Deck 5: Statistical Inference
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Statistical Inference
1
< p >If the average derived from a specific sample is $43,000, then 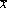 = 43,000 is the __________ of the population mean.< / p>
= 43,000 is the __________ of the population mean.< / p>
A) deviation
B) estimate
C) point
D) static point
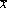 = 43,000 is the __________ of the population mean.< / p>
= 43,000 is the __________ of the population mean.< / p>A) deviation
B) estimate
C) point
D) static point
estimate
2
In a population set, 14 students of the 137 observations received a failing grade in the Accounting Principles course. What is the estimate of the sample proportion of failure in the course?
A) 0.1022
B) 9.786
C) 0.6879
D) 0.0102
A) 0.1022
B) 9.786
C) 0.6879
D) 0.0102
0.1022
3
In a population set, 13 students of the 132 observations received a failing grade in the Accounting Principles course. What is the estimate of the sample proportion of failure in the course?
A) 0.0985
B) 10.154
C) 0.6842
D) 0.0099
A) 0.0985
B) 10.154
C) 0.6842
D) 0.0099
0.0985
4
Cameron is the quality inspector for the Mason Pot Company, an artesian cooperative crafting bowls. In the smaller series, the mean diameter is 3 inches with a standard deviation of 0.3 inch. First, find the expected value. Then answer: what is the standard error of the sample mean derived from a random sample of 24 bowls?
A) 0.061
B) 0.6
C) 0.002
D) 0.24
A) 0.061
B) 0.6
C) 0.002
D) 0.24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Cameron is the quality inspector for the Mason Pot Company, an artesian cooperative crafting bowls. In the smaller series, the mean diameter is 4 inches with a standard deviation of 0.2 inch. First, find the expected value. Then answer: what is the standard error of the sample mean derived from a random sample of 12 bowls?
A) 0.058
B) 0.58
C) 0.001
D) 0.12
A) 0.058
B) 0.58
C) 0.001
D) 0.12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Megan ran an analysis with a population standard deviation? = 0.90. When reviewing sample sizes of 4 and 8, the standard error for the sample mean was 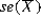 = 0.45 and
= 0.45 and 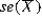 = 0.32 respectively. Doing a comparison, what does the expected value and the standard error of the sample mean reflect?< / p>
= 0.32 respectively. Doing a comparison, what does the expected value and the standard error of the sample mean reflect?< / p>
A) By comparison, the results confirm the sample is normally distributed with increased variability.
B) The standard error for the sample mean is lower confirming the initial population standard deviation is incorrect.
C) By comparing, the results confirm that averaging reduces variability.
D) The standard error for the sample mean is lower, increasing variability in the sample set.
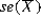 = 0.45 and
= 0.45 and 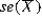 = 0.32 respectively. Doing a comparison, what does the expected value and the standard error of the sample mean reflect?< / p>
= 0.32 respectively. Doing a comparison, what does the expected value and the standard error of the sample mean reflect?< / p>A) By comparison, the results confirm the sample is normally distributed with increased variability.
B) The standard error for the sample mean is lower confirming the initial population standard deviation is incorrect.
C) By comparing, the results confirm that averaging reduces variability.
D) The standard error for the sample mean is lower, increasing variability in the sample set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The Central Limit Theorem, by definition, implies that as the sample size increases, the
A) average of the large number of independent observations has an approximate normal distribution.
B) average of the large number of independent observations reflects the leftmost tail of the distribution.
C) expected underlining distribution is only justified when n 30.
D) expected normal distribution declines.
A) average of the large number of independent observations has an approximate normal distribution.
B) average of the large number of independent observations reflects the leftmost tail of the distribution.
C) expected underlining distribution is only justified when n 30.
D) expected normal distribution declines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the expected value of the sample proportion?
A) number of success
B) sample population
C) standard error
D) population proportion
A) number of success
B) sample population
C) standard error
D) population proportion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
CNBC (2018) reported 53% of households are using streaming services compared to standard cable. What are the expected value and the standard error of the sample proportion derived from a random sample of 600?
A) EP¯ = 0.47 and seP¯ = 0.0204
B) EP¯= 0.0204 and seP¯ = 0.47
C) EP¯= 0.53 and seP¯ = 0.0204
D) EP¯= 0.7115 and seP¯ = 0.0324
A) EP¯ = 0.47 and seP¯ = 0.0204
B) EP¯= 0.0204 and seP¯ = 0.47
C) EP¯= 0.53 and seP¯ = 0.0204
D) EP¯= 0.7115 and seP¯ = 0.0324

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
CNBC (2018) reported 58% of households are using streaming services compared to standard cable. What are the expected value and the standard error of the sample proportion derived from a random sample of 500?
A)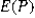 = 0.42 and <em>
= 0.42 and <em> 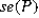 </em> = 0.0221< / p>
</em> = 0.0221< / p>
B)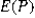 = 0.0221 and <em>
= 0.0221 and <em> 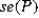 </em> = 0.42< / p>
</em> = 0.42< / p>
C)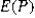 = 0.58 and <em>
= 0.58 and <em> 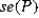 </em> = 0.0221< / p>
</em> = 0.0221< / p>
D)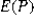 = 0.7615 and <em>
= 0.7615 and <em> 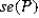 </em> = 0.0341< / p>
</em> = 0.0341< / p>
A)
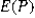 = 0.42 and <em>
= 0.42 and <em> 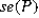 </em> = 0.0221< / p>
</em> = 0.0221< / p>B)
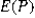 = 0.0221 and <em>
= 0.0221 and <em> 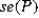 </em> = 0.42< / p>
</em> = 0.42< / p>C)
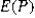 = 0.58 and <em>
= 0.58 and <em> 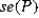 </em> = 0.0221< / p>
</em> = 0.0221< / p>D)
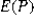 = 0.7615 and <em>
= 0.7615 and <em> 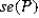 </em> = 0.0341< / p>
</em> = 0.0341< / p>
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A range of values used to estimate a population parameter of interest is called
A) estimated error.
B) confidence interval.
C) standard error.
D) probability of success.
A) estimated error.
B) confidence interval.
C) standard error.
D) probability of success.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a meeting, Matt estimates the average miles per gallon (mpg) of the fleet cars is 19 mpg. With a certain level of confidence, he announces the actual mpg is in the 16 to 22 mpg range. What is the Margin of Error?
A) 6 mpg
B) 0.50 mpg
C) 19 mpg
D) 3 mpg
A) 6 mpg
B) 0.50 mpg
C) 19 mpg
D) 3 mpg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a meeting, Matt estimates the average miles per gallon (mpg) of the fleet cars is 24 mpg. With a certain level of confidence, he announces the actual mpg is in the 22 to 26 mpg range. What is the Margin of Error?
A) 4 mpg
B) 0.50 mpg
C) 24 mpg
D) 2 mpg
A) 4 mpg
B) 0.50 mpg
C) 24 mpg
D) 2 mpg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the confidence coefficient is 0.77, what is the implied probability of error ?
A) 0.23
B) 0.77
C) 1
D) 0.5
A) 0.23
B) 0.77
C) 1
D) 0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If the confidence coefficient is 0.85, what is the implied probability of error ?
A) 0.15
B) 0.85
C) 1
D) 0.05
A) 0.15
B) 0.85
C) 1
D) 0.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
IIn a sample of 37, the mean is confidence interval for the population mean. The t Table = 1.688.
A) 90% confidence interval is 93.38± 2.84.
B) 90% confidence interval is 95.92.
C) 90% confidence interval is between 90.84 and 95.92.
D) 90% confidence interval is 93.28± 1.688.
A) 90% confidence interval is 93.38± 2.84.
B) 90% confidence interval is 95.92.
C) 90% confidence interval is between 90.84 and 95.92.
D) 90% confidence interval is 93.28± 1.688.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
<p>In a sample of 25, the mean is 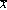 = 86.92 with a standard deviation of s = 9.87. Assuming the results follow a normal distribution, construct the 90% confidence interval for the population mean. The t Table = 1.711.
= 86.92 with a standard deviation of s = 9.87. Assuming the results follow a normal distribution, construct the 90% confidence interval for the population mean. The t Table = 1.711.
A) 90% confidence interval is 86.92± 3.68.
B) 90% confidence interval is 90.30.
C) 90% confidence interval is between 83.54 and 90.30.
D) 90% confidence interval is 86.82± 1.711.
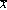 = 86.92 with a standard deviation of s = 9.87. Assuming the results follow a normal distribution, construct the 90% confidence interval for the population mean. The t Table = 1.711.
= 86.92 with a standard deviation of s = 9.87. Assuming the results follow a normal distribution, construct the 90% confidence interval for the population mean. The t Table = 1.711.A) 90% confidence interval is 86.92± 3.68.
B) 90% confidence interval is 90.30.
C) 90% confidence interval is between 83.54 and 90.30.
D) 90% confidence interval is 86.82± 1.711.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a sample of 23, the mean is confidence interval for the population mean. The t Table = 1.717.
A) 90% confidence interval is 90.88± 95.90.
B) 90% confidence interval is 2.51.
C) 90% confidence interval is between 90.71 and 96.07.
D) 90% confidence interval is 90.88± 1.72.
A) 90% confidence interval is 90.88± 95.90.
B) 90% confidence interval is 2.51.
C) 90% confidence interval is between 90.71 and 96.07.
D) 90% confidence interval is 90.88± 1.72.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
<p>In a sample of 60, the mean is 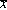 = 76.29 with a standard deviation of s = 7. Assuming the results follow a normal distribution, construct the 90% confidence interval for the population mean. The t Table = 1.684.
= 76.29 with a standard deviation of s = 7. Assuming the results follow a normal distribution, construct the 90% confidence interval for the population mean. The t Table = 1.684.
A) 90% confidence interval is 76.29± 1.52
B) 90% confidence interval is 77.97.
C) 90% confidence interval is between 74.61 and 77.97.
D) 90% confidence interval is 76.29± 1.684.
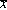 = 76.29 with a standard deviation of s = 7. Assuming the results follow a normal distribution, construct the 90% confidence interval for the population mean. The t Table = 1.684.
= 76.29 with a standard deviation of s = 7. Assuming the results follow a normal distribution, construct the 90% confidence interval for the population mean. The t Table = 1.684.A) 90% confidence interval is 76.29± 1.52
B) 90% confidence interval is 77.97.
C) 90% confidence interval is between 74.61 and 77.97.
D) 90% confidence interval is 76.29± 1.684.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In a sample of 19, and x¯= 81, with a standard deviation of s = 7, the standard error of the sample mean is
A) 0.684
B) 1.606
C) 1.725
D) 2.717
A) 0.684
B) 1.606
C) 1.725
D) 2.717

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
<p>In a sample of 9, and<em> 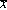 = 76, with a standard deviation of s = 5, the standard error of the sample mean is
= 76, with a standard deviation of s = 5, the standard error of the sample mean is
A) 0.745
B) 1.667
C) 1.786
D) 2.778
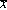 = 76, with a standard deviation of s = 5, the standard error of the sample mean is
= 76, with a standard deviation of s = 5, the standard error of the sample mean isA) 0.745
B) 1.667
C) 1.786
D) 2.778

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a sample of 33, 9 were found to have over 200 Blu-Ray Discs in one location. Construct the point estimate for the population proportion.
A) 0.54
B) 0.01
C) 0.14
D) 0.27
A) 0.54
B) 0.01
C) 0.14
D) 0.27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In a sample of 30, 9 were found to have over 200 Blu-Ray Discs in one location. Construct the point estimate for the population proportion.
A) 0.60
B) 0.045
C) 0.15
D) 0.30
A) 0.60
B) 0.045
C) 0.15
D) 0.30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In a sample of 23 iPhones, 10 had over 83 apps downloaded. Construct a 90% confidence interval for the population proportion of all iPhones that obtain over 83 apps. Assume z0.05 = 1.645.
A) 0.43± 0.17
B) 0.43± 0.08
C) 0.27± 0.16
D) 0.27± 0.17
A) 0.43± 0.17
B) 0.43± 0.08
C) 0.27± 0.16
D) 0.27± 0.17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In a sample of 25 iPhones, 12 had over 85 apps downloaded. Construct a 90% confidence interval for the population proportion of all iPhones that obtain over 85 apps. Assume z0.05 = 1.645.
A) 0.48± 0.16
B) 0.48± 0.09
C) 0.29± 0.15
D) 0.29± 0.16
A) 0.48± 0.16
B) 0.48± 0.09
C) 0.29± 0.15
D) 0.29± 0.16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a sample of 62 iPhones, 18 had over 100 apps downloaded. Construct a 99% confidence interval for the population proportion of all iPhones that obtain over 100 apps. Assume z0.005 = 2.576.
A) 0.18± 0.15
B) 0.18± 0.09
C) 0.29± 0.14
D) 0.29± 0.15
A) 0.18± 0.15
B) 0.18± 0.09
C) 0.29± 0.14
D) 0.29± 0.15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a sample of 50 iPhones, 13 had over 100 apps downloaded. Construct a 99% confidence interval for the population proportion of all iPhones that obtain over 100 apps. Assume z0.005 = 2.576.
A) 0.13± 0.16
B) 0.13± 0.09
C) 0.26± 0.15
D) 0.26± 0.16
A) 0.13± 0.16
B) 0.13± 0.09
C) 0.26± 0.15
D) 0.26± 0.16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to the National Retail Federation, the average shopper will spend $1,007.24 during the holiday shopping season. What is the null and alternate hypothesis?
A) Sample Population is needed to complete the hypothesis.
B) H0: 1007.24; HA = 1007.24
C) H0: 1007.24; HA 1007.24
D) H0: = 1007.24; HA 1007.24
A) Sample Population is needed to complete the hypothesis.
B) H0: 1007.24; HA = 1007.24
C) H0: 1007.24; HA 1007.24
D) H0: = 1007.24; HA 1007.24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Peter provided an analysis for the building of a multi-unit retail strip for Corning Construction using the following hypothesis:H0: = Do not build the Strip Mall; Build the Strip Mall. Based on his calculations of the area, and the probabilities for growth, he shows the project will be profitable. The client built the strip mall to a profit loss. What type of error would this represent?
A) Type I error because the building was built.
B) Type II error because the building was built.
C) Type I error because the building was built, but it was not profitable.
D) Type II error because the building was built and was profitable.
A) Type I error because the building was built.
B) Type II error because the building was built.
C) Type I error because the building was built, but it was not profitable.
D) Type II error because the building was built and was profitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Using R, what function is used to denote the hypothesized value of the mean?
A) alternative
B) option conf.
C) t.test
D) mu
A) alternative
B) option conf.
C) t.test
D) mu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In a sample of 530 students, 80% prefer online resources versus printed materials. The standard error for the sample proportion is
A) 0.003
B) 0.017
C) 0.013
D) 0.040
A) 0.003
B) 0.017
C) 0.013
D) 0.040

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In a sample of 500 students, 80% prefer online resources versus printed materials. The standard error for the sample proportion is
A) 0.002
B) 0.018
C) 0.014
D) 0.040
A) 0.002
B) 0.018
C) 0.014
D) 0.040

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which one of the following is not a characteristic of t distribution?
A) t distribution is defined by the degrees of freedom.
B) t distribution is bell-shaped.
C) t distribution is symmetric along zero.
D) t distribution is commonly known as population mean.
A) t distribution is defined by the degrees of freedom.
B) t distribution is bell-shaped.
C) t distribution is symmetric along zero.
D) t distribution is commonly known as population mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
According to the United States Census Bureau, the average single-family home constructed in 2016 was 2,438 square feet. Carmen wondered if families in her area still want a smaller home in comparison to the average. She randomly selected 45 people and asked what the ideal square footage of a home is for them. From the responses, she calculated the sample mean equals 1,550 square feet with a sample standard deviation of 54 square feet. What are the competing hypotheses?
A) H0: 2,438;HA = 2,438
B) H0: 1,550; HA = 1,550
C) H0: 2,438; HA < 2,438
D) H0: = 1,550; HA 1,550
A) H0: 2,438;HA = 2,438
B) H0: 1,550; HA = 1,550
C) H0: 2,438; HA < 2,438
D) H0: = 1,550; HA 1,550

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
According to the United States Census Bureau, the average single-family home constructed in 2016 was 2,431 square feet. Carmen wondered if families in her area still want a smaller home in comparison to the average. She randomly selected 67 people and asked what the ideal square footage of a home is for them. From the responses, she calculated the sample mean equals 1,390 square feet with a sample standard deviation of 65 square feet. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
A) -0.83
B) 1.82
C) -1.96
D) 0.83
A) -0.83
B) 1.82
C) -1.96
D) 0.83

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
According to the United States Census Bureau, the average single-family home constructed in 2016 was 2,438 square feet. Carmen wondered if families in her area still want a smaller home in comparison to the average. She randomly selected 45 people and asked what the ideal square footage of a home is for them. From the responses, she calculated the sample mean equals 1,550 square feet with a sample standard deviation of 54 square feet. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
A) -110.32
B) 110.54
C) -2.45
D) 1.32
A) -110.32
B) 110.54
C) -2.45
D) 1.32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If t34 = -4.322 and ? = 0.05, then what is the approximate of the p-value for a left-tailed test?
A) P(T34 -4.322) < 0.005.
B) P(T34 -4.322) < 0.05.
C) P(T34 - 4.322) < 0.05.
D) P(T34 4.322) < 0.50.
A) P(T34 -4.322) < 0.005.
B) P(T34 -4.322) < 0.05.
C) P(T34 - 4.322) < 0.05.
D) P(T34 4.322) < 0.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What does = 0.01 reflect?
A) There is a 1% chance of rejecting a true null hypothesis.
B) There is a 1% chance of accepting a true null hypothesis.
C) Without an identified , there is no significant meaning.
D) The 1% is the highest significance level.
A) There is a 1% chance of rejecting a true null hypothesis.
B) There is a 1% chance of accepting a true null hypothesis.
C) Without an identified , there is no significant meaning.
D) The 1% is the highest significance level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In a World Atlas study, 10% of people have blue eye color. Lane decided to observe 35 people and she concluded 6 people had blue eyes. Calculate the z-score.
A) 0.1714
B) 0.0710
C) 1.4086
D) 0.5675
A) 0.1714
B) 0.0710
C) 1.4086
D) 0.5675

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In a World Atlas study, 10% of people have blue eye color. Lane decided to observe 35 people and she concluded 5 people had blue eyes. Calculate the z-score.
A) 0.1428
B) 0.0430
C) 0.8452
D) 0.0041
A) 0.1428
B) 0.0430
C) 0.8452
D) 0.0041

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a 2019 Quinnipiac University poll of registered voters, 52% oppose making all U.S public colleges free. The Glangariff Group in Michigan collected data from 600 voters, where 342 support a taxpayer-funded free college program. What is the competing hypothesis?
A) H0:p = 0.52; HA:p 0.52
B) H0 = 0.51; HA 0.51
C) H0:p = 0.51; HA:p 0.51
D) H0:p = 0.57; HA:p 0.57
A) H0:p = 0.52; HA:p 0.52
B) H0 = 0.51; HA 0.51
C) H0:p = 0.51; HA:p 0.51
D) H0:p = 0.57; HA:p 0.57

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In a 2019 Quinnipiac University poll of registered voters, 58% oppose making all U.S public colleges free. The Glangariff Group in Michigan collected data from 610 voters, where 375 support a taxpayer-funded free college program. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
A) 1.38
B) 1.74
C) 11.31
D) 1.33
A) 1.38
B) 1.74
C) 11.31
D) 1.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In a 2019 Quinnipiac University poll of registered voters, 52% oppose making all US public colleges free. The Glangariff Group in Michigan collected data from 600 voters, where 342 support a taxpayer-funded free college program. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
A) 2.09
B) 2.45
C) 12.02
D) 2.04
A) 2.09
B) 2.45
C) 12.02
D) 2.04

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A p-value of 0.07698 was reported for a study with a 10% significance level. Should the null hypothesis be accepted or rejected?
A) Accept the null hypothesis because the p-value = 0.07698 is part of = 0.10
B) Accept the null hypothesis because the p-value = 0.07698 is less than = 0.10
C) Reject the null hypothesis because the p-value = 0.07698 is less than = 0.10
D) Not enough information to determine.
A) Accept the null hypothesis because the p-value = 0.07698 is part of = 0.10
B) Accept the null hypothesis because the p-value = 0.07698 is less than = 0.10
C) Reject the null hypothesis because the p-value = 0.07698 is less than = 0.10
D) Not enough information to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Many sample sizes can be drawn from a population, but there is only one overall population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The value of the sample mean will remain static even when the data set from the population is changed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
<p>The sampling distribution of P is closely related to the normal distribution.< / p>

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In general, a normal distribution approximation is justified for the sample proportion when np 5 and n (1 - p) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The more degrees of freedom, the broader the tails of the distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
With a df = 20, and = 0.05 and a referencing table value of 1.74742, the upper tail suggests that P(T20 1.74742) = 0.05.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The population proportion p is the essential measure for a quantitative variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An alternative hypothesis, denotedHA , is defined as the contradiction of the default state or status quo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In performing a test statistic for p, the formula is only valid if P </em> (approximately) follows a normal distribution.</ p>

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



