Deck 4: Economic Efficiency, Government Price Setting, and Taxes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Economic Efficiency, Government Price Setting, and Taxes
1
Which of the following is NOT a rent control policy goal in Dubai city?
A) Decreasing the profit of landlords.
B) Providing residents with affordable houses.
C) Helping residents to predict the annual increase in rent.
D) Suppressing the high inflation rate that prevailed in Dubai before the global financial crisis of 2008.
A) Decreasing the profit of landlords.
B) Providing residents with affordable houses.
C) Helping residents to predict the annual increase in rent.
D) Suppressing the high inflation rate that prevailed in Dubai before the global financial crisis of 2008.
Decreasing the profit of landlords.
2
Suppose there are two cities that have rent controlled apartments. In one city (Dubai) all apartments are subject to rent control; in the other city (Abu Dhabi) one -half of the apartments are rent controlled. Which of the following is most likely to be true?
A) It will be easier to find an affordable apartment in Abu Dhabi, either a rent -controlled apartment or another apartment, at a reasonable price.
B) It will be easier to find an affordable apartment in Dubai since rents will be low across the board.
C) It will be difficult to find a rent -controlled apartment in Dubai or Abu Dhabi; rents for the Abu Dhabi apartments not subject to controls will be higher than they would be without rent control.
D) It will be impossible to rent an apartment in either city at any price.
A) It will be easier to find an affordable apartment in Abu Dhabi, either a rent -controlled apartment or another apartment, at a reasonable price.
B) It will be easier to find an affordable apartment in Dubai since rents will be low across the board.
C) It will be difficult to find a rent -controlled apartment in Dubai or Abu Dhabi; rents for the Abu Dhabi apartments not subject to controls will be higher than they would be without rent control.
D) It will be impossible to rent an apartment in either city at any price.
It will be difficult to find a rent -controlled apartment in Dubai or Abu Dhabi; rents for the Abu Dhabi apartments not subject to controls will be higher than they would be without rent control.
3
Which of the following statements best describes the concept of consumer surplus?
A) "I sold my DVD copy of Home Alone for US$18 at a garage sale even though I was willing to sell it for US$10."
B) "Carrefour was having a sale on Mars ice cream so I bought 3 packs."
C) "I was ready to pay US$300 for a new leather jacket that I had seen in City Center Mall but I ended up paying only US$180 for the same jacket."
D) "I paid US$130 for a printer last week. This week the same store is selling the same printer for US$110."
A) "I sold my DVD copy of Home Alone for US$18 at a garage sale even though I was willing to sell it for US$10."
B) "Carrefour was having a sale on Mars ice cream so I bought 3 packs."
C) "I was ready to pay US$300 for a new leather jacket that I had seen in City Center Mall but I ended up paying only US$180 for the same jacket."
D) "I paid US$130 for a printer last week. This week the same store is selling the same printer for US$110."
"I was ready to pay US$300 for a new leather jacket that I had seen in City Center Mall but I ended up paying only US$180 for the same jacket."
4
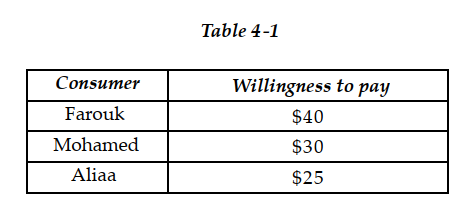
-Refer to Table 4 -1. The table above lists the highest prices three consumers, Farouk, Mohamed and Aliaa, are willing to pay for a short -sleeved polo shirt. If the price of one of the shirts is US$28 dollars
A) Farouk will receive US$12 of consumer surplus from buying one shirt.
B) Farouk and Mohamed receive a total of US$70 of consumer surplus from buying one shirt each. Aliaa will buy no shirts.
C) Aliaa will receive US$25 of consumer surplus since she will buy no shirts.
D) Farouk will buy two shirts, Mohamed will buy one shirt and Aliaa will buy no shirts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
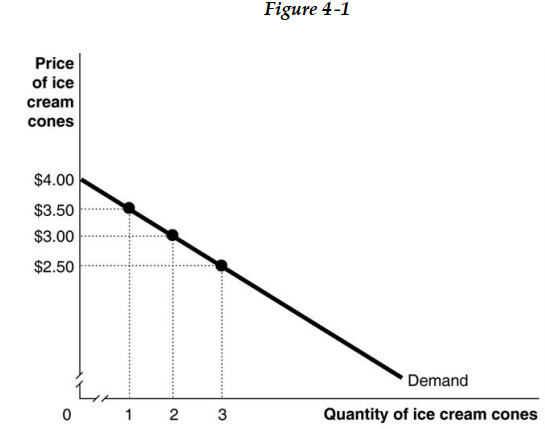
-Refer to Figure 4 -1. Magi's marginal benefit from consuming the second ice cream cone is
A) US$2.25.
B) US$6.50.
C) US$6.00.
D) US$3.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

-Refer to Figure 4 -1. If the market price is US$2.50, what is the consumer surplus on the second ice cream cone?
A) US$1.50
B) US$3.00
C) US$0.50
D) US$10.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

-Refer to Figure 4 -1. If the market price is US$2.50, what is Magi's consumer surplus?
A) US$7.50
B) US$9.00
C) US$1.50
D) US$0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

-Refer to Figure 4 -1. What is the total amount that Magi is willing to pay for 3 ice cream cones?
A) US$13.50
B) US$9.00
C) US$2.50
D) US$7.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Two economists from the University of Chicago estimated the benefit households received from subscribing to satellite television. The economists found that
A) one year's benefit to consumers who subscribe to satellite television is about US$2 billion.
B) most consumers of satellite television were not willing to pay more than US$81 per month.
C) the average consumer of satellite television received a marginal benefit equal to US$81.
D) the consumer surplus from cable television exceeded the consumer surplus from satellite television.
A) one year's benefit to consumers who subscribe to satellite television is about US$2 billion.
B) most consumers of satellite television were not willing to pay more than US$81 per month.
C) the average consumer of satellite television received a marginal benefit equal to US$81.
D) the consumer surplus from cable television exceeded the consumer surplus from satellite television.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
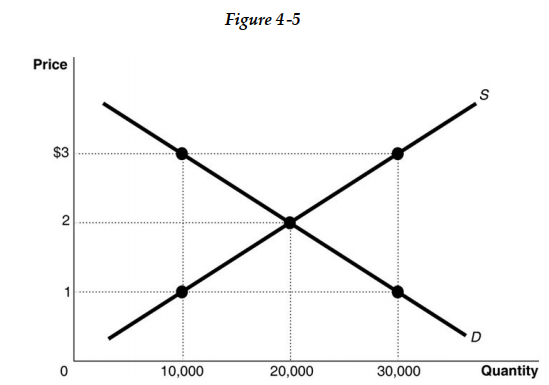
-Refer to Figure 4 -5. The figure above represents the market for iced tea. Assume that this is a competitive market. At a price of US$3
A) the marginal benefit of iced tea is greater than the marginal cost; therefore, output is inefficiently low.
B) the marginal benefit of iced tea is greater than the marginal cost; therefore, output is inefficiently high.
C) the marginal cost of iced tea is greater than the marginal benefit; therefore, output is inefficiently low.
D) producers should lower the price to US$1 in order to sell the quantity demanded of 10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11

-Refer to Figure 4 -5. The figure above represents the market for iced tea. Assume that this is a competitive market. If the price of iced tea is US$1
A) economic surplus is maximized.
B) not enough consumers want to buy iced tea.
C) the quantity supplied is less than the economically efficient quantity.
D) the quantity supplied is economically efficient but the quantity demanded is economically inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

-Refer to Figure 4 -5. The figure above represents the market for iced tea. Assume that this is a competitive market. If the price of iced tea is US$3, what changes in the market would result in an economically efficient output?
A) The quantity supplied would decrease, the quantity demanded would increase, and the equilibrium price would decrease.
B) The price would decrease, quantity demanded would increase, and quantity supplied would decrease.
C) The price would decrease, the quantity supplied would increase, and the quantity demanded would decrease.
D) The price would decrease, the demand would increase, and the supply would decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
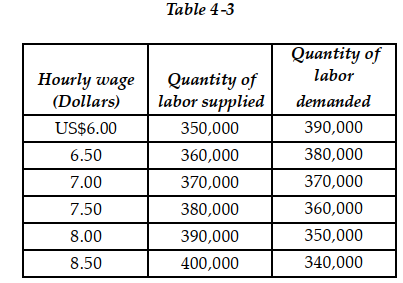 Table 4-3 shows a hypothetical demand and supply schedules for the low-skilled labor market in the city of Amman.
Table 4-3 shows a hypothetical demand and supply schedules for the low-skilled labor market in the city of Amman.-Refer to Table 4 -3. What is the equilibrium hourly wage (W*) and the equilibrium quantity of labor (Q*)?
A) W* = US$6.50; Q* = 360,000
B) W* = US$7.00; Q* = 740,000
C) W* = US$7.00; Q* = 370,000
D) W* = US$6.50; Q* = 380,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Government intervention in the cotton industry in Egypt began
A) in the 1990s.
B) in the 1980s.
C) in the 1960s.
D) in the 1970s.
A) in the 1990s.
B) in the 1980s.
C) in the 1960s.
D) in the 1970s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following describes the difference between "scarcity" and "shortage"?
A) In the economic sense, almost everything is scarce. A shortage of a product or service occurs when the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied at the current market price.
B) There is no difference; either word can be used to describe the situation that exists when there is less of a product or service available than people want.
C) In the economic sense, almost everything is scarce. A shortage of a product or service occurs when the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied at the equilibrium price.
D) There is a shortage of almost everything. Scarcity occurs only if the quantity demanded of a product or service is greater than the quantity supplied at the current market price.
A) In the economic sense, almost everything is scarce. A shortage of a product or service occurs when the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied at the current market price.
B) There is no difference; either word can be used to describe the situation that exists when there is less of a product or service available than people want.
C) In the economic sense, almost everything is scarce. A shortage of a product or service occurs when the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied at the equilibrium price.
D) There is a shortage of almost everything. Scarcity occurs only if the quantity demanded of a product or service is greater than the quantity supplied at the current market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In cities with rent controls, the actual rents paid can be higher than the legal maximum. One explanation for this is
A) landlords are allowed to charge more than the legal maximum on some apartments so long as they charge less on others.
B) because there is a shortage of apartments, tenants often are willing to pay rents higher than the law allows.
C) rent control laws are so complicated that landlords and tenants may not be aware of what the legal price is.
D) the legal penalty landlords face for charging more than the legal maximum rent is less than the revenue earned by charging their tenants more than the maximum rent.
A) landlords are allowed to charge more than the legal maximum on some apartments so long as they charge less on others.
B) because there is a shortage of apartments, tenants often are willing to pay rents higher than the law allows.
C) rent control laws are so complicated that landlords and tenants may not be aware of what the legal price is.
D) the legal penalty landlords face for charging more than the legal maximum rent is less than the revenue earned by charging their tenants more than the maximum rent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Some economists believe that giving Christmas gifts results in deadweight losses for gift recipients. Which of the following helps to explain this belief?
A) In many cases people would have chosen different gifts for themselves than the ones they received.
B) Economists have found that deadweight losses occur when people receive the same gifts from different people.
C) Many people resent receiving cash for presents rather than gifts.
D) Many people who give gifts do so because they feel they have to, not because they want to.
A) In many cases people would have chosen different gifts for themselves than the ones they received.
B) Economists have found that deadweight losses occur when people receive the same gifts from different people.
C) Many people resent receiving cash for presents rather than gifts.
D) Many people who give gifts do so because they feel they have to, not because they want to.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
John List and Jason Shogren conducted a study that tried to explain why people continue to give presents rather than cash for birthdays and holidays. Their study found that
A) as much as half the value of a gift to a recipient was its sentimental value.
B) on average, families and friends paid much more for presents than the recipients were willing to pay for them.
C) government restrictions are responsible for most of the deadweight losses associated with gift giving.
D) the deadweight loss from giving cash was twice as great as the deadweight loss from giving presents.
A) as much as half the value of a gift to a recipient was its sentimental value.
B) on average, families and friends paid much more for presents than the recipients were willing to pay for them.
C) government restrictions are responsible for most of the deadweight losses associated with gift giving.
D) the deadweight loss from giving cash was twice as great as the deadweight loss from giving presents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Government intervention in the cotton industry began in the Egypt in the 1990s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
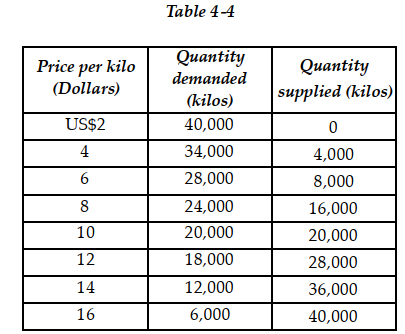 Table 4-4 above contains information about the corn market. Answer the following questions based on this table.
Table 4-4 above contains information about the corn market. Answer the following questions based on this table.-Refer to Table 4-4. An agricultural price floor is a price that the government guarantees farmers will receive for a particular crop. Suppose the federal government sets a price floor for corn at US$12 per kilo.
a. What is the amount of shortage or surplus in the corn market as result of the price floor?
b. If the government agrees to purchase any surplus output at US$12, how much will it cost the government?
c. If the government buys all of the farmers' output at the floor price, how many kilos of corn will it have to purchase and how much will it cost the government?
d. Suppose the government buys up all of the farmers' output at the floor price and then sells the output to consumers at whatever price it can get. Under this scheme, what is the price at which the government will be able to sell off all of the output it had purchased from farmers? What is the revenue received from the government's sale?
e. In this problem we have considered two government schemes: (1) a price floor is established and the government purchases any excess output and (2) the government buys all the farmers' output at the floor price and resells at whatever price it can get. Which scheme will taxpayers prefer?
f. Consider again the two schemes. Which scheme will the farmers prefer?
g. Consider again the two schemes. Which scheme will corn buyers prefer?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
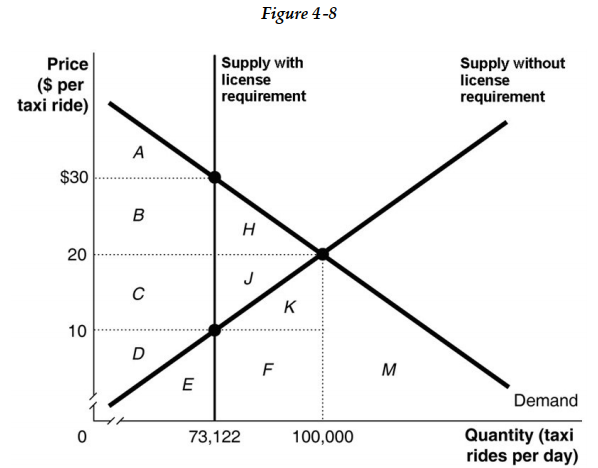 Figure 4-8 shows a hypothetical demand and supply of taxi rides in the city of Riyadh. The government imposes a restriction in this market that forces taxi drivers to get a license from the city government in order to be able to drive. The number of licenses is limited. The following question(s) are based on this figure.
Figure 4-8 shows a hypothetical demand and supply of taxi rides in the city of Riyadh. The government imposes a restriction in this market that forces taxi drivers to get a license from the city government in order to be able to drive. The number of licenses is limited. The following question(s) are based on this figure.-Refer to Figure 4-8. To legally drive a taxicab in Riyadh City, you must have a license issued by the city government. Assume that only 12,187 licenses have been issued. Let's also assume this puts an absolute limit on the number of taxi rides that can be supplied in Riyadh City on any day, because no one breaks the law by driving a taxi without a medallion. Assume as well that each taxi provides 6 trips per day. In that case, the quantity supplied of taxi rides is 73,122 (or 6 rides per taxi × 12,187 taxis). This is shown in the diagram with a vertical line at this quantity. Assume that there are no government controls on the prices that drivers can charge for rides.
a. What would the equilibrium price and quantity be in this market if there were no license requirement?
b. If there were no license requirement, indicate the area that represents consumer surplus.
c. If there were no license requirement, indicate the area that represents producer surplus.
d. If there were no license requirement, indicate the area that represents economic surplus.
e. What are the price and quantity with the license requirement?
f. With a license requirement in place, what area represents consumer surplus?
g. With a license requirement in place, what area represents producer surplus?
h. With a license requirement in place, what area represents the deadweight loss?
i. Based on your answers to parts (c) and (g) are taxicab drivers better off with the license requirement for taxicabs than without?
j. Are consumers better off with or without the license requirement for taxicabs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
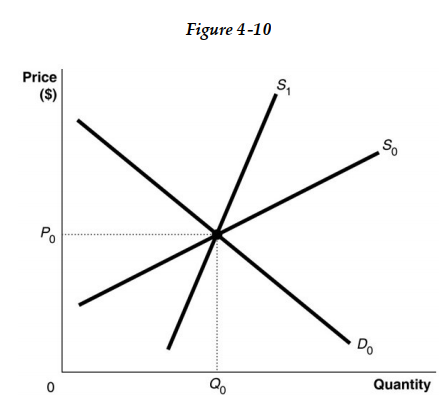
-Refer to Figure 4 -10. Suppose the market is initially in equilibrium at price P0 and now the government imposes a tax on every unit sold. Which of the following statements best describe the impact of the tax? For demand curve D0
A) the producer bears a greater share of the tax burden if the supply curve is S0.
B) the producer's share of the tax burden is the same whether the supply curve is S0 or S1.
C) the producer bears the entire burden of the tax if the supply curve is S0 and the consumer bears the entire burden of the tax if the supply curve is S1.
D) the producer bears a greater share of the tax burden if the supply curve is S1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23

-Refer to Figure 4 -11. Suppose the market is initially in equilibrium at price P0 and then the government imposes a tax on every unit sold. Which of the following statements best describes the impact of the tax?
A) The consumer will bear a greater share of the tax burden if the demand curve is D1.
B) The consumer's share of the tax burden is the same whether the demand curve is D0 or D1.
C) The consumer will bear the entire burden of the tax if the demand curve is D0 and the producer will bear the entire burden of the tax if the demand curve is D1.
D) The consumer will bear a greater share of the tax burden if the demand curve is D0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When Egypt passed a law that imposed Social Security tax, it wanted employers and workers to share the burden of the tax equally. Most economists who have studied the incidence of the tax have concluded
A) the tax is not high enough to cover the future costs of Social Security.
B) the burden of the tax falls almost entirely on workers.
C) the tax on employers is too high because it reduces the employment of low -skilled workers.
D) the tax rate should be greater for high income workers than for low income workers.
A) the tax is not high enough to cover the future costs of Social Security.
B) the burden of the tax falls almost entirely on workers.
C) the tax on employers is too high because it reduces the employment of low -skilled workers.
D) the tax rate should be greater for high income workers than for low income workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Social Security tax is a tax imposed on employers and workers that is used to fund Social Security payments. Which of the following statements regarding the tax is true?
A) Employers are required to pay a greater share of the tax than workers but most economists believe the burden of the tax is shared equally.
B) Most economists believe the burden of the tax falls almost entirely on workers.
C) Parliaments always allocate the burden of the tax in a way to be greater for employers than for workers.
D) Most economists believe the burden of the tax falls mostly on employers.
A) Employers are required to pay a greater share of the tax than workers but most economists believe the burden of the tax is shared equally.
B) Most economists believe the burden of the tax falls almost entirely on workers.
C) Parliaments always allocate the burden of the tax in a way to be greater for employers than for workers.
D) Most economists believe the burden of the tax falls mostly on employers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
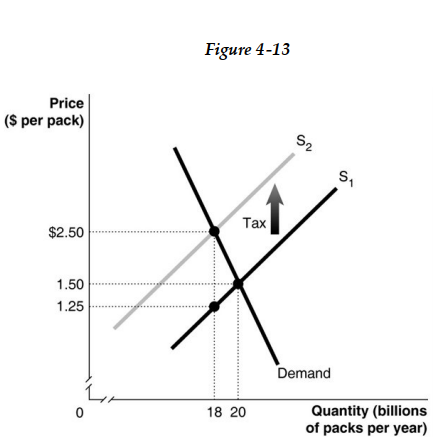
-Refer to Figure 4 -13. The figure above represents demand and supply in the market for cigarettes. Use the diagram to answer the following questions.
a. How much is the government tax on each pack of cigarettes?
b. What portion of the unit tax is paid by consumers?
c. What portion of the unit tax is paid by producers?
d. What is the quantity sold after the imposition of the tax?
e. What is the after -tax revenue per pack received by producers?
f. What is the total tax revenue collected by the government?
g. What is the value of the excess burden of the tax?
h. Is this cigarette tax efficient?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



