Deck 4: Combinational Logic Circuits
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Combinational Logic Circuits
1
Using Boolean algebra to simplify the expression Z = AB + A(B + C) + B(B + C), the completed first step would result in the expression:
A) Z = AA + AB + AB + AC + BB + BC
B) Z = AB + AB + AC + BB + BC
C) Z = AB + ABAC + BB + BC
D) Z = AB + AB + C + BB + C
A) Z = AA + AB + AB + AC + BB + BC
B) Z = AB + AB + AC + BB + BC
C) Z = AB + ABAC + BB + BC
D) Z = AB + AB + C + BB + C
Z = AB + AB + AC + BB + BC
2
Using Boolean algebra, the complete simplification of Z = AB + A(B + C) + B(B + C) gives us:
A) Z = AB = AC = BC
B) Z = AB + AC + B + BC
C) Z = B - AC
D) Z = AB + AC + B
A) Z = AB = AC = BC
B) Z = AB + AC + B + BC
C) Z = B - AC
D) Z = AB + AC + B
Z = B - AC
3
Using Boolean algebra, the expression Y = 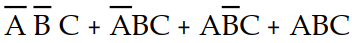 simplifies to:
simplifies to:
A) Y = BC +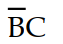
B) Y =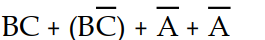
C) Y = C
D) Y =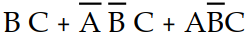
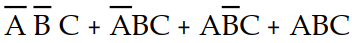 simplifies to:
simplifies to:A) Y = BC +
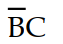
B) Y =
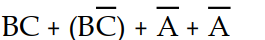
C) Y = C
D) Y =
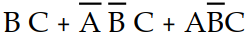
Y = C
4
Using Boolean algebra to simplify the expression Z = 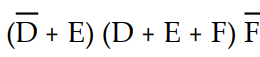 , the completed first step would result in the expression:
, the completed first step would result in the expression:
A) Z =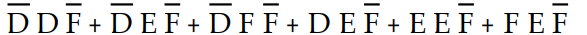
B) Z =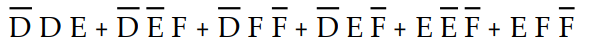
C) Z=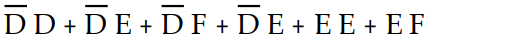
D) Z =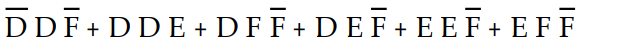
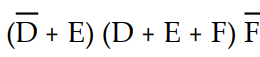 , the completed first step would result in the expression:
, the completed first step would result in the expression:A) Z =
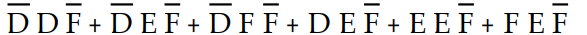
B) Z =
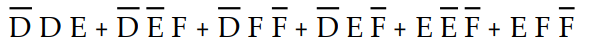
C) Z=
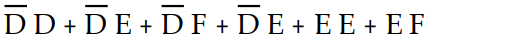
D) Z =
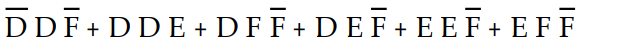

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Using Boolean algebra, the complete simplification of Z = (D + E + F) (D + E + F) 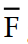 gives us:
gives us:
A) Z = 11eea421_7583_0206_97f4_c1f6b49e9a3c_TB9839_11
B) Z =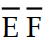
C) Z =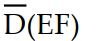
D) Z = (D + E)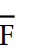
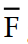 gives us:
gives us:A) Z = 11eea421_7583_0206_97f4_c1f6b49e9a3c_TB9839_11
B) Z =
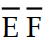
C) Z =
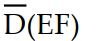
D) Z = (D + E)
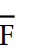

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The implementation of simplified sum- of- products expressions may be easily implemented into actual logic circuits using all______with little or no increase in circuit complexity.
A) OR gates
B) multiple- input inverters
C) NAND gates
D) AND gates
A) OR gates
B) multiple- input inverters
C) NAND gates
D) AND gates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Each "1" in a K- map square represents:
A) an input combination that results in a LOW output.
B) an input combination that results in a HIGH output.
C) an input combination that results in a DON'T CARE grouping.
D) None of the above.
A) an input combination that results in a LOW output.
B) an input combination that results in a HIGH output.
C) an input combination that results in a DON'T CARE grouping.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following Boolean expressions is in sum- of- products form
A) X =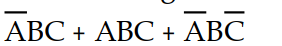
B) X =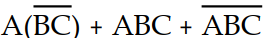
C) X =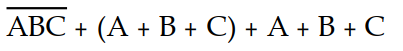
D) X =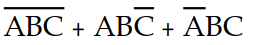
A) X =
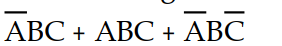
B) X =
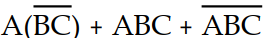
C) X =
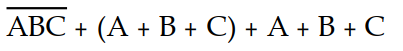
D) X =
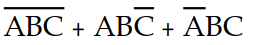

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The input combination of A = 1, B = 0, C = 0, and D = 1 would be represented on a Karnaugh map by the square labeled:
A)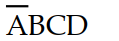
B) ABCD
C)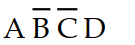
D)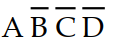
A)
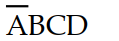
B) ABCD
C)
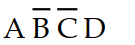
D)
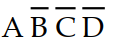

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A logic circuit allows a signal (A) to pass to the output without inversion when either (but not both) of the control signals (B1 and B2) are HIGH. Which of the following is the output expression for this circuit?
A) X=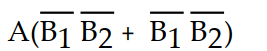
B) X=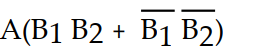
C) X =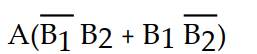
D) X =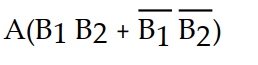
A) X=
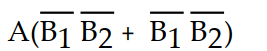
B) X=
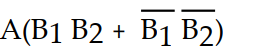
C) X =
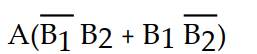
D) X =
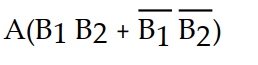

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The logic gates required to implement the logic circuit in the preceding question would be:
A) an Exclusive NOR gate with inputs B1 and B2 whose output is fed, along with input A, to an AND gate.
B) an Exclusive OR gate with inputs B1 and B2 whose output, is fed along with input A, to an AND gate.
C) an Exclusive OR gate with inputs B1 and B2 whose output is fed, along with input A, to an OR gate.
D) an Exclusive NOR gate with inputs B1 and B2 whose output is fed, along with input A, to an OR gate.
A) an Exclusive NOR gate with inputs B1 and B2 whose output is fed, along with input A, to an AND gate.
B) an Exclusive OR gate with inputs B1 and B2 whose output, is fed along with input A, to an AND gate.
C) an Exclusive OR gate with inputs B1 and B2 whose output is fed, along with input A, to an OR gate.
D) an Exclusive NOR gate with inputs B1 and B2 whose output is fed, along with input A, to an OR gate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The output of an OR gate is connected directly to the input of an AND gate. The other AND gate input is a constant "Enable" HIGH. A technician checks the inputs to the OR gate and notes a HIGH and LOW. The output of the OR gate is noted as being a HIGH. The "Enable" HIGH input to the AND gate is verified as normal. The technician checks the OR gate input to the AND gate and observes a LOW or no voltage condition. Of the probable causes listed, select the one that most likely is the problem. Assume CMOS gates.
A) A short between the OR gate output and the AND gate input
B) An internal short in the AND gate
C) An open connection between the OR gate output and the AND gate input
D) A short between the input terminals of the AND gate
A) A short between the OR gate output and the AND gate input
B) An internal short in the AND gate
C) An open connection between the OR gate output and the AND gate input
D) A short between the input terminals of the AND gate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements accurately represents the two best methods of logic circuit simplification?
A) Boolean algebra and Karnaugh mapping
B) Boolean algebra and actual circuit trial and error evaluation
C) Karnaugh mapping and circuit waveform analysis
D) Actual circuit trial and error evaluation and waveform analysis
A) Boolean algebra and Karnaugh mapping
B) Boolean algebra and actual circuit trial and error evaluation
C) Karnaugh mapping and circuit waveform analysis
D) Actual circuit trial and error evaluation and waveform analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Is it possible for a K- map to have two equally good solutions with each solution being dependent on how the 1s are looped?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The application of DeMorgan's theorems will reduce the expression X = 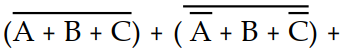
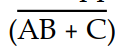 to which sum-of-products expression?
to which sum-of-products expression?
A) X =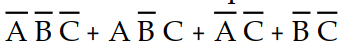
B) X =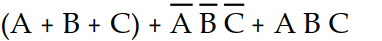
C) X =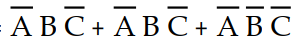
D) X =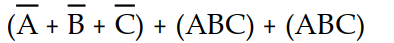
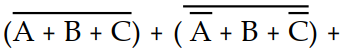
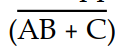 to which sum-of-products expression?
to which sum-of-products expression?A) X =
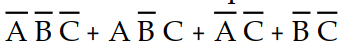
B) X =
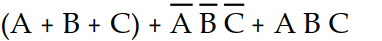
C) X =
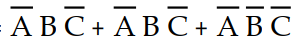
D) X =
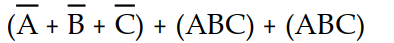

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
You are troubleshooting a TTL circuit board containing dozens of IC chips. You have taken several readings at numerous IC chips but the readings are inconclusive because of their erratic nature. Assuming the circuit worked properly at one time, what is the most likely cause of the problem?
A) A solder bridge between the inputs on the first IC chip on the board
B) An open connection between the inputs on the first IC chip on the board
C) A defective output IC chip that has an internal open to Vcc
D) A defective IC chip that is drawing excessive current from the power supply
A) A solder bridge between the inputs on the first IC chip on the board
B) An open connection between the inputs on the first IC chip on the board
C) A defective output IC chip that has an internal open to Vcc
D) A defective IC chip that is drawing excessive current from the power supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 3-input (A, B, and C) logic circuit has a HIGH output only when A=1, B=1, and C=1 or when A=0, B=1, and C=1. Which of the following sum-of-products expressions describes this function?
A) X =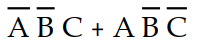
B) X =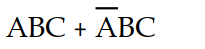
C) X =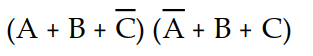
D) X =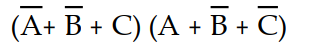
A) X =
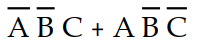
B) X =
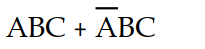
C) X =
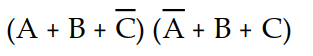
D) X =
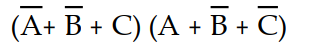

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A "floating" TTL logic input will usually act like a(n):
A) logic HIGH.
B) logic LOW.
C) active low input.
D) ground.
A) logic HIGH.
B) logic LOW.
C) active low input.
D) ground.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
ULSI circuits contain:
A) 100,000 to 999,999 gates.
B) 1,000,000 or more gates.
C) 100 to 9,999 gates.
D) 10,000 to 99,999 gates.
A) 100,000 to 999,999 gates.
B) 1,000,000 or more gates.
C) 100 to 9,999 gates.
D) 10,000 to 99,999 gates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The logic gate that produces a HIGH output whenever its two inputs are unequal is the:
A) Exclusive OR.
B) NOR.
C) NAND.
D) Exclusive NOR.
A) Exclusive OR.
B) NOR.
C) NAND.
D) Exclusive NOR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
GSI integrated circuits contain:
A) 106 or more gates.
B) 103 or more gates.
C) 109 or more gates.
D) none of the above
A) 106 or more gates.
B) 103 or more gates.
C) 109 or more gates.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which CMOS series has both pin and electrical compatibility with its TTL counterpart?
A) AC
B) HC
C) ACT
D) HCT
A) AC
B) HC
C) ACT
D) HCT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following voltage ranges defines acceptable low- level input for a CMOS IC?
A) 2 - 5 V
B) 0 - 1.5 V
C) 0 - 2 V
D) 0 - 0.8 V
A) 2 - 5 V
B) 0 - 1.5 V
C) 0 - 2 V
D) 0 - 0.8 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The TTL family of IC chips is composed of:
A) bipolar junction transistors.
B) discrete component unijunction transistors.
C) unipolar field- effect transistors.
D) discrete component bipolar junction transistors.
A) bipolar junction transistors.
B) discrete component unijunction transistors.
C) unipolar field- effect transistors.
D) discrete component bipolar junction transistors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is the simplest form of the expression Y = ABC[AB + C(BC + AC)]?
A) V = ABC
B) Y = BC
C) Y = AC + BC
D) Y = ABC + BC
A) V = ABC
B) Y = BC
C) Y = AC + BC
D) Y = ABC + BC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A logic circuit contains the following: a 3- input NOR gate with inputs A, B, and C, a 2- input NOR gate with inputs C and D, and a 2- input AND gate that is driven by the NOR gate outputs. The correct Boolean expression for the circuit output (X) is:
A) X =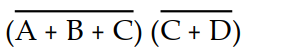
B) X =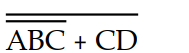
C) X =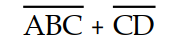
D) X = (A + B + C) (C + D)
A) X =
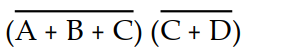
B) X =
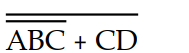
C) X =
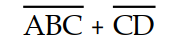
D) X = (A + B + C) (C + D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Select the statement that best describes the use of "Don't Care" conditions on a K- map.
A) Don't Care conditions should never occur and should not be included in K- map simplification procedures.
B) Don't Care conditions may only be changed to 1s.
C) Don't Care conditions may be changed to either a 0 or a 1.
D) Don't Care conditions may only be changed to 0s.
A) Don't Care conditions should never occur and should not be included in K- map simplification procedures.
B) Don't Care conditions may only be changed to 1s.
C) Don't Care conditions may be changed to either a 0 or a 1.
D) Don't Care conditions may only be changed to 0s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The logic gate that produces a HIGH output whenever its two inputs are equal is the:
A) Exclusive OR.
B) Exclusive NOR.
C) Neither A or B
D) Both A and B
A) Exclusive OR.
B) Exclusive NOR.
C) Neither A or B
D) Both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following expressions accurately describes the Exclusive- OR function?
A) X =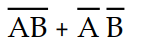
B) X =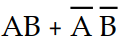
C) X =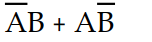
D) X =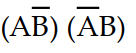
A) X =
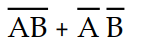
B) X =
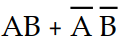
C) X =
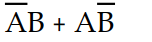
D) X =
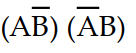

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A CMOS series that is NOT pin compatible but is electrically compatible with TTL is:
A) HC.
B) AC.
C) ACT.
D) HCT.
A) HC.
B) AC.
C) ACT.
D) HCT.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
_________________is an organization that has established a standard format for transferring programming data for PLDs.
A) ANSI
B) ASCII
C) JEDEC
D) IEEE
A) ANSI
B) ASCII
C) JEDEC
D) IEEE

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The input file for low- level development systems normally contains:
A) Boolean equations.
B) truth tables.
C) schematics.
D) timing diagrams.
A) Boolean equations.
B) truth tables.
C) schematics.
D) timing diagrams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
High- level logic compilers can receive input by all but what method?
A) schematic capture
B) narrative descriptions
C) truth tables
D) Boolean equations
A) schematic capture
B) narrative descriptions
C) truth tables
D) Boolean equations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is NOT a step in the development cycle for a PLD?
A) create source file
B) define the problem
C) compiling
D) draw a schematic
A) create source file
B) define the problem
C) compiling
D) draw a schematic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Simplifying logic circuits results in:
A) fewer gates.
B) fewer potential faults.
C) fewer connections.
D) all of the above
A) fewer gates.
B) fewer potential faults.
C) fewer connections.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
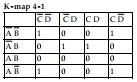
-Which of the following is the simplest output expression for the logic circuit represented by K- map 4- 1?
A) X =
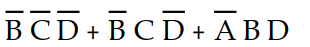
B) X =
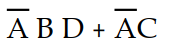
C) X =
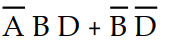
D) X =
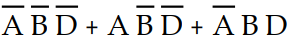

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

-K- map 4- 1 indicates that_______ input combinations cause the circuit to produce a HIGH output.
A) 9
B) 8
C) 4
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38

-Which of the following sum- of- products expressions accurately describes K- map 4- 1?
A) X =
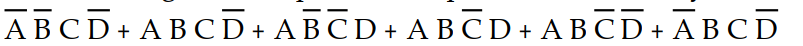
B) X =
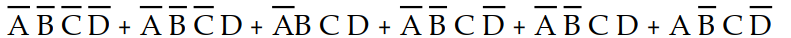
C) X =
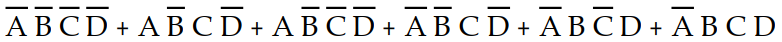
D) X =
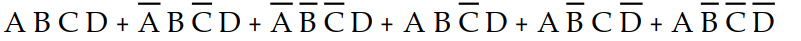

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
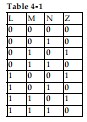
-Circuit implementation of the simplified expression for Table 4- 1 will require (as a minimum):
A) Two 2- input AND gates, two 2- input OR gates, and two inverters.
B) Three 2- input AND gates, two 2- input OR gates, and two inverters.
C) One 2- input AND gate, two 2- input OR gates, and two inverters.
D) Two 2- input AND gates, one 2- input OR gate, and one inverter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

-Using Boolean algebra, the original expression for Table 4- 1 simplifies to:
A) Z =
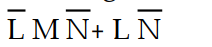
B) Z =
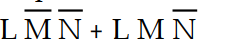
C) Z =
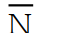
D) Z =
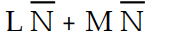

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41

-Actual circuit implementation of the sum- of- products expression for Table 4- 1 would require (as a minimum):
A) three 3- input AND gates, two 3- input OR gates, and five inverters.
B) one 3- input OR gate, two 3- input AND gates, and five inverters.
C) three 3- input OR gates, one 2- input AND gate, and five inverters.
D) three 3- input AND gates, one 3- input OR gate, and three inverters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42

-Refer to Table 4- 1. The sum- of- products expression that correctly defines the output of the logic circuit is:
A) Z =
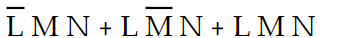
B) Z =
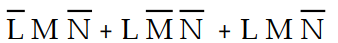
C) Z =
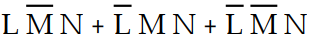
D) Z =
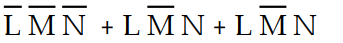

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The truth table in Table 4- 1 indicates that:
A) The output (Z) is HIGH only when the binary input count is an odd number.
B) The output (Z) is HIGH only when a single input is HIGH.
C) The output (Z) is HIGH only when the majority of the inputs are HIGH.
D) The output (Z) is HIGH only when the binary input count is an even number greater than zero.
A) The output (Z) is HIGH only when the binary input count is an odd number.
B) The output (Z) is HIGH only when a single input is HIGH.
C) The output (Z) is HIGH only when the majority of the inputs are HIGH.
D) The output (Z) is HIGH only when the binary input count is an even number greater than zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When labeling a K- map, it makes no difference if adjacent vertical and horizontal squares differ by more than one variable since the end result will be correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
One characteristic of an Exclusive- OR gate is that it can be used as a controlled inverter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A combinatorial logic circuit has memory characteristics that "remember" the inputs after they have been removed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A K- map indicates the output value for each possible combination of input values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In true sum- of- products expressions an inversion bar cannot cover more than single variables in a term.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Single looping in groups of three is an allowable K- map simplification technique.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A good rule of thumb for determining the pin numbers of dual- in- line package IC chips would be to place the notch to your right and pin 1 will always be in the lower right corner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
One of the primary steps in algebraic circuit simplification is to put the original expression into the sum- of- products form by repeated application of DeMorgan's theorems and multiplication of terms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Generally speaking, when AND and OR gates are used to enable signals, the output signal will follow the desired input signal exactly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A square in the top row of a K- map is considered to be adjacent to its corresponding square in the bottom row.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
One method of determining an output from a logic circuit is to simply track the inputs through the gates and determine the output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
DeMorgan's theorem can be repeated in the same logic expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A five gate- two input logic circuit could be described by a five input truth table with 32 combinations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A truth table is the basis for logic circuit design because the designer can assign outputs for particular input combinations and then determine the simplest circuitry required to implement the function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Exclusive gates can have any number of inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
TTL family of chips are indicated by a seventy- four at the beginning of the part number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A logic probe indicates only a HIGH voltage level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A _______ expression consists of two or more AND terms that are ORed together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
One characteristic of a sum- of- products expression is that it can be implemented using all _______ gates without much alteration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The goal in grouping K- map squares is to use the _______ number of loops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The _______ circuit produces a HIGH output whenever the two inputs are unequal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The dependent notation =1 inside a block and a triangle on the output indicates a(n) _______ gate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The _______ circuit produces a HIGH output whenever the two inputs are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Parity generators and checkers use _______ gates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Under normal circumstances, the output from a(n) _______ does not equal its input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
For TTL devices, Vcc is nominally _______ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
PLD chips pin assignments are becoming more standardized as a result of _______ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If an output were required when both inputs are either false or true, a(n) _______ gate would apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Exclusive OR and Exclusive NOR gates have _______ inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An _______ input allows a circuit to pass an input waveform to its output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
_______ circuits contain fewer than 12 gates per chip.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
_______ circuits contain 12 to 99 gates per chip.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
_______ circuits contain 100 to 9,999 gates per chip.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
_______ circuits contain 10,000 to 99,999 gates per chip.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
_______ circuits contain 100,000 to 999,999 gates per chip.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
_______ circuits contain 1,000,000 gates per chip.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
CMOS stands for complementary metal- oxide- _______ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



