Deck 8: Liquids and Solutions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Liquids and Solutions
1
Describe the difference between a solid, liquid, and gas on the macroscopic scale and on the atomic scale.
On the macroscopic level solids have a fixed volume and shape, liquids have a fixed volume but take the shape of their container and gases take the shape and volume of their container. On the atomic scale the particles which form solids are very close together and their motion is restricted to vibration. In liquids the particles are farther apart with some degree of motion allowed. In gases the particles are widely separated and are in constant random motion.
2
Distinguish between the three intermolecular forces: dipole-dipole interaction, dispersion forces and hydrogen bonding.
Dipole/dipole interaction is found between polar molecules where the negative end of one molecule is attracted to the positive end of another. Dispersion forces are found between all molecules. The motion of a molecule's electrons causes the formation of temporary dipoles which can induce dipoles in neighboring molecules leading to a force of attraction. Hydrogen bonding is a particularly strong dipole/dipole interaction that occurs when hydrogen is covalently bonded to O, N or F. This results in a large positive partial charge on hydrogen which is then strongly attracted to electronegative O, N, or F on neighboring atoms.
3
The melting point of hexane at 1 atm. pressure, C6H14, is 179 K; the melting point of octane, C8H18, at the same pressure is predicted to be:
A) a lot lower than 179 K
B) somewhat lower than 179 K
C) equal to 179 K
D) somewhat higher than 179 K
E) a lot higher than 179 K
A) a lot lower than 179 K
B) somewhat lower than 179 K
C) equal to 179 K
D) somewhat higher than 179 K
E) a lot higher than 179 K
somewhat higher than 179 K
4
In which of the following substances do you expect to find the strongest intermolecular hydrogen bonding forces?
A) NH3
B) H2S
C) H2O
D) CF4
E) NaH
A) NH3
B) H2S
C) H2O
D) CF4
E) NaH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Rare gases, such as xenon, can be frozen to form solids. The intermolecular forces responsible for maintaining the solid are best described as:
A) hydrogen bonds
B) covalent bonds
C) dipole-dipole forces
D) dipole-induced dipole forces
E) induced dipole-induced dipole forces
A) hydrogen bonds
B) covalent bonds
C) dipole-dipole forces
D) dipole-induced dipole forces
E) induced dipole-induced dipole forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Argon has a higher melting point (84 K) than neon (24 K) because there is:
A) stronger dipole-dipole interaction in argon
B) stronger hydrogen bonding in argon
C) stronger dispersion forces in argon
D) stronger ionic bonding in argon
E) none of these
A) stronger dipole-dipole interaction in argon
B) stronger hydrogen bonding in argon
C) stronger dispersion forces in argon
D) stronger ionic bonding in argon
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
refer to the table below:
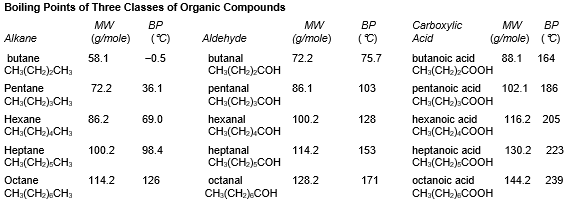
-What intermolecular force is most responsible for the difference in boiling point between octane and pentane?
A) dispersion
B) dipole-dipole interaction
C) dipole-induced dipole interaction
D) hydrogen bonding
E) all of these

-What intermolecular force is most responsible for the difference in boiling point between octane and pentane?
A) dispersion
B) dipole-dipole interaction
C) dipole-induced dipole interaction
D) hydrogen bonding
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
refer to the table below:

-What intermolecular force is most responsible for the difference in boiling point between hexanal and pentanoic acid?
A) dispersion
B) dipole-dipole
C) dipole-induced dipole
D) hydrogen bonding
E) all of these

-What intermolecular force is most responsible for the difference in boiling point between hexanal and pentanoic acid?
A) dispersion
B) dipole-dipole
C) dipole-induced dipole
D) hydrogen bonding
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
refer to the table below:

-Predict the boiling point of propanal, CH3CH2COH.
A) -40 C
C
B) -10 11ee9efa_bc25_a3cf_9fac_93ea23aeaad3_TB9692_11 C
C) 48 11ee9efa_bc25_a3cf_9fac_93ea23aeaad3_TB9692_11 C
D) 78 11ee9efa_bc25_a3cf_9fac_93ea23aeaad3_TB9692_11 C
E) 110 11ee9efa_bc25_a3cf_9fac_93ea23aeaad3_TB9692_11 C

-Predict the boiling point of propanal, CH3CH2COH.
A) -40
 C
CB) -10 11ee9efa_bc25_a3cf_9fac_93ea23aeaad3_TB9692_11 C
C) 48 11ee9efa_bc25_a3cf_9fac_93ea23aeaad3_TB9692_11 C
D) 78 11ee9efa_bc25_a3cf_9fac_93ea23aeaad3_TB9692_11 C
E) 110 11ee9efa_bc25_a3cf_9fac_93ea23aeaad3_TB9692_11 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The following three compounds have similar molecular weights. Place them in order of increasing boiling point.
Formaldehyde: H2C=O methanol: CH3OH ethane: CH3CH3
A) formaldehyde < ethane < methanol
B) ethane < methanol < formaldehyde
C) ethane < formaldehyde < methanol
D) methanol < formaldehyde < ethane
E) none of these
Formaldehyde: H2C=O methanol: CH3OH ethane: CH3CH3
A) formaldehyde < ethane < methanol
B) ethane < methanol < formaldehyde
C) ethane < formaldehyde < methanol
D) methanol < formaldehyde < ethane
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which force must be overcome to melt solid pentane, C5H12?
A) metallic bonding
B) covalent bonding
C) ionic bonding
D) dispersion forces
E) all of these must be overcome to melt pentane
A) metallic bonding
B) covalent bonding
C) ionic bonding
D) dispersion forces
E) all of these must be overcome to melt pentane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following characteristics is associated with a low boiling point for a molecular substance?
A) high molecular weight
B) high vapor pressure
C) strong intermolecular forces
D) large dipole moment
E) strong cohesion forces
A) high molecular weight
B) high vapor pressure
C) strong intermolecular forces
D) large dipole moment
E) strong cohesion forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following compounds has the lowest vapor pressure?
A) CCl4
B) CBr4
C) CF4
D) CH4
E) CI4
A) CCl4
B) CBr4
C) CF4
D) CH4
E) CI4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For which of the following is the boiling point incorrectly given?
A) CH3(CH2)2CH3, - 0.5 ℃
B) CH3(CH2)2CHO, 75 ℃
C) CH3(CH2)3OH, 100 ℃
D) CH3(CH2)2COOH, 95 ℃
E) CH3(CH2)3CHO, 103 ℃
A) CH3(CH2)2CH3, - 0.5 ℃
B) CH3(CH2)2CHO, 75 ℃
C) CH3(CH2)3OH, 100 ℃
D) CH3(CH2)2COOH, 95 ℃
E) CH3(CH2)3CHO, 103 ℃

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which compound would you expect to have the highest vapor pressure at 25°C?
A) C7H16 (BP = 98.4°C)
B) C8H18 (BP = 125.7°C)
C) C9H20 (BP = 150.8°C)
D) C10H22 (BP = 174.3°C)
E) It is impossible to tell which compound would have the highest vapor pressure because there is no relationship between vapor pressure and the boiling point of a compound.
A) C7H16 (BP = 98.4°C)
B) C8H18 (BP = 125.7°C)
C) C9H20 (BP = 150.8°C)
D) C10H22 (BP = 174.3°C)
E) It is impossible to tell which compound would have the highest vapor pressure because there is no relationship between vapor pressure and the boiling point of a compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A liquid is at its equilibrium vapor pressure at 20oC. The following changes are then made:
(1) The liquid is transferred into a container with a wider opening.
(2) More liquid is added to the container.
(3) The temperature is increased to 30oC.
The vapor pressure is then observed to increase. Which of these changes contributed to the increase in the vapor pressure?
A) (1) only
B) (2) only
C) (3) only
D) (1) and (2), but not (3)
E) (2) and (3), but not (1)
(1) The liquid is transferred into a container with a wider opening.
(2) More liquid is added to the container.
(3) The temperature is increased to 30oC.
The vapor pressure is then observed to increase. Which of these changes contributed to the increase in the vapor pressure?
A) (1) only
B) (2) only
C) (3) only
D) (1) and (2), but not (3)
E) (2) and (3), but not (1)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The boiling point of HF is lower than that of water despite the fact that the hydrogen bonds in HF are at least as strong as those in water because:
A) water is more polar than HF
B) water has the higher melting point
C) water is less dense
D) each water molecule forms more hydrogen bonds
E) the vapor pressure of HF is higher than that of water
A) water is more polar than HF
B) water has the higher melting point
C) water is less dense
D) each water molecule forms more hydrogen bonds
E) the vapor pressure of HF is higher than that of water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In most cases, reading from left to right across a phase diagram, what is the order in which you would find the three states of matter?
A) gas < liquid < solid
B) gas < solid < liquid
C) liquid < gas < solid
D) liquid < solid < gas
E) solid < liquid < gas
A) gas < liquid < solid
B) gas < solid < liquid
C) liquid < gas < solid
D) liquid < solid < gas
E) solid < liquid < gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which statement isn't consistent with the information contained in the phase diagram of a compound?
A) Liquids can be made to boil by raising the pressure at constant temperature.
B) Solids can be made to melt by raising the temperature at constant pressure.
C) Gases are most likely to be found at high temperatures and low pressures.
D) The boiling point of a compound is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the compound is equal to atmospheric pressure.
E) All of these statements are consistent with the information in the phase diagram of a compound.
A) Liquids can be made to boil by raising the pressure at constant temperature.
B) Solids can be made to melt by raising the temperature at constant pressure.
C) Gases are most likely to be found at high temperatures and low pressures.
D) The boiling point of a compound is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the compound is equal to atmospheric pressure.
E) All of these statements are consistent with the information in the phase diagram of a compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
refer to the phase diagram shown below.
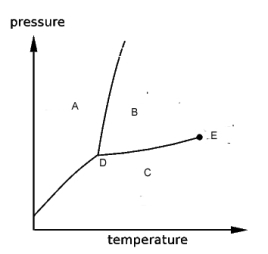
-The regions labeled A,B, and C are
A) the gas, liquid and solid phases, respectively.
B) the solid and liquid phases and the triple point, respectively.
C) the gas and liquid phases and the critical point, respectively.
D) the solid, liquid and gas phases, respectively.
E) pressure, temperature and moles, respectively.

-The regions labeled A,B, and C are
A) the gas, liquid and solid phases, respectively.
B) the solid and liquid phases and the triple point, respectively.
C) the gas and liquid phases and the critical point, respectively.
D) the solid, liquid and gas phases, respectively.
E) pressure, temperature and moles, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
refer to the phase diagram shown below.

-If the temperature and pressure are changed from the values at point B to the values at point C, the substance will change its phase from
A) liquid to gas.
B) liquid to solid
C) gas to solid.
D) solid to liquid.
E) gas to liquid.

-If the temperature and pressure are changed from the values at point B to the values at point C, the substance will change its phase from
A) liquid to gas.
B) liquid to solid
C) gas to solid.
D) solid to liquid.
E) gas to liquid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
refer to the phase diagram shown below.

-For this substance, as the pressure increases, the melting point will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) could either increase or decrease.
E) the phase diagram gives no information about the melting point.

-For this substance, as the pressure increases, the melting point will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) could either increase or decrease.
E) the phase diagram gives no information about the melting point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The best explanation for the fact that water and ethyl alcohol are completely miscible is that
A) both compounds are nonpolar.
B) water is polar and ethyl alcohol is nonpolar.
C) water has an unusually large dielectric constant.
D) ethyl alcohol dissociates in water.
E) hydrogen bonding takes place between the two substances.
A) both compounds are nonpolar.
B) water is polar and ethyl alcohol is nonpolar.
C) water has an unusually large dielectric constant.
D) ethyl alcohol dissociates in water.
E) hydrogen bonding takes place between the two substances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following will be most soluble in a nonpolar solvent such as carbon tetrachloride, CCl4?
A) KI
B) H2O
C) NH3
D) CBr4
E) HF
A) KI
B) H2O
C) NH3
D) CBr4
E) HF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which alcohol should be most soluble in a nonpolar solvent such as benzene, C6H6?
A) CH3OH
B) CH3CH2OH
C) CH3CH2CH2OH
D) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
E) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
A) CH3OH
B) CH3CH2OH
C) CH3CH2CH2OH
D) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
E) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Carboxylic acids with the general formula CH3(CH2)nCO2H have a nonpolar CH3-CH2- tail and a polar -CO2H head. What effect would increasing the value of "n" have on the solubility of carboxylic acids?
A) The solubility would increase in both water and in nonpolar solvents such as CCl4.
B) The solubility would decrease in both water and in nonpolar solvents such as CCl4.
C) The solubility would increase in water but decrease in CCl4.
D) The solubility would decrease in water but increase in CCl4.
E) The solubility of carboxylic acids in both water and CCl4 would remain the same.
A) The solubility would increase in both water and in nonpolar solvents such as CCl4.
B) The solubility would decrease in both water and in nonpolar solvents such as CCl4.
C) The solubility would increase in water but decrease in CCl4.
D) The solubility would decrease in water but increase in CCl4.
E) The solubility of carboxylic acids in both water and CCl4 would remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is correct for the solubilities of alcohols with the formula CH3(CH2)nOH?
A) The solubility in water is minimal because the compound is organic.
B) The solubility in water increases as n increases.
C) The solubility in water decreases as n increases.
D) The solubility in water is independent of n.
E) The solubility in water depends only on the extent of hydrogen bonding.
A) The solubility in water is minimal because the compound is organic.
B) The solubility in water increases as n increases.
C) The solubility in water decreases as n increases.
D) The solubility in water is independent of n.
E) The solubility in water depends only on the extent of hydrogen bonding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An alcohol is a compound with the formula CH3(CH2)nOH, in which the CH2(CH2)n group is nonpolar and the OH group is polar. As "n" increases for different alcohols, we would expect the solubilities of the alcohol to
A) increase in both polar and nonpolar solvents.
B) decrease in polar solvents and increase in nonpolar solvents.
C) decrease in both polar and nonpolar solvents.
D) stay the same in polar solvents and decrease in nonpolar solvents.
E) increase in polar solvents and stay the same in nonpolar solvents.
A) increase in both polar and nonpolar solvents.
B) decrease in polar solvents and increase in nonpolar solvents.
C) decrease in both polar and nonpolar solvents.
D) stay the same in polar solvents and decrease in nonpolar solvents.
E) increase in polar solvents and stay the same in nonpolar solvents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Aqueous 0.2M solutions of K2SO4 and Pb(NO3)2 are mixed together. Use the solubility rules to predict the identity of the precipitate.
A) KNO3
B) K2Pb
C) PbSO4
D) (NO3)2SO4
E) No precipitate will form.
A) KNO3
B) K2Pb
C) PbSO4
D) (NO3)2SO4
E) No precipitate will form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Aqueous 0.2M solutions of Sr(OH)2 and FeCl3 are mixed together. Use the solubility rules to predict the identity of the precipitate.
A) Cl(OH)3
B) SrCl2
C) Sr3Fe2
D) Fe(OH)3
E) No precipitate will form.
A) Cl(OH)3
B) SrCl2
C) Sr3Fe2
D) Fe(OH)3
E) No precipitate will form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Determine the spectator ions in the following reaction.
MgS(aq) + CuSO4(aq) CuS(s) + MgSO4(aq)
A) Cu2+ and Mg2+
B) S2- and SO42-
C) Cu2+ and S2-
D) Mg2+ and SO42-
E) There are no spectator ions in this reaction.
MgS(aq) + CuSO4(aq) CuS(s) + MgSO4(aq)
A) Cu2+ and Mg2+
B) S2- and SO42-
C) Cu2+ and S2-
D) Mg2+ and SO42-
E) There are no spectator ions in this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Based on the solubility rules, which of the following compounds should be most insoluble?
A) KCl
B) NaNO3
C) Cu(OH)2
D) Cu(NO3)2
E) KOH
A) KCl
B) NaNO3
C) Cu(OH)2
D) Cu(NO3)2
E) KOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is true?
A) Molarity (M) is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solute by the number of liters of solvent.
B) Molality (m) is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solute by the number of liters of solvent.
C) Mole fraction is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solvent by the number of moles of solute.
D) Mole fraction is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solute by the number of moles of solvent.
E) Statements (a) through (d) are all false.
A) Molarity (M) is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solute by the number of liters of solvent.
B) Molality (m) is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solute by the number of liters of solvent.
C) Mole fraction is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solvent by the number of moles of solute.
D) Mole fraction is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solute by the number of moles of solvent.
E) Statements (a) through (d) are all false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following concentration units would change when the temperature of the solution changes? (Hint: remember that liquids expand and contract as the temperature changes.)
(I) molarity
(II) molality
(III) mole fraction of solute
(IV) mole fraction of solvent
A) I
B) I and II
C) I, II and III
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
(I) molarity
(II) molality
(III) mole fraction of solute
(IV) mole fraction of solvent
A) I
B) I and II
C) I, II and III
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following correctly describes the behavior of the vapor pressure of liquids?
A) It remains constant as the temperature of the liquid increases.
B) It remains constant when a solute is dissolved in the liquid.
C) It increases when a solute is dissolved in the liquid.
D) If the vapor pressure of CH3OCH3 is much higher than CH3CH2OH at room temperature, CH3OCH3 should boil at a lower temperature than CH3CH2OH.
E) All of the above are correct.
A) It remains constant as the temperature of the liquid increases.
B) It remains constant when a solute is dissolved in the liquid.
C) It increases when a solute is dissolved in the liquid.
D) If the vapor pressure of CH3OCH3 is much higher than CH3CH2OH at room temperature, CH3OCH3 should boil at a lower temperature than CH3CH2OH.
E) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the mole fraction of CCl4 (MW = 154 g/mol) in a solution prepared by dissolving 32 grams of CCl4 in 75 grams of C6H6 (MW = 78.1 g/mol) ?
A) 0.18
B) 0.22
C) 0.30
D) 0.48
E) 0.82
A) 0.18
B) 0.22
C) 0.30
D) 0.48
E) 0.82

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For a solution of 2 g of solute (MW = 200 g/mol) dissolved in 200 g of solvent (MW = 20 g/mol), the mole ratio of solute to solvent is:
A) 1
B) 10-1
C) 10-2
D) 10-3
E) 10-4
A) 1
B) 10-1
C) 10-2
D) 10-3
E) 10-4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following liquid systems would be expected to have the lowest vapor pressure at room temperature?
A) a 1.00 m solution of ethanol in water
B) a 1.00 m solution of sucrose in water
C) a 1.00 m solution of acetone (CH3C(O)CH3) in water
D) a 1.00 m solution of NaCl in water
E) pure water
A) a 1.00 m solution of ethanol in water
B) a 1.00 m solution of sucrose in water
C) a 1.00 m solution of acetone (CH3C(O)CH3) in water
D) a 1.00 m solution of NaCl in water
E) pure water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Raoult's law predicts that the vapor pressure of solvent over a solution of a nonvolatile solute
A) increases with increasing mole fraction of solvent
B) increases with increasing mole fraction of solute
C) is independent of the solute concentration
D) decreases with increasing temperature.
E) decreases with decreasing room pressure.
A) increases with increasing mole fraction of solvent
B) increases with increasing mole fraction of solute
C) is independent of the solute concentration
D) decreases with increasing temperature.
E) decreases with decreasing room pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When a nonvolatile solute is dissolved in a volatile solvent, the vapor pressure of the solvent over the solution
A) increases as the mole fraction of solute increases.
B) decreases as the mole fraction of solute increases.
C) is independent of the mole fraction of solute.
D) changes in an unpredictable way with changes in the mole fraction of
The solute.
E) decreases as the temperature increases.
A) increases as the mole fraction of solute increases.
B) decreases as the mole fraction of solute increases.
C) is independent of the mole fraction of solute.
D) changes in an unpredictable way with changes in the mole fraction of
The solute.
E) decreases as the temperature increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When a nonvolatile solute is dissolved in a volatile solvent, the vapor pressure, freezing point, and boiling point
A) are all higher for the solution than for the pure solvent.
B) are all lower for the solution than for the pure solvent.
C) change differently, with vapor pressure increasing and boiling and freezing points decreasing.
D) change differently, with boiling point increasing and vapor pressure and freezing point decreasing.
E) do not change because the solute is nonvolatile.
A) are all higher for the solution than for the pure solvent.
B) are all lower for the solution than for the pure solvent.
C) change differently, with vapor pressure increasing and boiling and freezing points decreasing.
D) change differently, with boiling point increasing and vapor pressure and freezing point decreasing.
E) do not change because the solute is nonvolatile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A 10.0% by weight solution of NaCl (78.5 g/mol) in water has a molality of:
A) 0.127 m
B) 1.42 m
C) 1.50 m
D) 7.85 m
E) impossible to determine unless you know the density of the solution
A) 0.127 m
B) 1.42 m
C) 1.50 m
D) 7.85 m
E) impossible to determine unless you know the density of the solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
0.400 mole of CCl4 and 0.600 mole of CHCl3 are mixed at 43°C. The vapor pressure of pure CCl4 at this temperature is 0.354 atm and the vapor pressure of pure CHCl3 at this temperature is 0.526 atm. What is the vapor pressure of the solution?
A) 0.285 atm
B) 0.423 atm
C) 0.457 atm
D) 0.526 atm
E) 0.880 atm
A) 0.285 atm
B) 0.423 atm
C) 0.457 atm
D) 0.526 atm
E) 0.880 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the molality of a bromine solution made by dissolving 39.95 g of Br2 in 5.00 x 102 g of CCl4?
A) 0.0800
B) 0.250
C) 0.500
D) 1.00
E) 2.00
A) 0.0800
B) 0.250
C) 0.500
D) 1.00
E) 2.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
KCl is a strong electrolyte while sucrose (table sugar) is not. Which of the following lists 0.10 m KCl, 0.10 m sucrose, and pure water in order of increasing boiling point?
A) KCl < sucrose < water
B) water < KCl = sucrose
C) KCl = sucrose < water
D) water < sucrose < KCl
E) sucrose < KCl < water
A) KCl < sucrose < water
B) water < KCl = sucrose
C) KCl = sucrose < water
D) water < sucrose < KCl
E) sucrose < KCl < water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following solutions has the highest boiling point?
A) 0.1 m NaCl
B) 0.1 m sucrose
C) 0.1 m Na2CO3
D) 0.1 m NH3
E) 0.1 m NH4Cl
A) 0.1 m NaCl
B) 0.1 m sucrose
C) 0.1 m Na2CO3
D) 0.1 m NH3
E) 0.1 m NH4Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Pure ethanol has a boiling point of 78.0 °C. What is the boiling point of a solution that contains 12.7 grams of KI (MW = 166 g/mol) dissolved in 125 grams of ethanol (MW = 46.0 g/mol)? Assume that KI is a strong electrolyte in ethanol. (Ethanol: kb = 1.22 °C/m)
A) 76.5°C
B) 77.2°C
C) 78.7°C
D) 79.5°C
E) 81.0°C
A) 76.5°C
B) 77.2°C
C) 78.7°C
D) 79.5°C
E) 81.0°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When a 2.15 gram sample of a nonelectrolyte is dissolved in 105 grams of water, the freezing point of the solution is -0.62°C. If the molal freezing point depression constant for water is 1.86°C/m, what is the molecular weight of the nonelectrolyte?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The molal freezing point constant for water is 1.86 °C/m and the freezing point for pure water is 0°C. When 1.50 g of a compound is added to 47.8 g of water, the freezing point of the solution is found to change by 0.174°C. Calculate the molecular weight of the solute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Pure benzene melts at 5.5°C. A solution of 1.25 g of CCl4 in 1.00 x 102 g of benzene would have what freezing point? (Benzene: kb = 5.1°C/m)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Given dilute, equimolar solutions of NaCl and ZnCl2 in water, we would expect the freezing points for the solutions relative to pure water to
A) change by the same amount.
B) change by a ratio of 2:3, with the change for NaCl being 2/3rds that for ZnCl2.
C) change by a ratio of 1:3, with the change for NaCl being 1/3rd that for ZnCl2.
D) change by a ratio of 2:3, with the change for ZnCl2 being 2/3rds that of NaCl.
E) change by a ratio of 1:3, with the change for ZnCl2 being 1/3rd that for NaCl.
A) change by the same amount.
B) change by a ratio of 2:3, with the change for NaCl being 2/3rds that for ZnCl2.
C) change by a ratio of 1:3, with the change for NaCl being 1/3rd that for ZnCl2.
D) change by a ratio of 2:3, with the change for ZnCl2 being 2/3rds that of NaCl.
E) change by a ratio of 1:3, with the change for ZnCl2 being 1/3rd that for NaCl.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If freezing point depression was used to determine the molecular weight of an acid dissolved in water, and the dissociation of the acid wasn't taken into account, the determined value of the molecular weight of the acid would be:
A) accurate
B) too high
C) too low
D) inaccurate, but in a direction that cannot be predicted
A) accurate
B) too high
C) too low
D) inaccurate, but in a direction that cannot be predicted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following equations would be appropriate for calculating the change in the freezing point of an aqueous NaHSO4 solution? (NaHSO4 dissociates in solution in a two-step process.)
NaHSO4(s) Na+(aq) + HSO4-(aq) (100% dissociation)
HSO4-(aq) H+(aq) + SO42-(aq) (10% dissociation)
A) TFP = (1 + 0.10)kfm
B) TFP = (0.10)kfm
C) TFP = [1 + 2( 0.10)]kfm
D) TFP = (0.20)kfm
E) TFP = (2 + 0.10)kfm
NaHSO4(s) Na+(aq) + HSO4-(aq) (100% dissociation)
HSO4-(aq) H+(aq) + SO42-(aq) (10% dissociation)
A) TFP = (1 + 0.10)kfm
B) TFP = (0.10)kfm
C) TFP = [1 + 2( 0.10)]kfm
D) TFP = (0.20)kfm
E) TFP = (2 + 0.10)kfm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A 0.010 molal solution of ammonia in water is 4.1% ionized.
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
Given that pure water freezes at 0°C and the kF for water is 1.86°C/m, which of the following expressions gives the freezing point depression of the aqueous ammonia solution?
A) TFP = -(1.86 °C/m)(0.01 m)
B) TFP = -(1.86 °C/m)(0.01 m)(1.041)
C) TFP = -(1.86 °C/m)(0.01 m)(2.082)
D) TFP = -(1.86 °C/m)(0.01 m)(4.1)
E) TFP = -(1.86 °C/m)(0.01 m)(8.2)
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
Given that pure water freezes at 0°C and the kF for water is 1.86°C/m, which of the following expressions gives the freezing point depression of the aqueous ammonia solution?
A) TFP = -(1.86 °C/m)(0.01 m)
B) TFP = -(1.86 °C/m)(0.01 m)(1.041)
C) TFP = -(1.86 °C/m)(0.01 m)(2.082)
D) TFP = -(1.86 °C/m)(0.01 m)(4.1)
E) TFP = -(1.86 °C/m)(0.01 m)(8.2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



