Deck 9: Financial Markets, Interest Rates, Foreign Exchange Rates & AD
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/123
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Financial Markets, Interest Rates, Foreign Exchange Rates & AD
1
One's portfolio choice involves one of the following decisions, which is:
A) how to allocate one's income between consumption and savings.
B) how much more to consume when one's disposable income increases by one dollar.
C) how to allocate one's financial assets between money balances and interest-earning bonds.
D) how to find right agents to manage one's financial portfolio.
A) how to allocate one's income between consumption and savings.
B) how much more to consume when one's disposable income increases by one dollar.
C) how to allocate one's financial assets between money balances and interest-earning bonds.
D) how to find right agents to manage one's financial portfolio.
how to allocate one's financial assets between money balances and interest-earning bonds.
2
Suppose that you hold your money balances in cash (the most liquid assets) rather than holding some other less liquid assets (such as bonds). The opportunity cost of holding cash is:
A) zero.
B) the consumption that you give up by holding your money rather than spending it.
C) the foregone interest-income that you could have earned if you held your financial assets in bonds.
D) loss of purchasing power due to inflation.
A) zero.
B) the consumption that you give up by holding your money rather than spending it.
C) the foregone interest-income that you could have earned if you held your financial assets in bonds.
D) loss of purchasing power due to inflation.
the foregone interest-income that you could have earned if you held your financial assets in bonds.
3
Households and businesses often hold some of their wealth as non-interest earning money balances, because:
A) money balances always pay lower rates of return than the non-money assets.
B) money balances provide convenience and lower risk than many other assets.
C) the opportunity cost of holding money balances is lower than that of other assets.
D) money balances offer a better protection against rising prices than do many other assets.
A) money balances always pay lower rates of return than the non-money assets.
B) money balances provide convenience and lower risk than many other assets.
C) the opportunity cost of holding money balances is lower than that of other assets.
D) money balances offer a better protection against rising prices than do many other assets.
money balances provide convenience and lower risk than many other assets.
4
Other things constant, the opportunity cost of holding money balances falls when:
A) bond prices increase.
B) the interest rate rises.
C) national income increases.
D) bond prices decrease.
A) bond prices increase.
B) the interest rate rises.
C) national income increases.
D) bond prices decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
One of the costs of holding currency is that:
A) it is always cumbersome.
B) it earns no rate of return.
C) it requires constant attention.
D) its real value increases.
A) it is always cumbersome.
B) it earns no rate of return.
C) it requires constant attention.
D) its real value increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Diversification is the practice of spreading one's wealth over a variety of different financial investments in order to:
A) increase risk.
B) decrease risk.
C) increase returns.
D) decrease returns.
A) increase risk.
B) decrease risk.
C) increase returns.
D) decrease returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
"You shouldn't put all your eggs in one basket" illustrates the:
A) scarcity principle.
B) principle of comparative advantage.
C) benefits of diversification.
D) principle of increasing opportunity cost.
A) scarcity principle.
B) principle of comparative advantage.
C) benefits of diversification.
D) principle of increasing opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
One benefit of holding money rather than bonds is _______, while the opportunity cost of holding money is _______.
A) the nominal interest rate; the fees charged by banks
B) the nominal interest rate; its usefulness in carrying out transactions
C) increased income; lost purchasing power
D) reduced risk of capital loss; the nominal interest rate
A) the nominal interest rate; the fees charged by banks
B) the nominal interest rate; its usefulness in carrying out transactions
C) increased income; lost purchasing power
D) reduced risk of capital loss; the nominal interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The present value (PV) of a future sum of money is ____, if the interest rate is _____.
A) higher, higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) both B and C are correct
A) higher, higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) both B and C are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The yields of bonds increase as bond-prices increase.
B) The coupon rate is a fixed percentage of the principle value of the bond at the time of its issue.
C) The yields of bonds are equal to the market interest rate in equilibrium situations in the financial markets.
D) The coupon rates of bonds are equal to the market interest rate in equilibrium situations in the financial markets.
A) The yields of bonds increase as bond-prices increase.
B) The coupon rate is a fixed percentage of the principle value of the bond at the time of its issue.
C) The yields of bonds are equal to the market interest rate in equilibrium situations in the financial markets.
D) The coupon rates of bonds are equal to the market interest rate in equilibrium situations in the financial markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is false?
A) A bond coupon is the annual fixed money payment paid to a bond holder.
B) A bond is a financial contract that makes one or more fixed payments at specific dates in the future.
C) The present value of a bond increases as market interest rate increases.
D) The yields of bonds are inversely related to the prices of bonds.
A) A bond coupon is the annual fixed money payment paid to a bond holder.
B) A bond is a financial contract that makes one or more fixed payments at specific dates in the future.
C) The present value of a bond increases as market interest rate increases.
D) The yields of bonds are inversely related to the prices of bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If the annual interest rate is i = 0.02 (2 percent), the present value of the future sum of $100, expected to receive three years from today, is:
A) $99.94.
B) $98.04.
C) $96.12.
D) $94.23.
A) $99.94.
B) $98.04.
C) $96.12.
D) $94.23.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the annual interest rate is i = 0.02 (2 percent), the present value of the future sum of $100, expected to be paid in three years from today, is:
A) $99.94.
B) $98.04.
C) $96.12.
D) $94.23.
A) $99.94.
B) $98.04.
C) $96.12.
D) $94.23.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A bond's price and its yield:
A) have an inverse relationship.
B) have a positive relationship.
C) are positively related for low interest rates but negatively related for high interest rates.
D) are unrelated.
A) have an inverse relationship.
B) have a positive relationship.
C) are positively related for low interest rates but negatively related for high interest rates.
D) are unrelated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When the bond price rises, its yield:
A) declines.
B) increases.
C) first rises and then falls.
D) first falls and then rises.
A) declines.
B) increases.
C) first rises and then falls.
D) first falls and then rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A legal promise to repay a debt is called:
A) equity.
B) the principal amount.
C) a bond.
D) a dividend.
A) equity.
B) the principal amount.
C) a bond.
D) a dividend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Coupon payments are the:
A) amount originally lent divided by the number of years until a bond matures.
B) discounts bondholders receive when using coupons to make purchases.
C) regular interest payments made to bondholders.
D) additional interest payments made to bond holders to compensate for credit risk.
A) amount originally lent divided by the number of years until a bond matures.
B) discounts bondholders receive when using coupons to make purchases.
C) regular interest payments made to bondholders.
D) additional interest payments made to bond holders to compensate for credit risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the principal amount of a bond is $10,000,000, the coupon rate is 7%, the annual coupon payment made to the holders of the bond is:
A) $70,000.
B) $300,000.
C) $400,000.
D) $700,000.
A) $70,000.
B) $300,000.
C) $400,000.
D) $700,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the principal amount of a bond is $2,000,000, the coupon rate is 6%, the annual coupon payment made to the holder of the bond is:
A) $12,000.
B) $40,000.
C) $80,000.
D) $120,000.
A) $12,000.
B) $40,000.
C) $80,000.
D) $120,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consider a one-year bond with a principal value of $100 and a coupon value of $5. Which of the following statements is false?
A) If the interest rate is 5%, the present value of this bond is $105.
B) If the interest rate is 5%, the present value of this bond is $100.
C) If the interest rate is 6%, the present value of this bond is less than $100.
D) If the interest rate is 4%, the present value of this bond is more than $100.
A) If the interest rate is 5%, the present value of this bond is $105.
B) If the interest rate is 5%, the present value of this bond is $100.
C) If the interest rate is 6%, the present value of this bond is less than $100.
D) If the interest rate is 4%, the present value of this bond is more than $100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consider a one-year bond with a principal value of $100 and a coupon value of $5. Which of the following statements is false?
A) If the market interest rate is 5%, the bond is traded at par.
B) If the market interest rate is 4%, the bond is traded at a premium.
C) If the market interest rate is 6%, the bond is traded at a discount.
D) If the market interest rate is 6%, the bond is traded with capital gain.
A) If the market interest rate is 5%, the bond is traded at par.
B) If the market interest rate is 4%, the bond is traded at a premium.
C) If the market interest rate is 6%, the bond is traded at a discount.
D) If the market interest rate is 6%, the bond is traded with capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider a three-year bond with a principal amount of $5,000 and a 3% coupon rate paid annually. If this bond is sold one year from maturity, it will sell for _______(rounded to the nearest dollar) in the bond market, if current interest rates are 5%.
A) $4,762
B) $4,905
C) $5,000
D) $5,150
A) $4,762
B) $4,905
C) $5,000
D) $5,150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Consider a three-year bond with a principal amount of $5,000 and a 4% coupon rate paid annually. If this bond is sold one year from maturity, it will sell for _________ (rounded to the nearest dollar) in the bond market if current interest rates are 5%.
A) $4,762
B) $4,952
C) $5,000
D) $5,200
A) $4,762
B) $4,952
C) $5,000
D) $5,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consider a three-year bond with a principal amount of $5,000 and a 4% coupon rate paid annually. If this bond is sold today, it will sell for _________ (rounded to the nearest dollar) in the bond market if current interest rates are 5%.
A) $4,864
B) $4,952
C) $5,000
D) $5,200
A) $4,864
B) $4,952
C) $5,000
D) $5,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
One year before maturity, the price of a bond with a principal amount of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 5% paid annually was $981.31. Therefore, the market-interest rate in one year before maturity was:
A) 8.5%.
B) 7.0%.
C) 6.0%.
D) 5%.
A) 8.5%.
B) 7.0%.
C) 6.0%.
D) 5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
One year before maturity, the price of a bond with a principal amount of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 5% paid annually was $1,019.42. Therefore, the market interest rate in one year from maturity was:
A) 6.0%.
B) 5%.
C) 3%.
D) 2%.
A) 6.0%.
B) 5%.
C) 3%.
D) 2%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Antonio holds a two-year bond issued by Jetson Corp with a principal amount of $10,000. The annual coupon rate is 6 percent. After receiving the first coupon payment, Antonio sold this bond at a price of $10,000. Immediately after selling the bond, he observed that the market interest rate increased. Therefore, Antonio could conclude:
A) he suffered a capital loss.
B) the bond price remained unchanged at $10,000.
C) the bond price increased.
D) the bond price decreased.
A) he suffered a capital loss.
B) the bond price remained unchanged at $10,000.
C) the bond price increased.
D) the bond price decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The demand for money does not include:
A) investment demand.
B) transactions demand.
C) precautionary demand.
D) asset demand.
A) investment demand.
B) transactions demand.
C) precautionary demand.
D) asset demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The demand for money balances is part of:
A) the decision to spend or save current income.
B) the decision to divide financial asset between money balances and bonds.
C) the decision by business to invest in capital stock.
D) the decision by government to increase the net tax rate.
A) the decision to spend or save current income.
B) the decision to divide financial asset between money balances and bonds.
C) the decision by business to invest in capital stock.
D) the decision by government to increase the net tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Your portfolio diversified between money and bond-holdings:
A) reflects the desire to maximize interest-income earned by the portfolio.
B) reflects the desire to reduce the risk of the portfolio.
C) reflects a willingness to accept more risks in order to get higher returns on the portfolio.
D) none of the above.
A) reflects the desire to maximize interest-income earned by the portfolio.
B) reflects the desire to reduce the risk of the portfolio.
C) reflects a willingness to accept more risks in order to get higher returns on the portfolio.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If portfolio managers and private individuals expect market interest rates will rise in the near future, they will:
A) congratulate themselves on their wisdom in currently holding bonds in their portfolios.
B) move quickly and buy bonds to shift portfolios from money to bonds before interest rate rise.
C) move quickly and sell bonds to shift portfolios from bonds to money before interest rates rise.
D) do nothing because the coupon payments on bonds they will not change with a change in current market interest rates.
A) congratulate themselves on their wisdom in currently holding bonds in their portfolios.
B) move quickly and buy bonds to shift portfolios from money to bonds before interest rate rise.
C) move quickly and sell bonds to shift portfolios from bonds to money before interest rates rise.
D) do nothing because the coupon payments on bonds they will not change with a change in current market interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In times of relative tranquility in economic and political conditions:
A) the demand for money balances to hedge against economic uncertainty decreases.
B) higher incomes reduce the demand for money balances.
C) the demand for money balances to hedge against economic uncertainty increases.
D) falling prices increase the demand for money balances.
A) the demand for money balances to hedge against economic uncertainty decreases.
B) higher incomes reduce the demand for money balances.
C) the demand for money balances to hedge against economic uncertainty increases.
D) falling prices increase the demand for money balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose, the aggregate demand for money-holding is L = 0.25Y - 100i, where Y is the real GDP and i is the interest rate. In this equation:
A) the real money balance fraction for the purpose of transactions and precautionary reasons is 100.
B) the real money balance fraction for the purpose of transactions and precautionary reasons is 0.25.
C) the real money balance fraction for the purpose of transactions and precautionary reasons is 0.25(100).
D) the real money balance fraction for the purpose of transactions and precautionary reasons is 1/0.25.
A) the real money balance fraction for the purpose of transactions and precautionary reasons is 100.
B) the real money balance fraction for the purpose of transactions and precautionary reasons is 0.25.
C) the real money balance fraction for the purpose of transactions and precautionary reasons is 0.25(100).
D) the real money balance fraction for the purpose of transactions and precautionary reasons is 1/0.25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose, the aggregate demand for money-holding is L = 0.25Y - 100i, where Y is the real GDP and i is the interest rate. When we draw the above money demand function with interest rate in the vertical axis, we can see one of the following outcomes:
A) As Y increases, the money demand curve shifts to the left.
B) As real money-balance-fraction increases from 0.25 to 0.50, the money demand curve shifts to the right.
C) As interest rate increases, the money demand curve shifts to the right.
D) As interest rate increases, the money demand curve shifts to the left.
A) As Y increases, the money demand curve shifts to the left.
B) As real money-balance-fraction increases from 0.25 to 0.50, the money demand curve shifts to the right.
C) As interest rate increases, the money demand curve shifts to the right.
D) As interest rate increases, the money demand curve shifts to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The demand for real money balances rises when:
A) interest rate falls.
B) real income rises.
C) real cash balance fraction increases.
D) all of the above.
A) interest rate falls.
B) real income rises.
C) real cash balance fraction increases.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When the quantity of real money holdings falls this is often in response to interest rates:
A) rising.
B) falling.
C) not changing.
D) speculation.
A) rising.
B) falling.
C) not changing.
D) speculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The demand for money balances is negatively related to the interest rate because a decline in the interest rate:
A) encourages businesses to increase their level of investment spending.
B) means that the opportunity cost of holding an extra dollar as money balances as opposed to other assets decreases.
C) means that households spend more on all types of goods as the interest rate falls.
D) encourages households to hold other assets instead of money balances.
A) encourages businesses to increase their level of investment spending.
B) means that the opportunity cost of holding an extra dollar as money balances as opposed to other assets decreases.
C) means that households spend more on all types of goods as the interest rate falls.
D) encourages households to hold other assets instead of money balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose, the aggregate demand for money-holding is L = kY - hi, where Y is the real GDP, k is the real balance fraction, i is the interest rate and h is the extent by which interest rate affects money demand. We can conclude:
A) as the interest coefficient (h) increases, the money demand curve becomes steeper.
B) as the real cash balance fraction (k) increases, the money demand curve becomes steeper.
C) as Y increases, the money demand curve becomes steeper.
D) none of the above.
A) as the interest coefficient (h) increases, the money demand curve becomes steeper.
B) as the real cash balance fraction (k) increases, the money demand curve becomes steeper.
C) as Y increases, the money demand curve becomes steeper.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose, the aggregate demand for money-holding is L = kY - hi, where Y is the real GDP, k is the real balance fraction, i is the interest rate and h is the extent by which interest rate affects money demand. We can conclude:
A) when the interest-sensitivity of the money demand function increases, there will a parallel rightward shift of the money demand curve.
B) when the real cash balance fraction (k) increases, there will a parallel rightward shift of the money demand curve.
C) when both Y and i increases, there will a parallel rightward shift of the money demand curve.
D) none of the above.
A) when the interest-sensitivity of the money demand function increases, there will a parallel rightward shift of the money demand curve.
B) when the real cash balance fraction (k) increases, there will a parallel rightward shift of the money demand curve.
C) when both Y and i increases, there will a parallel rightward shift of the money demand curve.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The overall quantity of money balances demanded:
A) depends on the level of national income.
B) rises as the interest rate rises.
C) depends on the level of investment in the economy.
D) rises as the interest rate falls.
A) depends on the level of national income.
B) rises as the interest rate rises.
C) depends on the level of investment in the economy.
D) rises as the interest rate falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Variables that directly affect the demand for real balances include:
A) the level of income.
B) the supply of money.
C) the interest rate.
D) A and C, but not B
A) the level of income.
B) the supply of money.
C) the interest rate.
D) A and C, but not B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the aggregate economy, the interest rate represents:
A) the opportunity cost of holding money balances.
B) the rate of growth of the nominal money stock.
C) the price of non-money assets.
D) an index of the credit-worthiness of borrowers.
A) the opportunity cost of holding money balances.
B) the rate of growth of the nominal money stock.
C) the price of non-money assets.
D) an index of the credit-worthiness of borrowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which one of the following statements about the demand for money is not correct?
A) The amount of money that people hold is negatively related with the interest rate.
B) As the level of national income rises, the amount of money balances that individuals hold decreases.
C) Both the level of national income and the interest rate affect the demand for money balances.
D) Other things constant, an increase in the real interest rate reduces the demand for real money balances.
A) The amount of money that people hold is negatively related with the interest rate.
B) As the level of national income rises, the amount of money balances that individuals hold decreases.
C) Both the level of national income and the interest rate affect the demand for money balances.
D) Other things constant, an increase in the real interest rate reduces the demand for real money balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which one of the following would be unlikely to increase the typical household's demand for money balances that it uses to pay its bills?
A) Individual paydays change from once a month to once a week.
B) Individual paydays change from once a week to once a month.
C) The level of real national income rises.
D) The price level increases.
A) Individual paydays change from once a month to once a week.
B) Individual paydays change from once a week to once a month.
C) The level of real national income rises.
D) The price level increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose that prices fall by 50 per cent and nominal incomes fall by 50 per cent. We would expect:
A) households to attempt to double their real money holding.
B) households to reduce their real money holdings by 50 per cent.
C) the demand for real balances to remain unchanged.
D) none of the above.
A) households to attempt to double their real money holding.
B) households to reduce their real money holdings by 50 per cent.
C) the demand for real balances to remain unchanged.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following factors will increase the real cash balance fraction (k)?
A) The level of real income.
B) The price level.
C) Lower transaction costs of cash withdrawals.
D) Lower level of trust in the banking and financial institutions.
A) The level of real income.
B) The price level.
C) Lower transaction costs of cash withdrawals.
D) Lower level of trust in the banking and financial institutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A transactions demand for money exists, because:
A) households like to save more.
B) households are paid every two weeks, rather than once a month.
C) households receive their incomes and spend their incomes with perfect synchronization.
D) households' payments and receipts are not synchronized.
A) households like to save more.
B) households are paid every two weeks, rather than once a month.
C) households receive their incomes and spend their incomes with perfect synchronization.
D) households' payments and receipts are not synchronized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the demand for nominal money balances depends on both interest rates and nominal national income in could be expressed in simple algebra as:
A) kY + hi.
B) kPY - hi.
C) hi - kPY.
D) kY - hi.
A) kY + hi.
B) kPY - hi.
C) hi - kPY.
D) kY - hi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If the demand for real money balances depends on both interest rates and nominal national income in could be expressed in simple algebra as:
A) kY + hi.
B) kPY - hi.
C) hi - kPY.
D) kY - hi.
A) kY + hi.
B) kPY - hi.
C) hi - kPY.
D) kY - hi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the demand for real money balance function is kY - hi, then we can conclude:
A) an increase in real GDP (Y) increases the demand for money balances.
B) a rise in interest rates (i) reduces the demand for money balances.
C) the demand for money balances falls when income rises and interest rates rise.
D) both A and B, but not C.
A) an increase in real GDP (Y) increases the demand for money balances.
B) a rise in interest rates (i) reduces the demand for money balances.
C) the demand for money balances falls when income rises and interest rates rise.
D) both A and B, but not C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If price level increases:
A) the nominal money demand increases.
B) the nominal money demand stays constant.
C) the real money demand increases.
D) the real money demand stats constant.
A) the nominal money demand increases.
B) the nominal money demand stays constant.
C) the real money demand increases.
D) the real money demand stats constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose the demand for real money balance function is (MD/P) = kY - hi, where Y is real GDP and i is the market interest rate. Assuming Y is constant, the demand for money drawn in a diagram with respect to interest rates measured on the vertical axis and M/P on the horizontal is:
A) upward sloping from left to right.
B) horizontal at interest rate i0.
C) vertical at M0/P0.
D) downward sloping from left to right.
A) upward sloping from left to right.
B) horizontal at interest rate i0.
C) vertical at M0/P0.
D) downward sloping from left to right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose the demand for real money balance function is (MD/P) = kY - hi, where Y is real GDP and i is the market interest rate. The real money demand curve (drawn in a diagram with respect to interest rates measured on the vertical axis):
A) shift to the left when real GDP falls
B) shift to the right when real GDP falls
C) become steeper when real GDP falls
D) become flatter when real GDP falls.
A) shift to the left when real GDP falls
B) shift to the right when real GDP falls
C) become steeper when real GDP falls
D) become flatter when real GDP falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose the demand for real money balance function is kY - hi, where Y is real GDP and i is the market interest rate. The demand curve for real money balance in a diagram (with interest rates on the vertical axis):
A) will shift to the right as GDP decreases.
B) will move up the line as GDP decreases.
C) will shift to the left as GDP decreases.
D) will shift neither to the left nor to the right as GDP decreases.
A) will shift to the right as GDP decreases.
B) will move up the line as GDP decreases.
C) will shift to the left as GDP decreases.
D) will shift neither to the left nor to the right as GDP decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The money market:
A) in Canada is located in the Bay Street in Toronto.
B) in USA is located in the New York's financial district.
C) in Canada is located in the Canadian Mint.
D) in Canada refers to the demand for and supply of money.
A) in Canada is located in the Bay Street in Toronto.
B) in USA is located in the New York's financial district.
C) in Canada is located in the Canadian Mint.
D) in Canada refers to the demand for and supply of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When the money market is in equilibrium, the equilibrium interest rate is that rate at which:
A) bond prices are at a maximum.
B) the demand for investment goods equals the supply of investment goods.
C) the demand for money balances equals the supply of money balances.
D) the excess supply of money balances is negative.
A) bond prices are at a maximum.
B) the demand for investment goods equals the supply of investment goods.
C) the demand for money balances equals the supply of money balances.
D) the excess supply of money balances is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The money supply is:
A) currency in circulation outside the banking system, plus deposits of commercial banks.
B) currency in circulation inside the banking system, plus deposits of commercial banks.
C) currency in circulation.
D) currency in circulation plus commercial bank lending.
A) currency in circulation outside the banking system, plus deposits of commercial banks.
B) currency in circulation inside the banking system, plus deposits of commercial banks.
C) currency in circulation.
D) currency in circulation plus commercial bank lending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If the supply of money curve is drawn as a vertical line with interest rate in the vertical axis, it means that:
A) money supply decreases as the rate of interest increases.
B) money supply increases as the rate of interest increases.
C) money supply decreases as the rate of interest decreases.
D) money supply remains unchanged as the interest rate changes.
A) money supply decreases as the rate of interest increases.
B) money supply increases as the rate of interest increases.
C) money supply decreases as the rate of interest decreases.
D) money supply remains unchanged as the interest rate changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the money market the supply of money balances and the demand for money balances:
A) determine the equilibrium interest rate.
B) determine an interest rate at which portfolio managers are content with their holdings of money balances.
C) determine an interest rate at which portfolio managers are content with both their money balances and their bond holdings.
D) all of the above.
A) determine the equilibrium interest rate.
B) determine an interest rate at which portfolio managers are content with their holdings of money balances.
C) determine an interest rate at which portfolio managers are content with both their money balances and their bond holdings.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the prevailing interest rate is greater than the equilibrium rate, then:
A) portfolio managers will buy bonds and thus increase the liquidity of their portfolios.
B) portfolio managers will sell bonds and thus reduce the liquidity of their assets.
C) portfolio mangers will sell bonds and thus increase the liquidity of their assets.
D) portfolio managers will buy bonds and thus reduce the liquidity of their assets.
A) portfolio managers will buy bonds and thus increase the liquidity of their portfolios.
B) portfolio managers will sell bonds and thus reduce the liquidity of their assets.
C) portfolio mangers will sell bonds and thus increase the liquidity of their assets.
D) portfolio managers will buy bonds and thus reduce the liquidity of their assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Other things constant, an increase in money supply will lead to:
A) no changes in the interest rate.
B) an increase in the money demand.
C) higher interest rate.
D) lower interest rate.
A) no changes in the interest rate.
B) an increase in the money demand.
C) higher interest rate.
D) lower interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Other things constant, a decrease in the monetary base will lead to:
A) a reduction in the equilibrium interest rate and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of money balances held.
B) an increase in the equilibrium interest rate and a reduction in the equilibrium quantity of money balances held.
C) no change in the equilibrium interest rate but a decrease in the equilibrium quantity of money balances held.
D) an increase in the equilibrium interest rate but no change in the equilibrium quantity of money balances held.
A) a reduction in the equilibrium interest rate and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of money balances held.
B) an increase in the equilibrium interest rate and a reduction in the equilibrium quantity of money balances held.
C) no change in the equilibrium interest rate but a decrease in the equilibrium quantity of money balances held.
D) an increase in the equilibrium interest rate but no change in the equilibrium quantity of money balances held.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose that both the nominal money supply and the demand for money increase at the same time. We can conclude that:
A) the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium stock of money will fall.
B) the equilibrium interest rate will rise but we cannot say what happens to the equilibrium money stock.
C) the equilibrium money stock will rise but we cannot say whether the equilibrium interest rate will rise,
Fall, or remain constant.
D) the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium money stock will rise.
A) the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium stock of money will fall.
B) the equilibrium interest rate will rise but we cannot say what happens to the equilibrium money stock.
C) the equilibrium money stock will rise but we cannot say whether the equilibrium interest rate will rise,
Fall, or remain constant.
D) the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium money stock will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Suppose that an excess demand for money exists in the economy. As the money market moves toward an equilibrium interest rate, we can expect:
A) bond prices to rise and the interest rate to rise.
B) bond prices to rise and the interest rate to fall.
C) bond prices to fall and the interest rate to fall.
D) bond prices to fall and the interest rate to rise.
A) bond prices to rise and the interest rate to rise.
B) bond prices to rise and the interest rate to fall.
C) bond prices to fall and the interest rate to fall.
D) bond prices to fall and the interest rate to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
All of the following will affect the demand for real money balances except:
A) there is an increase in real income.
B) the real interest rate falls.
C) both the price level and the level of the nominal money supply rise by 10 per cent.
D) the definition of the money supply expands to include near monies.
A) there is an increase in real income.
B) the real interest rate falls.
C) both the price level and the level of the nominal money supply rise by 10 per cent.
D) the definition of the money supply expands to include near monies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Other things remaining the same, higher real income (Y) will lead to:
A) higher equilibrium interest rate.
B) higher equilibrium stock of money.
C) higher real balance fraction (k).
D) higher real money demand.
A) higher equilibrium interest rate.
B) higher equilibrium stock of money.
C) higher real balance fraction (k).
D) higher real money demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose, real cash balance fraction (k) increases due to the lack of confidence in the financial market increases, while things remain the same. As a result, we will see:
A) higher stock of money.
B) higher interest rate.
C) higher price of bonds.
D) lower stock of supply.
A) higher stock of money.
B) higher interest rate.
C) higher price of bonds.
D) lower stock of supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose that an excess demand for real money balances exists in the money market. Equilibrium will be established if:
A) bond prices decline increasing bond yields.
B) the level o f planned investment spending rises.
C) individuals enter the market to sell bonds and increase their liquidity.
D) any of the above.
A) bond prices decline increasing bond yields.
B) the level o f planned investment spending rises.
C) individuals enter the market to sell bonds and increase their liquidity.
D) any of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The equilibrium interest rate in the money market must rise as the real GDP (Y) increases, because:
A) there will be an increase in the demand for real money balances and a rightward shift of the money demand curve.
B) the higher interest rate will cause individuals to desire more real balances.
C) there will be an increase in the investment funds.
D) rising incomes means that the money supply must decrease.
A) there will be an increase in the demand for real money balances and a rightward shift of the money demand curve.
B) the higher interest rate will cause individuals to desire more real balances.
C) there will be an increase in the investment funds.
D) rising incomes means that the money supply must decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose that the quantity of money balances demanded exceeds the quantity supplied by the banking system. We can conclude that:
A) there will be pressure on interest rates to fall.
B) the money supply curve will shift to the right.
C) there will be pressure on interest rates to rise.
D) the demand curve for money balances will shift to the right.
A) there will be pressure on interest rates to fall.
B) the money supply curve will shift to the right.
C) there will be pressure on interest rates to rise.
D) the demand curve for money balances will shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When the money market attains an equilibrium outcome, it means that:
A) the borrowers and lenders have an excess demand or an excess supply of real balances.
B) the borrowers and lenders are equally satisfied.
C) the quantity of real money balances demanded equals the quantity supplied.
D) the interest rate is in equilibrium, while bond price may not be in equilibrium.
A) the borrowers and lenders have an excess demand or an excess supply of real balances.
B) the borrowers and lenders are equally satisfied.
C) the quantity of real money balances demanded equals the quantity supplied.
D) the interest rate is in equilibrium, while bond price may not be in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Other things being equal, an equilibrium interest rate:
A) decreases during periods of rising prices.
B) equates the quantity of real balances demanded and supplied.
C) is affected by fiscal policy but not by monetary policy.
D) increases during periods of deflation.
A) decreases during periods of rising prices.
B) equates the quantity of real balances demanded and supplied.
C) is affected by fiscal policy but not by monetary policy.
D) increases during periods of deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If interest rates are below the equilibrium rate, then:
A) there is an excess supply of bonds.
B) there is an excess demand for bonds.
C) the bond market is in equilibrium.
D) none of the above.
A) there is an excess supply of bonds.
B) there is an excess demand for bonds.
C) the bond market is in equilibrium.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
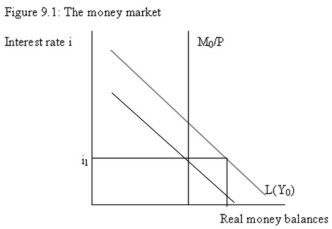
-Refer to Figure 9.1. The diagram shows that the initial equilibrium interest rate is i1. Assume that the demand for money has increased due to an increase in Y. The new money demand curve is L(Y0). Determine the false statement from the following statements.
A) There is an excess demand for money.
B) There is an excess supply of bonds.
C) There is an upward pressure on the interest rate.
D) There will be an upward pressure on the bond price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75

-Refer to Figure 9.1. The excess demand for money in the money market means:
A) excess supply of bonds, because portfolio managers will sell bonds to increase their money holdings.
B) excess demand for bonds, because portfolio managers will buy bonds to increase their money holdings.
C) neither excess demand nor excess supply of bonds.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The equilibrium interest rate is influenced by:
A) a change in money supply.
B) a change in real income.
C) a change in the desired reserve ratio in the banking system or the public's cash ratio.
D) all of the above.
A) a change in money supply.
B) a change in real income.
C) a change in the desired reserve ratio in the banking system or the public's cash ratio.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
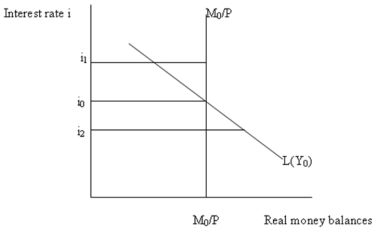
-Refer to Figure 9.3. The vertical money supply curve M0/P reflects the fact that:
A) bond prices and interest rates are inversely related.
B) the stock of money is determined by the monetary base, bank behaviour and public behaviour and does . not change when the interest rate changes.
C) higher interest rates result in higher opportunity costs of supplying money.
D) lower interest rates result in lower opportunity costs of supplying money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78

-Refer to Figure 9.3. The equilibrium interest rate in this money market is:
A) i1.
B) i0.
C) i2.
D) not determinable without further information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

-Refer to Figure 9.3. If the interest rate were i1 portfolio managers:
A) would buy bonds; as a result, there will be an excess demand for bond leading to higher bond prices and lower yields.
B) would be content with the mix of bonds and money balances in their portfolios.
C) would sell bonds; as a result, there will be an excess supply of bonds leading to lower prices of bonds and higher yields.
D) would spend funds on current financial portfolios.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following statements is false?
A) If Canadians want to buy foreign bonds, they need to buy foreign currency.
B) If foreigners want to buy Canadian bonds, they need to buy Canadian dollars.
C) The foreign exchange rate (er) is the price of one unit of foreign currency expressed in Canadian dollars.
D) If the exchange rate of one US dollar is $1.25 in Canada, it means the value of one Canadian dollar is US 0.75.
A) If Canadians want to buy foreign bonds, they need to buy foreign currency.
B) If foreigners want to buy Canadian bonds, they need to buy Canadian dollars.
C) The foreign exchange rate (er) is the price of one unit of foreign currency expressed in Canadian dollars.
D) If the exchange rate of one US dollar is $1.25 in Canada, it means the value of one Canadian dollar is US 0.75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



