Deck 10: Market Efficiency
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Market Efficiency
1
If an investor believes in the Efficient Market Hypothesis she would engage in:
A) market-timing strategies.
B) investing in an index fund.
C) investing based on technical indicators.
D) investing by active strategies.
A) market-timing strategies.
B) investing in an index fund.
C) investing based on technical indicators.
D) investing by active strategies.
investing in an index fund.
2
All known information does not include:
A) last year's earnings.
B) the current quarter's earnings.
C) stock splits that have been announced but are still forthcoming.
D) All of the above are included.
A) last year's earnings.
B) the current quarter's earnings.
C) stock splits that have been announced but are still forthcoming.
D) All of the above are included.
stock splits that have been announced but are still forthcoming.
3
Which is not a result of the widespread usage of the Internet with regards to efficient markets?
A) It makes information cheaper making markets more efficient..
B) It makes information more readily accessible making markets more efficient.
C) It increases the volatility of security prices making markets less efficient.
D) It increases competition among brokers, making markets more efficient.
A) It makes information cheaper making markets more efficient..
B) It makes information more readily accessible making markets more efficient.
C) It increases the volatility of security prices making markets less efficient.
D) It increases competition among brokers, making markets more efficient.
It increases the volatility of security prices making markets less efficient.
4
All of the following conditions must occur for a market to be considered efficient except:
A) Information is costless and widely available to market participants at approximately the same time.
B) Information is generated in a specific fashion such that announcements are basically dependent on each other.
C) There are a large number of rational, profit-maximizing investors who actively participate in the market.
D) Investors react quickly and fully to the new information, causing stock prices to adjust accordingly.
A) Information is costless and widely available to market participants at approximately the same time.
B) Information is generated in a specific fashion such that announcements are basically dependent on each other.
C) There are a large number of rational, profit-maximizing investors who actively participate in the market.
D) Investors react quickly and fully to the new information, causing stock prices to adjust accordingly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If stock prices are said to follow a random walk, it means:
A) that the market is inefficient.
B) that investors do not react to new information.
C) that price movements can be determined by technical analysis.
D) that changes in price are independent of past price changes and cannot be predicted.
A) that the market is inefficient.
B) that investors do not react to new information.
C) that price movements can be determined by technical analysis.
D) that changes in price are independent of past price changes and cannot be predicted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The different forms of market efficiency have differences owing to:
A) the different authors which first wrote about them.
B) the different speed that each form would react to new information.
C) the different type of information that would be reflected in the stock price in each form of efficiency.
D) the different cost structure that would be involved in generating each type of efficiency.
A) the different authors which first wrote about them.
B) the different speed that each form would react to new information.
C) the different type of information that would be reflected in the stock price in each form of efficiency.
D) the different cost structure that would be involved in generating each type of efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements concerning stock splits is true?
A) Stock splits represent unrealized gains in the company and should increase the stock's value.
B) Stock splits represent unrealized losses in the company and should decrease the stock's value.
C) Stock splits add nothing of value to a company and should not affect market value.
D) Stock splits subtract value from a company and should negatively affect market value.
A) Stock splits represent unrealized gains in the company and should increase the stock's value.
B) Stock splits represent unrealized losses in the company and should decrease the stock's value.
C) Stock splits add nothing of value to a company and should not affect market value.
D) Stock splits subtract value from a company and should negatively affect market value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not a requirement for the Efficient Market Hypothesis?
A) Stock prices reflect their true economic value.
B) All known information is quickly reflected in prices.
C) Technical analysts can consistently outperform the market.
D) An investor cannot make money in the stock market.
A) Stock prices reflect their true economic value.
B) All known information is quickly reflected in prices.
C) Technical analysts can consistently outperform the market.
D) An investor cannot make money in the stock market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which type of stock market analysis is the focus of analyzing the past movements in a stock's price in order to forecast future movements?
A) the 5 Cs of credit analysis.
B) financial statement analysis.
C) fundamental analysis.
D) technical analysis.
A) the 5 Cs of credit analysis.
B) financial statement analysis.
C) fundamental analysis.
D) technical analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following events does not support semi-strong-form efficiency?
A) IPO shares bought shortly after the initial trades.
B) Buying shares of companies involved in stock splits after the announcements were made.
C) Buying shares on momentum trades picking star performers for the last six to 12 months.
D) Buying shares of companies after they have had surprise dividend announcements.
A) IPO shares bought shortly after the initial trades.
B) Buying shares of companies involved in stock splits after the announcements were made.
C) Buying shares on momentum trades picking star performers for the last six to 12 months.
D) Buying shares of companies after they have had surprise dividend announcements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The most stringent form of market efficiency is:
A) weak-form efficiency.
B) semi-strong-form efficiency.
C) random-walk efficiency.
D) strong-form efficiency.
A) weak-form efficiency.
B) semi-strong-form efficiency.
C) random-walk efficiency.
D) strong-form efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Assuming that the efficient market hypothesis is true, which of the following regarding the implications of the EMH is incorrect?
A) Technical analysis and the weak form of the EMH directly conflict.
B) In theory, most investors can do a superior job of analysis and profit thereby.
C) Professional money managers would still have certain important tasks to perform.
D) Investors who use the same data and make the same interpretations as other investors will experience only average results.
A) Technical analysis and the weak form of the EMH directly conflict.
B) In theory, most investors can do a superior job of analysis and profit thereby.
C) Professional money managers would still have certain important tasks to perform.
D) Investors who use the same data and make the same interpretations as other investors will experience only average results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The small firm effect is most likely to exhibit the largest positive returns:
A) in December as blue chip companies are sold for tax loss strategies.
B) in January.
C) in late February and early March as RRSP money enters the market.
D) in October which has traditionally been the safest month to be in the stock market. accounting changes effect
A) in December as blue chip companies are sold for tax loss strategies.
B) in January.
C) in late February and early March as RRSP money enters the market.
D) in October which has traditionally been the safest month to be in the stock market. accounting changes effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which form of the EMH states that stock prices reflect all past price and volume data?
A) Weak form
B) Semi-strong form
C) Strong form
D) None of the above.
A) Weak form
B) Semi-strong form
C) Strong form
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In an efficient market, it is not necessary for a portfolio manager to:
A) determine and quantify the risk preferences of a client.
B) minimize total transaction costs.
C) ascertain the tax implications of alternative investments.
D) attempt to maximize the portfolio's rate of return by superior market timing.
A) determine and quantify the risk preferences of a client.
B) minimize total transaction costs.
C) ascertain the tax implications of alternative investments.
D) attempt to maximize the portfolio's rate of return by superior market timing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Investors who believe in the EMH think that technical analysts:
A) should look solely for resistance and support levels for stock prices.
B) should concentrate on looking at charts for patterns of stock price changes.
C) should concentrate on contrary indicators as investors make the most money when they go against the market.
D) should not bother doing technical analysis since stock prices already reflect all price and volume data.
A) should look solely for resistance and support levels for stock prices.
B) should concentrate on looking at charts for patterns of stock price changes.
C) should concentrate on contrary indicators as investors make the most money when they go against the market.
D) should not bother doing technical analysis since stock prices already reflect all price and volume data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Empirical research on semi-strong form tests of the EMH often involve using:
A) an economic study.
B) a statistical study.
C) an event study.
D) a study of financial statement.
A) an economic study.
B) a statistical study.
C) an event study.
D) a study of financial statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Tests of the speed of adjustment in the prices of securities to announcements of new information is:
A) a weak-form statistical test.
B) a weak-form test of technical trading rules.
C) a semi-strong-form test.
D) a strong test.
A) a weak-form statistical test.
B) a weak-form test of technical trading rules.
C) a semi-strong-form test.
D) a strong test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is the most persistent example of a market anomaly?
A) Stock splits
B) The size effect
C) Dividend announcements
D) Technical patterns and charting
A) Stock splits
B) The size effect
C) Dividend announcements
D) Technical patterns and charting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
With regard to market efficiency, identify the incorrect statement.
A) Information is the central issue of the efficient markets concept.
B) The most stringent form of market efficiency is the strong form.
C) The efficient market concept does not require a perfect adjustment in price following new information.
D) Tests of the usefulness of price data are semi-strong-form tests.
A) Information is the central issue of the efficient markets concept.
B) The most stringent form of market efficiency is the strong form.
C) The efficient market concept does not require a perfect adjustment in price following new information.
D) Tests of the usefulness of price data are semi-strong-form tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
According to the semi-strong form of the EMH, investors who invest in a stock after a highly positive announcement concerning the stock can expect to earn a(n):
A) normal return because the stock will be fairly priced when purchased.
B) extraordinary return because the new information will not affect the price until later.
C) loss because things often are not what they seem.
D) zero return because the next price is expected to be the same as the last price.
A) normal return because the stock will be fairly priced when purchased.
B) extraordinary return because the new information will not affect the price until later.
C) loss because things often are not what they seem.
D) zero return because the next price is expected to be the same as the last price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An investor purchased a board lot of a leading diamond mining company with an expected return of 20 per cent per year. The following day the company's president announced a major new discovery in the Northwest Territories. The stock price immediately doubled. This scenario probably best illustrates that the:
A) weak-form EMH does not hold.
B) semi-strong-form EMH does not hold.
C) stock prices are random and that the random walk theory holds.
D) the investor was lucky.
A) weak-form EMH does not hold.
B) semi-strong-form EMH does not hold.
C) stock prices are random and that the random walk theory holds.
D) the investor was lucky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
According to behavioural finance proponents:
A) Stock markets behave accordingly to patterns that repeat themselves every four years.
B) The economic cycle and stock market behave or exhibit a strong correlation with one another.
C) Investors behave rationally by considering all available information in the decision-making process.
D) Investors' emotions affect stock prices and markets and that those making investment decisions should be aware of this.
A) Stock markets behave accordingly to patterns that repeat themselves every four years.
B) The economic cycle and stock market behave or exhibit a strong correlation with one another.
C) Investors behave rationally by considering all available information in the decision-making process.
D) Investors' emotions affect stock prices and markets and that those making investment decisions should be aware of this.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The "overreaction hypothesis" as formulated by DeBondt and Thaler states that people overreact to unexpected and dramatic news events. As a result,
A) "winner" and "loser" portfolios show no difference in performance over a three-year period.
B) "winner" portfolios generally outperform the market over a three-year period.
C) "loser" portfolios generally continue losing.
D) "loser" portfolios tend to outperform the market over a three-year period.
A) "winner" and "loser" portfolios show no difference in performance over a three-year period.
B) "winner" portfolios generally outperform the market over a three-year period.
C) "loser" portfolios generally continue losing.
D) "loser" portfolios tend to outperform the market over a three-year period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Evidence concerning the "overreaction hypothesis" indicates that:
A) investors sometimes act irrationally.
B) investors are consistently risk-averse value maximizers.
C) the market is even more efficient than the weak-form EMH proposes.
D) most overreactions occur within the first two days of an economic event.
A) investors sometimes act irrationally.
B) investors are consistently risk-averse value maximizers.
C) the market is even more efficient than the weak-form EMH proposes.
D) most overreactions occur within the first two days of an economic event.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a perfectly efficient market, investors are able to use available information to earn abnormal returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Under the semi-strong form of the EMH, technical analysis that relies on past history of price information is of little or no value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A dividend announcement effect would be considered a good test of the semi-strong weak form of the EMH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Short-lived inefficiencies appearing on a random basis constitute evidence of market inefficiencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Consecutive stock price changes have been shown to have zero correlation with one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The evidence obtained on weak-form efficiency casts serious doubts on technical analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Overall, the low P/E strategy should be viewed as a strategy that would best help investors in the short-run as opposed to the intermediate or long-run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A belief in the size effect anomaly should encourage investors to buy large-firm stocks in January.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Efficient markets are characterized by a large number of speculators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The January effect is most pronounced for large company stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Careful adherence to a low P/E strategy should lead to a well-diversified portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Tests of the strong-form EMH include studies of corporate insiders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Over the 10-year period ending September 30, 1997, less than 50% of mutual funds beat their category average in five out of the ten years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Insider trading is illegal in Canada. How is this related to the strong-form EMH?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What are the findings of studies regarding changes in accounting practices and the semi-strong-form EMH?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Do investors stand to earn abnormal profits on initial public offerings? How can this be reconciled with the semi-strong form of the EMH?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Technical analysis involves identifying historical price and volume patterns in order to predict future price movements. What does the EMH say about technical analysis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If securities are fairly priced, then the portfolio manager, it might be argued, has little to do, since searching for undervalued stocks is a losing proposition. What other activities do money managers perform?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An oil company's P/E ratio is 15; its projected EPS is $8; and its price is $120. Expectations are that a new field will add $1 EPS the next year. If the P/E remains constant, what should happen to the price in an efficient market? How soon? Are investors that pay the price after adjustment paying a fair price and are they expected to earn a normal return? Could insiders make an illegal profit before the announcement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Explain the neglected firm effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Indexing is becoming more popular as an investment strategy. Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Listed below are the actual returns on two stocks X and Y, and on the market (RM), along with their systematic risk measures (Betas) relative to the time period, t.
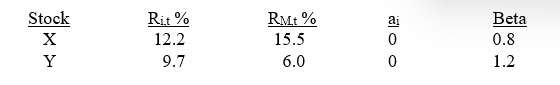
(a) What is the abnormal return for stock X when you consider its systematic risk measure?
(b) What is the abnormal return for stock Y when you consider its systematic risk measure?

(a) What is the abnormal return for stock X when you consider its systematic risk measure?
(b) What is the abnormal return for stock Y when you consider its systematic risk measure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The Auto Company (AC) had expected returns and realized returns for the periods shown below:
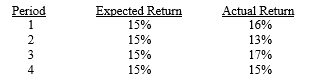
Calculate the cumulative abnormal return for the four periods.
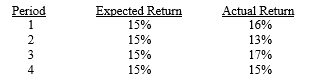
Calculate the cumulative abnormal return for the four periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



