Deck 15: Interest Rates and Monetary Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Interest Rates and Monetary Policy
1
The asset demand for money and the rate of interest are:
A) inversely related.
B) directly related.
C) unrelated.
D) both stable.
A) inversely related.
B) directly related.
C) unrelated.
D) both stable.
inversely related.
2
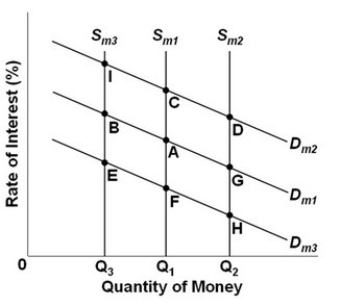
- Refer to the above graph, which shows the supply and demand for money where Dm1, Dm2, and Dm3 represent different demands for money and Sm1, Sm2, and Sm3 represent different levels of the money supply. The initial equilibrium point is A. What will be the new equilibrium point following an increase in the asset demand for money?
A) C.
B) D.
C) G.
D) I.
C.
3
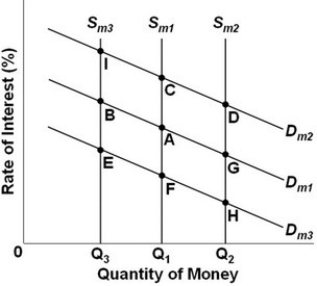
- Refer to the above graph, which shows the supply and demand for money where Dm1, Dm2, and Dm3 represent different demands for money and Sm1, Sm2, and Sm3 represent different levels of the money supply. The initial equilibrium point is A. What will be the new equilibrium point following a decrease in the asset demand for money?
A) B.
B) E.
C) F.
D) I.
F.
4
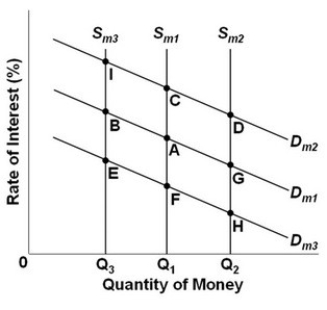
-Refer to the above graph, which shows the supply and demand for money where Dm1, Dm2, and Dm3 represent different demands for money and Sm1, Sm2, and Sm3 represent different levels of the money supply. The initial equilibrium point is A. What will be the new equilibrium point following an increase in the money supply?
A) C.
B) D.
C) G.
D) H.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
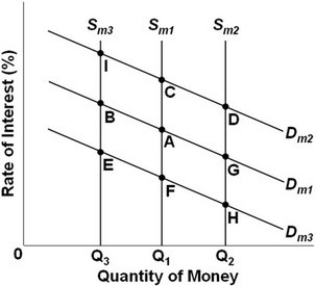
- Refer to the above graph, which shows the supply and demand for money where Dm1, Dm2, and Dm3 represent different demands for money and Sm1, Sm2, and Sm3 represent different levels of the money supply. The initial equilibrium point is A. What will be the new equilibrium point following a decrease in the money supply?
A) B.
B) E.
C) F.
D) I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
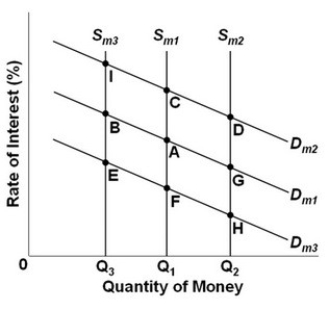
-Refer to the above graph, which shows the supply and demand for money where Dm1, Dm2, and Dm3 represent different demands for money and Sm1, Sm2, and Sm3 represent different levels of the money supply. The initial equilibrium point is A. What will be the new equilibrium point following a decrease in both the asset demand for money and the money supply?
A) B.
B) E.
C) F.
D) I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If interest rates rise, there will be a(n):
A) increase in the total amount of money demanded.
B) decrease in the total amount of money demanded.
C) decrease in the total amount of money supplied.
D) increase in the asset demand for money.
A) increase in the total amount of money demanded.
B) decrease in the total amount of money demanded.
C) decrease in the total amount of money supplied.
D) increase in the asset demand for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
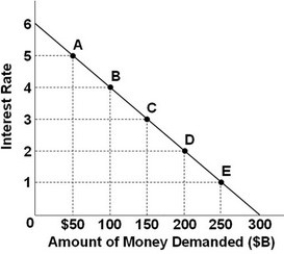 Refer to the above graph. If the Federal Reserve wants to lower the interest rate from 4 percent to 1 percent, how much must it increase the money supply?
Refer to the above graph. If the Federal Reserve wants to lower the interest rate from 4 percent to 1 percent, how much must it increase the money supply?A) $100 billion.
B) $200 billion.
C) $150 billion.
D) $250 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the interest rate is above equilibrium, the:
A) quantity of money demanded would be greater than the quantity of money supplied.
B) quantity of money demanded would be less than the quantity of money supplied.
C) supply of money would increase and the demand for money would decrease.
D) demand for money would increase and the supply of money would decrease.
A) quantity of money demanded would be greater than the quantity of money supplied.
B) quantity of money demanded would be less than the quantity of money supplied.
C) supply of money would increase and the demand for money would decrease.
D) demand for money would increase and the supply of money would decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the demand for money and the supply of money both increase, then the new equilibrium:
A) quantity of money and the interest rate will both increase.
B) quantity of money and the interest rate will both decrease.
C) quantity of money will increase, but the change in the interest rate cannot be predicted.
D) interest rate will increase, but the change in the interest rate cannot be predicted.
A) quantity of money and the interest rate will both increase.
B) quantity of money and the interest rate will both decrease.
C) quantity of money will increase, but the change in the interest rate cannot be predicted.
D) interest rate will increase, but the change in the interest rate cannot be predicted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The tools of monetary policy for altering the reserves of commercial banks are the:
A) tax rate and level of government spending.
B) Consumer Price Index and unemployment rate.
C) public debt, budget surplus, and budget deficit.
D) discount rate, reserve ratio, open-market operations, and interest on excess reserves.
A) tax rate and level of government spending.
B) Consumer Price Index and unemployment rate.
C) public debt, budget surplus, and budget deficit.
D) discount rate, reserve ratio, open-market operations, and interest on excess reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System can encourage the lending of commercial bank excess reserves by:
A) increasing the discount rate.
B) increasing the reserve ratio.
C) decreasing the prime interest rate.
D) lowering the interest rate on excess reserves.
A) increasing the discount rate.
B) increasing the reserve ratio.
C) decreasing the prime interest rate.
D) lowering the interest rate on excess reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the Federal Reserve raises the interest rate on excess reserves, this will:
A) expand the money supply.
B) encourage commercial banks to lend excess reserves.
C) decrease the prime interest rate.
D) discourage commercial banks from lending excess reserves.
A) expand the money supply.
B) encourage commercial banks to lend excess reserves.
C) decrease the prime interest rate.
D) discourage commercial banks from lending excess reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When the Fed undertakes a repo transaction:
A) it pulls excess reserves out of the financial system.
B) banks have defaulted on loans, prompting the Fed to repossess assets of the bank.
C) it borrows money, using government bonds for collateral.
D) it loans money in exchange for government bonds being posted as collateral.
A) it pulls excess reserves out of the financial system.
B) banks have defaulted on loans, prompting the Fed to repossess assets of the bank.
C) it borrows money, using government bonds for collateral.
D) it loans money in exchange for government bonds being posted as collateral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Repurchase agreements by the Fed:
A) are used primarily to ease inflationary pressure.
B) were temporarily implemented during the financial crisis as a way for the Fed to consolidate failing banks.
C) are a contractionary form of open market operations.
D) are an expansionary form of open market operations.
A) are used primarily to ease inflationary pressure.
B) were temporarily implemented during the financial crisis as a way for the Fed to consolidate failing banks.
C) are a contractionary form of open market operations.
D) are an expansionary form of open market operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is an example of a tight money policy action?
A) Reverse repo transactions.
B) Repo transactions.
C) Lowering the interest rate paid on excess reserves.
D) Quantitative easing.
A) Reverse repo transactions.
B) Repo transactions.
C) Lowering the interest rate paid on excess reserves.
D) Quantitative easing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the Fed buys government securities from the public in the open market:
A) the Fed gives the securities to the public; the public pays for the securities by writing checks that when cleared will increase commercial bank reserves at the Fed.
B) the Fed gives the securities to the public; the public pays for them by writing checks that when cleared will decrease commercial bank reserves at the Fed.
C) the public gives the securities to the Fed; the Fed pays for the securities by check, which when deposited at commercial banks will increase their reserves at the Fed.
D) the public gives the securities to the Fed; the Fed pays for the securities by check, which when deposited at commercial banks will decrease their reserves at the Fed.
A) the Fed gives the securities to the public; the public pays for the securities by writing checks that when cleared will increase commercial bank reserves at the Fed.
B) the Fed gives the securities to the public; the public pays for them by writing checks that when cleared will decrease commercial bank reserves at the Fed.
C) the public gives the securities to the Fed; the Fed pays for the securities by check, which when deposited at commercial banks will increase their reserves at the Fed.
D) the public gives the securities to the Fed; the Fed pays for the securities by check, which when deposited at commercial banks will decrease their reserves at the Fed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the Fed sells government securities to commercial banks in the open market:
A) the Fed gives the securities to the commercial banks, and the commercial banks pay for them by writing a check that increases their reserves at the Fed.
B) the Fed gives the securities to the commercial banks, and commercial banks pay for them by writing a check that decreases their reserves at the Fed.
C) commercial banks give the securities to the Fed, and the Fed pays for them by increasing the reserves of commercial banks at the Fed.
D) commercial banks give the securities to the Fed, and the Fed pays for them by decreasing the reserves of commercial banks at the Fed.
A) the Fed gives the securities to the commercial banks, and the commercial banks pay for them by writing a check that increases their reserves at the Fed.
B) the Fed gives the securities to the commercial banks, and commercial banks pay for them by writing a check that decreases their reserves at the Fed.
C) commercial banks give the securities to the Fed, and the Fed pays for them by increasing the reserves of commercial banks at the Fed.
D) commercial banks give the securities to the Fed, and the Fed pays for them by decreasing the reserves of commercial banks at the Fed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the Fed sells government securities to the public in the open market:
A) the Fed gives the securities to the public; the public pays for the securities by writing checks that when cleared will increase commercial bank reserves at the Fed.
B) the Fed gives the securities to the public; the public pays for the securities by writing checks that when cleared will decrease commercial bank reserves at the Fed.
C) the public gives the securities to the Fed; the Fed pays for the securities by check, which when deposited at commercial banks will increase their reserves at the Fed.
D) the public gives the securities to the Fed; the Fed pays for the securities by check, which when deposited at commercial banks will decrease their reserves at the Fed.
A) the Fed gives the securities to the public; the public pays for the securities by writing checks that when cleared will increase commercial bank reserves at the Fed.
B) the Fed gives the securities to the public; the public pays for the securities by writing checks that when cleared will decrease commercial bank reserves at the Fed.
C) the public gives the securities to the Fed; the Fed pays for the securities by check, which when deposited at commercial banks will increase their reserves at the Fed.
D) the public gives the securities to the Fed; the Fed pays for the securities by check, which when deposited at commercial banks will decrease their reserves at the Fed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Assume the required reserve ratio is 20 percent. If the Federal Reserve buys $80 million in government securities from the public, then the money supply will immediately:
A) increase by $80 million, and the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will increase by $80 million.
B) increase by $80 million, but the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will decrease by $80 million.
C) increase by $80 million, and the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will increase by $400 million.
D) decrease because the securities are an asset to the commercial banks and a liability to the Federal Reserve.
A) increase by $80 million, and the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will increase by $80 million.
B) increase by $80 million, but the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will decrease by $80 million.
C) increase by $80 million, and the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will increase by $400 million.
D) decrease because the securities are an asset to the commercial banks and a liability to the Federal Reserve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Assume the required reserve ratio is 25 percent. If the Federal Reserve sells $120 million in government securities to the public, the money supply will immediately:
A) decrease by $120 million and the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will decrease by $120 million.
B) decrease by $120 million and the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will decrease by $480 million.
C) increase by $120 million and the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will increase by $480 million.
D) increase because the securities are an asset to the commercial banks and a liability to the Federal Reserve.
A) decrease by $120 million and the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will decrease by $120 million.
B) decrease by $120 million and the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will decrease by $480 million.
C) increase by $120 million and the maximum money-lending potential of the commercial banking system will increase by $480 million.
D) increase because the securities are an asset to the commercial banks and a liability to the Federal Reserve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Assume that there is a 25 percent reserve ratio and that the Federal Reserve buys $200 million worth of government securities. If the securities are purchased from the public, then this action has the potential to increase bank lending by a maximum of:
A) $600 million, and also by $600 million if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
B) $800 million, and also by $800 million if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
C) $600 million, but by $800 million if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
D) $800 million, but only by $600 million if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
A) $600 million, and also by $600 million if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
B) $800 million, and also by $800 million if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
C) $600 million, but by $800 million if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
D) $800 million, but only by $600 million if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Assume that there is a 25 percent reserve ratio and that the Federal Reserve buys $4 billion worth of government securities. If the securities are purchased from the public, this action has the potential to increase bank lending by a maximum of:
A) $4 billion, but only by $1 billion if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
B) $4 billion, but by $16 billion if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
C) $12 billion, or by $16 billion if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
D) $20 billion, or by $20 billion if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
A) $4 billion, but only by $1 billion if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
B) $4 billion, but by $16 billion if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
C) $12 billion, or by $16 billion if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.
D) $20 billion, or by $20 billion if the securities are purchased directly from commercial banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System decreases the interest paid on excess reserves, the primary effect of this change is to:
A) encourage commercial bank lending of excess reserves and increase the money supply.
B) discourage commercial bank lending of excess reserves and increase the money supply.
C) decrease the excess reserves of member banks and thus decrease the money supply.
D) increase the excess reserves of member banks and thus increase the money supply.
A) encourage commercial bank lending of excess reserves and increase the money supply.
B) discourage commercial bank lending of excess reserves and increase the money supply.
C) decrease the excess reserves of member banks and thus decrease the money supply.
D) increase the excess reserves of member banks and thus increase the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25

- Refer to the above graphs, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve, respectively. All numbers are in billions of dollars. The interest rate and the level of investment spending in the economy are at point D on the investment demand curve. To achieve the long-run goal of a noninflationary full-employment output Qf in the economy, the Fed should:
A) decrease aggregate demand by increasing the interest rate from 2 to 4 percent.
B) decrease aggregate demand by increasing the interest rate from 4 to 6 percent.
C) increase aggregate demand by decreasing the interest rate from 4 to 2 percent.
D) increase the level of investment spending from $120 billion to $150 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

- Refer to the above graphs, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve, respectively. All numbers are in billions of dollars. The interest rate and the level of investment spending in the economy are at point B on the investment demand curve. To achieve the long-run goal of a noninflationary full-employment output Qf in the economy, the Fed should:
A) decrease the interest rate from 10 to 8 percent.
B) decrease the interest rate from 8 to 6 percent.
C) decrease the interest rate from 6 to 4 percent.
D) increase investment spending from $30 to $60 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27

- Refer to the above graphs, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve, respectively. All numbers are in billions of dollars. The interest rate and the level of investment spending in the economy are at point C on the investment demand curve. To achieve the long-run goal of a noninflationary full-employment output Qf in the economy, the Fed should:
A) increase aggregate demand by increasing the interest rate.
B) decrease aggregate demand by increasing the interest rate.
C) increase aggregate demand by decreasing the interest rate.
D) make no change in the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
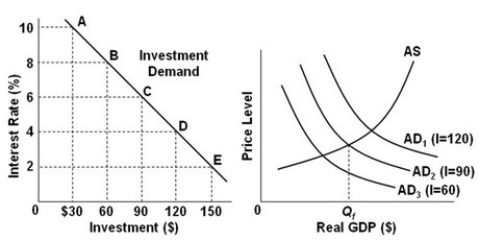
-Refer to the above graphs, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve, respectively. All numbers are in billions of dollars. The level of investment spending in the economy is $90 billion. What should the monetary authorities do to achieve the long-run goal of a noninflationary full-employment output Qf in the economy?
A) Increase the interest rate from 6 to 8 percent.
B) Decrease the interest rate from 8 to 6 percent.
C) Decrease the interest rate from 6 to 4 percent.
D) Make no change in the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the chain of cause and effect between changes in the excess reserves of commercial banks and the resulting changes in output and employment in the economy:
A) a decrease in aggregate demand will increase output.
B) an increase in the money supply will decrease the rate of interest.
C) a decrease in excess reserves will increase the money supply.
D) a decrease in the rate of interest will decrease aggregate demand.
A) a decrease in aggregate demand will increase output.
B) an increase in the money supply will decrease the rate of interest.
C) a decrease in excess reserves will increase the money supply.
D) a decrease in the rate of interest will decrease aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which would provide the most accurate description of events when monetary authorities increase the size of commercial banks' excess reserves?
A) A fall in interest rates decreases the money supply, causing an increase in investment spending, output, and employment.
B) A rise in interest rates increases the money supply, causing a decrease in investment spending, output, and employment.
C) The money supply is decreased, which increases the interest rate and causes investment spending, output, and employment to decrease.
D) The money supply is increased, which decreases the interest rate and causes investment spending, output, and employment to increase.
A) A fall in interest rates decreases the money supply, causing an increase in investment spending, output, and employment.
B) A rise in interest rates increases the money supply, causing a decrease in investment spending, output, and employment.
C) The money supply is decreased, which increases the interest rate and causes investment spending, output, and employment to decrease.
D) The money supply is increased, which decreases the interest rate and causes investment spending, output, and employment to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following best describes what occurs when monetary authorities sell government securities?
A) There is a decrease in the size of commercial banks' excess reserves, the money supply increases, and interest rates fall, thereby causing a decrease in investment spending and real GDP.
B) There is a decrease in the size of commercial banks' excess reserves, the money supply decreases, and interest rates rise, thereby causing a decrease in investment spending and real GDP.
C) There is a decrease in the size of commercial banks' excess reserves, the money supply decreases, and interest rates rise, thereby causing an increase in investment spending and real GDP.
D) There is an increase in the size of commercial bank reserves, the money supply increases, and interest rates fall, thereby causing an increase in investment spending and real GDP.
A) There is a decrease in the size of commercial banks' excess reserves, the money supply increases, and interest rates fall, thereby causing a decrease in investment spending and real GDP.
B) There is a decrease in the size of commercial banks' excess reserves, the money supply decreases, and interest rates rise, thereby causing a decrease in investment spending and real GDP.
C) There is a decrease in the size of commercial banks' excess reserves, the money supply decreases, and interest rates rise, thereby causing an increase in investment spending and real GDP.
D) There is an increase in the size of commercial bank reserves, the money supply increases, and interest rates fall, thereby causing an increase in investment spending and real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

- Refer to the above diagrams, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve. All figures are in billions. The interest rate in the economy is 4 percent. What should the Fed do to achieve a noninflationary full-employment level of real GDP (Qf)?
A) Increase the money supply from $75 to $150 billion.
B) Increase the money supply from $150 to $225 billion.
C) Decrease the money supply from $225 to $150 billion.
D) Make no change in the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
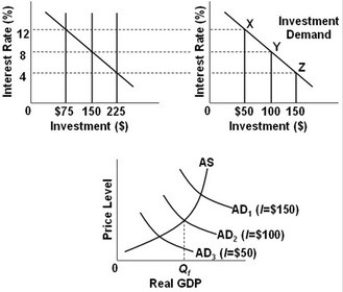
-Refer to the above diagrams, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve. All figures are in billions. The economy is at point X on the investment demand curve. Given these conditions, what policy should the Fed pursue to achieve a noninflationary full-employment level of real GDP (Qf)?
A) Decrease aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2.
B) Increase the money supply from $75 to $150 billion.
C) Increase interest rates from 4 to 8 percent.
D) Make no change in monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
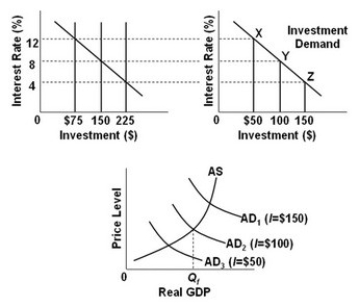
- Refer to the above diagrams, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve. All figures are in billions. The economy is at point Y on the investment demand curve. Given these conditions, what policy should the Fed pursue to achieve a noninflationary full-employment level of real GDP (Qf)?
A) Increase aggregate demand from AD3 to AD2.
B) Decrease the money supply from $225 to $150 billion.
C) Increase interest rates from 4 to 8 percent.
D) Make no change in monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
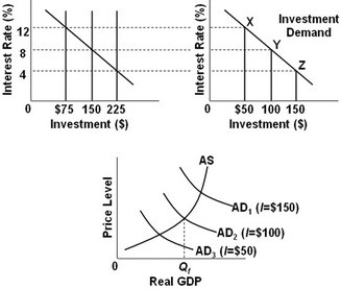
- Refer to the above diagrams, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve. All figures are in billions. The economy is at point Z on the investment demand curve. Given these conditions, what policy should the monetary authorities pursue to achieve a noninflationary full-employment level of real GDP (Qf)?
A) Decrease the reserve ratio.
B) Decrease the discount rate.
C) Sell government securities in the open market.
D) Make no change in monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
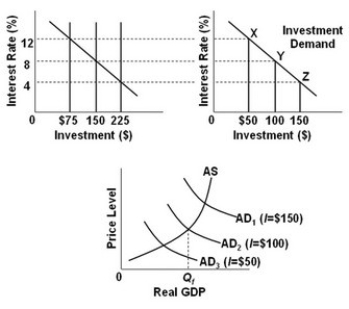
-Refer to the above diagrams, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the levels of investment spending associated with each curve. All figures are in billions. A shift in the aggregate demand curve from AD3 to AD2 can be achieved by Federal Reserve action to:
A) increase the interest rate paid on excess reserves.
B) increase the discount rate.
C) buy government securities in the open market.
D) sell government securities in the open market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
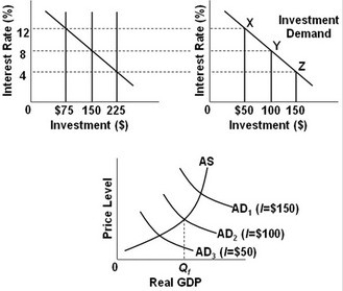
-Refer to the above diagrams, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the levels of investment spending associated with each curve. All figures are in billions. What is the desired level of investment spending in this economy if it is to achieve a noninflationary full-employment level of real GDP (Qf)?
A) $50.
B) $100.
C) $150.
D) $225.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If Federal Reserve officials attempt to pull the economy out of a recession when the price level is relatively stable, the policies they would most likely use would be to:
A) buy government securities and increase the discount rate.
B) sell government securities and decrease the discount rate.
C) buy government securities and decrease the discount rate.
D) sell government securities and increase the discount rate.
A) buy government securities and increase the discount rate.
B) sell government securities and decrease the discount rate.
C) buy government securities and decrease the discount rate.
D) sell government securities and increase the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Assume the economy faces high unemployment but stable prices. Which combination of government policies is most likely to reduce unemployment?
A) The purchase of government securities in the open market and an increase in taxes.
B) The sale of government securities in the open market and a decrease in taxes.
C) The sale of government securities in the open market and a decrease in government spending.
D) The purchase of government securities in the open market and an increase in government spending.
A) The purchase of government securities in the open market and an increase in taxes.
B) The sale of government securities in the open market and a decrease in taxes.
C) The sale of government securities in the open market and a decrease in government spending.
D) The purchase of government securities in the open market and an increase in government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The major problem facing the economy is high unemployment and weak economic growth. The inflation rate is low and stable. Therefore, the Federal Reserve decides to pursue a policy to increase the rate of economic growth. Which policy changes by the Fed would reinforce each other to achieve that objective?
A) Selling government securities and raising the discount rate.
B) Selling government securities and lowering the discount rate.
C) Buying government securities and lowering the interest rate paid on excess reserves.
D) Buying government securities and raising the reserve ratio.
A) Selling government securities and raising the discount rate.
B) Selling government securities and lowering the discount rate.
C) Buying government securities and lowering the interest rate paid on excess reserves.
D) Buying government securities and raising the reserve ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The major problem facing the economy is high unemployment and weak economic growth. The inflation rate is low and stable. Therefore, the Federal Reserve decides to pursue a policy to increase the rate of economic growth. Which policy changes by the Fed would tend to offset each other in trying to achieve that objective?
A) Selling government securities and raising the discount rate.
B) Selling government securities and raising the reserve ratio.
C) Buying government securities and raising the discount rate.
D) Buying government securities and lowering the reserve ratio.
A) Selling government securities and raising the discount rate.
B) Selling government securities and raising the reserve ratio.
C) Buying government securities and raising the discount rate.
D) Buying government securities and lowering the reserve ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Inflationary pressure is a growing problem for the economy. Therefore, the Federal Reserve decides to pursue a policy to reduce the inflationary pressure. Which policy changes by the Fed would reinforce each other to achieve that objective?
A) Selling government securities and raising the discount rate.
B) Selling government securities and lowering the discount rate.
C) Buying government securities and lowering the discount rate.
D) Buying government securities and lowering the reserve ratio.
A) Selling government securities and raising the discount rate.
B) Selling government securities and lowering the discount rate.
C) Buying government securities and lowering the discount rate.
D) Buying government securities and lowering the reserve ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Inflationary pressure is a growing problem for the economy. Therefore, the Federal Reserve decides to pursue a policy to reduce the inflationary pressure. Which policy changes by the Fed would reinforce each other to achieve that objective?
A) Selling government securities and raising the interest rate paid on excess reserves.
B) Selling government securities and lowering the discount rate.
C) Buying government securities and raising the discount rate.
D) Buying government securities and lowering the reserve ratio.
A) Selling government securities and raising the interest rate paid on excess reserves.
B) Selling government securities and lowering the discount rate.
C) Buying government securities and raising the discount rate.
D) Buying government securities and lowering the reserve ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Inflationary pressure is a growing problem for the economy. Therefore, the Federal Reserve decides to pursue a policy to reduce the inflationary pressure. Which policy changes by the Fed would tend to offset each other in trying to achieve that objective?
A) Selling government securities and raising the discount rate.
B) Selling government securities and lowering the discount rate.
C) Buying government securities and lowering the discount rate.
D) Buying government securities and lowering the reserve ratio.
A) Selling government securities and raising the discount rate.
B) Selling government securities and lowering the discount rate.
C) Buying government securities and lowering the discount rate.
D) Buying government securities and lowering the reserve ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In the chain of cause and effect between changes in the excess reserves of commercial banks and the resulting changes in output and employment in the economy:
A) a decrease in aggregate demand will increase output and employment.
B) a decrease in the rate of interest will decrease aggregate demand.
C) an increase in the money supply will decrease the rate of interest.
D) an increase in excess reserves will decrease the money supply.
A) a decrease in aggregate demand will increase output and employment.
B) a decrease in the rate of interest will decrease aggregate demand.
C) an increase in the money supply will decrease the rate of interest.
D) an increase in excess reserves will decrease the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Changes in the rate of interest will most likely affect:
A) the reserve ratio.
B) government spending.
C) investment spending.
D) aggregate supply.
A) the reserve ratio.
B) government spending.
C) investment spending.
D) aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which monetary policy would most likely increase aggregate demand?
A) Increasing reserve requirements at commercial banks and thrift institutions.
B) Increasing margin requirements on stock purchases.
C) Purchasing government securities in the open market.
D) Increasing the discount rate.
A) Increasing reserve requirements at commercial banks and thrift institutions.
B) Increasing margin requirements on stock purchases.
C) Purchasing government securities in the open market.
D) Increasing the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When the Federal Reserve acts to tighten money and credit in the economy, then the aggregate:
A) demand curve will shift to the right.
B) demand curve will shift to the left.
C) supply curve will shift to the left.
D) demand curve will stay the same but there will be a movement along the existing demand curve.
A) demand curve will shift to the right.
B) demand curve will shift to the left.
C) supply curve will shift to the left.
D) demand curve will stay the same but there will be a movement along the existing demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A Federal Reserve official notes: "A tight monetary policy can force a contraction of the money supply, but an expansionary monetary policy may not achieve an expansion of the economy." The official has described the problem of the:
A) inflexibility of monetary policy tools.
B) change in taxes on monetary policy.
C) cyclical asymmetry of monetary policy.
D) political acceptability of monetary policy.
A) inflexibility of monetary policy tools.
B) change in taxes on monetary policy.
C) cyclical asymmetry of monetary policy.
D) political acceptability of monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In a severe recession, the Fed's implementation of an easy money policy may have little to no impact on lending, borrowing, investment or aggregate demand. This describes the:
A) inflexibility of monetary policy tools.
B) lags that hinder monetary policy.
C) liquidity trap.
D) monetary political business cycle.
A) inflexibility of monetary policy tools.
B) lags that hinder monetary policy.
C) liquidity trap.
D) monetary political business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The term "liquidity trap" describes a situation where:
A) potential borrowers and lenders do not respond to expansionary monetary policies implemented during a recession.
B) excessive injections of money into the system create an inflationary cycle that is difficult to break.
C) nominal interest rates become negative.
D) political pressures prevent the Federal Reserve from implementing the appropriate monetary policy actions.
A) potential borrowers and lenders do not respond to expansionary monetary policies implemented during a recession.
B) excessive injections of money into the system create an inflationary cycle that is difficult to break.
C) nominal interest rates become negative.
D) political pressures prevent the Federal Reserve from implementing the appropriate monetary policy actions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The expression, "You can lead a horse to water, but you can't make it drink" is an analogy describing the:
A) inflexibility of monetary policy tools.
B) long operational lags faced by monetary policy.
C) liquidity trap.
D) long recognition lags faced by monetary policy.
A) inflexibility of monetary policy tools.
B) long operational lags faced by monetary policy.
C) liquidity trap.
D) long recognition lags faced by monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The acronym "ZIRP" stands for:
A) Zero inflation rate plan.
B) Zero investment returns problem.
C) Zero interest rate policy.
D) none of these.
A) Zero inflation rate plan.
B) Zero investment returns problem.
C) Zero interest rate policy.
D) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the Fed implements a zero interest rate policy, it will:
A) cause the U.S. dollar to appreciate against foreign currencies from nations with positive interest rates.
B) be in the pursuit of lower inflation.
C) set real interest rates at or near zero.
D) set nominal interest rates at or near zero.
A) cause the U.S. dollar to appreciate against foreign currencies from nations with positive interest rates.
B) be in the pursuit of lower inflation.
C) set real interest rates at or near zero.
D) set nominal interest rates at or near zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The Federal Reserve implemented a series of new policies and tools in response to the 2007-2008 financial crisis and recession. Which of those policies did the Fed continue to use after 2010?
A) Commercial Paper Lending Facility.
B) Primary Dealer Credit Facility.
C) Term Auction Facility.
D) Quantitative easing.
A) Commercial Paper Lending Facility.
B) Primary Dealer Credit Facility.
C) Term Auction Facility.
D) Quantitative easing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The Federal Reserve implemented a series of new policies and tools in response to the 2007-2008 financial crisis and recession. Many economists believe these policies helped avert another Great Depression, but exacerbated what problem in the financial system?
A) Moral hazard.
B) Liquidity trap.
C) Cyclical asymmetry.
D) Quantitative easing.
A) Moral hazard.
B) Liquidity trap.
C) Cyclical asymmetry.
D) Quantitative easing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In 2014, the European Central Bank took the unusual step of:
A) returning to the gold standard.
B) raising interest rates during a recession.
C) dissolving the euro as a common currency.
D) setting negative interest rates.
A) returning to the gold standard.
B) raising interest rates during a recession.
C) dissolving the euro as a common currency.
D) setting negative interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Negative interest rates set by the European Central Bank:
A) encouraged banks to lend excess reserves, but also discouraged the deposits that provide those excess reserves.
B) encouraged banks to lend excess reserves and customers to increase deposits.
C) encouraged people to turn cash into electronic bank balances.
D) discouraged bank lending.
A) encouraged banks to lend excess reserves, but also discouraged the deposits that provide those excess reserves.
B) encouraged banks to lend excess reserves and customers to increase deposits.
C) encouraged people to turn cash into electronic bank balances.
D) discouraged bank lending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In an environment of negative interest rates:
A) people are paid to borrow money.
B) people are encouraged to hold less in bank deposits and more in cash.
C) banks are better off lending at any interest rate greater than the negative interest rates they face on unloaned excess reserves, even if those rates are negative.
D) all of these occur.
A) people are paid to borrow money.
B) people are encouraged to hold less in bank deposits and more in cash.
C) banks are better off lending at any interest rate greater than the negative interest rates they face on unloaned excess reserves, even if those rates are negative.
D) all of these occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Aggregate demand tends to be increased when the Federal Reserve System sells government securities in the open market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If the Federal Reserve Bank sells $10 million in government securities to commercial banks, the effect will be to increase the excess reserves of commercial banks by $10 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Repurchase (repo) agreements are an expansionary form of open-market operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The Federal Open Market Committee meets regularly to choose a desired Federal funds rate and directs the Federal Reserve Bank of New York to undertake open-market operations to achieve and maintain that rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A restrictive monetary policy lowers the Federal funds rate, increases the money supply, and lowers other interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
An expansionary monetary policy lowers the Federal funds rate, increases the money supply, and lowers other interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The most effective and most-often-used tool of monetary policy is open-market operations, where government securities are bought and sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
"ZIRP" stands for "Zero Inflation Rate Policy."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Quantitative easing was a policy implemented by the Federal Reserve when monetary policy suffered from a zero lower bound problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Recognition and operation lags enhance the effectiveness of monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



