Deck 13: Economic Growth
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/118
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Economic Growth
1
With flexible wages and prices:
A) as price increases, output increases.
B) as demand increases, supply increases.
C) aggregate supply equals potential output, whatever the inflation rate.
D) aggregate supply curve becomes a horizontal line.
A) as price increases, output increases.
B) as demand increases, supply increases.
C) aggregate supply equals potential output, whatever the inflation rate.
D) aggregate supply curve becomes a horizontal line.
aggregate supply equals potential output, whatever the inflation rate.
2
The long-run aggregate supply curve:
A) is vertical and shows that long-run output is not determined by the price level or inflation.
B) is horizontal and shows that long-run output is sensitive to changes in the price level and inflation.
C) shows how aggregate output changes when the price level or inflation rate changes.
D) slopes up and to the right.
A) is vertical and shows that long-run output is not determined by the price level or inflation.
B) is horizontal and shows that long-run output is sensitive to changes in the price level and inflation.
C) shows how aggregate output changes when the price level or inflation rate changes.
D) slopes up and to the right.
is vertical and shows that long-run output is not determined by the price level or inflation.
3
An increase in the capital stock that increases the amount of capital per worker:
A) shifts potential output and the aggregate supply curve to the left.
B) makes labour more productive, so there is an increase in potential output and long-run supply.
C) raises the inflation rate, given aggregate demand.
D) all the above.
A) shifts potential output and the aggregate supply curve to the left.
B) makes labour more productive, so there is an increase in potential output and long-run supply.
C) raises the inflation rate, given aggregate demand.
D) all the above.
makes labour more productive, so there is an increase in potential output and long-run supply.
4
Potential output is determined by all the following variables except one, which is:
A) technology.
B) capital.
C) aggregate demand.
D) labour.
A) technology.
B) capital.
C) aggregate demand.
D) labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
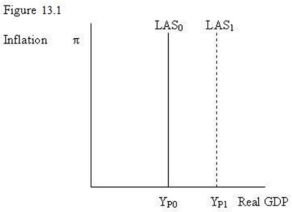
-Refer to Figure 13.1. For a given stock of capital, supply of labour and state of technology, the long run supply curve is:
A) vertical at the level of potential output YP0.
B) upward-sloping because potential output depends upon the inflation rate.
C) shifts leftward if potential output increases.
D) actual output and is less than potential output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

-Refer to Figure 13.1. The shift in the LAS curve from LAS0 to LAS1 could be caused by:
A) an increase in imports from other countries.
B) a rise in AD that causes a rise in the inflation rate.
C) an increase in the stock of capital, or the supply of labour, or an improvement in technology.
D) increased government expenditure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In terms of the production function Y = A0 x F(L,K0) where A is the state of technology, L the level of
Employment and K the stock of capital:
A) improved technology would shift the potential output and the LAS curve to the left.
B) growth in the labour force that increased the full employment level of employment would increase potential output and shift LAS to the right.
C) increased government expenditure would increase potential output.
D) a decline in the stock of capital K0 would increase the level of employment and potential output.
Employment and K the stock of capital:
A) improved technology would shift the potential output and the LAS curve to the left.
B) growth in the labour force that increased the full employment level of employment would increase potential output and shift LAS to the right.
C) increased government expenditure would increase potential output.
D) a decline in the stock of capital K0 would increase the level of employment and potential output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In terms of the production function Y = A0 x F(L,K0) where A is the state of technology, L the level of employment and K the stock of capital:
A) short-run AS comes from changes in the level of employment L.
B) potential output YP is the level of output when employment is 'full employment' LF.
C) changes in the stock of capital or the state of technology change the level of potential output.
D) all of the above.
A) short-run AS comes from changes in the level of employment L.
B) potential output YP is the level of output when employment is 'full employment' LF.
C) changes in the stock of capital or the state of technology change the level of potential output.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The level of potential output is treated as a long-run aggregate supply:
A) because the long run is the time required for adjustment in wages and prices to their equilibrium values.
B) because it appears only once every 100 years.
C) because it reflects money illusion on the part of either households, business or government.
D) because the economy cannot operate at potential output in the short run.
A) because the long run is the time required for adjustment in wages and prices to their equilibrium values.
B) because it appears only once every 100 years.
C) because it reflects money illusion on the part of either households, business or government.
D) because the economy cannot operate at potential output in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A vertical line showing the economy's potential output is called the:
A) aggregate demand (AD) curve.
B) long-run aggregate supply curve (LAS).
C) Phillips curve.
D) the short-run aggregate supply curve (AS).
A) aggregate demand (AD) curve.
B) long-run aggregate supply curve (LAS).
C) Phillips curve.
D) the short-run aggregate supply curve (AS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The real interest rate is equal to nominal interest rate minus inflation rate.
B) If nominal interest rate increases by 2%, while inflation rate is 3%, then real interest rate decreases by 1%.
C) If nominal interest rate decreases by 2%, while deflation rate is 3%, then real interest rate decreases by 1%.
D) The nominal interest rate is equal to real interest rate plus inflation rate.
A) The real interest rate is equal to nominal interest rate minus inflation rate.
B) If nominal interest rate increases by 2%, while inflation rate is 3%, then real interest rate decreases by 1%.
C) If nominal interest rate decreases by 2%, while deflation rate is 3%, then real interest rate decreases by 1%.
D) The nominal interest rate is equal to real interest rate plus inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Assume that AE = 200 + 0.5Y - 10r. Further assume that the central bank sets the interest rate as r = ro +
1)5(? -1), where ro is the interest rate where Y = YP. If ro is 2.0, AE function will be:
A) AE = 200 + 0.5Y - 0.5?.
B) AE = 200 + 0.5Y - 5?.
C) AE = 195 + 0.5Y + 5?.
D) AE = 195 + 0.5Y - 5?.
1)5(? -1), where ro is the interest rate where Y = YP. If ro is 2.0, AE function will be:
A) AE = 200 + 0.5Y - 0.5?.
B) AE = 200 + 0.5Y - 5?.
C) AE = 195 + 0.5Y + 5?.
D) AE = 195 + 0.5Y - 5?.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the following equations: AE = 200 + 0.5Y - 10r
R = 2 + 1.5(? -1) [Target ?* is one] AE=Y
Y = 390 - 30?
On the basis of the above, select the false statement from the following statements.
A) If ? = 1, r = 2.
B) If ? = 1, Y = 360.
C) If ? is greater than target ?*, the central bank will raise r. As a result, Y will decline.
D) If ? is greater than target ?*, the central bank will raise r. As a result, Y will remain unchanged.
R = 2 + 1.5(? -1) [Target ?* is one] AE=Y
Y = 390 - 30?
On the basis of the above, select the false statement from the following statements.
A) If ? = 1, r = 2.
B) If ? = 1, Y = 360.
C) If ? is greater than target ?*, the central bank will raise r. As a result, Y will decline.
D) If ? is greater than target ?*, the central bank will raise r. As a result, Y will remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following will not shift the AD curve?
A) Changes of target interest rate (ro) by the central bank.
B) Changes in the inflation rate (?).
C) Changes in autonomous expenditures.
D) Changes in the government expenditure.
A) Changes of target interest rate (ro) by the central bank.
B) Changes in the inflation rate (?).
C) Changes in autonomous expenditures.
D) Changes in the government expenditure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
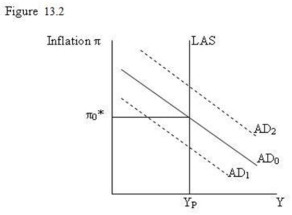
-Refer to Figure 13.2. In the diagram, the intersection of the AD0 curve and the LAS curve determines:
A) the short-run equilibrium level of output.
B) the long-run equilibrium level of employment.
C) the equilibrium interest rate.
D) the equilibrium inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16

-Refer to Figure 13.2. The AD curve can be shifted from AD0 to AD1 by the central bank by:
A) increasing government spending.
B) raising interest rates.
C) increasing transfer payments.
D) reducing taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

-Refer to Figure 13.2. If an increase in exports shifted the AD curve from AD0 to AD2 the equilibrium inflation rate would increase:
A) regardless of the reaction of the central bank.
B) only if government expenditure increased as much as exports.
C) only if the central bank raised its inflation target and adjusted monetary policy.
D) regardless of the fiscal policy implemented by government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
At long-run equilibrium, inflation _______ and actual output equals ______.
A) equals the value determined by past expectations and pricing decisions; potential
B) equals the value determined by past expectations and pricing decisions; the level of short-run equilibrium output consistent with that inflation rate
C) equals the value consistent with potential output; the level of output consistent with zero inflation
D) is stable; potential output
A) equals the value determined by past expectations and pricing decisions; potential
B) equals the value determined by past expectations and pricing decisions; the level of short-run equilibrium output consistent with that inflation rate
C) equals the value consistent with potential output; the level of output consistent with zero inflation
D) is stable; potential output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
To achieve an inflation target, the central bank forecasts AD then sets a ________________________ to achieve the required __________________.
A) nominal interest rate, real interest rate
B) nominal interest rate, nominal interest rate
C) real interest rate, real interest rate
D) real interest rate, nominal interest rate
A) nominal interest rate, real interest rate
B) nominal interest rate, nominal interest rate
C) real interest rate, real interest rate
D) real interest rate, nominal interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
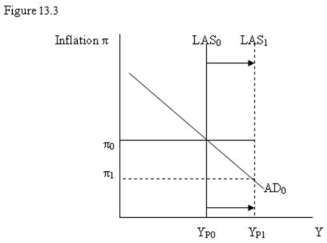
-Refer to Figure 13.3. The diagram shows that a benefit of an increase in potential output is to permit higher output without experiencing:
A) higher unemployment.
B) higher wages.
C) lower output.
D) higher inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21

-Refer to Figure 13.3 The diagram shows that if &61552;0 is the central bank's inflation target an increase in potential output calls for:
A) monetary stimulus through lower interest rates and higher money supply growth.
B) higher wage rates to cover the increased cost of living.
C) monetary restraint through higher interest rates and lower money supply growth.
D) higher imports to provide the increase in long run supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A rise in __________ must lead to a larger rise in the ________________, for only then will the real interest rate be higher and support a return to the equilibrium inflation rate.
A) money supply, velocity of circulation
B) growth, technical progress
C) inflation, nominal interest rate
D) output, productivity
A) money supply, velocity of circulation
B) growth, technical progress
C) inflation, nominal interest rate
D) output, productivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
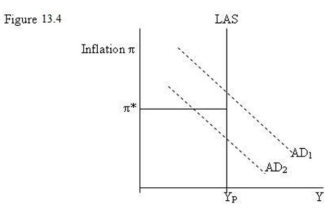
-Refer to Figure 13.4. If the central bank's target inflation rate is &61552;*, AD2 is too weak. The central bank adjusts monetary policy by __________ interest rates and ____ the AD function to the ____.
A) raising, shifting, right
B) lowering, shifting, left
C) fixing, leaving, unchanged
D) lowering, shifting, right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24

-Refer to Figure 13.4. If AD1 makes the inflation rate exceed the inflation target &61552;*, a tighter monetary policy ____ the interest rate and ________ the AD schedule ____.
A) raises, moves along, to the right
B) raises, shifts, to the left
C) lowers, moves along, to the left
D) lowers, shifts, to the right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When the economy is in long-run equilibrium at potential output even though unemployment is not zero, further demand expansion is ________________.
A) pointless
B) beneficial
C) a potential solution
D) necessary
A) pointless
B) beneficial
C) a potential solution
D) necessary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When the economy is in long-run equilibrium at potential output but with unemployment, there is no spare _________ and all remaining unemployment is __________.
A) capacity, involuntary
B) capacity, voluntary
C) capital, involuntary
D) materials, involuntary
A) capacity, involuntary
B) capacity, voluntary
C) capital, involuntary
D) materials, involuntary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider a graph with inflation rate in the vertical axis and real GDP in the horizontal axis and determine the false statement from the following statements.
A) The long-run aggregate supply (LASo) curve is a vertical line.
B) The AD curve and inflation rate is negatively related.
C) The AD curve intersects the long-run aggregate supply where inflation rate is the target inflation rate (r*).
D) Higher inflation target rate will cause a leftward shift of the AD curve.
A) The long-run aggregate supply (LASo) curve is a vertical line.
B) The AD curve and inflation rate is negatively related.
C) The AD curve intersects the long-run aggregate supply where inflation rate is the target inflation rate (r*).
D) Higher inflation target rate will cause a leftward shift of the AD curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider a given AD curve with a given inflation target in a graph with inflation rate in the vertical axis and real GDP in the horizontal axis. Currently, the economy is at YP, where the AD curve intersects the long-run aggregate supply curve at the target inflation- rate. If the economy faces an adverse demand shock, the AD curve shift to the _______; and as a result, the central bank will ________ the target interest rate to offset the adverse demand shocks.
A) left; increase
B) right; increase
C) right; decrease
D) left; decrease
A) left; increase
B) right; increase
C) right; decrease
D) left; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Slow wage rate adjustments:
A) increase the time it takes for the economy to adjust to output gaps.
B) raise costs in both the long run and the short run.
C) reduce costs in both the long run and the short run.
D) reduce the need for the economy to adjust to output gaps.
A) increase the time it takes for the economy to adjust to output gaps.
B) raise costs in both the long run and the short run.
C) reduce costs in both the long run and the short run.
D) reduce the need for the economy to adjust to output gaps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Wage rates do not respond quickly because:
A) workers and firms cannot agree on new wage rate increases.
B) wage rates are set by daily auctions for labour services.
C) different workers and firms have wage rate agreements that overlap in time.
D) wage bargaining is not pleasant.
A) workers and firms cannot agree on new wage rate increases.
B) wage rates are set by daily auctions for labour services.
C) different workers and firms have wage rate agreements that overlap in time.
D) wage bargaining is not pleasant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When aggregate demand falls and output falls:
A) employers reduce the wage rates they pay their employees.
B) employers reduce their labour inputs by reducing hours of work and numbers of employees.
C) employers increase the overtime work available to their employees.
D) labour contracts prevent changes in either wage rates or employment.
A) employers reduce the wage rates they pay their employees.
B) employers reduce their labour inputs by reducing hours of work and numbers of employees.
C) employers increase the overtime work available to their employees.
D) labour contracts prevent changes in either wage rates or employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Recessionary gaps result in:
A) higher wage rate increases for all employees.
B) lower levels of employment across the economy.
C) lower prices and inflation with no changes in wages or employment.
D) higher wage rate increase but lower levels of employment.
A) higher wage rate increases for all employees.
B) lower levels of employment across the economy.
C) lower prices and inflation with no changes in wages or employment.
D) higher wage rate increase but lower levels of employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Inflationary gaps result in:
A) higher wage rate increase for all employees.
B) higher inflation and wage rate increases and higher unemployment.
C) lower unemployment rates across the economy.
D) lower wage rate increases and lower levels of employment.
A) higher wage rate increase for all employees.
B) higher inflation and wage rate increases and higher unemployment.
C) lower unemployment rates across the economy.
D) lower wage rate increases and lower levels of employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Differences in countries' adjustments to output gaps reflect differences in:
A) the collective bargaining techniques pursued in each country.
B) the general attitude among countries toward inflation and unemployment.
C) central banks' approaches to monetary policy.
D) all of the above.
A) the collective bargaining techniques pursued in each country.
B) the general attitude among countries toward inflation and unemployment.
C) central banks' approaches to monetary policy.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A reduction in output and the demand for labour will eventually cause unemployment to __________ and the growth of wage rates to __________.
A) decrease, increase
B) decrease, decrease
C) increase, decrease
D) increase, increase
A) decrease, increase
B) decrease, decrease
C) increase, decrease
D) increase, increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The persistence of inflation in times of output gaps is the result of the behaviour of ____ and the existence of ______.
A) the central bank; the Bank of Canada's reaction function
B) real and nominal interest rates; an output gap
C) autonomous aggregate demand; the Bank of Canada's policy reaction function
D) inflation expectations; long-term wage and price contracts
A) the central bank; the Bank of Canada's reaction function
B) real and nominal interest rates; an output gap
C) autonomous aggregate demand; the Bank of Canada's policy reaction function
D) inflation expectations; long-term wage and price contracts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Firms are reluctant to make frequent changes in wage rates because fair and stable wage rates seem to:
A) minimize short-run costs.
B) maximize short-run profits.
C) increase worker productivity.
D) increase worker rivalry.
A) minimize short-run costs.
B) maximize short-run profits.
C) increase worker productivity.
D) increase worker rivalry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Real-world firms often meet workers' demands for higher wages because:
A) the majority of workers belong to a labour union.
B) the labour market is highly competitive.
C) the government requires them to do so.
D) it helps maintain morale and prevents turnover of key workers.
A) the majority of workers belong to a labour union.
B) the labour market is highly competitive.
C) the government requires them to do so.
D) it helps maintain morale and prevents turnover of key workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The Phillips curve shows that the rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment are:
A) negatively related.
B) linearly related.
C) positively related.
D) independent of each other.
A) negatively related.
B) linearly related.
C) positively related.
D) independent of each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose that businesses and labour anticipate the inflation rate will increase and act to protect their interests. This will cause:
A) the Phillips curve to shift toward higher rates of inflation at each unemployment rate.
B) the Phillips curve to shift toward lower rates of inflation at each unemployment rate.
C) no change in the unemployment rate but a higher price level.
D) no change in the actual price level but a higher level of unemployment.
A) the Phillips curve to shift toward higher rates of inflation at each unemployment rate.
B) the Phillips curve to shift toward lower rates of inflation at each unemployment rate.
C) no change in the unemployment rate but a higher price level.
D) no change in the actual price level but a higher level of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The Phillips curve suggests that:
A) a trade-off exists between the rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment.
B) as the economy approaches full employment, the more rapid the rise in the price level.
C) when there are significant amounts of unemployed resources in the economy, there is little pressure for higher rates of wage increases.
D) all of the above.
A) a trade-off exists between the rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment.
B) as the economy approaches full employment, the more rapid the rise in the price level.
C) when there are significant amounts of unemployed resources in the economy, there is little pressure for higher rates of wage increases.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The long-run Phillips curve will be vertical because:
A) the economy will eventually return to the natural rate of unemployment.
B) unemployment varies with inflation.
C) people care more about the size of their wage packets than what it will buy.
D) unemployment is not affected by the inflation rate.
A) the economy will eventually return to the natural rate of unemployment.
B) unemployment varies with inflation.
C) people care more about the size of their wage packets than what it will buy.
D) unemployment is not affected by the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which one of the following is not illustrated by the Phillips curve?
A) Given any particular rate of unemployment, there will be some particular level of inflation.
B) If the unemployment rate is above its natural rate, then we would expect a rapid increase in wages and
Prices.
C) If the rate of unemployment is below the natural rate of unemployment, then we would expect wages and prices to increase rapidly.
D) If the unemployment rate is equal to the natural rate, then there will be little, if any, pressure on inflation to rise or fall.
A) Given any particular rate of unemployment, there will be some particular level of inflation.
B) If the unemployment rate is above its natural rate, then we would expect a rapid increase in wages and
Prices.
C) If the rate of unemployment is below the natural rate of unemployment, then we would expect wages and prices to increase rapidly.
D) If the unemployment rate is equal to the natural rate, then there will be little, if any, pressure on inflation to rise or fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The Phillips curve shows the relationship between the rate of increase in wage rates and the:
A) level of government spending.
B) level of consumer spending.
C) demand for real balances.
D) unemployment rate.
A) level of government spending.
B) level of consumer spending.
C) demand for real balances.
D) unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In its simplest form, the Phillips curve shows the relationship between:
A) the rate of inflation and the level of government spending.
B) the level of unemployment and the price level.
C) the rate of wage rate increase and the output gap.
D) the rate of inflation and the growth in the demand for real balances.
A) the rate of inflation and the level of government spending.
B) the level of unemployment and the price level.
C) the rate of wage rate increase and the output gap.
D) the rate of inflation and the growth in the demand for real balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The Phillips curve is important to macroeconomic analysis because:
A) it explains a key part of the economy's adjustment to short-run output gaps.
B) it provides a basis for government wage rate policy.
C) it makes the link between monetary policy and inflation.
D) it explains the impact of fiscal policy on output.
A) it explains a key part of the economy's adjustment to short-run output gaps.
B) it provides a basis for government wage rate policy.
C) it makes the link between monetary policy and inflation.
D) it explains the impact of fiscal policy on output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which one of the following statements is not a true statement?
A) A demand shock like the recession of 2009 created a recessionary gap.
B) A demand shock like the recession of 2009 led to the leftward of the demand curve for labour.
C) A demand shock like the recession of 2009 led to speedy downward adjustment of equilibrium wage rate.
D) A demand shock like the recession of 2009 led to recessionary gap and cyclical unemployment.
A) A demand shock like the recession of 2009 created a recessionary gap.
B) A demand shock like the recession of 2009 led to the leftward of the demand curve for labour.
C) A demand shock like the recession of 2009 led to speedy downward adjustment of equilibrium wage rate.
D) A demand shock like the recession of 2009 led to recessionary gap and cyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
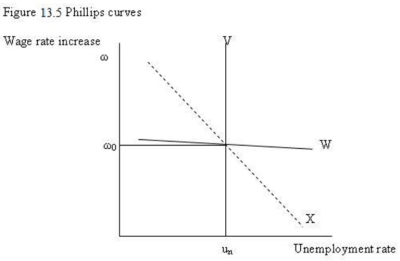
-Refer to figure 13.5. In terms of the illustration, if the rate of increase in wages was not much affected by output gaps and unemployment rates the Phillips curve would be:
A) X.
B) V.
C) W.
D) none of the curves shown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

-Refer to Figure 13.5. In the long run there is enough time to adjust the rates of increase in wages and prices and move the economy to equilibrium at potential output and the natural unemployment rate. The Phillips curve would be:
A) V.
B) W.
C) X.
D) W and X combined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50

-Refer to Figure 13.5. If the economy's institutions and wage bargaining practices change to make wage rate increases more sensitive to output gaps and unemployment rates, the Phillips curve:
A) would be vertical like V.
B) would be horizontal and therefore flatter than W.
C) would change its slope as illustrated by a movement from curve X to curve W.
D) would change its slope as illustrated by a movement from curve W to curve X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which one of the following statements is not a true statement with regard to Phillips curve with inflation-unemployment trade-off?
A) Each Phillips curve assumes a given expected inflation.
B) Flatter the short-run aggregate supply curve, flatter is the given Phillips curve.
C) A higher expected inflation will cause an upward shift of the Phillips curve.
D) In the long-run, the Phillips curve is a vertical line. because expected inflation is zero.
A) Each Phillips curve assumes a given expected inflation.
B) Flatter the short-run aggregate supply curve, flatter is the given Phillips curve.
C) A higher expected inflation will cause an upward shift of the Phillips curve.
D) In the long-run, the Phillips curve is a vertical line. because expected inflation is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The short-run AS curve is drawn on the assumption:
A) that AD is constant.
B) that wage rates and other input prices increase at constant rates.
C) that net indirect taxes fall as output increases.
D) that there is no foreign trade to provide a supply of imported goods and services.
A) that AD is constant.
B) that wage rates and other input prices increase at constant rates.
C) that net indirect taxes fall as output increases.
D) that there is no foreign trade to provide a supply of imported goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The short-run AS curve is upward-sloping because:
A) as output rises the rate of increase in wage rates falls and inflation falls.
B) rising output calls for an increase in capital stock to provide production capacity.
C) inflation rates higher than wage rate increases raise prices relative to costs and make higher output more profitable.
D) higher inflation rates draw in more imports.
A) as output rises the rate of increase in wage rates falls and inflation falls.
B) rising output calls for an increase in capital stock to provide production capacity.
C) inflation rates higher than wage rate increases raise prices relative to costs and make higher output more profitable.
D) higher inflation rates draw in more imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The aggregate supply (AS) curve will shift up if:
A) productivity increases.
B) wage rates are decreasing.
C) productivity is increasing faster than wages.
D) wage rates are increasing faster than productivity.
A) productivity increases.
B) wage rates are decreasing.
C) productivity is increasing faster than wages.
D) wage rates are increasing faster than productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When there is a recessionary gap, wage rate increases will ______, the rate of increase in costs and prices will ____ and the AS curve will _____.
A) decline; rise; shift up
B) increase; fall; shift up
C) decline; fall; shift down
D) increase; rise; shift down
A) decline; rise; shift up
B) increase; fall; shift up
C) decline; fall; shift down
D) increase; rise; shift down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When there is an inflationary gap:
A) upward pressure on the growth of wage rates shifts the AS curve up.
B) increased output levels raise aggregate demand.
C) downward pressure on the growth of wage rates shift the AS curve down.
D) wage rates will raise more rapidly and productivity will rise.
A) upward pressure on the growth of wage rates shifts the AS curve up.
B) increased output levels raise aggregate demand.
C) downward pressure on the growth of wage rates shift the AS curve down.
D) wage rates will raise more rapidly and productivity will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a short-run equilibrium with a recessionary gap persists:
A) low unemployment rates will raise wage rate increases and employment.
B) high unemployment rates will raise wage rate increases and AD.
C) high unemployment rates will reduce wage rate increases and shift AS down.
D) unemployment at the natural rate has no effect on wage rates or AS.
A) low unemployment rates will raise wage rate increases and employment.
B) high unemployment rates will raise wage rate increases and AD.
C) high unemployment rates will reduce wage rate increases and shift AS down.
D) unemployment at the natural rate has no effect on wage rates or AS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
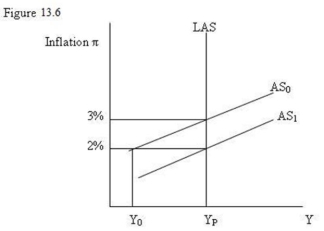
-Refer to Figure 13.6. If wage rates had been increasing at 3% a year and a recessionary gap lowered that rate of wage growth to 2% a year:
A) AS would be unaffected and remain at AS0.
B) the level of real GDP would fall from YP to Y0.
C) AS would shift up from AS1 to AS0.
D) AS would shift down from AS0 to AS1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59

-Refer to Figure 13.6. If a rise in the expected rate of inflation from 2% to 3% led to wage rates increasing at 3% a year:
A) AS would shift down from AS0 to AS1.
B) real GDP would rise from Y0 to YP.
C) AS would shift up from AS1 to AS0.
D) the change in wage rate increases would shift LAS from YP to Y0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Like Phillips curve, the long-run aggregate supply curve is a vertical line.
B) A given short-run aggregate supply curve is up-sloping, because the movement up the given supply curve shows higher prices and higher wages by the same magnitude.
C) If wage-increases are equal to price-increases, real GDP will remain unchanged.
D) If actual inflation exceeds the expected inflation and if wage-increases are less than price-increases, we will observe increases in real output in the short-run
A) Like Phillips curve, the long-run aggregate supply curve is a vertical line.
B) A given short-run aggregate supply curve is up-sloping, because the movement up the given supply curve shows higher prices and higher wages by the same magnitude.
C) If wage-increases are equal to price-increases, real GDP will remain unchanged.
D) If actual inflation exceeds the expected inflation and if wage-increases are less than price-increases, we will observe increases in real output in the short-run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If an output gap exists in the short-run, then over time:
A) AS line will move upward or downward until actual output equals potential output.
B) AD line will move left or right until actual output equals potential output.
C) LAS line will move left or right until actual output equals potential output.
D) LAS line will move upward or downward until actual output equals potential output.
A) AS line will move upward or downward until actual output equals potential output.
B) AD line will move left or right until actual output equals potential output.
C) LAS line will move left or right until actual output equals potential output.
D) LAS line will move upward or downward until actual output equals potential output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The long-run adjustments that eliminate recessionary and inflationary output gaps in the economy assume that:
A) the growth in wages and production costs adjusts over time.
B) the inflation rate adjusts over time.
C) actual output (Y) adjusts along the AD function towards potential output (YP) over time.
D) all of the above.
A) the growth in wages and production costs adjusts over time.
B) the inflation rate adjusts over time.
C) actual output (Y) adjusts along the AD function towards potential output (YP) over time.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The built-in long-run adjustment process that eliminates a recessionary gap (Y < YP) in the economy requires that:
A) growth in wages and production costs slow down over time.
B) the inflation rate declines over time.
C) aggregate demand and output Y increase along the AD function over time.
D) all of the above.
A) growth in wages and production costs slow down over time.
B) the inflation rate declines over time.
C) aggregate demand and output Y increase along the AD function over time.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When an AD shock raises equilibrium output and actual output exceeds potential output, there is ____
Output gap and the rate of wage increase and price inflation will tend to ____.
A) an inflationary; increase
B) an inflationary; decrease
C) no; remain the same
D) a recessionary; increase
Output gap and the rate of wage increase and price inflation will tend to ____.
A) an inflationary; increase
B) an inflationary; decrease
C) no; remain the same
D) a recessionary; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The long-run self-correcting mechanism that eliminates an inflationary gap (Y > YP) in the economy assumes that:
A) growth in wages and production costs speeds up over time.
B) the inflation rate increases over time.
C) aggregate demand and actual output Y increase towards potential output Y* over time.
D) all of the above.
A) growth in wages and production costs speeds up over time.
B) the inflation rate increases over time.
C) aggregate demand and actual output Y increase towards potential output Y* over time.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose the economy is initially at full-employment equilibrium real GDP. If a sudden adverse demand shock causes recessionary gap, we can expect one of the following adjustments to occur:
A) Lower wage rates and rightward shifts of the short-run aggregate supply curve over time until the short-
run aggregate supply curve intersects the AD curve at potential GDP (YP).
B) Lower wage rates and rightward shifts of the AD curve over time until the AD curve intersects the
short-run aggregate supply curve at potential GDP (YP).
C) Higher wage rates and rightward shifts of the short-run aggregate supply curve over time until the short-
run aggregate supply curve intersects the AD curve at potential GDP (YP).
D) Higher wage rates and rightward shifts of the AD curve over time until the AD curve intersects the
short-run aggregate supply curve at potential GDP (YP)
A) Lower wage rates and rightward shifts of the short-run aggregate supply curve over time until the short-
run aggregate supply curve intersects the AD curve at potential GDP (YP).
B) Lower wage rates and rightward shifts of the AD curve over time until the AD curve intersects the
short-run aggregate supply curve at potential GDP (YP).
C) Higher wage rates and rightward shifts of the short-run aggregate supply curve over time until the short-
run aggregate supply curve intersects the AD curve at potential GDP (YP).
D) Higher wage rates and rightward shifts of the AD curve over time until the AD curve intersects the
short-run aggregate supply curve at potential GDP (YP)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
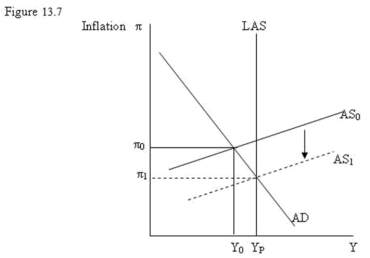
-Refer to Figure 13.7. Reliance on the economy's internal adjustment process for the elimination of the output gap shown in the diagram can take a long time because:
A) wage rate growth may be slow to adjust downward.
B) growth in production costs may be slow to adjust downward.
C) inflation and inflation expectations may be slow to adjust downward.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68

-Refer to Figure 13.7. If wage rate increases and price increases were very flexible the deviation of output from potential output would _____________________ to restore output to _________ output.
A) quickly shift rates of wage and price increases, potential
B) adjust interest rates, equilibrium
C) call for government expenditure, full employment
D) call for exports, potential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When an AD shock reduces actual output to less than potential output, there is ____ output gap and the rate of inflation will tend to ____.
A) an inflationary; increase
B) an inflationary; decrease
C) no; remain the same
D) a recessionary; decrease
A) an inflationary; increase
B) an inflationary; decrease
C) no; remain the same
D) a recessionary; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When a recessionary gap exists, actual output _____ potential output, unemployment is __________ the natural rate, wage rate growth _________ and the AS curve shifts ______ to ___________ the gap.
A) exceeds; higher than; increases; up; increase
B) exceeds; lower than; increases; up; decrease
C) is less than; higher than; falls; down; decrease
D) is less than; lower than; falls; up; eliminate
A) exceeds; higher than; increases; up; increase
B) exceeds; lower than; increases; up; decrease
C) is less than; higher than; falls; down; decrease
D) is less than; lower than; falls; up; eliminate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When an inflationary gap exists, actual output _____ potential output and the rate of wage and price inflation will tend to ______.
A) exceeds; increase
B) exceeds; decrease
C) equals; remain the same
D) is less than; increase
A) exceeds; increase
B) exceeds; decrease
C) equals; remain the same
D) is less than; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Recessionary gaps are eventually eliminated by:
A) rising wage and price inflation.
B) falling wage and price inflation and falling real interest rates.
C) increasing potential output.
D) decreasing potential output.
A) rising wage and price inflation.
B) falling wage and price inflation and falling real interest rates.
C) increasing potential output.
D) decreasing potential output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Inflationary gaps are eventually eliminated by:
A) falling wage and falling prices.
B) rising wage and price inflation and rising real interest rates.
C) increasing potential output.
D) decreasing potential output.
A) falling wage and falling prices.
B) rising wage and price inflation and rising real interest rates.
C) increasing potential output.
D) decreasing potential output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
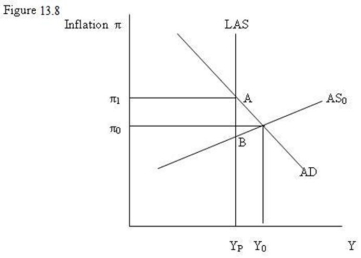
-Refer to Figure 13.8. If the AD conditions illustrated persist:
A) high unemployment rates will reduce rates of wage growth and shift AS up to A.
B) high unemployment rates will reduce rates of wage growth and shift AS down to B.
C) low unemployment rates will raise rates of wage growth and shift AD to B.
D) low unemployment rates will raise rates of wage growth and shift AS up to A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75

-Refer to Figure 13.8. If the AD conditions illustrated persist, the economy's adjustment process will:
A) push up the rate of wage increase and raise the AS curve to intersect AD at YP.
B) lower the rate of wage increase and lower the AD curve to intersect As at YP.
C) increase both wage and price inflation shifting both AS and AD up to a new equilibrium.
D) fail to eliminate the output gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Suppose that the economy experiences a series of adverse aggregate supply shocks, and the central bank does not change its interest rate setting to accommodate them. The result will be:
A) increasing unemployment.
B) actual output greater than potential output.
C) a decrease in the inflation rate.
D) the economy operating at full employment.
A) increasing unemployment.
B) actual output greater than potential output.
C) a decrease in the inflation rate.
D) the economy operating at full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If continuous increases in oil prices permanently reduce aggregate supply, AS shifts _____________ and the economy faces ____________________.
A) down; lower unemployment and inflation
B) up; higher unemployment and inflation
C) down; lower unemployment and higher inflation
D) up; lower unemployment and lower inflation
A) down; lower unemployment and inflation
B) up; higher unemployment and inflation
C) down; lower unemployment and higher inflation
D) up; lower unemployment and lower inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A permanent supply shock _______ potential output. A temporary supply shock shifts the short-run aggregate supply schedule, and _____________ potential output.
A) changes, does not change
B) changes, changes
C) does not change, does not change
D) does not change, changes
A) changes, does not change
B) changes, changes
C) does not change, does not change
D) does not change, changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
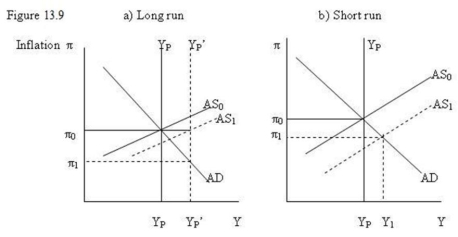
-Refer to Figure 13.9. In panel a) of the diagram growth in the labour force shifts YP to YP'. This is called a ________________ and the new short run equilibrium is determined by ________.
A) temporary supply shock; AD and YP'
B) permanent supply shock; AD and AS1
C) permanent demand shock; AD and AS0
D) temporary demand shock; AD and YP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80

-Refer to Figure 13.9. In panel a) of the diagram, based on the economy's built-in adjustment process, over time:
A) wage rate growth and inflation will accelerate and shift AS1 up to AS0.
B) wage rate growth and inflation will accelerate and shift AD to intersect AS1 at ?0.
C) wage rate growth and inflation will decline and shift AS1 down to intersect AD at ?1.
D) wage rate growth and inflation will not change but AD will shift to intersect AS1 at YP'.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



