Deck 6: The Returns and Risks Form Investing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/43
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The Returns and Risks Form Investing
1
The return component that is concerned with the capital appreciation (depreciation) in an asset is known as:
A) capital gain (loss).
B) interest rate.
C) yield.
D) unrealized gain.
A) capital gain (loss).
B) interest rate.
C) yield.
D) unrealized gain.
capital gain (loss).
2
Investors should be willing to purchase a particular asset:
A) if the holding period is long enough to recoup the purchase price of the asset through dividends or interest payments.
B) if the expected return is adequate to compensate for the risk.
C) if the expected return is greater than the return paid on treasury bills.
D) if they are true speculators.
A) if the holding period is long enough to recoup the purchase price of the asset through dividends or interest payments.
B) if the expected return is adequate to compensate for the risk.
C) if the expected return is greater than the return paid on treasury bills.
D) if they are true speculators.
if the expected return is adequate to compensate for the risk.
3
If interest rates are expected to fall, you would expect:
A) bond prices to fall more than stock prices.
B) bond prices to rise more than stock prices.
C) stock prices to fall more than bond prices.
D) stock prices to rise and bond prices to fall.
A) bond prices to fall more than stock prices.
B) bond prices to rise more than stock prices.
C) stock prices to fall more than bond prices.
D) stock prices to rise and bond prices to fall.
bond prices to rise more than stock prices.
4
Liquidity risk is associated with:
A) the use of equity financing by corporations.
B) the use of debt financing by corporations.
C) the price concession in a secondary market transaction.
D) debt investments held by corporations.
A) the use of equity financing by corporations.
B) the use of debt financing by corporations.
C) the price concession in a secondary market transaction.
D) debt investments held by corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The measure that best shows returns over time in relation to the initial investment is the:
A) total return.
B) return relative.
C) cumulative wealth index.
D) total yield.
A) total return.
B) return relative.
C) cumulative wealth index.
D) total yield.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If an investor had a one-year holding period for an investment and would receive cash flows only at the end of that period without the potential to reinvest, then the best measure of return for that investment would be:
A) arithmetic mean.
B) geometric mean.
C) calculus mean.
D) arithmetic median.
A) arithmetic mean.
B) geometric mean.
C) calculus mean.
D) arithmetic median.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Another name for inflation-adjusted returns is:
A) real returns.
B) nominal returns.
C) money returns.
D) dollar denominated returns.
A) real returns.
B) nominal returns.
C) money returns.
D) dollar denominated returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to the text, total return is:
A) the difference between the sale price and the purchase price of an investment.
B) measured by dividing the sum of all cash flows by the amount invested.
C) the reciprocal of a return relative.
D) measured by dividing all cash flows received by its selling price.
A) the difference between the sale price and the purchase price of an investment.
B) measured by dividing the sum of all cash flows by the amount invested.
C) the reciprocal of a return relative.
D) measured by dividing all cash flows received by its selling price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The cumulative wealth index:
A) is measured by adding up the total returns over the holding period and dividing by the investment.
B) uses index values to have a specified beginning value.
C) is the present value of the future cash flows expected from the investment.
D) uses the arithmetic mean as the rate of growth of one's wealth.
A) is measured by adding up the total returns over the holding period and dividing by the investment.
B) uses index values to have a specified beginning value.
C) is the present value of the future cash flows expected from the investment.
D) uses the arithmetic mean as the rate of growth of one's wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
On average which of the following is false concerning total returns for major financial assets, 1938 to 2007?
A) US common Stocks have higher returns than Canadian stocks.
B) Canadian common stocks have higher returns than long-term Government of Canada bonds.
C) The return on 91-Day Government of Canada T-bills has consistently been less than inflation.
D) Long-term Government of Canada bonds have higher rates than short-term issues.
A) US common Stocks have higher returns than Canadian stocks.
B) Canadian common stocks have higher returns than long-term Government of Canada bonds.
C) The return on 91-Day Government of Canada T-bills has consistently been less than inflation.
D) Long-term Government of Canada bonds have higher rates than short-term issues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When a Canadian investor buys stock in Great Britain, her dollar-denominated return will increase if the pound:
A) appreciates in value.
B) depreciates in value.
C) remains unchanged.
D) moves to a net gain position.
A) appreciates in value.
B) depreciates in value.
C) remains unchanged.
D) moves to a net gain position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The equity risk premium is the difference between:
A) stocks and bonds.
B) high-grade stocks and low-grade stocks.
C) stocks and the risk-free rate.
D) a stock market index and the inflation rate.
A) stocks and bonds.
B) high-grade stocks and low-grade stocks.
C) stocks and the risk-free rate.
D) a stock market index and the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The bond horizon premium is:
A) the difference between the rates on long-term government bonds and the same maturity corporate bonds.
B) the difference between the rates on long-term government bonds and a risk-free rate.
C) the difference between rates on long-term corporate bonds and a risk-free rate.
D) the difference in returns on the longest maturity government bond and the shortest maturity risk-free rate bond.
A) the difference between the rates on long-term government bonds and the same maturity corporate bonds.
B) the difference between the rates on long-term government bonds and a risk-free rate.
C) the difference between rates on long-term corporate bonds and a risk-free rate.
D) the difference in returns on the longest maturity government bond and the shortest maturity risk-free rate bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Calculation of wealth indexes involve compounding:
A) at the geometric mean return.
B) at the arithmetic mean return.
C) based upon the standard deviation.
D) based on the systematic risk factor.
A) at the geometric mean return.
B) at the arithmetic mean return.
C) based upon the standard deviation.
D) based on the systematic risk factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The total risk of an asset or a portfolio is measured by:
A) its geometric return.
B) its correlation with the market portfolio.
C) its standard deviation.
D) its covariance with the market portfolio.
A) its geometric return.
B) its correlation with the market portfolio.
C) its standard deviation.
D) its covariance with the market portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The bond default premium is measured by the difference between the:
A) return on long-term corporate bonds and short-term corporate bonds.
B) return on long-term government bonds and short-term government bonds.
C) return on long-term corporate bonds and long-term government bonds.
D) return on short-term corporate bonds and short-term government bonds.
A) return on long-term corporate bonds and short-term corporate bonds.
B) return on long-term government bonds and short-term government bonds.
C) return on long-term corporate bonds and long-term government bonds.
D) return on short-term corporate bonds and short-term government bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements regarding risk is false?
A) Nonsystematic risk is also known as specific risk or issuer risk
B) Systematic risk is attributable to broad macro factors affecting all securities
C) Nonsystematic risk refers to the amount of interest rate risk that will affect the market.
D) Systematic risk is also referred to as market risk or general risk.
A) Nonsystematic risk is also known as specific risk or issuer risk
B) Systematic risk is attributable to broad macro factors affecting all securities
C) Nonsystematic risk refers to the amount of interest rate risk that will affect the market.
D) Systematic risk is also referred to as market risk or general risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements regarding returns from 1938 to 2007 is true?
A) Most investments underperformed inflation over that time period.
B) Treasury bills outperformed the CPI by less than 1%.
C) Bonds outperformed stocks during this period.
D) Canadian common stocks returns were greater than the standard deviation.
A) Most investments underperformed inflation over that time period.
B) Treasury bills outperformed the CPI by less than 1%.
C) Bonds outperformed stocks during this period.
D) Canadian common stocks returns were greater than the standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The cumulative wealth index is composed of the:
A) yield component and the price change component.
B) price change component and the inflation rate.
C) yield component and the risk-free rate.
D) total return and return relative.
A) yield component and the price change component.
B) price change component and the inflation rate.
C) yield component and the risk-free rate.
D) total return and return relative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
New regulations on open pit mining that affects the base metals industry is a type of:
A) market risk.
B) financial risk.
C) business risk.
D) liquidity risk.
A) market risk.
B) financial risk.
C) business risk.
D) liquidity risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Return and risk are directly related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Yield measures relate periodic cash flows to the price paid for a security.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The greater variability of return, the greater the risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
It would be expected that most security prices would increase if interest rates declined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
New regulations concerning open pit mining would be a type of market risk for the mining industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Consumer Price Index is typically used as the measure of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
For a normal distribution, the probability that a particular outcome will be above or below a specified value is determined without knowing the standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The best estimate of the average return for stock in any one year would be the average geometric mean annual return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Present value is based on the technique of compounding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Non-systematic risk directly encompasses interest rate risk, financial risk, and inflation risk for the market as a whole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What are two other names for systematic risk? For non-systematic risk?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Assume you are a Canadian citizen who purchases long-term fixed coupon bonds of the Deep Shaft Mining Company in South Africa. What sources of risk can you identify with this investment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Jack invests primarily in Canada Treasury bills. Since T-bills are short-term, they must be replaced as they mature, resulting in significant turnover through the reinvestment in subsequent T-bill issues. Mack invests primarily in three growth-oriented stock mutual funds, adding to them monthly through constant dollar averaging by investing the same fixed amount each month through automatic debit to his bank account. Both have been following their investment strategies over the past 10 years. Would Jack or Mack be more interested in inflation adjusted returns on their investments? Which would be more interested in transaction costs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the best measure of risk for returns of a sole proprietorship? For a diversified portfolio of stocks?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Does the risk-free rate of return include an inflation premium? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Why do Canada Treasury bills have a standard deviation in Table 6-5 if they are considered to be risk-free?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Why are semi-logarithmic charts used to plot wealth indices?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How do small company stocks compare to large company stocks in terms of wealth accumulation over the past 70 years? In terms of annual percentage growth rates (geometric mean)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A stock is purchased for $25 on January 1 and sold on December 31 for $35. A $2.50 per share dividend is paid during the year.
(a) Calculate the TR.
(b) Calculate the RR.
(a) Calculate the TR.
(b) Calculate the RR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The S&P/TSX Composite Index showed the following TRs for a 6 year period: 11.1 per cent, -5.2 per cent, 20.3 per cent, 26.7 per cent, -12.4 per cent, and 2.2 per cent.
(a) Calculate the arithmetic mean return for the 6 year period.
(b) Calculate the geometric mean return for the 6 year period.
(a) Calculate the arithmetic mean return for the 6 year period.
(b) Calculate the geometric mean return for the 6 year period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Listed below are the end-of-year prices and annual dividends for XYZ Corp.
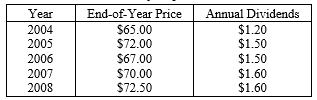
a. Calculate the total returns in dollars and decimal form and the corresponding return relatives for the period 2004 - 2008.
b. Calculate the arithmetic mean return over the holding period 2004 - 2008.
c. Calculate the geometric mean return over the holding period 2004 - 2008.
d. What is the dividend yield earned by an investor who purchases the stock at the end of 2004 and holds it until the end of 2005?
e. If someone asked you to calculate the risk level of this stock, what would you do? Do the calculation.
f. Compute the cumulative wealth index (Wn) that would result over the four-year holding period. (Assume W0 = $1).
g. If Joe Finance had invested $2000 dollars in XYZ Corp. at the end of 2004, by how many dollars would his wealth have increased at the end of 2008?

a. Calculate the total returns in dollars and decimal form and the corresponding return relatives for the period 2004 - 2008.
b. Calculate the arithmetic mean return over the holding period 2004 - 2008.
c. Calculate the geometric mean return over the holding period 2004 - 2008.
d. What is the dividend yield earned by an investor who purchases the stock at the end of 2004 and holds it until the end of 2005?
e. If someone asked you to calculate the risk level of this stock, what would you do? Do the calculation.
f. Compute the cumulative wealth index (Wn) that would result over the four-year holding period. (Assume W0 = $1).
g. If Joe Finance had invested $2000 dollars in XYZ Corp. at the end of 2004, by how many dollars would his wealth have increased at the end of 2008?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
John Crossborder buys 1 share of Telmex at 140 pesos when the value of the peso is stated in dollars at $0.35. One year later, Telmex is selling for 155 pesos and paid a dividend of 5 pesos during the year. If, after 1 year, the value of the pesos is $0.29, what will John's rate of return be in Canadian dollars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The cumulative wealth index for small size stocks was $23,000 for 2008 and $22,400 for 2007. What was the total annual rate of return for small size stocks for 1994?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



