Deck 12: Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition
1
U.S. Code Title 18 § 1696 states
Whoever establishes any private express for the conveyance of letters or packets, or in any manner causes or provides for the conveyance of the same by regular trips or at stated periods over any post route which is or may be established by law, or from any city, town, or place to any other city, town, or place, between which the mail is regularly carried, shall be fined not more than $500 or imprisoned not more than six months, or both.
The Code of Federal Regulation (CFR) Title 39 Section 310.2 states
It is generally unlawful under the Private Express Statutes for any person other than the Postal Service in any manner to send or carry a letter on a post route or in any manner to cause or assist such activity. Violation may result in injunction, fine or imprisonment or both and payment of postage lost as a result of the illegal activity.
Under these laws, the U.S. Postal Service ________.
A) has a monopoly power over private express mail
B) has a comparative advantage over private express mail
C) competes in an oligopoly market for private express mail
D) competes in a monopolistic competition against other private express mail carriers
Whoever establishes any private express for the conveyance of letters or packets, or in any manner causes or provides for the conveyance of the same by regular trips or at stated periods over any post route which is or may be established by law, or from any city, town, or place to any other city, town, or place, between which the mail is regularly carried, shall be fined not more than $500 or imprisoned not more than six months, or both.
The Code of Federal Regulation (CFR) Title 39 Section 310.2 states
It is generally unlawful under the Private Express Statutes for any person other than the Postal Service in any manner to send or carry a letter on a post route or in any manner to cause or assist such activity. Violation may result in injunction, fine or imprisonment or both and payment of postage lost as a result of the illegal activity.
Under these laws, the U.S. Postal Service ________.
A) has a monopoly power over private express mail
B) has a comparative advantage over private express mail
C) competes in an oligopoly market for private express mail
D) competes in a monopolistic competition against other private express mail carriers
has a monopoly power over private express mail
2
The market demand for soccer balls in a small town is 2,500 units, and there are two rival sports brands selling soccer balls in this town, Sporty and Go! The products of the two brands are identical.
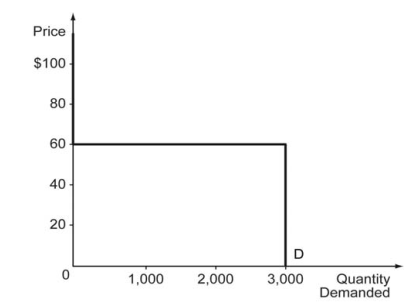
-Refer to the scenario above. If Aqua Inc. charges a price of $70 for each unit of Good A and Blu Corp. charges a price of $50, Blu Corp. will face a demand of ________ units.
A) 1,000
B) 1,500
C) 2,000
D) 3,000

-Refer to the scenario above. If Aqua Inc. charges a price of $70 for each unit of Good A and Blu Corp. charges a price of $50, Blu Corp. will face a demand of ________ units.
A) 1,000
B) 1,500
C) 2,000
D) 3,000
3,000
3
The market demand for soccer balls in a small town is 2,500 units, and there are two rival sports brands selling soccer balls in this town, Sporty and Go! The products of the two brands are identical.

-Refer to the scenario above. Each firm will face a demand of ________ units of Good A if both of them charge a price of $60.
A) 1,000
B) 1,500
C) 2,000
D) 3,000

-Refer to the scenario above. Each firm will face a demand of ________ units of Good A if both of them charge a price of $60.
A) 1,000
B) 1,500
C) 2,000
D) 3,000
1,500
4
There are two firms in an industry, Firm A and Firm B. Both firms sell a homogenous product. If one firm sets a price higher than the other firm, then all the demand goes to the firm setting the lower price. If prices are equal, the demand is shared equally between the two firms. The following figure depicts the demand faced by Firm A. What is Firm B's strategy that could explain such a demand curve faced by Firm A? 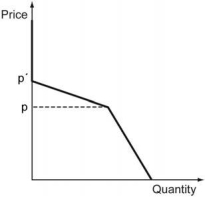
A) Firm B sets its price to p.
B) Firm B sets its price to p'.
C) Firm B equates Firm A's price for any price between p and p' and never sets a price outside this interval.
D) Firm B sets its price to p' whenever the price of Firm A is greater than p, and sets a price equal to Firm A's whenever Firm A sets its price below p.

A) Firm B sets its price to p.
B) Firm B sets its price to p'.
C) Firm B equates Firm A's price for any price between p and p' and never sets a price outside this interval.
D) Firm B sets its price to p' whenever the price of Firm A is greater than p, and sets a price equal to Firm A's whenever Firm A sets its price below p.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is a difference between an oligopoly with homogeneous products and an oligopoly with differentiated products?
A) There are a large number of sellers in an oligopoly with homogeneous products, while there are only a few sellers in an oligopoly with differentiated products.
B) Firms in an oligopoly with homogeneous products earn positive economic profits in equilibrium, while firms in an oligopoly with differentiated products earn zero economic profits in equilibrium.
C) There are huge barriers to entry in an oligopoly with homogeneous products, while there are no barriers to entry in an oligopoly with differentiated products.
D) Firms in an oligopoly with homogeneous products earn zero economic profits in equilibrium, while firms in an oligopoly with differentiated products earn positive economic profits in equilibrium.
A) There are a large number of sellers in an oligopoly with homogeneous products, while there are only a few sellers in an oligopoly with differentiated products.
B) Firms in an oligopoly with homogeneous products earn positive economic profits in equilibrium, while firms in an oligopoly with differentiated products earn zero economic profits in equilibrium.
C) There are huge barriers to entry in an oligopoly with homogeneous products, while there are no barriers to entry in an oligopoly with differentiated products.
D) Firms in an oligopoly with homogeneous products earn zero economic profits in equilibrium, while firms in an oligopoly with differentiated products earn positive economic profits in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In 1981, the DeBeers Diamond cartel member country Zaire broke free of the cartel's marketing arrangement, the Central Selling Organization, and began to market some of its country's industrial diamonds (called boart) outside the DeBeers cartel. Even though DeBeers was generally pursuing a practice of stockpiling diamonds to prop up world diamond prices, the cartel flooded the market with industrial diamonds, significantly lowering their price to levels at-or even below-marginal cost. Within 2 years, Zaire returned to the DeBeers marketing cartel and sold all the country's diamond production through the cartel. DeBeers' actions between 1981 and 1983 represent ________.
A) a competitive strategy
B) a grim strategy
C) price-fixing
D) none of the above
A) a competitive strategy
B) a grim strategy
C) price-fixing
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The following figure shows the demand and cost curves faced by a monopolistic competitor.
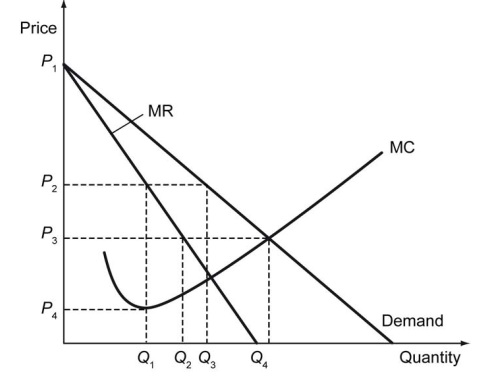
-Refer to the figure above. The optimal quantity produced by the monopolistic competitor is ________.
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) Q4

-Refer to the figure above. The optimal quantity produced by the monopolistic competitor is ________.
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) Q4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The table below summarizes the information possessed by a firm in a monopolistically competitive market. Quantity demanded is in thousands of units.
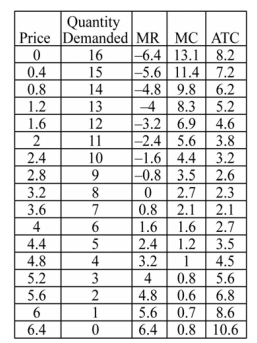
-Refer to the table above. The maximum profit earned by the firm is ________.
A) $6,450
B) $7,800
C) $8,160
D) $10,240

-Refer to the table above. The maximum profit earned by the firm is ________.
A) $6,450
B) $7,800
C) $8,160
D) $10,240

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The table below summarizes the information possessed by a firm in a monopolistically competitive market. Quantity demanded is in thousands of units.

-Refer to the table above. The optimal price charged by the monopolistic competitor is ________.
A) $4.00
B) $3.60
C) $5.20
D) $2.80

-Refer to the table above. The optimal price charged by the monopolistic competitor is ________.
A) $4.00
B) $3.60
C) $5.20
D) $2.80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The price charged by a monopolistic competitor for each unit of a good is $7. If it produces 5,000 units of the good at a total cost of $25,000, what is its profit?
A) $8,000
B) $10,000
C) $7,000
D) $35,000
A) $8,000
B) $10,000
C) $7,000
D) $35,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The figure below depicts a monopolistically competitive firm in the short run.
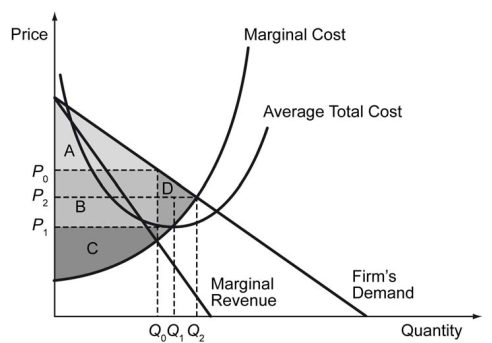
-Refer to the figure above. In the short-run, the firm will product at output level ________ and charge price ________.
A) Q0; P0
B) Q1; P1
C) Q2; P2
D) none of the above

-Refer to the figure above. In the short-run, the firm will product at output level ________ and charge price ________.
A) Q0; P0
B) Q1; P1
C) Q2; P2
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The table below summarizes the information possessed by a firm in a monopolistically competitive market. Quantity demanded is in thousands of units.
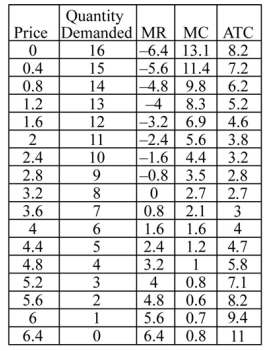
-Refer to the table above. If this market were perfectly competitive, the long-run equilibrium price would be ________.
A) $3.20
B) $2.70
C) $4.00
D) $2.80

-Refer to the table above. If this market were perfectly competitive, the long-run equilibrium price would be ________.
A) $3.20
B) $2.70
C) $4.00
D) $2.80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Markets in which the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index ________ are considered not concentrated.
A) is less than 1,000
B) is between 1,800 and 2,000
C) is between 1,000 and 1,800
D) is above 2,000
A) is less than 1,000
B) is between 1,800 and 2,000
C) is between 1,000 and 1,800
D) is above 2,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Tire Rack.com is an online seller of tires that currently has a 14 percent share of the replacement passenger and light truck tire market in the United States and has a 25 percent share in Canada. Tire Rack not only sells tires but also sells wheels and offers mounting and balancing services. It does not offer installation services, but it partners with 8,100 installation providers in the United States, all of whom agree to charge standard installation fees based on tire size. The online presence of Tire Rack.com ________.
A) lowers search costs for the best tire deal and makes local tire markets more competitive regardless of the number of brick-and-mortar tire dealers
B) lowers search costs for the best tire deal but has no impact on local tire markets, because it does not provide tire installation services
C) lowers search costs for the best tire deal but actually makes local tire markets less competitive, because it has partnerships with tire installers
D) does none of the above
A) lowers search costs for the best tire deal and makes local tire markets more competitive regardless of the number of brick-and-mortar tire dealers
B) lowers search costs for the best tire deal but has no impact on local tire markets, because it does not provide tire installation services
C) lowers search costs for the best tire deal but actually makes local tire markets less competitive, because it has partnerships with tire installers
D) does none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Market research finds that nearly 80 percent of vehicle owners purchase tires at the business that performs routine maintenance on their vehicles. Increasingly, new car dealers carry tires and sell to car owners who bring their vehicles to the dealer for maintenance. Many car manufacturers negotiate prices on replacement tires and sell through to their dealers. The growing incidence of new car dealers selling replacement tires spiked up in the aftermath of the Great Recession, as new car dealers looked for ways to boost franchise sales in the face of low levels of new car sales. Given that Bresnahan and Reiss's paper was published more than 25 years ago, local tire markets are ________.
A) likely more competitive today
B) likely equally competitive as 25 years ago
C) less competitive today
D) none of the above
A) likely more competitive today
B) likely equally competitive as 25 years ago
C) less competitive today
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



