Deck 18: The Markets for Labor and Other Factors of Production
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: The Markets for Labor and Other Factors of Production
1
What is the difference between labor's marginal product and marginal revenue product?
A) The marginal product of labor is the additional labor's contribution to the firm's total output while the marginal revenue product is the additional labor's contribution to the firm's total sales revenue.
B) The marginal product of labor is the increase in output as a result of hiring an additional worker while the marginal revenue product of labor is the increase in profit as a result of hiring an additional worker.
C) The marginal revenue product of labor is the dollar value of hiring an additional worker while the marginal product of labor is the increase in the firm's physical output as a result of hiring an additional worker.
D) Labor's marginal product is a measure of labor's productivity while labor's marginal revenue product is a measure of labor's ability to sell the firm's products.
A) The marginal product of labor is the additional labor's contribution to the firm's total output while the marginal revenue product is the additional labor's contribution to the firm's total sales revenue.
B) The marginal product of labor is the increase in output as a result of hiring an additional worker while the marginal revenue product of labor is the increase in profit as a result of hiring an additional worker.
C) The marginal revenue product of labor is the dollar value of hiring an additional worker while the marginal product of labor is the increase in the firm's physical output as a result of hiring an additional worker.
D) Labor's marginal product is a measure of labor's productivity while labor's marginal revenue product is a measure of labor's ability to sell the firm's products.
The marginal product of labor is the additional labor's contribution to the firm's total output while the marginal revenue product is the additional labor's contribution to the firm's total sales revenue.
2
For an output price taker, market value of labor's marginal product is also labor's marginal revenue product.
True
3
For an output price maker such as a monopolist, the market value of labor's marginal product is also labor's marginal revenue product.
False
4
An increase in the amount of human capital acquired by workers will lead to a rightward shift of the labor demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A change in the market price of the firm's product causes a movement along the labor demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose firms hire janitors in a perfectly competitive market. An increase in the number of firms that uses janitorial service will lead to an increase in the wage rate that firms have to pay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The combined effect (both income and substitution) of a wage increase is that
A) if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect, labor supply curve is backward bending, but if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect, labor supply slopes upward.
B) the income effect always dominates, leading to less work at a higher wage.
C) if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect, labor supply curve slopes upward, but if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect, labor supply is backward bending.
D) the substitution effect always dominates, leading to more work at a higher wage.
A) if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect, labor supply curve is backward bending, but if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect, labor supply slopes upward.
B) the income effect always dominates, leading to less work at a higher wage.
C) if the substitution effect outweighs the income effect, labor supply curve slopes upward, but if the income effect outweighs the substitution effect, labor supply is backward bending.
D) the substitution effect always dominates, leading to more work at a higher wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
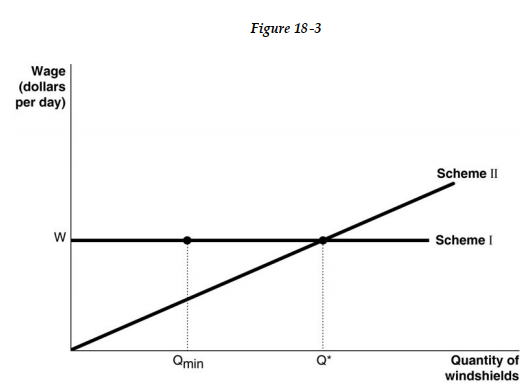 Figure 18-3 shows two different compensation schemes for the Youness Corporation, an installer of auto glass windshields. Under Scheme I, the firm pays a consistent daily wage of $80 per day based on an 8-hour workday. QMin in represents the cut-off point under the hourly-wage system: if a worker installed fewer than QMin in windshields, the worker got fired. Scheme II represents a piece-rate scheme with an earnings floor: no worker would get less than $80 per day (for an 8-hour workday) and would have to produce at least QMin in. For any output level beyond Q* the worker earned an additional $20 for each unit produced.
Figure 18-3 shows two different compensation schemes for the Youness Corporation, an installer of auto glass windshields. Under Scheme I, the firm pays a consistent daily wage of $80 per day based on an 8-hour workday. QMin in represents the cut-off point under the hourly-wage system: if a worker installed fewer than QMin in windshields, the worker got fired. Scheme II represents a piece-rate scheme with an earnings floor: no worker would get less than $80 per day (for an 8-hour workday) and would have to produce at least QMin in. For any output level beyond Q* the worker earned an additional $20 for each unit produced.-Refer to Figure 18 -2. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Panel B correctly describes a situation in which the income effect dominate the substitution effect at low wages (segment i) and again at very high wages (segment iii).
B) Panel B incorrectly describes a situation in which the income effect dominate the substitution effect at low wages (segment i).
C) Panel B incorrectly describes a situation in which the income effect dominate the substitution effect at low wages (segment i) and a situation in which the substitution effect dominate the income effect at very high wages (segment iii).
D) Panel B incorrectly describes a situation in which the income effect dominate the substitution effect at very high wages (segment iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
 Figure 18-3 shows two different compensation schemes for the Youness Corporation, an installer of auto glass windshields. Under Scheme I, the firm pays a consistent daily wage of $80 per day based on an 8-hour workday. QMin in represents the cut-off point under the hourly-wage system: if a worker installed fewer than QMin in windshields, the worker got fired. Scheme II represents a piece-rate scheme with an earnings floor: no worker would get less than $80 per day (for an 8-hour workday) and would have to produce at least QMin in. For any output level beyond Q* the worker earned an additional $20 for each unit produced.
Figure 18-3 shows two different compensation schemes for the Youness Corporation, an installer of auto glass windshields. Under Scheme I, the firm pays a consistent daily wage of $80 per day based on an 8-hour workday. QMin in represents the cut-off point under the hourly-wage system: if a worker installed fewer than QMin in windshields, the worker got fired. Scheme II represents a piece-rate scheme with an earnings floor: no worker would get less than $80 per day (for an 8-hour workday) and would have to produce at least QMin in. For any output level beyond Q* the worker earned an additional $20 for each unit produced.-Refer to Figure 18 -2. Panel D is appropriate when used to represent
A) the quantity of labor supplied by someone working a fixed number of hours.
B) the quantity of labor demanded by an input price taker.
C) the highly skilled labor market supply curve.
D) the labor supply curve facing an input price taker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose the following two events occur in the domestic market for radiologists:
A. Some hospitals are outsourcing some radiology services such as reading x-rays.
B. Some medical schools have closed down their radiology departments as fewer students enroll in this field.
What is likely to happen to the equilibrium wage and quantity of radiologists following these two events?
A) The equilibrium quantity falls and the effect on the equilibrium wage of radiologists is
Indeterminate.
B) The equilibrium wage and the equilibrium quantity of radiologists rise.
C) The equilibrium wage and the equilibrium quantity of radiologists fall.
D) The equilibrium wage falls and the effect on equilibrium quantity of radiologists is indeterminate.
A. Some hospitals are outsourcing some radiology services such as reading x-rays.
B. Some medical schools have closed down their radiology departments as fewer students enroll in this field.
What is likely to happen to the equilibrium wage and quantity of radiologists following these two events?
A) The equilibrium quantity falls and the effect on the equilibrium wage of radiologists is
Indeterminate.
B) The equilibrium wage and the equilibrium quantity of radiologists rise.
C) The equilibrium wage and the equilibrium quantity of radiologists fall.
D) The equilibrium wage falls and the effect on equilibrium quantity of radiologists is indeterminate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose the following two events occur in the market for elementary school teachers:
A. Overcrowded schools and education budget cuts have discouraged young college students from pursuing careers in teaching.
B. With an increasing birth rate, the number of children entering the elementary school system is expected to increase significantly over the next ten years.
What is likely to happen to the equilibrium wage and quantity of teachers as a result of these two events?
A) The equilibrium quantity falls and the equilibrium wage of elementary school teachers rises.
B) The equilibrium quantity falls and the effect on the equilibrium wage of elementary school teachers is indeterminate.
C) The equilibrium quantity and the equilibrium wage of elementary school teachers fall.
D) The equilibrium wage rises and the effect on the equilibrium quantity of elementary school teachers is indeterminate.
A. Overcrowded schools and education budget cuts have discouraged young college students from pursuing careers in teaching.
B. With an increasing birth rate, the number of children entering the elementary school system is expected to increase significantly over the next ten years.
What is likely to happen to the equilibrium wage and quantity of teachers as a result of these two events?
A) The equilibrium quantity falls and the equilibrium wage of elementary school teachers rises.
B) The equilibrium quantity falls and the effect on the equilibrium wage of elementary school teachers is indeterminate.
C) The equilibrium quantity and the equilibrium wage of elementary school teachers fall.
D) The equilibrium wage rises and the effect on the equilibrium quantity of elementary school teachers is indeterminate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consider the following statements about the signaling hypothesis of education:
A. The signaling hypothesis of education is based on the idea that college graduates are more productive than non -college graduates.
B. The signaling hypothesis of education suggests that firms rely on human capital requirements to ensure worker quality.
C. Employers rely on certain signals, such as a college diploma to gauge a potential employee's abilities because it could lower the cost of acquiring information about the person that is not easily observed.
Which of the statements above is true about the signaling hypothesis of education?
A) a, b, and c
B) a and b only
C) b and c only
D) a and c only
A. The signaling hypothesis of education is based on the idea that college graduates are more productive than non -college graduates.
B. The signaling hypothesis of education suggests that firms rely on human capital requirements to ensure worker quality.
C. Employers rely on certain signals, such as a college diploma to gauge a potential employee's abilities because it could lower the cost of acquiring information about the person that is not easily observed.
Which of the statements above is true about the signaling hypothesis of education?
A) a, b, and c
B) a and b only
C) b and c only
D) a and c only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is not a possible consequence of illegal immigration of unskilled workers?
A) Rental rates in low -income neighborhoods rise.
B) The distribution of income becomes less unequal.
C) The crime rate increases.
D) The supply of labor in some occupations increases.
A) Rental rates in low -income neighborhoods rise.
B) The distribution of income becomes less unequal.
C) The crime rate increases.
D) The supply of labor in some occupations increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is an example of a compensating wage differential?
A) Workers in a dynamite mine receive higher wages than if they worked in other jobs that require the same level of skills.
B) Nurse anesthetists are paid less than anesthesiologists (who have medical degrees).
C) In the market for lawyers, top graduates from the top programs earn starting salaries that are significantly higher than the starting salaries earned by lower -ranked graduates from the
Lower -ranked programs.
D) Popular movie stars like George Clooney command much higher salaries than other talented but lesser known actors.
A) Workers in a dynamite mine receive higher wages than if they worked in other jobs that require the same level of skills.
B) Nurse anesthetists are paid less than anesthesiologists (who have medical degrees).
C) In the market for lawyers, top graduates from the top programs earn starting salaries that are significantly higher than the starting salaries earned by lower -ranked graduates from the
Lower -ranked programs.
D) Popular movie stars like George Clooney command much higher salaries than other talented but lesser known actors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Men in the Arab world are more likely to have direct access to waged employment than women. Which of these factors helped creating this gap between male and female employment opportunities?
A) Culture.
B) The use of capital -intensive technologies that require few workers.
C) Males receive relatively higher wages.
D) All of the above
A) Culture.
B) The use of capital -intensive technologies that require few workers.
C) Males receive relatively higher wages.
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
One of the important challenges in the Arab world is education. How does education contribute to the growth of national income?
A) Education has no effect on growth of national income.
B) Education teaches people about math, a very important subject for income growth.
C) Education improves the productive capacities of the labour force.
D) None of the above.
A) Education has no effect on growth of national income.
B) Education teaches people about math, a very important subject for income growth.
C) Education improves the productive capacities of the labour force.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Scenario 18-1: In academia, professors in some disciplines receive higher salaries than others. For example, professors teaching in business schools receive higher salaries than professors in the English department. Suppose in Unity College, assistant professors in the business school earn $Wb while assistant professors in the English department earn $We < Wb. Now suppose the government passes comparable worth legislation that requires academic institutions to pay all faculty the same salaries.
-Following the passage of comparable worth legislation, Unity College responds by placing salaries for all assistant professors at $Wb. Which of the following is the result of the legislation?
A) There will be a surplus in the market for English professors and the market for business professors will not be affected.
B) The demand for English professors decrease; the market for business professors is not affected.
C) The supply of English professors increase; the market for business professors is not affected.
D) There will be a surplus in the market for English professors and a shortage in the market for business professors.
-Following the passage of comparable worth legislation, Unity College responds by placing salaries for all assistant professors at $Wb. Which of the following is the result of the legislation?
A) There will be a surplus in the market for English professors and the market for business professors will not be affected.
B) The demand for English professors decrease; the market for business professors is not affected.
C) The supply of English professors increase; the market for business professors is not affected.
D) There will be a surplus in the market for English professors and a shortage in the market for business professors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Scenario 18-1: In academia, professors in some disciplines receive higher salaries than others. For example, professors teaching in business schools receive higher salaries than professors in the English department. Suppose in Unity College, assistant professors in the business school earn $Wb while assistant professors in the English department earn $We < Wb. Now suppose the government passes comparable worth legislation that requires academic institutions to pay all faculty the same salaries.
-Following the passage of comparable worth legislation, Unity College responds by placing salaries at $Wa between the two existing salaries. Which of the following is the result of the legislation?
A) There will be a surplus in the market for English professors and the market for business professors will not be affected.
B) The demand for English professors decrease and the demand for business professors increase.
C) The supply of English professors increase and the supply of business professors decrease.
D) There will be a surplus in the market for English professors and a shortage in the market for business professors.
-Following the passage of comparable worth legislation, Unity College responds by placing salaries at $Wa between the two existing salaries. Which of the following is the result of the legislation?
A) There will be a surplus in the market for English professors and the market for business professors will not be affected.
B) The demand for English professors decrease and the demand for business professors increase.
C) The supply of English professors increase and the supply of business professors decrease.
D) There will be a surplus in the market for English professors and a shortage in the market for business professors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Compensating wage differentials compensate workers for some negative job characteristics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Wage differences in the labor market are largely due to economic discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Paying unionized workers higher wages than non -unionized workers is evidence of economic discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements about commission systems of compensation is false?
A) The lack of income stability will induce the more productive workers to leave in search of more secure employment.
B) During sluggish periods, an employer's payroll expenses will decline along with sales.
C) If workers are paid on the basis of the number of units produced, they may become less concerned about quality.
D) They increase the risk to workers because sometimes output declines for reasons not connected to the worker's effort.
A) The lack of income stability will induce the more productive workers to leave in search of more secure employment.
B) During sluggish periods, an employer's payroll expenses will decline along with sales.
C) If workers are paid on the basis of the number of units produced, they may become less concerned about quality.
D) They increase the risk to workers because sometimes output declines for reasons not connected to the worker's effort.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
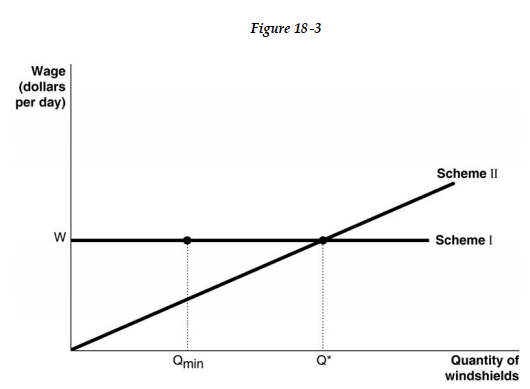 Figure 18-3 shows two different compensation schemes for the Youness Corporation, an installer of auto glass windshields. Under Scheme I, the firm pays a consistent daily wage of $80 per day based on an 8-hour workday. QMin in represents the cut-off point under the hourly-wage system: if a worker installed fewer than QMin in windshields, the worker got fired. Scheme II represents a piece-rate scheme with an earnings floor: no worker would get less than $80 per day (for an 8-hour workday) and would have to produce at least QMin in. For any output level beyond Q* the worker earned an additional $20 for each unit produced.
Figure 18-3 shows two different compensation schemes for the Youness Corporation, an installer of auto glass windshields. Under Scheme I, the firm pays a consistent daily wage of $80 per day based on an 8-hour workday. QMin in represents the cut-off point under the hourly-wage system: if a worker installed fewer than QMin in windshields, the worker got fired. Scheme II represents a piece-rate scheme with an earnings floor: no worker would get less than $80 per day (for an 8-hour workday) and would have to produce at least QMin in. For any output level beyond Q* the worker earned an additional $20 for each unit produced.-Refer to Figure 18 -3. Under Scheme I,
A) workers compete with each other to see who can produce beyond QMin in the shortest possible time.
B) the incentive to increase productivity depends on where QMin is set; if it is at a very high level, then workers will rise to the challenge for fear of losing their jobs.
C) workers signal their productivity to the firm by consistently producing above QMin.
D) workers have no incentive to produce beyond QMin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
 Figure 18-3 shows two different compensation schemes for the Youness Corporation, an installer of auto glass windshields. Under Scheme I, the firm pays a consistent daily wage of $80 per day based on an 8-hour workday. QMin in represents the cut-off point under the hourly-wage system: if a worker installed fewer than QMin in windshields, the worker got fired. Scheme II represents a piece-rate scheme with an earnings floor: no worker would get less than $80 per day (for an 8-hour workday) and would have to produce at least QMin in. For any output level beyond Q* the worker earned an additional $20 for each unit produced.
Figure 18-3 shows two different compensation schemes for the Youness Corporation, an installer of auto glass windshields. Under Scheme I, the firm pays a consistent daily wage of $80 per day based on an 8-hour workday. QMin in represents the cut-off point under the hourly-wage system: if a worker installed fewer than QMin in windshields, the worker got fired. Scheme II represents a piece-rate scheme with an earnings floor: no worker would get less than $80 per day (for an 8-hour workday) and would have to produce at least QMin in. For any output level beyond Q* the worker earned an additional $20 for each unit produced.-Refer to Figure 18 -3. Suppose QMin = 2 windshields and Q*=5 windshields. Under Scheme II, a worker has to install Q* windshields before she earns an additional $20 per windshield installed. What is a potential problem with this scheme?
A) Workers have no incentive to produce output to between QMin and Q*.
B) Workers might be more concerned with increasing output beyond Q* and less concerned with the quality of their work.
C) It violates labor laws because workers are not compensated for output between QMin and Q*.
D) Any increase in output between QMin and Q* benefits the employer only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which the following is NOT one of the three benefits suggested for increasing flexible employment in the GCC?
A) Improving business agility
B) Reducing structural unemployment
C) Increasing levels of training
D) Increasing labor participation
A) Improving business agility
B) Reducing structural unemployment
C) Increasing levels of training
D) Increasing labor participation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which the following is the key benefit of improving business agility through flexible employment?
A) Businesses can react seamlessly to economic cycles.
B) There is an increase in structural unemployment.
C) Employees get continuity of employment.
D) There is increased participation in the labor market.
A) Businesses can react seamlessly to economic cycles.
B) There is an increase in structural unemployment.
C) Employees get continuity of employment.
D) There is increased participation in the labor market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



