Deck 8: Money Creation, Monetary Theory, and Monetary Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/241
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Money Creation, Monetary Theory, and Monetary Policy
1
The primary determinant of the overall level of economic activity is:
A) consumer confidence.
B) government regulation.
C) the size of the money supply.
D) total spending by households, businesses, government, and foreign buyers.
A) consumer confidence.
B) government regulation.
C) the size of the money supply.
D) total spending by households, businesses, government, and foreign buyers.
total spending by households, businesses, government, and foreign buyers.
2
Spending by households and businesses is influenced by:
A) the availability of loans.
B) the size of the money supply.
C) the interest rates charged on loans.
D) all of the above.
A) the availability of loans.
B) the size of the money supply.
C) the interest rates charged on loans.
D) all of the above.
all of the above.
3
Increasing the amount of loans available should:
A) increase spending by businesses and households and the overall level of economic activity.
B) increase spending by businesses and households but reduce the overall level of economic activity.
C) increase spending by businesses and households but have no impact on the overall level of economic activity.
D) reduce business spending and increase household spending as households take advantage of the greater availability of loans.
A) increase spending by businesses and households and the overall level of economic activity.
B) increase spending by businesses and households but reduce the overall level of economic activity.
C) increase spending by businesses and households but have no impact on the overall level of economic activity.
D) reduce business spending and increase household spending as households take advantage of the greater availability of loans.
increase spending by businesses and households and the overall level of economic activity.
4
An increase in loans by financial depository institutions increases:
A) total spending, but takes dollars out of circulation.
B) the money supply, but has no effect on total spending.
C) the money supply, and leads to an increase in total spending.
D) consumer indebtedness, which leads to a decrease in total spending.
A) total spending, but takes dollars out of circulation.
B) the money supply, but has no effect on total spending.
C) the money supply, and leads to an increase in total spending.
D) consumer indebtedness, which leads to a decrease in total spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The equation of exchange states that:
A) MP = VQ.
B) MQ = VP.
C) MV = PQ.
D) M = VP/Q.
A) MP = VQ.
B) MQ = VP.
C) MV = PQ.
D) M = VP/Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Based on the equation of exchange, the amount of money in the economy is shown by the expression:
A) M = PQ/V.
B) M = V/PQ.
C) M = V(PQ).
D) M = PQ - V.
A) M = PQ/V.
B) M = V/PQ.
C) M = V(PQ).
D) M = PQ - V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The equation of exchange shows that the supply of money in the economy can influence:
A) the level of output.
B) the level of prices.
C) both the levels of output and prices.
D) neither the levels of output or prices.
A) the level of output.
B) the level of prices.
C) both the levels of output and prices.
D) neither the levels of output or prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
V in the equation of exchange stands for the:
A) value of money.
B) dollar value of GDP.
C) variation in the consumer price index.
D) number of times each dollar is spent on new goods and services during one year.
A) value of money.
B) dollar value of GDP.
C) variation in the consumer price index.
D) number of times each dollar is spent on new goods and services during one year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the equation of exchange, MV and PQ can be interpreted as, respectively:
A) current GDP and constant GDP.
B) constant GDP and current GDP.
C) total spending and the dollar value of output in the economy.
D) the dollar value of output in the economy and total spending.
A) current GDP and constant GDP.
B) constant GDP and current GDP.
C) total spending and the dollar value of output in the economy.
D) the dollar value of output in the economy and total spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements about the velocity of money is true?
A) Velocity does not change over time.
B) Velocity has been rapidly increasing every year since the early 1980s.
C) Changes in velocity are directly related to changes in the money supply.
D) At any particular moment in time the velocity of money can be considered fixed because velocity does not change significantly from month to month.
A) Velocity does not change over time.
B) Velocity has been rapidly increasing every year since the early 1980s.
C) Changes in velocity are directly related to changes in the money supply.
D) At any particular moment in time the velocity of money can be considered fixed because velocity does not change significantly from month to month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Given the equation of exchange, MV = PQ, increasing the money supply will increase:
A) the price level.
B) the economy's total output.
C) the economy's total output and the price level.
D) any of the above could be correct, depending on the state of the economy.
A) the price level.
B) the economy's total output.
C) the economy's total output and the price level.
D) any of the above could be correct, depending on the state of the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Given the equation of exchange, MV = PQ, increasing the money supply when the economy is at full employment should primarily increase:
A) employment.
B) the price level.
C) the economy's total output.
D) all of the above.
A) employment.
B) the price level.
C) the economy's total output.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Given the equation of exchange, MV = PQ, increasing the money supply when the economy is operating at less than full employment should primarily increase:
A) total output.
B) the price level.
C) unemployment.
D) all of the above.
A) total output.
B) the price level.
C) unemployment.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Given the equation of exchange, MV=PQ, decreasing the money supply when the economy is at full employment should lead primarily to a decrease in the:
A) price level.
B) economy's total output.
C) level of unemployment.
D) all of the above.
A) price level.
B) economy's total output.
C) level of unemployment.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An increase in the money supply when the economy is experiencing significant unemployment would lead primarily to an increase in:
A) prices.
B) total output.
C) total output and the level of prices.
D) the level of prices, and a decrease in total output.
A) prices.
B) total output.
C) total output and the level of prices.
D) the level of prices, and a decrease in total output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An increase in the money supply when the economy is at full employment generally results in:
A) inflation.
B) significant increases in the interest rate.
C) substantial gains in output and employment.
D) all of the above.
A) inflation.
B) significant increases in the interest rate.
C) substantial gains in output and employment.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A decrease in the supply of money generally leads to a decrease in:
A) the level of prices.
B) output and employment.
C) output, employment, and the level of prices.
D) the level of prices, followed by an increase in output and employment.
A) the level of prices.
B) output and employment.
C) output, employment, and the level of prices.
D) the level of prices, followed by an increase in output and employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Given the equation of exchange, MV = PQ, if the money supply is increased when the economy is operating at full employment the expected result will be an increase in:
A) output (Q).
B) velocity (V).
C) the price level (P).
D) unemployment (Q-V).
A) output (Q).
B) velocity (V).
C) the price level (P).
D) unemployment (Q-V).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Given the equation of exchange, MV=PQ, if the money supply is increased when the economy is operating at less than full employment, the expected result will be an increase in:
A) output (Q).
B) velocity (V).
C) the price level (P).
D) unemployment (Q-V).
A) output (Q).
B) velocity (V).
C) the price level (P).
D) unemployment (Q-V).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Given the equation of exchange, MV = PQ, if the money supply is reduced when the economy is operating at full employment, the primary expected result will be:
A) a decrease in output (Q).
B) an increase in velocity (V).
C) a decrease in the price level (P).
D) all of the above.
A) a decrease in output (Q).
B) an increase in velocity (V).
C) a decrease in the price level (P).
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
According to the equation of exchange, if the economy is at full employment and M is increased while V is held constant:
A) an increase in P will occur.
B) an increase in Q only will occur.
C) an increase in P and a decrease in Q will occur.
D) an increase in Q and a decrease in P will occur.
A) an increase in P will occur.
B) an increase in Q only will occur.
C) an increase in P and a decrease in Q will occur.
D) an increase in Q and a decrease in P will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose that in the equation of exchange M = $1 trillion, V = 8, P = 1.0 and Q = $8 trillion. If the money supply is increased by $1 trillion, velocity is constant and the economy is at full employment then:
A) output will decrease to $4 trillion.
B) output will increase to $12 trillion.
C) output will increase to $16 trillion.
D) the price level will increase to 2.0.
A) output will decrease to $4 trillion.
B) output will increase to $12 trillion.
C) output will increase to $16 trillion.
D) the price level will increase to 2.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose that in the equation of exchange M = $1 trillion, V = 6, P = 1.0 and Q = $6 trillion. If the money supply is increased by $1 trillion and V is constant, then:
A) both P and Q could increase.
B) the price level could increase to 2.0 if the economy is at full employment.
C) output could increase to $12 trillion assuming that the economy is not at full employment and can produce this level of output.
D) all of the above.
A) both P and Q could increase.
B) the price level could increase to 2.0 if the economy is at full employment.
C) output could increase to $12 trillion assuming that the economy is not at full employment and can produce this level of output.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The correct policy to expand the level of economic activity would be to:
A) increase the money supply.
B) decrease the money supply.
C) leave the money supply unchanged.
D) do anything, because there is no relationship between the money supply and economic activity.
A) increase the money supply.
B) decrease the money supply.
C) leave the money supply unchanged.
D) do anything, because there is no relationship between the money supply and economic activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Money is created when:
A) Congress orders it to be created.
B) the Treasury prints a new securities issue.
C) loans made by the federal government are repaid.
D) financial depository institutions such as commercial banks make loans.
A) Congress orders it to be created.
B) the Treasury prints a new securities issue.
C) loans made by the federal government are repaid.
D) financial depository institutions such as commercial banks make loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A financial depository institution's actual reserves are equal to the:
A) amount of deposits in the institution.
B) reserve requirement times the institution's deposits.
C) reserve requirement times the institution's reserve account.
D) amount the institution has in its reserve account plus its vault cash.
A) amount of deposits in the institution.
B) reserve requirement times the institution's deposits.
C) reserve requirement times the institution's reserve account.
D) amount the institution has in its reserve account plus its vault cash.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A financial depository institution's actual reserves are equal to its:
A) reserve account balance plus vault cash.
B) required reserves minus excess reserves.
C) demand deposit balances plus vault cash.
D) demand deposit balances minus excess reserves.
A) reserve account balance plus vault cash.
B) required reserves minus excess reserves.
C) demand deposit balances plus vault cash.
D) demand deposit balances minus excess reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A financial depository institution's reserve account balance plus vault cash equal its:
A) actual reserves.
B) excess reserves.
C) required reserves.
D) in-house reserves.
A) actual reserves.
B) excess reserves.
C) required reserves.
D) in-house reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A financial depository institution's reserve requirement is a specific percentage of:
A) deposits that the institution must keep as actual reserves.
B) deposits that the institution must keep as excess reserves.
C) actual reserves that the institution must keep as excess reserves.
D) required reserves that the institution must keep as actual reserves.
A) deposits that the institution must keep as actual reserves.
B) deposits that the institution must keep as excess reserves.
C) actual reserves that the institution must keep as excess reserves.
D) required reserves that the institution must keep as actual reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A financial depository institution's required reserves are:
A) equal to 10% of its actual reserves.
B) equal to its deposits plus its vault cash.
C) the percentage of actual reserves that must be kept on reserve.
D) the amount of actual reserves that must be kept to back deposits.
A) equal to 10% of its actual reserves.
B) equal to its deposits plus its vault cash.
C) the percentage of actual reserves that must be kept on reserve.
D) the amount of actual reserves that must be kept to back deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Excess reserves are equal to:
A) actual reserves minus vault cash.
B) required reserves minus vault cash.
C) actual reserves minus required reserves.
D) required reserves divided by the reserve requirement.
A) actual reserves minus vault cash.
B) required reserves minus vault cash.
C) actual reserves minus required reserves.
D) required reserves divided by the reserve requirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Excess reserves:
A) equal actual reserves minus required reserves.
B) determine the value of new loans that can be made by a depository institution.
C) are actual reserves over and above the amount a depository institution is required to hold as actual reserves.
D) are all of the above.
A) equal actual reserves minus required reserves.
B) determine the value of new loans that can be made by a depository institution.
C) are actual reserves over and above the amount a depository institution is required to hold as actual reserves.
D) are all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Assume that your bank has no excess reserves when you deposit a check for $500 in your account. How much in excess reserves will this check create for your bank?
A) $0.
B) $400.
C) $500.
D) Not enough information to answer the question.
A) $0.
B) $400.
C) $500.
D) Not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The CC&S Bank has $800 million in deposits, a 20 percent reserve requirement, and $400 million in actual reserves. How much must CC&S keep in required reserves?
A) $80 million.
B) $160 million.
C) $240 million.
D) $640 million.
A) $80 million.
B) $160 million.
C) $240 million.
D) $640 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The B&L Bank has $120 million in deposits, a 15 percent reserve requirement, and $24 million in actual reserves. How much does B&L have in excess reserves?
A) $6 million.
B) $18 million.
C) $96 million.
D) $102 million.
A) $6 million.
B) $18 million.
C) $96 million.
D) $102 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The RDW Bank has deposits of $250 million, excess reserves of $50 million, and a reserve requirement of 20 percent. RDW Bank's actual reserves are:
A) $50 million.
B) $100 million.
C) $200 million.
D) $300 million.
A) $50 million.
B) $100 million.
C) $200 million.
D) $300 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The OBL bank has $320 million in deposits, $80 million in actual reserves, and a reserve requirement of 20 percent. How much must OBL keep in required reserves?
A) $16 million.
B) $32 million.
C) $64 million.
D) $256 million.
A) $16 million.
B) $32 million.
C) $64 million.
D) $256 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The CKN Bank has actual reserves of $240 million, deposits of $800 million, and a reserve requirement of 10 percent. CKN Bank's excess reserves are:
A) $24 million.
B) $80 million.
C) $160 million.
D) $720 million.
A) $24 million.
B) $80 million.
C) $160 million.
D) $720 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The P&LK Bank has actual reserves of $80 million, excess reserves of $20 million, and deposits of $400 million. What is P&LK Bank's reserve requirement?
A) 5 percent.
B) 15 percent.
C) 20 percent.
D) 25 percent.
A) 5 percent.
B) 15 percent.
C) 20 percent.
D) 25 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is CCIM Bank's reserve requirement if it has actual reserves of $72 million, excess reserves of $24 million, and deposits of $240 million?
A) 10 percent.
B) 15 percent.
C) 20 percent.
D) 30 percent.
A) 10 percent.
B) 15 percent.
C) 20 percent.
D) 30 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The required reserves for a bank with demand deposits totaling $500 million and a reserve requirement of 10% are:
A) $50 million.
B) $450 million.
C) $500 million.
D) none of the above.
A) $50 million.
B) $450 million.
C) $500 million.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The excess reserves for a bank with demand deposits totaling $200 million, actual reserves of $30 million and a reserve requirement of 10% are:
A) $10 million.
B) $20 million.
C) $30 million.
D) cannot determine from available information.
A) $10 million.
B) $20 million.
C) $30 million.
D) cannot determine from available information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If a commercial bank has $160 million in deposits, $40 million in actual reserves, and a reserve requirement of 20 percent, that bank can make new loans of:
A) $8 million.
B) $32 million.
C) $128 million.
D) $160 million.
A) $8 million.
B) $32 million.
C) $128 million.
D) $160 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The ZKL Bank has $200 million in deposits, $60 million in actual reserves and $40 million in required reserves. The bank can make new loans of:
A) $20 million.
B) $40 million.
C) $60 million.
D) $160 million.
A) $20 million.
B) $40 million.
C) $60 million.
D) $160 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
LJW Bank has $200 million in deposits, $30 million in actual reserves and a 15 percent reserve requirement. LJW Bank can make:
A) no new loans.
B) $4.5 million in new loans.
C) $25.5 million in new loans.
D) $30.0 million in new loans.
A) no new loans.
B) $4.5 million in new loans.
C) $25.5 million in new loans.
D) $30.0 million in new loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The MBK Bank has $120 million in deposits, $20 million in actual reserves, and a reserve requirement of 10%. The bank can make:
A) no new loans.
B) $2 million in new loans.
C) $8 million in new loans.
D) $12 million in new loans.
A) no new loans.
B) $2 million in new loans.
C) $8 million in new loans.
D) $12 million in new loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
County Bank has deposits of $200 million, a reserve requirement of 20%, and $36 million in actual reserves. Currently, the bank:
A) is not meeting its reserve requirement.
B) is just meeting its reserve requirement.
C) is meeting its reserve requirement and can make new loans.
D) does not have enough information to determine its reserve and loan-making position.
A) is not meeting its reserve requirement.
B) is just meeting its reserve requirement.
C) is meeting its reserve requirement and can make new loans.
D) does not have enough information to determine its reserve and loan-making position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
TS&B Bank has deposits of $200 million, a reserve requirement of 20 percent, $50 million in actual reserves, and $6 million in other assets. Based on this information, TS&B:
A) can make no additional loans.
B) must call in $6 million in loans.
C) can make an additional $4 million in loans.
D) can make an additional $10 million in loans.
A) can make no additional loans.
B) must call in $6 million in loans.
C) can make an additional $4 million in loans.
D) can make an additional $10 million in loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
IZY Bank wants to make a $7 million loan. It has a reserve requirement of 15 percent. If the bank has $25 million in actual reserves to make this loan and meet its reserve requirement, IZY Bank's deposits can be no more than:
A) $18 million.
B) $48 million.
C) $120 million.
D) $375 million.
A) $18 million.
B) $48 million.
C) $120 million.
D) $375 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A financial depository institution can make new loans up to the value of its:
A) deposits.
B) actual reserves.
C) excess reserves.
D) required reserves.
A) deposits.
B) actual reserves.
C) excess reserves.
D) required reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) When a bank makes a loan and the loan is spent, the lending bank can lose reserves.
B) Loans made by financial depository institutions increase the size of the money supply.
C) Financial institutions, such as commercial banks, take money from depositors to give to borrowers when making a loan.
D) If a bank lends more than the amount of its excess reserves, it will not meet its reserve requirement when the loans clear.
A) When a bank makes a loan and the loan is spent, the lending bank can lose reserves.
B) Loans made by financial depository institutions increase the size of the money supply.
C) Financial institutions, such as commercial banks, take money from depositors to give to borrowers when making a loan.
D) If a bank lends more than the amount of its excess reserves, it will not meet its reserve requirement when the loans clear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The excess reserves of a bank determine the:
A) amount in loans the bank can make.
B) interest rate the bank pays on savings accounts.
C) funds that must be maintained in the bank's vault cash to back its loans.
D) all of the above.
A) amount in loans the bank can make.
B) interest rate the bank pays on savings accounts.
C) funds that must be maintained in the bank's vault cash to back its loans.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When a financial depository institution makes a loan it:
A) creates money.
B) borrows funds from the Federal Reserve.
C) converts vault cash to a demand deposit.
D) shifts funds from depositors' accounts to borrowers' accounts.
A) creates money.
B) borrows funds from the Federal Reserve.
C) converts vault cash to a demand deposit.
D) shifts funds from depositors' accounts to borrowers' accounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When a bank makes a loan, the funds for that loan are drawn down from:
A) nowhere.
B) the bank's vault cash.
C) balances in the bank depositors' accounts.
D) the Federal Reserve Bank's borrowing fund.
A) nowhere.
B) the bank's vault cash.
C) balances in the bank depositors' accounts.
D) the Federal Reserve Bank's borrowing fund.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When a loan is repaid to a bank, the money is:
A) destroyed.
B) stored by the bank for another use.
C) returned by the bank to the Federal Reserve bank from which it got the money.
D) returned to the bank depositors' accounts from which it was taken to make the loan.
A) destroyed.
B) stored by the bank for another use.
C) returned by the bank to the Federal Reserve bank from which it got the money.
D) returned to the bank depositors' accounts from which it was taken to make the loan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
According to Application 8.1, "Questions and Answers about Reserves and Loans," which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) The Federal Reserve specifies the prime rate for each type of financial institution.
B) Financial depository institutions keep adequate currency in their vaults to serve customers, and not excessive amounts because of security risks.
C) Banks can borrow from a Federal Reserve Bank or from other banks through the Federal Funds market.
D) A financial depository institution averages deposits and reserves over a period of time rather than daily when determining whether it meets its reserve requirement.
A) The Federal Reserve specifies the prime rate for each type of financial institution.
B) Financial depository institutions keep adequate currency in their vaults to serve customers, and not excessive amounts because of security risks.
C) Banks can borrow from a Federal Reserve Bank or from other banks through the Federal Funds market.
D) A financial depository institution averages deposits and reserves over a period of time rather than daily when determining whether it meets its reserve requirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The money multiplier is the multiple by which an initial change in depository institutions':
A) deposits can change actual reserves.
B) vault cash can change the money supply.
C) excess reserves can change the money supply.
D) reserve requirements can change excess reserves.
A) deposits can change actual reserves.
B) vault cash can change the money supply.
C) excess reserves can change the money supply.
D) reserve requirements can change excess reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The money multiplier is the multiple by which an initial change in:
A) nonincome-determined spending can change the money supply.
B) excess reserves in the depository institutions system can change the money supply.
C) nonincome-determined spending can change total output and income in the economy.
D) excess reserves in the depository institutions system can change total output and income in the economy.
A) nonincome-determined spending can change the money supply.
B) excess reserves in the depository institutions system can change the money supply.
C) nonincome-determined spending can change total output and income in the economy.
D) excess reserves in the depository institutions system can change total output and income in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Because of the money multiplier, an initial change in excess reserves in the depository institutions system can lead to a multiple change in the:
A) number of institutions in the system.
B) amount of money required to secure a loan.
C) amount of required reserves needed to back a single deposit.
D) amount that can be loaned by all institutions, taken together, in the system.
A) number of institutions in the system.
B) amount of money required to secure a loan.
C) amount of required reserves needed to back a single deposit.
D) amount that can be loaned by all institutions, taken together, in the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
After getting an additional $5,000 in excess reserves, Bank A gives John Jones a $5,000 student loan, which his school deposits in Bank B. If the reserve requirement is 20 percent, this $5,000 increase in Bank A's excess reserves will allow Bank B to make:
A) no new loans.
B) $1,000 in new loans.
C) $3,200 in new loans.
D) $4,000 in new loans.
A) no new loans.
B) $1,000 in new loans.
C) $3,200 in new loans.
D) $4,000 in new loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
After getting an additional $5,000 in excess reserves, Bank A gives Sarah Smith a $5,000 student loan, which her school deposits in Bank B. If the reserve requirement is 20 percent, this $5,000 increase in Bank A's excess reserves will allow Bank A and Bank B together to make:
A) $5,000 in new loans.
B) $6,000 in new loans.
C) $9,000 in new loans.
D) $10,000 in new loans.
A) $5,000 in new loans.
B) $6,000 in new loans.
C) $9,000 in new loans.
D) $10,000 in new loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The money multiplier is equal to:
A) 1/reserve requirement.
B) 1 - reserve requirement.
C) actual reserves/excess reserves.
D) required reserves/reserve requirement.
A) 1/reserve requirement.
B) 1 - reserve requirement.
C) actual reserves/excess reserves.
D) required reserves/reserve requirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the economy, a maximum change in the money supply would be equal to an initial change in:
A) actual reserves.
B) excess reserves times the reserve requirement.
C) actual reserves divided by the initial change in excess reserves.
D) excess reserves times the money multiplier.
A) actual reserves.
B) excess reserves times the reserve requirement.
C) actual reserves divided by the initial change in excess reserves.
D) excess reserves times the money multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The maximum amount by which an economy's money supply can increase is equal to an initial change in:
A) excess reserves.
B) actual reserves times the reserve requirement.
C) excess reserves divided by the reserve requirement.
D) actual reserves divided by the initial change in excess reserves.
A) excess reserves.
B) actual reserves times the reserve requirement.
C) excess reserves divided by the reserve requirement.
D) actual reserves divided by the initial change in excess reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The maximum amount by which the money supply can change following an initial change in excess reserves in the depository institutions system can be determined by calculating:
A) the initial change in excess reserves x money multiplier.
B) the initial change in excess reserves/reserve requirement.
C) both of the above.
D) none of the above.
A) the initial change in excess reserves x money multiplier.
B) the initial change in excess reserves/reserve requirement.
C) both of the above.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The amount by which the money supply could change following an initial change in excess reserves in the depository institutions system can be determined from the formula:
A) .
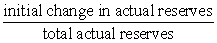
B) .
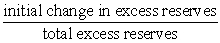
C) .
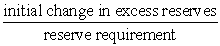
D) initial change in excess reserves x reserve requirement.
A) .
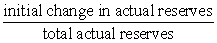
B) .
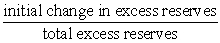
C) .
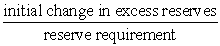
D) initial change in excess reserves x reserve requirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The size of the money multiplier is:
A) directly related to the discount rate.
B) inversely related to the discount rate.
C) directly related to the size of the reserve requirement.
D) inversely related to the size of the reserve requirement.
A) directly related to the discount rate.
B) inversely related to the discount rate.
C) directly related to the size of the reserve requirement.
D) inversely related to the size of the reserve requirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If excess reserves in the depository institutions system are increased by $10 million and the reserve requirement is 10 percent, then the total money supply could increase by up to:
A) $1 million.
B) $10 million.
C) $100 million.
D) cannot determine with available information.
A) $1 million.
B) $10 million.
C) $100 million.
D) cannot determine with available information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If excess reserves in the depository institutions system increase by $16 million and the reserve requirement is 20 percent, the maximum amount by which the money supply can increase is:
A) $3.2 million.
B) $12.8 million.
C) $19.2 million.
D) $80.0 million.
A) $3.2 million.
B) $12.8 million.
C) $19.2 million.
D) $80.0 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Assume the Federal Reserve injects $10 billion of new excess reserves into the depository institutions system. If the reserve requirement is 20 percent, how much new money could be created by this action?
A) $5 billion.
B) $50 billion.
C) $5.5 billion.
D) $500 billion.
A) $5 billion.
B) $50 billion.
C) $5.5 billion.
D) $500 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Assume RST Bank has a reserve requirement of 20 percent. If RST Bank borrows $3 million from the Fed, how much new money could be created in the depository institutions system as a result?
A) $3 million.
B) $12 million.
C) $15 million.
D) $600 thousand.
A) $3 million.
B) $12 million.
C) $15 million.
D) $600 thousand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If the reserve requirement were decreased from 20 percent to 15 percent, the money multiplier would:
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not be affected.
D) change in no predictable way.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not be affected.
D) change in no predictable way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following would cause the money supply to increase by less than the amount indicated by the money multiplier?
A) A financial institution lends less than its increase in excess reserves.
B) A person borrowing money converts part of it to cash rather than putting it all in a demand deposit account.
C) Both of the above.
D) None of the above.
A) A financial institution lends less than its increase in excess reserves.
B) A person borrowing money converts part of it to cash rather than putting it all in a demand deposit account.
C) Both of the above.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The most common method for stimulating business and household borrowing from depository institutions is to:
A) reduce the rate of interest.
B) reduce the actual reserves of depository institutions.
C) reduce the excess reserves of depository institutions.
D) pass laws requiring businesses and households to borrow.
A) reduce the rate of interest.
B) reduce the actual reserves of depository institutions.
C) reduce the excess reserves of depository institutions.
D) pass laws requiring businesses and households to borrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Increases in the money supply result in higher:
A) spending, output, and prices if the economy is at full employment.
B) spending and prices if the economy is at less than full employment.
C) spending, output, and employment if the economy is at full employment.
D) spending, output, and employment if the economy is at less than full employment.
A) spending, output, and prices if the economy is at full employment.
B) spending and prices if the economy is at less than full employment.
C) spending, output, and employment if the economy is at full employment.
D) spending, output, and employment if the economy is at less than full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The price paid to borrow money, which is expressed as a percentage of the amount borrowed, is the:
A) fund rate.
B) interest rate.
C) reserve requirement.
D) balance requirement.
A) fund rate.
B) interest rate.
C) reserve requirement.
D) balance requirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The interest rate is:
A) the price paid to lenders for making loans.
B) the price paid by borrowers to borrow money.
C) calculated as a percentage of the amount borrowed.
D) all of the above.
A) the price paid to lenders for making loans.
B) the price paid by borrowers to borrow money.
C) calculated as a percentage of the amount borrowed.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The quantity of loans demanded:
A) increases when the interest rate increases.
B) increases when the interest rate decreases.
C) decreases when the interest rate decreases.
D) is unaffected by changes in the interest rate.
A) increases when the interest rate increases.
B) increases when the interest rate decreases.
C) decreases when the interest rate decreases.
D) is unaffected by changes in the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
An increase in the interest rate will lead to:
A) an increase in business investment spending and the amount of loans demanded.
B) a decrease in business investment spending and the amount of loans demanded.
C) an increase in business investment spending and a decrease in the amount of loans demanded.
D) a decrease in business investment spending and an increase in the amount of loans demanded.
A) an increase in business investment spending and the amount of loans demanded.
B) a decrease in business investment spending and the amount of loans demanded.
C) an increase in business investment spending and a decrease in the amount of loans demanded.
D) a decrease in business investment spending and an increase in the amount of loans demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An increase in the interest rate will:
A) increase the amount of loans demanded and the amount of loans supplied.
B) decrease the amount of loans demanded and the amount of loans supplied.
C) increase the amount of loans demanded and decrease the amount of loans supplied.
D) decrease the amount of loans demanded and increase the amount of loans supplied.
A) increase the amount of loans demanded and the amount of loans supplied.
B) decrease the amount of loans demanded and the amount of loans supplied.
C) increase the amount of loans demanded and decrease the amount of loans supplied.
D) decrease the amount of loans demanded and increase the amount of loans supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 241 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



