ingested tissue to be flushed through the herbivores gut before nutrition can be extracted.
C) Tannins neutralise the pH of the herbivores gut, thereby preventing gastric juices from degrading the plant material.
D) Tannins denature the gut enzymes of the herbivores, preventing breakdown of the plant material.
E) Tannins combine with proteins in leaves, producing a high indigestible compound.
A) Tannins bind to the gut walls of herbivores, inhibiting nutrient uptake.
B) Tannins disrupt the osmotic gradient in the digestive tract, causing ingested tissue to be flushed through the herbivores gut before nutrition can be extracted.
C) Tannins neutralise the pH of the herbivores gut, thereby preventing gastric juices from degrading the plant material.
D) Tannins denature the gut enzymes of the herbivores, preventing breakdown of the plant material.
E) Tannins combine with proteins in leaves, producing a high indigestible compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Two different species of ants compete in the same area for food. One of the species prevents the other from accessing food by plugging the holes of its nest with rocks. What kind of competition is this an example of?
A) Intraspecific, interference competition
B) Interspecific, exploitative competition
C) Intraspecific, exploitative competition
D) Interspecific, interference competition
E) Interspecific, exclusion competition
A) Intraspecific, interference competition
B) Interspecific, exploitative competition
C) Intraspecific, exploitative competition
D) Interspecific, interference competition
E) Interspecific, exclusion competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The region of an environment within which a species can exist indefinitely is defined by all the biotic and abiotic factors that impinge on the survival and reproduction of the species. This is otherwise known as
A) the realised niche.
B) the observed niche.
C) the active niche.
D) the ecological niche.
E) the fundamental niche.
A) the realised niche.
B) the observed niche.
C) the active niche.
D) the ecological niche.
E) the fundamental niche.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



