Deck 7: Technology, Production, and Costs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/17
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Technology, Production, and Costs
1
The difference between technology and technological change is that
A) technology is product -centered, that is, developing new products with our limited resources, while technological change is process -centered in that it focuses on developing new production techniques.
B) technology is carried out by firms producing physical goods while technological change is an intellectual exercise into seeking ways to improve production.
C) technology refers to the processes used by a firm to transform inputs into output while technological change is a change in a firm's ability to produce a given level of output with a given quantity of inputs.
D) technology involves the use of capital equipment while technological change requires the use of brain power.
A) technology is product -centered, that is, developing new products with our limited resources, while technological change is process -centered in that it focuses on developing new production techniques.
B) technology is carried out by firms producing physical goods while technological change is an intellectual exercise into seeking ways to improve production.
C) technology refers to the processes used by a firm to transform inputs into output while technological change is a change in a firm's ability to produce a given level of output with a given quantity of inputs.
D) technology involves the use of capital equipment while technological change requires the use of brain power.
technology refers to the processes used by a firm to transform inputs into output while technological change is a change in a firm's ability to produce a given level of output with a given quantity of inputs.
2
Suppose a chain of convenience stores reorganized its system of supplying its stores with food. This led to a sharp reduction in the number of trucks that the company had to use and increased the amount of fresh food on store shelves. Which of the following statements best describes the chain stores' actions?
A) Technological change refers only to the introduction of new products or improvements to existing products. As such, the scenario described in the question is not technological change.
B) The scenario described is an example of management efficiency and not technological change. Essentially, the chain changes the way it operates its business..
C) The firm is able to produce more output (increase its sales) using fewer inputs (less trucks). Therefore, the chain of convenience stores has implemented a positive technological change.
D) The change implemented is not an example of technological change because it did not require the use of new machinery or equipment.
A) Technological change refers only to the introduction of new products or improvements to existing products. As such, the scenario described in the question is not technological change.
B) The scenario described is an example of management efficiency and not technological change. Essentially, the chain changes the way it operates its business..
C) The firm is able to produce more output (increase its sales) using fewer inputs (less trucks). Therefore, the chain of convenience stores has implemented a positive technological change.
D) The change implemented is not an example of technological change because it did not require the use of new machinery or equipment.
The firm is able to produce more output (increase its sales) using fewer inputs (less trucks). Therefore, the chain of convenience stores has implemented a positive technological change.
3
Rola quit her job as a buyer for Center Point to start her own hair dressing salon, Goldilocks. She gave up a salary of US$40,000 per year, invested her savings of US$30,000 (which was earning 5 percent interest) and borrowed US$10,000 from a close friend, agreeing to pay 5 percent interest per year. In her first year, Rola spent US$18,000 to rent a salon, hired a part -time assistant for US$12,000 and incurred another US$15,000 on equipment and hairdressing material. Based on this information, what is the amount of her explicit costs?
A) US$45,500
B) US$87,000
C) US$47,000
D) US$45,000
A) US$45,500
B) US$87,000
C) US$47,000
D) US$45,000
US$45,500
4
Rola quit her job as a buyer for Center Point to start her own hair dressing salon, Goldilocks. She gave up a salary of US$40,000 per year, invested her savings of US$30,000 (which was earning 5 percent interest) and borrowed US$10,000 from a close friend, agreeing to pay 5 percent interest per year. In her first year, Rola spent US$18,000 to rent a salon, hired a part -time assistant for US$12,000 and incurred another US$15,000 on equipment and hairdressing material. Based on this information, what is the amount of her implicit costs?
A) US$41,500
B) US$42,000
C) US$80,000
D) US$70,000
A) US$41,500
B) US$42,000
C) US$80,000
D) US$70,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The law of diminishing marginal returns
A) holds even when there are no fixed factors.
B) applies only in the short run.
C) explains ultimately that production displays diseconomies of scale.
D) sets in because not all workers are equally productive.
A) holds even when there are no fixed factors.
B) applies only in the short run.
C) explains ultimately that production displays diseconomies of scale.
D) sets in because not all workers are equally productive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
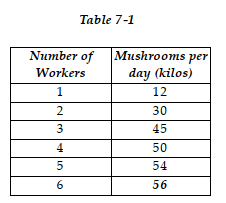 Table 7-1 shows the technology of production at the Mostafa's Mushroom Farm for the month of May 2007.
Table 7-1 shows the technology of production at the Mostafa's Mushroom Farm for the month of May 2007.-Refer to Table 7 -1. What is the marginal product of the fourth worker?
A) 5 kilos
B) 12.5 kilos
C) 137 kilos
D) 50 kilos

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Average fixed costs of production
A) appear as a U -shaped curve on graphs.
B) remain constant.
C) fall as long as output is increased.
D) will rise at a fixed rate as more is produced.
A) appear as a U -shaped curve on graphs.
B) remain constant.
C) fall as long as output is increased.
D) will rise at a fixed rate as more is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Adam spent US$10,000 on new equipment for his small business, "Adam's Fitness Studio". Membership at his fitness center is very low and at this rate, Adam needs an additional US$12,000 per year to keep his studio open. Which of the following is true?
A) The US$10,000 Adam spent on equipment is the total cost of starting the business and the US$12,000 he'll need to continue operations is a marginal cost.
B) The fixed cost of running the studio is US$22,000.
C) The variable cost of running the studio is US$22,000.
D) The US$10,000 Adam spent on equipment is a fixed cost of business and the US$12,000 he'll need to continue operations is a variable cost.
A) The US$10,000 Adam spent on equipment is the total cost of starting the business and the US$12,000 he'll need to continue operations is a marginal cost.
B) The fixed cost of running the studio is US$22,000.
C) The variable cost of running the studio is US$22,000.
D) The US$10,000 Adam spent on equipment is a fixed cost of business and the US$12,000 he'll need to continue operations is a variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose you have just opened a store to sell espresso machines. Both you and a competing store buy this machine from a manufacturer for US$130 each. Your competitor, who has a store the same size as yours, is currently selling about 10 machines a month at a price of US$200 per machine. You expect to sell about six machines a month at a price of US$220 per machine. If you lower your price, you expect to make a loss. Which of the following could explain why your competitor is able to sell the machine at a lower price profitably although the cost of purchasing the machine is the same for the both of you?
A) The competing store's goal is to maximize revenue and not profit.
B) The competing store probably has a lower average cost because average fixed costs falls as output increases.
C) The competing store probably has a lower average variable cost of production.
D) The competing store probably has a lower marginal cost of production.
A) The competing store's goal is to maximize revenue and not profit.
B) The competing store probably has a lower average cost because average fixed costs falls as output increases.
C) The competing store probably has a lower average variable cost of production.
D) The competing store probably has a lower marginal cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
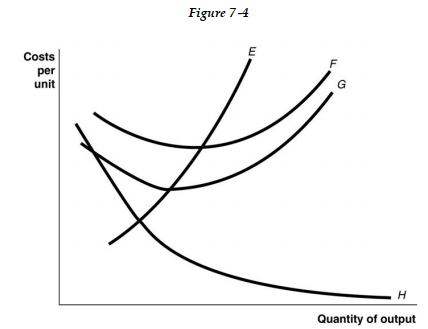
-Refer to Figure 7 -4. Identify the curves in the diagram.
A) E = average fixed cost curve; F = variable cost curve; G = total cost curve; H = marginal cost curve.
B) E = marginal cost curve; F = total cost curve; G = variable cost curve; H = average fixed cost curve
C) E = average fixed cost curve; F = average total cost curve; G = average variable cost curve; H = marginal cost curve.
D) E = marginal cost curve; F = average total cost curve; G = average variable cost curve; H = average fixed cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In 2004, the Egyptian government implemented an economic reform program that led to a sharp reduction in tariffs on imported cars. This helped GB Auto Ghabbour to
A) attract skilled workers.
B) increase production and generate economies of scale.
C) save on transport costs.
D) locate its production centers closer to its customers.
A) attract skilled workers.
B) increase production and generate economies of scale.
C) save on transport costs.
D) locate its production centers closer to its customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
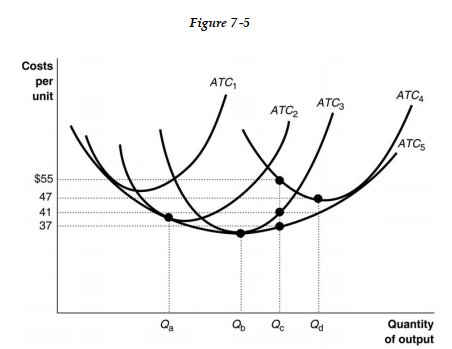
-Refer to Figure 7 -5. Suppose for the past 8 years the firm has been producing Qd units per period using plant size ATC4. Now, following a permanent change in demand, it plans to cut production to Qc units. What will happen to its average cost of production?
A) In the short run, its average cost falls from US$47 to US$37, and in the long run, average cost rises to US$41.
B) In the short run, its average cost rises from US$47 to US$55, and in the long run, average cost falls to US$37.
C) In the short run, its average cost falls from US$47 to US$41, and in the long run, average cost falls even further to US$37.
D) In the short run, its average cost rises from US$47 to US$55, and in the long run, average cost falls to US$41.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

-Refer to Figure 7 -5. Identify the minimum efficient scale of production.
A) Qb
B) Qa
C) Qc
D) Qd

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A decrease in the price of inputs used to produce flat -panel televisions causes
A) a movement downwards along a given average cost curve only.
B) the marginal cost curve to shift downwards but not the average cost curve.
C) the average cost curve to shift downwards but not the marginal cost curve.
D) the average cost curve and the marginal cost curve to shift downwards.
A) a movement downwards along a given average cost curve only.
B) the marginal cost curve to shift downwards but not the average cost curve.
C) the average cost curve to shift downwards but not the marginal cost curve.
D) the average cost curve and the marginal cost curve to shift downwards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Manufacturers of flat -panel televisions expect continued rapid increases in the demand for their products. In response to this forecast, manufacturers are building increasingly larger plants. At the same time, they expect to sell flat -panel televisions at lower prices. Which of the following must be true if manufacturers plan to lower prices and yet expect to cover the average cost of production in their larger plants?
A) They expect that the demand for flat -panel televisions is relatively elastic and therefore lowering the price will lead to an increase in total revenue which will comfortably cover the average cost of production.
B) The cost of building a larger plant must be lower than the cost of building smaller plants.
C) Larger plants are more efficient than smaller plants because the bulk of the cost of production is a fixed cost.
D) They expect that economies of scale will make the cost of production in the larger plants lower than the cost of production in the smaller plants.
A) They expect that the demand for flat -panel televisions is relatively elastic and therefore lowering the price will lead to an increase in total revenue which will comfortably cover the average cost of production.
B) The cost of building a larger plant must be lower than the cost of building smaller plants.
C) Larger plants are more efficient than smaller plants because the bulk of the cost of production is a fixed cost.
D) They expect that economies of scale will make the cost of production in the larger plants lower than the cost of production in the smaller plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
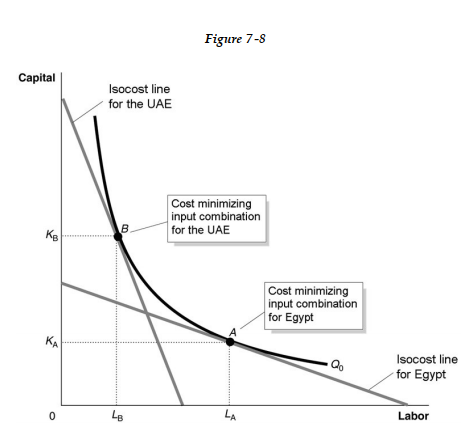 Figure 7-8 shows the optimal input combinations for the production of a given quantity of cotton in the United Arab Emirates and in Egypt
Figure 7-8 shows the optimal input combinations for the production of a given quantity of cotton in the United Arab Emirates and in Egypt-Refer to Figure 7 -8. Consider the following statements:
A. For each country, the marginal product per dollar spent on labor is equal to the marginal product per dollar spent on capital.
B. The price of labor is relatively higher in the United Arab Emirates than in Egypt and the price of capital is relatively lower in the United Arab Emirates than in Egypt.
C. The price of labor and the price of capital are relatively higher in the United Arab Emirates than in Egypt.
Based on Figure 7-8, which of the above statementsare true?
A) Statements b and c only.
B) All of the statements are true.
C) Statements a and c only.
D) Statements a and b only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
 Figure 7-8 shows the optimal input combinations for the production of a given quantity of cotton in the United Arab Emirates and in Egypt
Figure 7-8 shows the optimal input combinations for the production of a given quantity of cotton in the United Arab Emirates and in Egypt-Refer to Figure 7 -8. Which of the following could explain why the United Arab Emirates and Egypt use different input combinations to produce a given quantity of cotton, and yet each country produces that quantity at the lowest possible cost?
A) because the prices of inputs are not the same for the two countries: labor is relatively lower priced and capital is relatively higher priced in the United Arab Emirates
B) because the prices of inputs are not the same for the two countries: labor is relatively lower priced and capital is relatively higher priced in Egypt
C) because the United Arab Emirates has more sophisticated technology and therefore is more efficient in cotton production
D) because the marginal product per dollar spent on capital yields a higher return in the United Arab Emirates than in Egypt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



