Deck 11: Waves
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Waves
1
intensity of the sound wave from an airplane is at . What is the intensity at ?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)
2
sound source of power 100 watts radiates sound uniformly in all directions. The intensity of the sound at a distance of is
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) .
E) .
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) .
E) .
.
3
sound source of power 150 watts radiates sound uniformly in all directions. The intensity of the sound at a distance of is
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) .
E) .
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) .
E) .
.
4
string with a length of has a mass of . The velocity of wave propagation along the string is . The tension of the stretched string is
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) .
E) .
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) .
E) .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
string on a violin is stretched between two points apart with a tension of . The mass/length of the string is . The frequency of the overtone is
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) .
E) .
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) .
E) .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Visible light consists of electromagnetic waves with wavelengths (in air) in the range . The speed of light in air is . What are the frequencies of visible light?
A) to
B) to
C) to
D) to
A) to
B) to
C) to
D) to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
transverse wave travels at along the -axis. If the frequency of the periodic vibrations of the wave is , then what is the wavelength of the wave?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
frequency of a periodic wave is . The period of the vibration motion of the wave is
A) 4.25 milliseconds.
B) 2.94 milliseconds.
C) 3.94 milliseconds.
D) 2.56 milliseconds.
E) 3.55 milliseconds.
A) 4.25 milliseconds.
B) 2.94 milliseconds.
C) 3.94 milliseconds.
D) 2.56 milliseconds.
E) 3.55 milliseconds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
wavelength of a periodic wave is . If the frequency is , then what is the angular frequency of the wave?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
wavelength of a periodic wave is . If the frequency is , then what is the wavenumber of the wave?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
wavelength of a periodic wave is . If the frequency is , then what is the angular frequency of the wave?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
wavelength of a periodic wave is . If the frequency is , then what is the wavenumber of the wave?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
longitudinal wave travels on a slinky or any long spring. The wave is represented by the equation . What is the direction of propagation of the wave?
A) the direction
B) the direction
C) the direction
D) the direction
A) the direction
B) the direction
C) the direction
D) the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
longitudinal wave travels on a slinky or any long spring. The wave is represented by the equation . What is the direction of motion of a point on the spring due to the wave?
A) the direction
B) the direction
C) the \textbackslash pm y direction
A) the direction
B) the direction
C) the \textbackslash pm y direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
longitudinal wave travels on a slinky or any long spring. The wave is represented by the equation . What is the velocity of the wave?
A) in the direction
B) in the direction
C) in the direction
D) in the direction
A) in the direction
B) in the direction
C) in the direction
D) in the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
longitudinal wave travels on a slinky or any long spring. The wave is represented by the equation . What are the wavenumber and direction of propagation of the wave?
A) ; traveling in the direction
B) ; traveling in the direction
C) ; traveling in the direction
D) ; traveling in the direction
A) ; traveling in the direction
B) ; traveling in the direction
C) ; traveling in the direction
D) ; traveling in the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . What is the direction of the vibration of the wave?
A) the direction
B) the direction
C) the direction
A) the direction
B) the direction
C) the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . What is the direction of the velocity of the wave?
A) the direction
B) the direction
C) the direction
D) the direction
E) the direction
F) the direction
A) the direction
B) the direction
C) the direction
D) the direction
E) the direction
F) the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . What is the velocity of the wave?
A) in the direction
B) in the direction
C) in the direction
D) in the direction
E) in the direction
A) in the direction
B) in the direction
C) in the direction
D) in the direction
E) in the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . What are the wavenumber and direction of propagation of the wave?
A) ; traveling in the direction
B) ; traveling in the direction
C) ; traveling in the direction
D) ; traveling in the direction
E) ; traveling in the direction
A) ; traveling in the direction
B) ; traveling in the direction
C) ; traveling in the direction
D) ; traveling in the direction
E) ; traveling in the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . What is the frequency of the vibration of the wave?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . What is the direction of the vibration of the wave?
A) the direction
B) the direction
C) the direction
A) the direction
B) the direction
C) the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . What is the direction of the velocity of the wave?
A) the direction
B) the y direction
C) the direction
D) the direction
A) the direction
B) the y direction
C) the direction
D) the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . What is the velocity of the wave?
A) in the direction
B) in the direction
C) in the direction
D) in the direction
E) in the direction
A) in the direction
B) in the direction
C) in the direction
D) in the direction
E) in the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . What are the wavenumber and direction of propagation of the wave?
A) ; traveling in the direction
B) ; traveling in the direction
C) ; traveling in the direction
D) ; traveling in the direction
E) ; traveling in the direction
A) ; traveling in the direction
B) ; traveling in the direction
C) ; traveling in the direction
D) ; traveling in the direction
E) ; traveling in the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . What is the frequency of the vibration of the wave?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . Another transverse wave is represented by the equation . What is the equation that represents the superposition of the two waves?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . Another transverse wave is represented by the equation . What is the equation that represents the superposition of the two waves?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . Another transverse wave is represented by the equation . What is the equation that represents the superposition of the two waves?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . Another transverse wave is represented by the equation . What is the equation that represents the superposition of the two waves?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . Another transverse wave is represented by the equation . What is the equation that represents the superposition of the two waves?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation . Another transverse wave is represented by the equation . What is the equation that represents the superposition of the two waves?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
following figure is a graph of a wave at a fixed position.
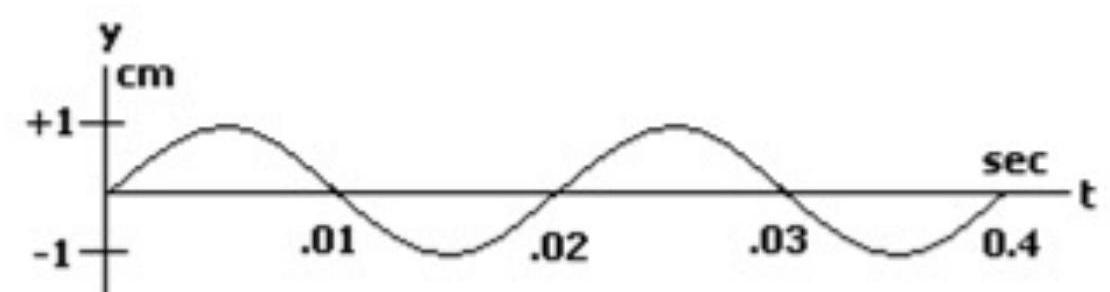
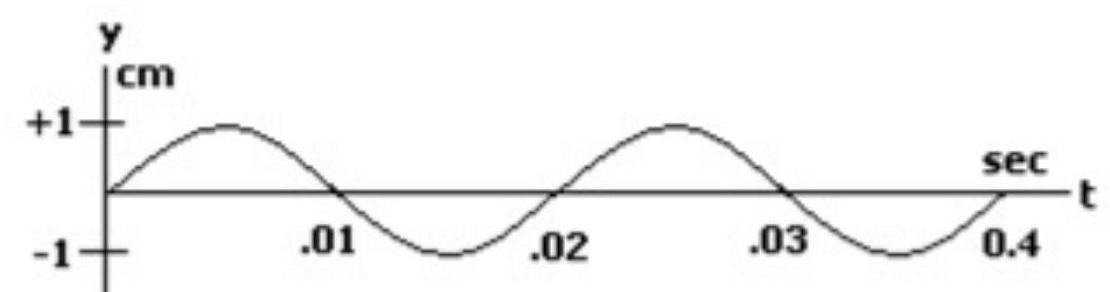
The following figure is a graph of the same wave at a fixed time.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

The following figure is a graph of the same wave at a fixed time.

A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
wave is represented by the equation . Another wave, with the same wavelength and frequency, has an amplitude of . If the two waves interfere constructively, then which equation could represent the superposition of the two waves?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
wave is represented by the equation . Another wave, with the same wavelength and frequency, has an amplitude of . If the two waves interfere destructively, then which equation could represent the superposition of the two waves?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
longitudinal wave is represented by the equation . Another longitudinal wave is represented by the equation . What is the equation that represents the superposition of the two waves?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
speakers are emitting coherent sound waves at a frequency of . The waves are emitted in phase. If the speed of sound is , and it is observed that no sound is heard from one speaker, which of the following is a possible distance to the second speaker?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
cello plays a note of frequency using a length of one of its strings. What length of the same string must be used in order to play a fundamental frequency of ? Assume in each case that the note played is the fundamental frequency of the string at the given length and that the tension and mass per unit length are not changed when selecting a different length of the same string.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
is the mass of a string that is long and has a fundamental frequency of when under a tension of ?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
sound wave radiates from a source uniformly in all directions. If the power of the sound source is 200 watts, then the intensity of the sound wave from the source is
A)
B) .
C) .
D) .
E) .
A)
B) .
C) .
D) .
E) .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
speed of sound in water is 4.3 times the speed of sound in air. A whistle produces a sound wave in air with a frequency . When this sound wave enters the water, its frequency will be
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) not enough information
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



