Deck 35: Ecosystems and Biomes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/57
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 35: Ecosystems and Biomes
1
The pathways that macronutrients and micronutrients follow through ecosystems are:
A) one-way flow cycles.
B) biogeochemical cycles.
C) decomposer-detrital cycles.
D) energy cycles.
A) one-way flow cycles.
B) biogeochemical cycles.
C) decomposer-detrital cycles.
D) energy cycles.
biogeochemical cycles.
2
One of the proposed solutions to global warming is to grow a large number of trees. This could be effective because:
A) plant biomass is a storage pool of carbon.
B) plant gross primary production is stored as carbon on Earth's surface, taking carbon out of the atmosphere.
C) plant carbon is effectively recycled through biodegradation by organisms, leaving little to no residue.
D) plant net primary production is stored as carbon on Earth's surface, taking carbon out of the atmosphere.
E) plants are the base of all ecological food chains.
A) plant biomass is a storage pool of carbon.
B) plant gross primary production is stored as carbon on Earth's surface, taking carbon out of the atmosphere.
C) plant carbon is effectively recycled through biodegradation by organisms, leaving little to no residue.
D) plant net primary production is stored as carbon on Earth's surface, taking carbon out of the atmosphere.
E) plants are the base of all ecological food chains.
plant biomass is a storage pool of carbon.
3
Legumes planted as a cover crop may improve the N fertility of a soil via:
A) decomposition.
B) nitrification.
C) denitrification.
D) assimilation.
E) fixation.
A) decomposition.
B) nitrification.
C) denitrification.
D) assimilation.
E) fixation.
fixation.
4
The amount of nitrogen produced by the Haber process, compared to natural fixation, is:
A) two times greater than the amount produced by natural fixation.
B) about equal to the amount produced by natural fixation.
C) about 10 percent of the amount produced by natural fixation.
D) about 1 percent of the amount produced by natural fixation.
E) not well known and varies with climate.
A) two times greater than the amount produced by natural fixation.
B) about equal to the amount produced by natural fixation.
C) about 10 percent of the amount produced by natural fixation.
D) about 1 percent of the amount produced by natural fixation.
E) not well known and varies with climate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is not involved with the nitrogen cycle?
A) fixation
B) transpiration
C) fungi
D) nitrification
E) decomposition
A) fixation
B) transpiration
C) fungi
D) nitrification
E) decomposition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Glaciers make up about 20 percent of Earth's freshwater pool.
B) An aquifer is a pool of freshwater perched over the base groundwater that is accessible by humans.
C) Transpiration moves salt water to the atmosphere and then to freshwater pools on Earth's surface.
D) About 2.5 percent of Earth's water is fresh at any given time.
E) The process of respiration is critical for maintaining the freshwater pools on Earth's surface.
A) Glaciers make up about 20 percent of Earth's freshwater pool.
B) An aquifer is a pool of freshwater perched over the base groundwater that is accessible by humans.
C) Transpiration moves salt water to the atmosphere and then to freshwater pools on Earth's surface.
D) About 2.5 percent of Earth's water is fresh at any given time.
E) The process of respiration is critical for maintaining the freshwater pools on Earth's surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Transpiration moves water from saltwater pools to freshwater pools.
B) Humans have increased current atmospheric CO2 levels by a factor of about 150 percent.
C) Humans have appropriated much of Earth's freshwater supply.
D) California's Owens Valley is an example of human-caused conversion of water to energy for human consumption.
E) Both A and B are true.
A) Transpiration moves water from saltwater pools to freshwater pools.
B) Humans have increased current atmospheric CO2 levels by a factor of about 150 percent.
C) Humans have appropriated much of Earth's freshwater supply.
D) California's Owens Valley is an example of human-caused conversion of water to energy for human consumption.
E) Both A and B are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Carbon, an element essential to life as we know it,
A) is present at all trophic levels.
B) is a stable element and of no ecological concern.
C) is present only at higher trophic levels.
D) is in limited supply on Earth.
E) is being locked permanently into the atmosphere.
A) is present at all trophic levels.
B) is a stable element and of no ecological concern.
C) is present only at higher trophic levels.
D) is in limited supply on Earth.
E) is being locked permanently into the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An N2-fixing legume planted as a cover crop in a wheat field is a:
A) producer.
B) primary consumer.
C) secondary consumer.
D) tertiary consumer.
E) detritivore.
A) producer.
B) primary consumer.
C) secondary consumer.
D) tertiary consumer.
E) detritivore.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why are big, fierce animals rare?
A) Nutrients are preferentially lost from one trophic level to the next.
B) Available energy is greatly reduced from one trophic level to the next.
C) The evolution of the hunting strategy has limited the evolution of predators.
D) Energy lost in the prey strategy limits the energy that can be transferred to higher trophic levels.
E) All of the above are correct.
A) Nutrients are preferentially lost from one trophic level to the next.
B) Available energy is greatly reduced from one trophic level to the next.
C) The evolution of the hunting strategy has limited the evolution of predators.
D) Energy lost in the prey strategy limits the energy that can be transferred to higher trophic levels.
E) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Gross primary production is:
A) energy received by plants that is assimilated.
B) energy received by plants that is transferred up one trophic level.
C) energy received by plants from sunlight in usable wavelengths.
D) energy received by plants from sunlight.
E) energy received by plants that is turned into plant materials (leaf, stem, roots, and so on).
A) energy received by plants that is assimilated.
B) energy received by plants that is transferred up one trophic level.
C) energy received by plants from sunlight in usable wavelengths.
D) energy received by plants from sunlight.
E) energy received by plants that is turned into plant materials (leaf, stem, roots, and so on).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Net primary production is:
A) energy received by plants that is turned into plant materials (leaf, stem, roots, and so on).
B) energy received by plants that is transferred up one trophic level.
C) energy received by plants from sunlight.
D) energy received by plants from sunlight in usable wavelengths.
E) energy received by plants that is assimilated.
A) energy received by plants that is turned into plant materials (leaf, stem, roots, and so on).
B) energy received by plants that is transferred up one trophic level.
C) energy received by plants from sunlight.
D) energy received by plants from sunlight in usable wavelengths.
E) energy received by plants that is assimilated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When researchers measure the amount of grass produced in a field, they are measuring:
A) gross primary production.
B) detrital potential.
C) autotrophic potential.
D) net primary production.
E) heterotrophic production.
A) gross primary production.
B) detrital potential.
C) autotrophic potential.
D) net primary production.
E) heterotrophic production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following would not be likely to limit the primary production of an ecosystem?
A) efficiency of secondary consumers
B) the amount of water
C) light quality
D) nutrient availability
E) temperature
A) efficiency of secondary consumers
B) the amount of water
C) light quality
D) nutrient availability
E) temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The maximum number of trophic levels in an ecosystem could be limited by:
A) available energy.
B) favorable temperatures.
C) available water.
D) All are correct answers.
A) available energy.
B) favorable temperatures.
C) available water.
D) All are correct answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Grass and herbs in an old-field community produce 500 grams of organic matter per square meter per year that is available for other organisms in the community to consume. This amount is known as the:
A) consumer production efficiency.
B) net primary production.
C) secondary productivity.
D) availability factor for the community.
E) trophic efficiency.
A) consumer production efficiency.
B) net primary production.
C) secondary productivity.
D) availability factor for the community.
E) trophic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The energy lost as it passes from one trophic level to another is usually at least
A) 50 percent.
B) 10 percent.
C) 75 percent.
D) 90 percent.
E) 99 percent.
A) 50 percent.
B) 10 percent.
C) 75 percent.
D) 90 percent.
E) 99 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Decomposers are organisms that:
A) don't really need energy, because they work with very simple molecules.
B) rely on heat from Earth itself for their energy.
C) get the energy they need to decompose things directly from the sun.
D) find the last bits of energy left in the remains of other organisms.
A) don't really need energy, because they work with very simple molecules.
B) rely on heat from Earth itself for their energy.
C) get the energy they need to decompose things directly from the sun.
D) find the last bits of energy left in the remains of other organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
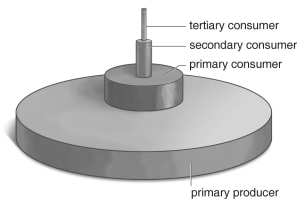 Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.
Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.-It doesn't take many steps to reach the end of a food chain, because:
A) so much energy gets lost in the process of living.
B) life always finds the most efficient way of doing things.
C) organisms at the top hold on to the energy so long.
D) there's room on Earth only for so many living organisms.
E) so much energy gets trapped along the way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A retired hiker has walked up Mount Washington every weekend for the last few decades. She has noticed that it rains more near the summit than the base. The reason is that:
A) mountains trap fog and cloud input, thus reducing rainfall at sea level.
B) cool air descending from the summit warms, picking up moisture as it travels.
C) warm air cools as it rises and can't hold as much moisture.
D) dry, hot air from the base rises, picking up moisture.
E) Both B and C are correct.
A) mountains trap fog and cloud input, thus reducing rainfall at sea level.
B) cool air descending from the summit warms, picking up moisture as it travels.
C) warm air cools as it rises and can't hold as much moisture.
D) dry, hot air from the base rises, picking up moisture.
E) Both B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The "rain shadow effect occurs because:
A) cloud shadows move from east to west, dropping moisture on the east of mountain ranges in the northern hemisphere.
B) cool air masses warm as they move closer to the sun, dropping moisture on the wet side of mountains.
C) warm air rises and drops moisture on one side of the mountain.
D) clouds don't pass over mountain chains and thus drop warm. moist air.
E) precipitation patterns follow the tilt of Earth's axis.
A) cloud shadows move from east to west, dropping moisture on the east of mountain ranges in the northern hemisphere.
B) cool air masses warm as they move closer to the sun, dropping moisture on the wet side of mountains.
C) warm air rises and drops moisture on one side of the mountain.
D) clouds don't pass over mountain chains and thus drop warm. moist air.
E) precipitation patterns follow the tilt of Earth's axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
At about 30° north and south of the equator there are dry regions on Earth. Why does this occur?
A) Warm air rises and evaporates, leaving dry, cool air.
B) Cool air falls, is warmed, and absorbs moisture.
C) Warm air falls and absorbs moisture.
D) Cool air rises, and water condenses.
E) Air flows laterally across the land from the temperate zone.
A) Warm air rises and evaporates, leaving dry, cool air.
B) Cool air falls, is warmed, and absorbs moisture.
C) Warm air falls and absorbs moisture.
D) Cool air rises, and water condenses.
E) Air flows laterally across the land from the temperate zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Earth is generally hotter at the equator because:
A) The sun shines over the equator evenly through the year, rather than seasonally.
B) Earth's rotation on a tilted axis increases seasonality.
C) The natural oval shape of Earth places the equator nearer the sun than the poles.
D) The sun's rays strike Earth at nearly a right angle at the equator.
E) Earth's rotation on a tilted axis creates an atmospheric drag at the equator, warming the air.
A) The sun shines over the equator evenly through the year, rather than seasonally.
B) Earth's rotation on a tilted axis increases seasonality.
C) The natural oval shape of Earth places the equator nearer the sun than the poles.
D) The sun's rays strike Earth at nearly a right angle at the equator.
E) Earth's rotation on a tilted axis creates an atmospheric drag at the equator, warming the air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The prevailing winds in Oregon are from the west. The Oregon Cascades are south of the Washington Cascades, which are also near the coast. Which side of the Oregon Cascades will receive the highest levels of precipitation?
A) west
B) north
C) east
D) south
A) west
B) north
C) east
D) south

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Susan was flying a small glider in a terrific storm and got hopelessly lost. When she landed, the ground was hot and dry, with quite sparse vegetation. She could not see any mountains. She guessed that she was:
A) 30° north of the equator.
B) 30° south of the equator.
C) 60° north of the equator.
D) 60° south of the equator.
E) Either A or B could be true.
A) 30° north of the equator.
B) 30° south of the equator.
C) 60° north of the equator.
D) 60° south of the equator.
E) Either A or B could be true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A significant human contribution to apparently rising temperatures on Earth may be the result of a change in how well:
A) the oceans can transfer heat from the atmosphere.
B) long wavelengths of light pass through the atmosphere.
C) Earth's surface absorbs long wavelengths.
D) Earth's surface absorbs short wavelengths.
E) short wavelengths of light pass through the atmosphere.
A) the oceans can transfer heat from the atmosphere.
B) long wavelengths of light pass through the atmosphere.
C) Earth's surface absorbs long wavelengths.
D) Earth's surface absorbs short wavelengths.
E) short wavelengths of light pass through the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Permafrost is a characteristic of ________ and is ________.
A) taiga; deep ice below the surface caused by deep percolation
B) tundra; surface ice that is seasonal
C) taiga; surface ice that is seasonal
D) taiga; permanent ice
E) tundra; permanent ice
A) taiga; deep ice below the surface caused by deep percolation
B) tundra; surface ice that is seasonal
C) taiga; surface ice that is seasonal
D) taiga; permanent ice
E) tundra; permanent ice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Taiga is characterized by:
A) pines as an early successional stage before deciduous trees, rich understory, and cold climate.
B) few ecological dominants, short growing seasons, and sparse deciduous trees.
C) poor drainage over permafrost, few to no trees, and short growing season; shrubs and sedges dominate.
D) permafrost, short growing seasons, and sparse coniferous trees.
E) coniferous forest, low tree diversity, and no permafrost.
A) pines as an early successional stage before deciduous trees, rich understory, and cold climate.
B) few ecological dominants, short growing seasons, and sparse deciduous trees.
C) poor drainage over permafrost, few to no trees, and short growing season; shrubs and sedges dominate.
D) permafrost, short growing seasons, and sparse coniferous trees.
E) coniferous forest, low tree diversity, and no permafrost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Choose the correct type of ecosystem for the following descriptions.
-An ecosystem commonly used for agriculture because of the highly fertile soils
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna
-An ecosystem commonly used for agriculture because of the highly fertile soils
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Choose the correct type of ecosystem for the following descriptions.
-Characterized by shrubby vegetation; mild, wet winters; and dry summers
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna
-Characterized by shrubby vegetation; mild, wet winters; and dry summers
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Choose the correct type of ecosystem for the following descriptions.
-Characterized by permafrost
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna
-Characterized by permafrost
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Choose the correct type of ecosystem for the following descriptions.
-Characterized by seasonal drought, generally warm temperatures through the year, and scattered trees
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna
-Characterized by seasonal drought, generally warm temperatures through the year, and scattered trees
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Choose the correct type of ecosystem for the following descriptions.
-Too dry for tree vegetation, more water than deserts, and often in continental centers
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna
-Too dry for tree vegetation, more water than deserts, and often in continental centers
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Choose the correct type of ecosystem for the following descriptions.
-Mediterranean climate, usually on the west coast of a land mass
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna
-Mediterranean climate, usually on the west coast of a land mass
A) tundra
B) taiga
C) grassland
D) chaparral
E) savanna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Choose the correct type of ecosystem for the following descriptions.
-Desertification:
A) may be caused by natural climate variations.
B) refers to the transformation of grassland into desert.
C) may be caused by human activity.
D) Both A and B are true.
E) A, B, and C are all correct.
-Desertification:
A) may be caused by natural climate variations.
B) refers to the transformation of grassland into desert.
C) may be caused by human activity.
D) Both A and B are true.
E) A, B, and C are all correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Choose the correct type of ecosystem for the following descriptions.
-A large percentage (about 90 percent) of the nutrient and organic matter capital is in the soil of a ________ ecosystem.
A) chaparral
B) temperate grassland
C) tropical rain forest
D) deciduous forest
E) desert
-A large percentage (about 90 percent) of the nutrient and organic matter capital is in the soil of a ________ ecosystem.
A) chaparral
B) temperate grassland
C) tropical rain forest
D) deciduous forest
E) desert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The temperate deciduous forest is composed of a high diversity of deciduous trees that lose their leaves in the fall because of low soil fertility.
B) Agriculture is often not very successful in a tropical forest because of the poor soils.
C) The high species diversity of a tropical rain forest is supported by a high diversity of soil organisms, high soil fertility, and high rainfall.
D) None of the above statements is true.
A) The temperate deciduous forest is composed of a high diversity of deciduous trees that lose their leaves in the fall because of low soil fertility.
B) Agriculture is often not very successful in a tropical forest because of the poor soils.
C) The high species diversity of a tropical rain forest is supported by a high diversity of soil organisms, high soil fertility, and high rainfall.
D) None of the above statements is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Is there photosynthetic activity in the benthic zone of the ocean?
A) No, because nutrient availability is too low.
B) No, because this is below the photic zone.
C) Yes, because this is the zone of high light penetration and photosynthetic activity.
D) Yes, because this is the richest zone for nutrient turnover due to microbial activity.
E) Yes, because high light and high nutrient conditions are optimal for phytoplankton production.
A) No, because nutrient availability is too low.
B) No, because this is below the photic zone.
C) Yes, because this is the zone of high light penetration and photosynthetic activity.
D) Yes, because this is the richest zone for nutrient turnover due to microbial activity.
E) Yes, because high light and high nutrient conditions are optimal for phytoplankton production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A marine biologist designs a study to measure net primary productivity in the world's oceans. She travels to the coastal zone of each continent, takes measurements from north, south, east and west points along the continent, and combines her data into a global average. Will these measurements be accurate?
A) No, because ocean productivity is greatest past the intertidal zone.
B) Yes, but only if she is sure to sample different climatic zones carefully, because production in different climatic zones may vary by an order of magnitude.
C) No, because the continental edges have higher productivities than the open ocean.
D) No, because ocean life is greatest near the poles and decreases toward the equator.
E) Yes, because although production in different climate zones differs, the open ocean is well mixed because of strong ocean circulation patterns.
A) No, because ocean productivity is greatest past the intertidal zone.
B) Yes, but only if she is sure to sample different climatic zones carefully, because production in different climatic zones may vary by an order of magnitude.
C) No, because the continental edges have higher productivities than the open ocean.
D) No, because ocean life is greatest near the poles and decreases toward the equator.
E) Yes, because although production in different climate zones differs, the open ocean is well mixed because of strong ocean circulation patterns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Coral reefs are highly productive because they:
A) are made of limestone that supports many species of zooplankton with high productivity.
B) create habitat for many of the ocean's species.
C) are composed of polyps that live in and are adapted to warm, shallow tropical waters with high nutrient availability.
D) have high turnover rates with high polyp production.
A) are made of limestone that supports many species of zooplankton with high productivity.
B) create habitat for many of the ocean's species.
C) are composed of polyps that live in and are adapted to warm, shallow tropical waters with high nutrient availability.
D) have high turnover rates with high polyp production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a popular resort town, many dead fish were found floating on the surface of the main swimming lake. What was the likely cause of the fish death?
A) The lake was eutrophic, and the low phytoplankton production caused a collapse in the lake's food chain.
B) The lake was eutrophic, so algal blooms caused low oxygen in the profundal zone.
C) The lake was oligotrophic, and, thus, higher trophic levels could not be supported by the reduction in phytoplankton/zooplankton production.
D) The lake was oligotrophic, so algal blooms caused low oxygen in the limnetic zone.
E) Artificial eutrophication caused an overproduction of phytoplankton, leading to a CO2 buildup in the limnetic zone.
A) The lake was eutrophic, and the low phytoplankton production caused a collapse in the lake's food chain.
B) The lake was eutrophic, so algal blooms caused low oxygen in the profundal zone.
C) The lake was oligotrophic, and, thus, higher trophic levels could not be supported by the reduction in phytoplankton/zooplankton production.
D) The lake was oligotrophic, so algal blooms caused low oxygen in the limnetic zone.
E) Artificial eutrophication caused an overproduction of phytoplankton, leading to a CO2 buildup in the limnetic zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Eutrophic lakes have:
A) few phytoplankton.
B) clear water with high production.
C) high nutrient levels and high production by phytoplankton.
D) clear water with deep light penetration.
E) low oxygen concentrations and low nutrient concentrations.
A) few phytoplankton.
B) clear water with high production.
C) high nutrient levels and high production by phytoplankton.
D) clear water with deep light penetration.
E) low oxygen concentrations and low nutrient concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Estuaries:
A) can range from temporarily waterlogged sites to boggy, permanently saturated zones.
B) are zones of high nutrient availability and high production with constant water movement.
C) are zones of low nutrient availability but high production because of the shallow waters.
D) are regions near continental edges where inland bays cause calm waters and thus high plant and animal diversity.
E) are zones of low production between highly productive wetlands and the coastal ocean.
A) can range from temporarily waterlogged sites to boggy, permanently saturated zones.
B) are zones of high nutrient availability and high production with constant water movement.
C) are zones of low nutrient availability but high production because of the shallow waters.
D) are regions near continental edges where inland bays cause calm waters and thus high plant and animal diversity.
E) are zones of low production between highly productive wetlands and the coastal ocean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The most productive freshwater lake is likely to be the one with:
A) the widest photic zone.
B) the deepest profundal zone.
C) the largest littoral zone.
D) the most pronounced benthic zone.
E) the most efficient pelagic zone.
A) the widest photic zone.
B) the deepest profundal zone.
C) the largest littoral zone.
D) the most pronounced benthic zone.
E) the most efficient pelagic zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
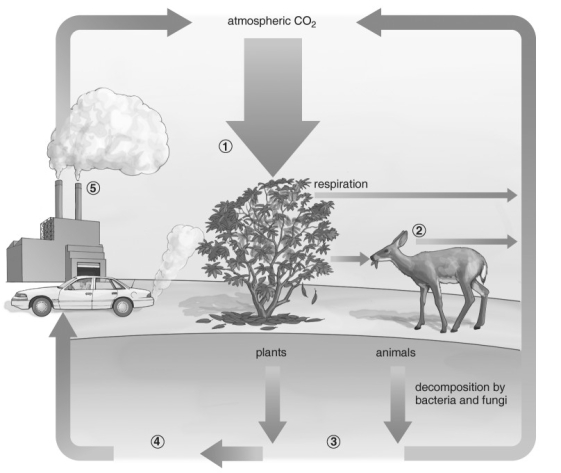 Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.
Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.-Which of the following sequences represents the numbered steps in the carbon cycle?
A) photosynthesis, respiration, fossil fuels, dead organisms, burning of fossil fuels
B) fossil fuels, respiration, photosynthesis, dead organisms, burning of fossil fuels
C) photosynthesis, dead organisms, fossil fuels, burning of fossil fuels, respiration
D) photosynthesis, respiration, dead organisms, fossil fuels, burning of fossil fuels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
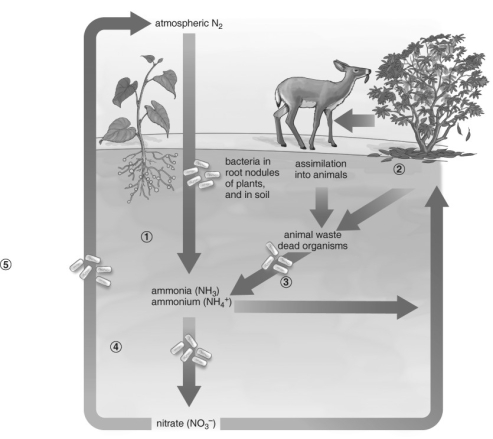 Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.
Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.-Which of the following sequences represents the numbered steps in the nitrogen cycle?
A) nitrifying bacteria, assimilation into plants, decomposition by bacteria and fungi, nitrogen fixation, denitrifying bacteria
B) decomposition by bacteria and fungi, assimilation into plants, denitrifying bacteria, nitrogen fixation, nitrifying bacteria
C) nitrogen fixation, assimilation into plants, decomposition by bacteria and fungi, nitrifying bacteria, denitrifying bacteria
D) nitrogen fixation, assimilation into plants, denitrifying bacteria, decomposition by bacteria and fungi, nitrifying bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Human beings are not separate from the Earth they live on. Rather, they are intertwined with Earth in some basic, physical ways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Nutrients flow through ecosystems, whereas energy is recycled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
There is little evidence that increasing levels of carbon dioxide and other "greenhouse gases are raising Earth's temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Temperature, available water, the seasons, and nutrient availability all contribute to determining which biome exists in a given area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Many animal rights activists have claimed that if beef cows were eliminated, more people could be fed. What is the ecological theory behind the argument in support of this position, and what is an argument against this position?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What causes the "ozone hole, and why do we care?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Why do greenhouses gases such as CO2 affect the temperature of the air?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A farmer in Brazil burns a section of the tropical rain forest to plant corn. The corn does well for a year, but the second crop does poorly, and the third crop fails. Why might this have happened?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A student who went to study the tundra measured low rainfall but noted that the ground was commonly damp in the summer. Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Corn usually grows very well in the prairie compared to converted forest land. Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What could cause an algal bloom in a lake? What are some of the chemical and biological effects that an algal bloom could have on a lake?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 57 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



