Deck 7: Translating and Consolidating Subsidiary Financial Statements
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Translating and Consolidating Subsidiary Financial Statements
1
Which of the following statements are correct?
A) On the balance sheet, monetary items include cash and marketable securities on the assets side and investor supplied debt capital on the passive side. All other entries are nonmonetary.
B) Monetary items are denominated in nominal money units while nonmonetary items can only be measured in nominal money units.
C) When exchange rates change, the real value of nonmonetary items tends to be preserved to a greater extent than if the items were monetary in nature.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements b and c are correct.
A) On the balance sheet, monetary items include cash and marketable securities on the assets side and investor supplied debt capital on the passive side. All other entries are nonmonetary.
B) Monetary items are denominated in nominal money units while nonmonetary items can only be measured in nominal money units.
C) When exchange rates change, the real value of nonmonetary items tends to be preserved to a greater extent than if the items were monetary in nature.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements b and c are correct.
Only statements b and c are correct.
2
Regarding translation methodologies, which of the following statements are correct?
A) The current spot exchange rate is always used to translate monetary assets and liabilities in all permitted translation methods.
B) Equity accounts are always translated at a weighted average historical exchange rate in all permitted translation methods.
C) The current rate method for translating financial statements almost always results in a net asset exposure.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements b and c are correct.
A) The current spot exchange rate is always used to translate monetary assets and liabilities in all permitted translation methods.
B) Equity accounts are always translated at a weighted average historical exchange rate in all permitted translation methods.
C) The current rate method for translating financial statements almost always results in a net asset exposure.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements b and c are correct.
All of the statements above are correct.
3
If the temporal method for translating foreign currency financial statements into the reporting or functional currency is used, then
A) Any gains or losses must flow through the income statement and affect directly the amount of net income reported.
B) The current spot exchange rate on the statement date is used to translate all monetary items.
C) A decrease in the value of the local currency relative to the reporting or functional currency will always result in a translation loss.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements a and b are correct.
A) Any gains or losses must flow through the income statement and affect directly the amount of net income reported.
B) The current spot exchange rate on the statement date is used to translate all monetary items.
C) A decrease in the value of the local currency relative to the reporting or functional currency will always result in a translation loss.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements a and b are correct.
Only statements a and b are correct.
4
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) An operating unit located in another country that operates as a separate going concern and is largely independent of the parent has the local currency as its functional currency and its financial statements in this case are translated using the current rate method.
B) An operating unit located in another country that functions as an extension of the parent and whose cash flows are interrelated with those of the parent has the local currency as its functional currency and its financial statements in this case are translated using the temporal method.
C) When translating from a local currency into a functional currency, the procedure is called remeasuring the financial statements.
D) When translating from a functional currency into a reporting currency, the procedure is called restating the financial statements.
E) None of the statements above; all are correct correct.
A) An operating unit located in another country that operates as a separate going concern and is largely independent of the parent has the local currency as its functional currency and its financial statements in this case are translated using the current rate method.
B) An operating unit located in another country that functions as an extension of the parent and whose cash flows are interrelated with those of the parent has the local currency as its functional currency and its financial statements in this case are translated using the temporal method.
C) When translating from a local currency into a functional currency, the procedure is called remeasuring the financial statements.
D) When translating from a functional currency into a reporting currency, the procedure is called restating the financial statements.
E) None of the statements above; all are correct correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When a country experiences hyperinflation, special challenges are created for accounting and extraordinary measures are required to preserve the economic integrity of financial statements. Which of the following statements about the accounting treatment of hyperinflation is incorrect?
A) If a country is experiencing hyperinflation, loosely defined as cumulative annual inflation of approximately 100 percent over three years, then the FASB in the U.S. requires that the U.S. dollar be deemed the functional currency, the financial statements are remeasured into dollars using the temporal method, and gains or losses are recorded in the cumulative translation adjustment or CTA account.
B) The treatment of hyperinflation under international accounting standards differs from the procedure in the U.S. in the sense that in local currency financial statements, nonmonetary assets are "grossed up" or restated in current-value money units by applying an inflation index (such as the consumer price index or CPI) adjustment.
C) The bias caused by hyperinflation exists when nonmonetary assets are listed on the balance sheet (and the associated depreciation on the income statement) at historical costs, and when inflation is high the accounting records no longer approximate their real economic value-in fact, they will be grossly undervalued.
D) The problem with the financial statements caused by hyperinflation is that the local money unit no longer serves as a stable storehouse of value (which is implicitly assumed to be the case in accounting), so the procedures required by both FASB and IASB are intended to restore this real economic stability.
E) None of the statements above; all are correct correct.
A) If a country is experiencing hyperinflation, loosely defined as cumulative annual inflation of approximately 100 percent over three years, then the FASB in the U.S. requires that the U.S. dollar be deemed the functional currency, the financial statements are remeasured into dollars using the temporal method, and gains or losses are recorded in the cumulative translation adjustment or CTA account.
B) The treatment of hyperinflation under international accounting standards differs from the procedure in the U.S. in the sense that in local currency financial statements, nonmonetary assets are "grossed up" or restated in current-value money units by applying an inflation index (such as the consumer price index or CPI) adjustment.
C) The bias caused by hyperinflation exists when nonmonetary assets are listed on the balance sheet (and the associated depreciation on the income statement) at historical costs, and when inflation is high the accounting records no longer approximate their real economic value-in fact, they will be grossly undervalued.
D) The problem with the financial statements caused by hyperinflation is that the local money unit no longer serves as a stable storehouse of value (which is implicitly assumed to be the case in accounting), so the procedures required by both FASB and IASB are intended to restore this real economic stability.
E) None of the statements above; all are correct correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) in the U.S. uses what it calls a "functional currency approach" to differentiate among various intracorporate relationship scenarios and, on that basis, specify how financial statement translation must be done. The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) uses a different approach, but the end result is usually identical. Basically,
A) If an operating affiliate is classified as a "self-sustaining foreign entity," in the absence of hyperinflation, its functional currency will be its local currency and translation will be done using the current rate method.
B) If the functional currency is neither the local currency nor the reporting currency (assume the U.S. dollar), then the local currency financial statements must be remeasured into the functional currency using the temporal method and then restated into the U.S. dollar (the reporting currency) using the current rate method.
C) If an operating affiliate is classified as an "integrated foreign entity," in the absence of hyperinflation, its functional currency will be the reporting currency (U.S. dollar) and translation will be done using the temporal method.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements a and c are correct.
A) If an operating affiliate is classified as a "self-sustaining foreign entity," in the absence of hyperinflation, its functional currency will be its local currency and translation will be done using the current rate method.
B) If the functional currency is neither the local currency nor the reporting currency (assume the U.S. dollar), then the local currency financial statements must be remeasured into the functional currency using the temporal method and then restated into the U.S. dollar (the reporting currency) using the current rate method.
C) If an operating affiliate is classified as an "integrated foreign entity," in the absence of hyperinflation, its functional currency will be the reporting currency (U.S. dollar) and translation will be done using the temporal method.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements a and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
After all foreign entity financial statements have been translated into the reporting currency, they must be combined to prepare consolidated financial statements. This is a straight-forward process but several adjustments must be made prior to consolidation. These include
A) Cancellation of all accounts receivable and accounts payable.
B) Cancellation of short-term debts and marketable securities (on the assets side).
C) Cancellation of subsidiary equity and investment in subsidiaries (on the assets side).
D) All of the adjustments above must be made.
E) Only adjustments a and c must be made.
A) Cancellation of all accounts receivable and accounts payable.
B) Cancellation of short-term debts and marketable securities (on the assets side).
C) Cancellation of subsidiary equity and investment in subsidiaries (on the assets side).
D) All of the adjustments above must be made.
E) Only adjustments a and c must be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Accounting or translation exposures give rise to gains or losses (in most cases) if the exchange rate between the local currency and the reporting currency changes. When considering whether these exposures should be hedged, the following points are considered to be valid except
A) If the temporal method for translation is required, the gains or losses must flow through the income statement thus affecting taxes paid and reported net income.
B) Because it is possible that gains during one accounting period will be offset by losses during the next one, there is little reason to engage in costly economic transactions (even if the cost is low) to offset risks that might be reversed by themselves and, anyway, have no impact on economic cash flows.
C) If the company has debt covenants specifying minimum accounting ratios, because accounting gains and losses affect consolidated equity, it is conceivable that a debt ratio covenant could be violated if a company has significant translation losses, so hedging may deserve consideration.
D) If there is hyperinflation in a country and it is unlikely to be reversed in the future, then exposed assets will lose value and hedging may deserve consideration.
E) None of the statements above; all are correct.
A) If the temporal method for translation is required, the gains or losses must flow through the income statement thus affecting taxes paid and reported net income.
B) Because it is possible that gains during one accounting period will be offset by losses during the next one, there is little reason to engage in costly economic transactions (even if the cost is low) to offset risks that might be reversed by themselves and, anyway, have no impact on economic cash flows.
C) If the company has debt covenants specifying minimum accounting ratios, because accounting gains and losses affect consolidated equity, it is conceivable that a debt ratio covenant could be violated if a company has significant translation losses, so hedging may deserve consideration.
D) If there is hyperinflation in a country and it is unlikely to be reversed in the future, then exposed assets will lose value and hedging may deserve consideration.
E) None of the statements above; all are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Inflation introduces several types of distortions in accounting data, some of which have very real economic consequences for the firm. Which of the following statements regarding inflation is incorrect?
A) Nonmonetary assets that are carried at their historical cost, have substantially greater real economic value during periods of high inflation than implied by the current money unit, so if they are translated into the reporting currency using the current rate method, the dollar-equivalent amount does not reflect the real value of the underlying assets (they would be seriously undervalued).
B) When calculating taxable income for a period in which inflation was high, one uses current period revenues but deducts historical costs that were recorded when the purchasing power of the currency was higher. Hence, costs are understated, taxable income is overstated, and taxes due are overstated.
C) In periods of high inflation, the first-in-first-out or FIFO method for inventory valuation should be used to calculate taxable income so that old inventory, whose true economic value is higher than implied at the current value of the money unit, will be eliminated quickly from the accounting records and the company will not have to take a large loss when their value is written down.
D) Accounting principles assume that the money unit in which the accounting records are maintained remains essentially stable over time, serves as a unit of exchange, and functions as a storehouse of value. These principles are violated during periods of high inflation, and that is why special accounting treatment is required during hyperinflation.
E) None of the statements above; all are correct.
A) Nonmonetary assets that are carried at their historical cost, have substantially greater real economic value during periods of high inflation than implied by the current money unit, so if they are translated into the reporting currency using the current rate method, the dollar-equivalent amount does not reflect the real value of the underlying assets (they would be seriously undervalued).
B) When calculating taxable income for a period in which inflation was high, one uses current period revenues but deducts historical costs that were recorded when the purchasing power of the currency was higher. Hence, costs are understated, taxable income is overstated, and taxes due are overstated.
C) In periods of high inflation, the first-in-first-out or FIFO method for inventory valuation should be used to calculate taxable income so that old inventory, whose true economic value is higher than implied at the current value of the money unit, will be eliminated quickly from the accounting records and the company will not have to take a large loss when their value is written down.
D) Accounting principles assume that the money unit in which the accounting records are maintained remains essentially stable over time, serves as a unit of exchange, and functions as a storehouse of value. These principles are violated during periods of high inflation, and that is why special accounting treatment is required during hyperinflation.
E) None of the statements above; all are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A U.S.-based MNE has four operating units/subsidiaries in the U.S., Mexico, Germany, and Poland. The following are the operating relationships existing among them: 1. The U.S. supplies all production inputs to Mexico except for labor (invoiced in dollars) and all Mexican production is sold to the U.S. parent and invoiced in dollars.
2) Germany supplies all production inputs to Poland except for labor (invoiced in euros) and all Polish production is sold to Germany and is invoiced in euros.
3) The global marketplace for the company's products is divided into two non-overlapping areas, one supplied from the U.S. and the other one from Germany. Only when demand is particularly high in one region or the other is part of it supplied by other than the designated supplier.
In order to prepare consolidate financial statements, each subsidiary's financial statements must be translated into the reporting currency (the U.S. dollar). For each subsidiary, the functional currency is __________ and the required translation method is _______________.
A) U.S.: dollar, none; Mexico: peso, current rate; Germany: euro, current rate; Poland: zloty, current rate.
B) U.S.: dollar, none; Mexico: dollar, temporal; Germany: euro, current rate; Poland: euro, temporal to euros then current rate to dollars.
C) U.S.: dollar, none; Mexico: dollar, current rate; Germany: euro, current rate; Poland: dollar, temporal.
D) U.S.: dollar, none; Mexico: peso, temporal; Germany: euro, current rate; Poland: euro, current rate to euros then temporal to dollars.
E) None of the statements above is correct.
2) Germany supplies all production inputs to Poland except for labor (invoiced in euros) and all Polish production is sold to Germany and is invoiced in euros.
3) The global marketplace for the company's products is divided into two non-overlapping areas, one supplied from the U.S. and the other one from Germany. Only when demand is particularly high in one region or the other is part of it supplied by other than the designated supplier.
In order to prepare consolidate financial statements, each subsidiary's financial statements must be translated into the reporting currency (the U.S. dollar). For each subsidiary, the functional currency is __________ and the required translation method is _______________.
A) U.S.: dollar, none; Mexico: peso, current rate; Germany: euro, current rate; Poland: zloty, current rate.
B) U.S.: dollar, none; Mexico: dollar, temporal; Germany: euro, current rate; Poland: euro, temporal to euros then current rate to dollars.
C) U.S.: dollar, none; Mexico: dollar, current rate; Germany: euro, current rate; Poland: dollar, temporal.
D) U.S.: dollar, none; Mexico: peso, temporal; Germany: euro, current rate; Poland: euro, current rate to euros then temporal to dollars.
E) None of the statements above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Culverson Manufacturing had sales of $150 million last year. It is deciding whether to use FIFO or LIFO to value its inventory costs. If FIFO is used, the inventory cost is $120 million, but if LIFO is used, the inventory cost is $132 million. The firm's marginal tax rate is 40 percent. If the LIFO method is used over the FIFO method, what is the change in net inflow the company realizes?
A) +$2.6 million
B) +$3.8 million
C) +$4.8 million
D) +$6.2 million
E) +$7.6 million
A) +$2.6 million
B) +$3.8 million
C) +$4.8 million
D) +$6.2 million
E) +$7.6 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Tomlinson Industries had sales of $162 million last year. It is analyzing the difference in cash flows between certain inventory valuation methods. It is looking at both the FIFO and replacement cost valuation methods. If FIFO is used, the inventory cost is $135 million, but if the replacement value method is used, the inventory cost is $157 million. The firm's marginal tax rate is 40 percent. If the LIFO method is used over the replacement value method, what is the change in net inflow the company would realize?
A) -$5.4 million
B) +$6.2 million
C) -$6.8 million
D) +$7.2 million
E) -$8.8 million
A) -$5.4 million
B) +$6.2 million
C) -$6.8 million
D) +$7.2 million
E) -$8.8 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Differentiate between local, functional, and reporting currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is a balance sheet hedge?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the difference between remeasuring and restating financial statements?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Why is it important for financial managers to have a basic understanding of the financial statement translation and consolidation process?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Differentiate between the current rate and temporal translation methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How do the current rate and temporal methods handle translation gains and losses?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What unique characteristics does the cumulative translation adjustment (CTA) account possess?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Differentiate between self-sustaining and integrated foreign subsidiaries, and describe how financial statements are translated differently in each case.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a subsidiary is in a country with dangerously high inflation, how should the translation of its financial statements be handled? Consider both FASB and IASB procedures in your discussion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How does a company develop a hedged balance sheet?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Generally speaking, accounting translation gains and losses have no economic impact on the firm's cash flows and do not reflect a change in the firm's value. What are some exceptions to this conclusion?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Witten Publishing, a U.S. multinational, has a subsidiary in Mexico with the following balance sheet (denominated in pesos).
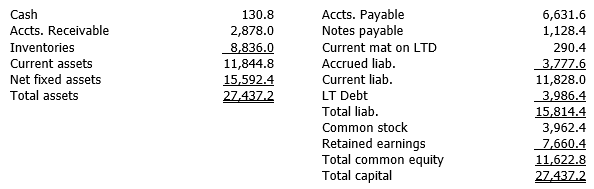 The spot exchange rate is $0.097430/peso. The company's CFO has estimated the following average exchange rates for inventories, fixed assets, common stock, and retained earnings: $0.109240, $0.103580, $0.101160, and $0.121641, respectively. The subsidiary is classified as an integrated foreign entity. Translate the balance sheet into U.S. dollars, which is the reporting currency. (Hint: Depending upon the translation method used, all of the exchange rates may not be used.)
The spot exchange rate is $0.097430/peso. The company's CFO has estimated the following average exchange rates for inventories, fixed assets, common stock, and retained earnings: $0.109240, $0.103580, $0.101160, and $0.121641, respectively. The subsidiary is classified as an integrated foreign entity. Translate the balance sheet into U.S. dollars, which is the reporting currency. (Hint: Depending upon the translation method used, all of the exchange rates may not be used.)
Financial statement translation Diff: T
 The spot exchange rate is $0.097430/peso. The company's CFO has estimated the following average exchange rates for inventories, fixed assets, common stock, and retained earnings: $0.109240, $0.103580, $0.101160, and $0.121641, respectively. The subsidiary is classified as an integrated foreign entity. Translate the balance sheet into U.S. dollars, which is the reporting currency. (Hint: Depending upon the translation method used, all of the exchange rates may not be used.)
The spot exchange rate is $0.097430/peso. The company's CFO has estimated the following average exchange rates for inventories, fixed assets, common stock, and retained earnings: $0.109240, $0.103580, $0.101160, and $0.121641, respectively. The subsidiary is classified as an integrated foreign entity. Translate the balance sheet into U.S. dollars, which is the reporting currency. (Hint: Depending upon the translation method used, all of the exchange rates may not be used.)Financial statement translation Diff: T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Gard Tennis Supply, a U.S. multinational, has a subsidiary in France with the following balance sheet (denominated in euros).
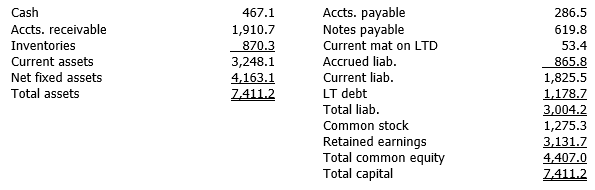 The spot exchange rate is $0.97380/euro. The company's CFO has estimated the following average exchange rates for inventories, fixed assets, common stock, and retained earnings: $0.96152, $0.9558, $1.1041, and $1.0853, respectively. The subsidiary is classified as a self-sustaining foreign entity. Translate the balance sheet into U.S. dollars, which is the reporting currency. (Hint: Depending upon the translation method used, all of the exchange rates may not be used.)
The spot exchange rate is $0.97380/euro. The company's CFO has estimated the following average exchange rates for inventories, fixed assets, common stock, and retained earnings: $0.96152, $0.9558, $1.1041, and $1.0853, respectively. The subsidiary is classified as a self-sustaining foreign entity. Translate the balance sheet into U.S. dollars, which is the reporting currency. (Hint: Depending upon the translation method used, all of the exchange rates may not be used.)
 The spot exchange rate is $0.97380/euro. The company's CFO has estimated the following average exchange rates for inventories, fixed assets, common stock, and retained earnings: $0.96152, $0.9558, $1.1041, and $1.0853, respectively. The subsidiary is classified as a self-sustaining foreign entity. Translate the balance sheet into U.S. dollars, which is the reporting currency. (Hint: Depending upon the translation method used, all of the exchange rates may not be used.)
The spot exchange rate is $0.97380/euro. The company's CFO has estimated the following average exchange rates for inventories, fixed assets, common stock, and retained earnings: $0.96152, $0.9558, $1.1041, and $1.0853, respectively. The subsidiary is classified as a self-sustaining foreign entity. Translate the balance sheet into U.S. dollars, which is the reporting currency. (Hint: Depending upon the translation method used, all of the exchange rates may not be used.)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



