Deck 19: Options
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/55
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Options
1
Securities that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a stated number of shares of stock within a specified period at a specified price is a(n):
A) futures contract.
B) option contract.
C) swap contract.
D) forward contract.
A) futures contract.
B) option contract.
C) swap contract.
D) forward contract.
option contract.
2
The standard option contract on an organized exchange is written on:
A) 10 shares of stock.
B) 50 shares of stock.
C) 100 shares of stock.
D) 1 share of stock.
A) 10 shares of stock.
B) 50 shares of stock.
C) 100 shares of stock.
D) 1 share of stock.
100 shares of stock.
3
Investors purchase call options when they expect the price of the underlying stock to:
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) show great price volatility.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) show great price volatility.
increase.
4
Another name for the premium of the option is:
A) price paid by the option writer to the option buyer.
B) price paid by the option buyer to the writer of the option.
C) the per-share price that the option writer receives when the option is exercised.
D) the per-share prices that the option holder pays when the option is exercised.
A) price paid by the option writer to the option buyer.
B) price paid by the option buyer to the writer of the option.
C) the per-share price that the option writer receives when the option is exercised.
D) the per-share prices that the option holder pays when the option is exercised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The exercise price on an option :
A) changes as the price of the underlying stock increases or decreases.
B) has a series of standardized strike prices.
C) is not adjusted for stock splits.
D) is also known as the option premium.
A) changes as the price of the underlying stock increases or decreases.
B) has a series of standardized strike prices.
C) is not adjusted for stock splits.
D) is also known as the option premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is true regarding a put writer?
A) The put writer expects the stock to remain the same or move upward.
B) The put writer expects the stock to remain the same or move down.
C) The put writer expects the stock to split.
D) The put writer expects to sell the stock prior to expiration of the option.
A) The put writer expects the stock to remain the same or move upward.
B) The put writer expects the stock to remain the same or move down.
C) The put writer expects the stock to split.
D) The put writer expects to sell the stock prior to expiration of the option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which one is not a determinant of the value of a call option in the Black-Scholes model?
A) Volatility of the continuously compounded rate of return on the underlying stock
B) Exercise price of the option
C) Price of the underlying stock
D) The expected dividends on the underlying stock
A) Volatility of the continuously compounded rate of return on the underlying stock
B) Exercise price of the option
C) Price of the underlying stock
D) The expected dividends on the underlying stock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In order to hedge a short sale, which of the following basic option strategies would that investor follow?
A) buy a call.
B) write a call.
C) buy a put.
D) write a put.
A) buy a call.
B) write a call.
C) buy a put.
D) write a put.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the price of the common stock is below the exercise price of a put contract on the stock the put is said to be:
A) at the money.
B) out of the money.
C) in the money.
D) covered.
A) at the money.
B) out of the money.
C) in the money.
D) covered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Options that trade on organized exchanges are protected against:
A) default risk.
B) stock splits.
C) interest rate movements.
D) inflation.
A) default risk.
B) stock splits.
C) interest rate movements.
D) inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Other things being equal, after an option first trades in the market:
A) its time value begins to decline and approaches zero as time gets closer to expiration.
B) its time value increases eventually reaching intrinsic value at expiration.
C) its time value increases if it is a call and decreases if it is a put.
D) if it is out of the money, it will have no time value.
A) its time value begins to decline and approaches zero as time gets closer to expiration.
B) its time value increases eventually reaching intrinsic value at expiration.
C) its time value increases if it is a call and decreases if it is a put.
D) if it is out of the money, it will have no time value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A writer of a call can terminate that particular contract anytime before its expiration by:
A) writing a second call.
B) buying a put.
C) buying a comparable call.
D) writing a put.
A) writing a second call.
B) buying a put.
C) buying a comparable call.
D) writing a put.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The writer of a naked call faces:
A) limited potential profit and limited potential loss.
B) limited potential profit and unlimited potential loss.
C) unlimited potential profit and limited potential loss.
D) unlimited potential profit and unlimited potential loss.
A) limited potential profit and limited potential loss.
B) limited potential profit and unlimited potential loss.
C) unlimited potential profit and limited potential loss.
D) unlimited potential profit and unlimited potential loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is true for the time value of an option?
A) time value = option price - intrinsic value.
B) time value = intrinsic value + option price.
C) Time value is another name for intrinsic value.
D) Time value is zero for out of the money options.
A) time value = option price - intrinsic value.
B) time value = intrinsic value + option price.
C) Time value is another name for intrinsic value.
D) Time value is zero for out of the money options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Questions are based on the following options data for XYZ Corporation:
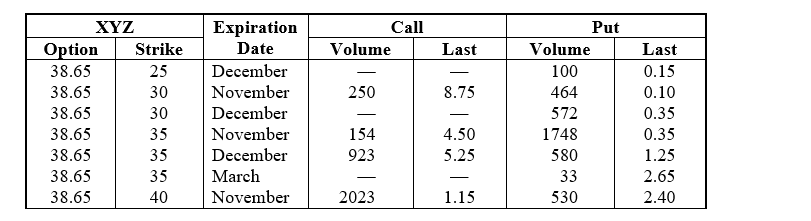
-Of the series of options shown above, how many of the put contracts are currently trading out of the money?
A) 6
B) 5
C) 4
D) 1

-Of the series of options shown above, how many of the put contracts are currently trading out of the money?
A) 6
B) 5
C) 4
D) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Questions are based on the following options data for XYZ Corporation:

-Which of the following options is furthest in the money?
A) November 30 Call
B) November 35 Call.
C) December 35Call
D) November 40 Call

-Which of the following options is furthest in the money?
A) November 30 Call
B) November 35 Call.
C) December 35Call
D) November 40 Call

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements is false?
A) An in the money call occurs if the stock price exceeds the exercise price.
B) An out of the money call occurs if the stock price is less than the exercise price.
C) If a call is out of the money, the intrinsic value is zero.
D) If a call is in the money, the intrinsic value is zero.
A) An in the money call occurs if the stock price exceeds the exercise price.
B) An out of the money call occurs if the stock price is less than the exercise price.
C) If a call is out of the money, the intrinsic value is zero.
D) If a call is in the money, the intrinsic value is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Options are a wasting asset.
B) Option prices almost always exceed intrinsic values.
C) As expiration approaches, the value of the option declines to zero.
D) The intrinsic value of a call is equal to its market value.
A) Options are a wasting asset.
B) Option prices almost always exceed intrinsic values.
C) As expiration approaches, the value of the option declines to zero.
D) The intrinsic value of a call is equal to its market value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The option premium is paid by the option writer.
B) The further that an option is in the money, the lower the option's intrinsic value.
C) An option's premium is usually below its intrinsic value.
D) When a call's exercise price is below the market price of the stock it is in the money.
A) The option premium is paid by the option writer.
B) The further that an option is in the money, the lower the option's intrinsic value.
C) An option's premium is usually below its intrinsic value.
D) When a call's exercise price is below the market price of the stock it is in the money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In addition to options trading on stocks, listed options are also offered on which of the following underlying assets:
A) stock-index options
B) interest rate options
C) currency options
D) All of the above have listed option contracts.
A) stock-index options
B) interest rate options
C) currency options
D) All of the above have listed option contracts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is false regarding options prices?
A) At expiration, a call must have a value that is the maximum of 0 or its intrinsic value.
B) At expiration, a put must have a value that is the maximum of 0 or its intrinsic value.
C) The minimum price for a put is the price of the underlying stock.
D) The maximum price for a call is the price of the underlying stock.
A) At expiration, a call must have a value that is the maximum of 0 or its intrinsic value.
B) At expiration, a put must have a value that is the maximum of 0 or its intrinsic value.
C) The minimum price for a put is the price of the underlying stock.
D) The maximum price for a call is the price of the underlying stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
All of the following will lead to an increase of the market value of a call option except:
A) The price of the underlying increases.
B) The exercise price of the option contract increases.
C) The volatility of the continuously compounded rate of return on the underlying stock increases.
D) The time remaining to the expiration of the option increases
A) The price of the underlying increases.
B) The exercise price of the option contract increases.
C) The volatility of the continuously compounded rate of return on the underlying stock increases.
D) The time remaining to the expiration of the option increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The three provisions which investors should carefully examine when selecting puts and calls are the:
A) option premium, expiration date, and striking price.
B) leverage ratio, time to maturity, and conversion premium.
C) hedge ratio, the speculative premium, and current stock price.
D) premium, maturity, and dividend yield.
A) option premium, expiration date, and striking price.
B) leverage ratio, time to maturity, and conversion premium.
C) hedge ratio, the speculative premium, and current stock price.
D) premium, maturity, and dividend yield.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not true concerning stock-index options?
A) Stock-index options enable investors to trade on general stock market movements.
B) Stock-index options are available on the S&P/TSX 60 and various ETFs.
C) Most index-options are European style, including the S&P/TSX 60 Index options.
D) In Canada stock-index options trade on the TSX.
A) Stock-index options enable investors to trade on general stock market movements.
B) Stock-index options are available on the S&P/TSX 60 and various ETFs.
C) Most index-options are European style, including the S&P/TSX 60 Index options.
D) In Canada stock-index options trade on the TSX.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When an investor purchases one put contract and one call contract on the same stock with the same exercise price and expiry date he or she has formed a:
A) strip.
B) straddle.
C) strap.
D) spread.
A) strip.
B) straddle.
C) strap.
D) spread.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A purchaser of a straddle:
A) believes that the underlying stock price will exhibit small volatility.
B) believes that the underlying stock price is highly volatile.
C) believes that the stock price will go up only a little.
D) believes that the stock price will go down only a little.
A) believes that the underlying stock price will exhibit small volatility.
B) believes that the underlying stock price is highly volatile.
C) believes that the stock price will go up only a little.
D) believes that the stock price will go down only a little.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A combination of two puts and one call on the same stock with the same exercise price and expiry date is called a:
A) strip.
B) strap.
C) straddle.
D) spread.
A) strip.
B) strap.
C) straddle.
D) spread.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is not a major difference between calls and warrants?
A) Warrants are generally longer term than calls.
B) Warrants are issued by corporation; calls are not.
C) Warrants provide more leverage than calls.
D) Warrants are not standardized; calls are.
A) Warrants are generally longer term than calls.
B) Warrants are issued by corporation; calls are not.
C) Warrants provide more leverage than calls.
D) Warrants are not standardized; calls are.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is not a factor that affects the premium of a warrant?
A) price volatility of the common stock
B) current price of the warrant
C) dividend on the common stock
D) potential leverage of the warrant
A) price volatility of the common stock
B) current price of the warrant
C) dividend on the common stock
D) potential leverage of the warrant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a right?
A) Rights generally have short maturities consisting of a few weeks to three months.
B) Rights have certificates mailed to shareholders on the record date.
C) Rights are usually transferable.
D) The subscription price for a right is generally higher than the current market price.
A) Rights generally have short maturities consisting of a few weeks to three months.
B) Rights have certificates mailed to shareholders on the record date.
C) Rights are usually transferable.
D) The subscription price for a right is generally higher than the current market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A protective put is a strategy in which a short seller sells a call.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The strategies with stock index options are considerably different from those for individual stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An option buyer has three courses of action available: exercise the option, sell it or let it expire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A straddle is considered a type of spread.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Warrants are issued by corporations while puts and calls are written by investors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Warrants usually have expiration dates than are longer than rights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The options clearing corporation ensures fulfillment of option obligations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
There is direct relationship between the price of a call option and the volatility of the underlying common stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Writing a naked call can result in a greater loss than writing a naked put.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Option trades settle on the next business day after the trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The hedge ratio is the ratio of options written to shares of stock held long in a riskless portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Put-call parity exists when the call and the put on the same stock for the same strike price and same expiration date have the same price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Stock index options are always used for hedging and not for speculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Call options are normally bought by investors who expect the stock price to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Compare warrants with listed calls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What does the purchaser of a straddle think about the future of the underlying stock?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What are the price boundaries for a warrant?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A stock investor wants to hedge the BMO stock in his portfolio. How can he use a covered call to do this?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A stock investor wants to hedge the TELUS Corp. stock in his portfolio. How can he use a protective put to do this?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How would you replicate the payoff on a short position in a stock, using a call, a put, and a risk-free bond?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
SCORP has puts and calls available for trading for the expiration months of June, September, and December. For the trading day May 2, 20XX, SCORP closed at $40 per share. Strike prices for SCORP are $35, $40, and $45. The following prices for the nine call options (three expiration dates and three strike prices) for this date were (in scrambled order):

Fill in the following matrix of prices for these calls, using letters only (i.e., A through I)


Fill in the following matrix of prices for these calls, using letters only (i.e., A through I)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
ABC, which closed at $151, has call options trading in April, July, and October with the following values:
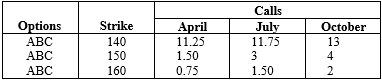
(a) Calculate the intrinsic value of the April 150 call.
(b) Calculate the intrinsic value of the April 140 call.
(c) Should the price of ABC rise to $156, what is the minimum value that the April 150 call should trade at?

(a) Calculate the intrinsic value of the April 150 call.
(b) Calculate the intrinsic value of the April 140 call.
(c) Should the price of ABC rise to $156, what is the minimum value that the April 150 call should trade at?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Listed below are the option quotes on JUP, Inc., in January of this year.
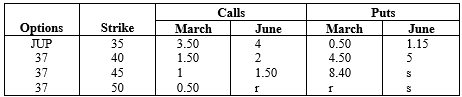
(a) Which calls are in the money?
(b) Which puts are in the money?
(c) Why are investors willing to pay 3.50 for the March 35 call but only 0.50 for the March 35 put?
(d) Calculate the intrinsic value of the June 35 call.
(e) Calculate the intrinsic value of the March 40 put.

(a) Which calls are in the money?
(b) Which puts are in the money?
(c) Why are investors willing to pay 3.50 for the March 35 call but only 0.50 for the March 35 put?
(d) Calculate the intrinsic value of the June 35 call.
(e) Calculate the intrinsic value of the March 40 put.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the Black-Scholes model to calculate the theoretical value of a DBA December 45 call option. Assume that the risk free rate of return is 6 per cent, the stock has a variance of 36 per cent, there are 91 days until expiration of the contract, and DBA stock is currently selling at $50 in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
You buy 1,000 shares of Sunbeam at 11.15 and write 10 calls at a premium of 4.40 with a strike price of 7.50 1/2. The stock goes to 20 in 6 months. You receive an 8 cent dividend per share. If the calls are exercised (which is the likely assumption), what is your percentage return?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



