Deck 2: Theories, Models and Data
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Theories, Models and Data
1
Economists frequently use economic models. These models:
A) are tools used in the analysis of economic relationships.
B) may be graphs expressing the relationship between two economic variables.
C) may be equations expressing a relationship between two or more variables.
D) all of the above.
A) are tools used in the analysis of economic relationships.
B) may be graphs expressing the relationship between two economic variables.
C) may be equations expressing a relationship between two or more variables.
D) all of the above.
all of the above.
2
The primary reason why economists use models in their analysis is because a model:
A) permits economic relationships to be quickly and easily specified.
B) makes it possible to predict exact economic relationships.
C) helps organize and clarify the thinking process about an issue.
D) incorporates all the inner workings of real-world economy.
A) permits economic relationships to be quickly and easily specified.
B) makes it possible to predict exact economic relationships.
C) helps organize and clarify the thinking process about an issue.
D) incorporates all the inner workings of real-world economy.
helps organize and clarify the thinking process about an issue.
3
Which one of the following statements does not characterize an economic model?
A) Models are controlled experiments with the economy.
B) Models should contain a set of stated assumptions.
C) Models may very well omit some important economic relationships.
D) Models may be an imprecise representation of the real world.
A) Models are controlled experiments with the economy.
B) Models should contain a set of stated assumptions.
C) Models may very well omit some important economic relationships.
D) Models may be an imprecise representation of the real world.
Models are controlled experiments with the economy.
4
When specifying economic models, economists often make assumptions about the real world. The purpose of assumptions in economics is to:
A) make the model more realistic.
B) simplify the model and provide a primary focus for the theory.
C) ensure that the model only covers specific conditions.
D) guarantee the accuracy of the theory.
A) make the model more realistic.
B) simplify the model and provide a primary focus for the theory.
C) ensure that the model only covers specific conditions.
D) guarantee the accuracy of the theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Economic models and data allow us to study:
A) assumptions.
B) the future.
C) economic relationships.
D) people in laboratories.
A) assumptions.
B) the future.
C) economic relationships.
D) people in laboratories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is false?
A) An economic theory is validated on the basis of observation.
B) An economic theory is a mathematically deduced equation and it is unrelated to observations in the real world.
C) An economic theory is rejected if it does not pass the test of empirical scrutiny.
D) An economic theory can be validated with data.
A) An economic theory is validated on the basis of observation.
B) An economic theory is a mathematically deduced equation and it is unrelated to observations in the real world.
C) An economic theory is rejected if it does not pass the test of empirical scrutiny.
D) An economic theory can be validated with data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Pieces of evidence about economic behaviour are:
A) data.
B) assumptions.
C) theories.
D) models.
A) data.
B) assumptions.
C) theories.
D) models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A sensible theoretical relationship not rejected by evidence over a long period is a(n):
A) tautology.
B) axiom.
C) assumption.
D) behavioural model.
A) tautology.
B) axiom.
C) assumption.
D) behavioural model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Time series data:
A) are used very infrequently in economic analysis.
B) measure different variables for different economic units at a point in time.
C) measure a given variable for different economic units at a point in time.
D) measure a variable or variables at different points in time.
A) are used very infrequently in economic analysis.
B) measure different variables for different economic units at a point in time.
C) measure a given variable for different economic units at a point in time.
D) measure a variable or variables at different points in time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which one of the following statements is false?
A) If the economist wants to examine the distribution of income in 1987, time-series data should be used.
B) If the economist wants to examine the relationship between advertising expenditures and sales during 1987, cross-section data is used.
C) If the economist wants to examine the effect of intellectual ability upon earnings, cross-section data could be used.
D) If the economist wants to forecast gross national product based upon observations from previous years, time-series data should be used.
A) If the economist wants to examine the distribution of income in 1987, time-series data should be used.
B) If the economist wants to examine the relationship between advertising expenditures and sales during 1987, cross-section data is used.
C) If the economist wants to examine the effect of intellectual ability upon earnings, cross-section data could be used.
D) If the economist wants to forecast gross national product based upon observations from previous years, time-series data should be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Data that follow the same individuals over time are called:
A) time-series data.
B) cross-section data.
C) longitudinal data.
D) survey data.
A) time-series data.
B) cross-section data.
C) longitudinal data.
D) survey data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A basket of goods in 1987 cost $783, while the value of the same basket in 1997 was $1133. The value of this price index in 1997, based on 1987 = 100, was:
A) 144.7.
B) 242.
C) 69.1.
D) 117.4.
A) 144.7.
B) 242.
C) 69.1.
D) 117.4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The weights used in the consumer price index:
A) show the relative importance of the prices of the different components in the household's expenditures.
B) do not affect changes in the household's cost of living.
C) sum to 100.
D) are determined by the cost of producing each good in the index.
A) show the relative importance of the prices of the different components in the household's expenditures.
B) do not affect changes in the household's cost of living.
C) sum to 100.
D) are determined by the cost of producing each good in the index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A table titled "Commodity Price Index, 1950-1998 (1970 = 100)" has a base year of:
A) 1950.
B) 1998.
C) 1970.
D) none of the above.
A) 1950.
B) 1998.
C) 1970.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The most frequently recognized and widely used price index is the:
A) wholesale price index.
B) producers price index.
C) consumer price index.
D) index of leading economic indicators.
A) wholesale price index.
B) producers price index.
C) consumer price index.
D) index of leading economic indicators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The CPI measures:
A) the number of housing starts during a month.
B) the prices of goods that households consume.
C) changes in the level of unemployment during a given year.
D) hourly wage rates of manufacturing workers.
A) the number of housing starts during a month.
B) the prices of goods that households consume.
C) changes in the level of unemployment during a given year.
D) hourly wage rates of manufacturing workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the CPI for 2005 was 284.1, and economists predicted an inflation rate of 3.5 per cent for 2006, the predicted CPI at the end of 2006 was:
A) 287.1.
B) 290.1.
C) 297.5.
D) 294.1.
A) 287.1.
B) 290.1.
C) 297.5.
D) 294.1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Adjusting for changes in prices allows us to:
A) create cross-section data.
B) derive a real value from a nominal value.
C) create time-series data.
D) create a paradigm.
A) create cross-section data.
B) derive a real value from a nominal value.
C) create time-series data.
D) create a paradigm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When economists compute the real value of an economic variable denominated in dollars, they do so by:
A) dividing the nominal value by 100.
B) multiplying the nominal value by the price level.
C) dividing the nominal value by the price index.
D) subtracting the price level from the nominal value and multiplying by 100.
A) dividing the nominal value by 100.
B) multiplying the nominal value by the price level.
C) dividing the nominal value by the price index.
D) subtracting the price level from the nominal value and multiplying by 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The nominal value of an economic variable is:
A) a measure of the goods it will buy.
B) expressed in current dollar terms.
C) adjusted for changes in the overall price level in the economy.
D) affected by the prices of all other goods in the economy.
A) a measure of the goods it will buy.
B) expressed in current dollar terms.
C) adjusted for changes in the overall price level in the economy.
D) affected by the prices of all other goods in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Deflation describes periods when:
A) the average level of prices is falling.
B) real output neither increases nor decreases.
C) relative prices remain constant.
D) the average level of prices is rising.
A) the average level of prices is falling.
B) real output neither increases nor decreases.
C) relative prices remain constant.
D) the average level of prices is rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If your nominal income has increased by 2 per cent in one year, while the inflation rate for the same year is 3 per cent, you can conclude that your real income:
A) has increased by 1% approximately.
B) has decreased by 1% approximately.
C) has remained constant.
D) has either increased or decreased by 1%
A) has increased by 1% approximately.
B) has decreased by 1% approximately.
C) has remained constant.
D) has either increased or decreased by 1%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The real value of an economic variable is:
A) a measure of the purchasing power of the variable.
B) adjusted for changes in the price level.
C) expressed in constant dollars.
D) all of the above.
A) a measure of the purchasing power of the variable.
B) adjusted for changes in the price level.
C) expressed in constant dollars.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose that an individual has earned $400 per week since 1967 and the CPI is currently 340 (1967 =
100). The real weekly income of this individual in 1967 dollars is:
A) 361.4.
B) 117.6.
C) 400.
D) 185.9.
100). The real weekly income of this individual in 1967 dollars is:
A) 361.4.
B) 117.6.
C) 400.
D) 185.9.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If you earn a salary of $24,000 and the CPI is 300 (1970 = 100), then the real value of your income, expressed in 1970s dollars is:
A) 8,000.
B) 6,000.
C) 24,000.
D) 18,600.
A) 8,000.
B) 6,000.
C) 24,000.
D) 18,600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the weekly earnings index for the construction industry was 340 for 1987 (1970 = 100), then:
A) the workers in the construction industry earned $340 per week.
B) the workers earned 340 per cent as much in 1987 as they did in 1970.
C) the workers earned $100 per week in 1970 and $340 in 1987.
D) the real weekly earnings of workers fell by 3.4 percent.
A) the workers in the construction industry earned $340 per week.
B) the workers earned 340 per cent as much in 1987 as they did in 1970.
C) the workers earned $100 per week in 1970 and $340 in 1987.
D) the real weekly earnings of workers fell by 3.4 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Product prices, consumer income, and the level of employment:
A) are types of economic variables.
B) affect the "what," "how," and for "whom" decisions made in an economic system.
C) are measured by economic data.
D) all of the above are correct.
A) are types of economic variables.
B) affect the "what," "how," and for "whom" decisions made in an economic system.
C) are measured by economic data.
D) all of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose that the consumer price index has a value of 87 (1980 = 100) for 1987. This means that:
A) on average, prices rose by 13 per cent since 1980.
B) all prices fell by 13 per cent since 1980.
C) all prices rose by 87 per cent since 1980.
D) on average, prices fell by 13 per cent since 1980.
A) on average, prices rose by 13 per cent since 1980.
B) all prices fell by 13 per cent since 1980.
C) all prices rose by 87 per cent since 1980.
D) on average, prices fell by 13 per cent since 1980.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An individual's real income per year measures the:
A) amount of income subject to income tax.
B) number of dollars earned during the year.
C) amount of goods and services that can be purchased by the individual.
D) number of hours worked by the individual.
A) amount of income subject to income tax.
B) number of dollars earned during the year.
C) amount of goods and services that can be purchased by the individual.
D) number of hours worked by the individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Other things equal, suppose that the general level of prices decreases. You would be correct if you concluded that the real value of your income:
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) may either increase or decrease, depending on the percentage fall in prices.
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) may either increase or decrease, depending on the percentage fall in prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
All of the following statements are correct except:
A) Generally, what matters most to consumers is what a good costs in dollars.
B) The relative price of a good is its price measured relative to the price of other goods.
C) The real price of a good is calculated by adjusting its nominal price to account for changes in the prices of goods in general.
D) When the price of eggs goes up by the same proportion as prices of all other goods, the relative price of eggs does not change.
A) Generally, what matters most to consumers is what a good costs in dollars.
B) The relative price of a good is its price measured relative to the price of other goods.
C) The real price of a good is calculated by adjusting its nominal price to account for changes in the prices of goods in general.
D) When the price of eggs goes up by the same proportion as prices of all other goods, the relative price of eggs does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose that in 2006, the CPI was 285, (1982 = 100). This index shows that the real value of a dollar in 2006:
A) has remained essentially unchanged since 1982.
B) is much less than it was in 1982.
C) is 2.85 times as large as it was in 1982.
D) has increased since prices have decreased.
A) has remained essentially unchanged since 1982.
B) is much less than it was in 1982.
C) is 2.85 times as large as it was in 1982.
D) has increased since prices have decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
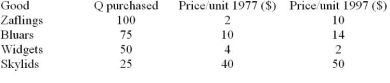 Table 2.1
Table 2.1-Table 2.1 shows the prices and quantities purchased of four different goods by the typical household in
1977 and 1997. Using 1977 as the base year, the value of the consumer price index in 1977 was:
A) 200.
B) 175.
C) 100.
D) between 150 and 200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
 Table 2.1
Table 2.1-Using Table 2.1, in 1977 the greatest share of household income was spent on:
A) bluars.
B) widgets.
C) zaflings.
D) skylids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
 Table 2.1
Table 2.1-Hyperinflation is:
A) an unusually low level of price increases in the economy.
B) a high inflation rate.
C) a purely temporary increase in the inflation rate.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
 Table 2.1
Table 2.1-Using Table 2.1, the price index in 1997, using 1977 as the base year, for this basket of goods is:
A) 100.
B) 158.
C) 200.
D) 173.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
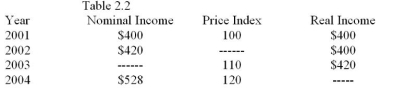 Table 2.2
Table 2.2-The price index in 2002 was:
A) 100
B) 105
C) 115
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
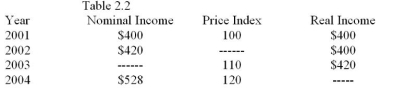 Table 2.2
Table 2.2-Jim's weekly nominal income in 2003 was:
A) $440
B) $460
C) $462
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
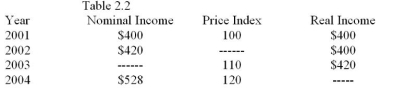 Table 2.2
Table 2.2-Jim's weekly real income in 2004 was:
A) $440
B) $460
C) $462
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is true about an economic model?
A) It is built on a series of assumptions.
B) It establishes cause and effect between variables.
C) It could also be called an economic theory.
D) All of the above.
A) It is built on a series of assumptions.
B) It establishes cause and effect between variables.
C) It could also be called an economic theory.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A road map is like an economic model, because it provides us with:
A) all the details of the real world.
B) an analysis with no resemblances with the real world.
C) an analysis of the real world.
D) an abstraction of the real world.
A) all the details of the real world.
B) an analysis with no resemblances with the real world.
C) an analysis of the real world.
D) an abstraction of the real world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The use of economic models means economists believe that:
A) this is how people explicitly choose between alternatives.
B) this is a reasonable abstraction of how people choose between alternatives.
C) those who explicitly make decisions this way are smarter.
D) with enough education, all people will start to explicitly make decisions this way.
A) this is how people explicitly choose between alternatives.
B) this is a reasonable abstraction of how people choose between alternatives.
C) those who explicitly make decisions this way are smarter.
D) with enough education, all people will start to explicitly make decisions this way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In order for an economic model to be valid:
A) all people must explicitly mimic the model.
B) most people must explicitly mimic the model.
C) most people must act as if they explicitly mimic the model.
D) it must gain professional acceptance.
A) all people must explicitly mimic the model.
B) most people must explicitly mimic the model.
C) most people must act as if they explicitly mimic the model.
D) it must gain professional acceptance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When economists make predictions using the framework of a given economic model, it is usually based on:
A) personal experiences.
B) cause-and-effect explanations.
C) mathematical abstractions.
D) normative analysis.
A) personal experiences.
B) cause-and-effect explanations.
C) mathematical abstractions.
D) normative analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Given the equation Q = 16 - 1.5P, when P has a value of 4, Q has a value of:
A) 16.
B) 22.
C) 6.
D) 10.
A) 16.
B) 22.
C) 6.
D) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The solution to the equations P = 14 - 2Q and Q = 6, yields a solution for P of:
A) 2.
B) 3.
C) 6.
D) 10.
A) 2.
B) 3.
C) 6.
D) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The solution to the equations P = 2 + 0.5Q and P = 10 yields a solution for Q of:
A) 12.
B) 20.
C) 16.
D) 24.
A) 12.
B) 20.
C) 16.
D) 24.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Solving the equations P = 2 + 3Q and P = 6 + 3Q yields a solution for Q of:
A) 100.
B) -100.
C) 0.
D) no solution.
A) 100.
B) -100.
C) 0.
D) no solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Solving the equations P = 6 + 3Q and P = -3Q yields a solution for Q of:
A) 1.
B) -1.
C) -2.
D) 2.
A) 1.
B) -1.
C) -2.
D) 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When a negative relationship exists between x and y,:
A) an increase in x results in a decrease in y.
B) an increase in x results in an increase in y.
C) a graph of the relationship slopes up and to the right.
D) a graph of the relationship is horizontal.
A) an increase in x results in a decrease in y.
B) an increase in x results in an increase in y.
C) a graph of the relationship slopes up and to the right.
D) a graph of the relationship is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose that a positive relationship exists between the variables x and y. This relationship means that:
A) a plot of the variables will slope downward and to the right.
B) as x increases, the value of y decreases.
C) as x increases, the value of y also increases.
D) as y increases, the value of x decreases.
A) a plot of the variables will slope downward and to the right.
B) as x increases, the value of y decreases.
C) as x increases, the value of y also increases.
D) as y increases, the value of x decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Knowing the intercept and slope enables you to draw:
A) a curve.
B) a circle.
C) an ellipse.
D) a straight line.
A) a curve.
B) a circle.
C) an ellipse.
D) a straight line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If you have the equation Q = 20 - 3P, then:
A) a plot of the equation will result in a graph with a negative slope.
B) a negative relationship exists between P and Q.
C) every time P increases by 1 unit, Q falls by 3 units.
D) all of the above are correct.
A) a plot of the equation will result in a graph with a negative slope.
B) a negative relationship exists between P and Q.
C) every time P increases by 1 unit, Q falls by 3 units.
D) all of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The reason that economists often use a scatter diagram in their analysis is that:
A) it provides a precise relationship between two variables.
B) it reveals whether there may be an obvious relationship between two variables.
C) it will always plot as a simple linear relationship.
D) it may be plotted with many explanatory variables.
A) it provides a precise relationship between two variables.
B) it reveals whether there may be an obvious relationship between two variables.
C) it will always plot as a simple linear relationship.
D) it may be plotted with many explanatory variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Consider a negatively sloped linear line in a graph where the vertical axis represents variable Y and the horizontal axis represents variable X. If the vertical intercept is 10 and the slope is -0.5, the horizontal intercept must be:
A) 5.
B) 10.
C) 20.
D) none of the above.
A) 5.
B) 10.
C) 20.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Consider a negatively sloped linear line in a graph where the vertical axis represents variable Y and the horizontal axis represents variable X. If the vertical intercept is 10 and the slope is -0.5, the correct equation is:
A) X = 10 - 0.5Y.
B) X=20-2Y.
C) Y=20-2X.
D) Y=10-2X.
A) X = 10 - 0.5Y.
B) X=20-2Y.
C) Y=20-2X.
D) Y=10-2X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
All of the following statements are characteristic of economic theories except:
A) theories may change over time as new evidence is discovered.
B) theories are the basis for economic principles.
C) theories are based upon abstract ideas and hence cannot be tested.
D) theories are tested by applying economic data to a model.
A) theories may change over time as new evidence is discovered.
B) theories are the basis for economic principles.
C) theories are based upon abstract ideas and hence cannot be tested.
D) theories are tested by applying economic data to a model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which one of the following steps does not belong in the economists' approach to problem solving?
A) Observe the phenomenon.
B) Disregard all previous theories.
C) Develop a theory to explain the phenomenon.
D) Test the predictions of the theory with data.
A) Observe the phenomenon.
B) Disregard all previous theories.
C) Develop a theory to explain the phenomenon.
D) Test the predictions of the theory with data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which one of the following will not usually be included in an economic theory?
A) A set of assumptions.
B) A set of definitions.
C) An overall statement of the theory.
D) A set of value judgments.
A) A set of assumptions.
B) A set of definitions.
C) An overall statement of the theory.
D) A set of value judgments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Why is there often disagreement amongst economists?
A) Some who claim to be economists may not be sufficiently well trained.
B) There is disagreement over what is, and what is not, a legitimate goal for society to try to achieve, possibly because some economists are 'left wing' and others are 'right wing.'
C)The discipline is so wide and complex that no one person could be expected to cover the whole range of possible knowledge.
D) There is truth in all of the above
A) Some who claim to be economists may not be sufficiently well trained.
B) There is disagreement over what is, and what is not, a legitimate goal for society to try to achieve, possibly because some economists are 'left wing' and others are 'right wing.'
C)The discipline is so wide and complex that no one person could be expected to cover the whole range of possible knowledge.
D) There is truth in all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A theory is a logical view of how the world and its parts work and it is frequently formulated on the basis of observation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When economists use cross-section data, they collect and analyze information about the same economic variable at different points in time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An economic variable is anything that affects the what, how, and for whom questions that every society must answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When economists use time-series data, they collect and analyze information about different economic variables at a particular point in time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Nominal income is the real income divided by the price index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A rising average price level does not mean that all prices in the economy are rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If nominal GNP is $1,000 billion and the GNP deflator is 250, then real GNP is $400 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The CPI is not affected by rising prices of imported consumer goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the price of apples is $1 per pound and the price of peaches is 50 cents per pound, then the relative price ratio of apples to peaches is 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An increase in the price level as reflected by a rising consumer price index causes the real value of an economic variable to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The inflation rate is nothing more than the growth rate of the average price level, and it can be either positive or negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The slope of a line measures its steepness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Economic theories, like physics or chemistry, can be tested in a laboratory environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Econometrics is the study of fitting relationships through scatter diagrams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Economic theories are worthless unless they are verified through scientific testing and hold true under all circumstances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Human behaviour, as well as the behaviour of an individual, can always be predicted accurately.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An important frequent assumption in economic theories is that all other things remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Assumptions are used in economic theories in order to simplify the theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Linear relationships are always more accurate representations of reality than non-linear relationships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The primary reason for building and using models in economic analysis is to reveal basic economic principles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



