Deck 12: The Phillips Curve, Expectations, and Monetary Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: The Phillips Curve, Expectations, and Monetary Policy
1
The questions with which Chapter 12 is concerned include each of the following except
A) what can shift the Phillips curve?
B) how has the natural rate of unemployment changed in the United States over the past couple of generations?
C) what determines the Fiscal Policy Reaction Function, and what determines its slope?
D) what does it mean for expectations of inflation to be static? Adaptive? Rational?
A) what can shift the Phillips curve?
B) how has the natural rate of unemployment changed in the United States over the past couple of generations?
C) what determines the Fiscal Policy Reaction Function, and what determines its slope?
D) what does it mean for expectations of inflation to be static? Adaptive? Rational?
what determines the Fiscal Policy Reaction Function, and what determines its slope?
2
The questions with which Chapter 12 is concerned include each of the following except
A) what is the IS curve?
B) how do we connect the sticky-price model with the flexible price model?
C) what is the natural rate of unemployment? What determines its value
D) how has the expected rate of inflation changed in the United States over the past couple of generations??
A) what is the IS curve?
B) how do we connect the sticky-price model with the flexible price model?
C) what is the natural rate of unemployment? What determines its value
D) how has the expected rate of inflation changed in the United States over the past couple of generations??
what is the IS curve?
3
The questions with which Chapter 12 is concerned include each of the following except
A) how do we connect the sticky-price model with the flexible price model?
B) how has the natural rate of unemployment changed in the United States over the past couple of generations?
C) what can shift the Phillips curve?
D) how can we tell how expectations of money supply changes are formed?
A) how do we connect the sticky-price model with the flexible price model?
B) how has the natural rate of unemployment changed in the United States over the past couple of generations?
C) what can shift the Phillips curve?
D) how can we tell how expectations of money supply changes are formed?
how can we tell how expectations of money supply changes are formed?
4
The questions with which Chapter 12 is concerned include each of the following except
A) how do we connect the sticky-price model with the flexible price model?
B) how has the potential output changed in the United States over the past couple of generations?
C) what can shift the Phillips curve?
D) what does it mean for expectations of inflation to be static? Adaptive? Rational?
A) how do we connect the sticky-price model with the flexible price model?
B) how has the potential output changed in the United States over the past couple of generations?
C) what can shift the Phillips curve?
D) what does it mean for expectations of inflation to be static? Adaptive? Rational?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The Phillips curve describes the relationship between
A) employment and potential output.
B) the unemployment rate and real GDP.
C) the inflation rate and the unemployment rate.
D) the interest rate and the exchange rate.
A) employment and potential output.
B) the unemployment rate and real GDP.
C) the inflation rate and the unemployment rate.
D) the interest rate and the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Okun's law relates
A) employment and potential output.
B) the unemployment rate to real GDP.
C) the unemployment rate and the inflation rate.
D) the interest rate and the exchange rate.
A) employment and potential output.
B) the unemployment rate to real GDP.
C) the unemployment rate and the inflation rate.
D) the interest rate and the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The specific form of Okun's law relates
A) deviations from the natural level of employment to deviations from potential output.
B) deviations from the natural level of the unemployment rate to deviations from the potential inflation rate.
C) deviations from the natural rate of unemployment to deviations from potential output.
D) deviations from the natural interest to deviations from the natural exchange rate.
A) deviations from the natural level of employment to deviations from potential output.
B) deviations from the natural level of the unemployment rate to deviations from the potential inflation rate.
C) deviations from the natural rate of unemployment to deviations from potential output.
D) deviations from the natural interest to deviations from the natural exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The specific form of Okun's law is
A) u - u* = -0.4 x (Y - Y*).
B) u - u* = -0.4 x ((Y + Y*)/Y*).
C) u - u* = -0.4 x ((Y - Y*)/Y*).
D) u + u* = -0.4 x ((Y - Y*)/Y*).
A) u - u* = -0.4 x (Y - Y*).
B) u - u* = -0.4 x ((Y + Y*)/Y*).
C) u - u* = -0.4 x ((Y - Y*)/Y*).
D) u + u* = -0.4 x ((Y - Y*)/Y*).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to Okun's law,
A) when real GDP is above potential output, unemployment will be relatively low.
B) when real GDP is above potential output, unemployment will be relatively high.
C) when the inflation rate is above the natural inflation rate, unemployment will be relatively low.
D) when the inflation rate is above the natural inflation rate, unemployment will be relatively high.
A) when real GDP is above potential output, unemployment will be relatively low.
B) when real GDP is above potential output, unemployment will be relatively high.
C) when the inflation rate is above the natural inflation rate, unemployment will be relatively low.
D) when the inflation rate is above the natural inflation rate, unemployment will be relatively high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
According to Okun's law,
A) when real GDP is below potential output, unemployment will be relatively low
B) when real GDP is below potential output, unemployment will be relatively high.
C) when the inflation rate is below the natural inflation rate, unemployment will be relatively low.
D) when the inflation rate is below the natural inflation rate, unemployment will be relatively high.
A) when real GDP is below potential output, unemployment will be relatively low
B) when real GDP is below potential output, unemployment will be relatively high.
C) when the inflation rate is below the natural inflation rate, unemployment will be relatively low.
D) when the inflation rate is below the natural inflation rate, unemployment will be relatively high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The equation for the Phillips curve is
A) B = Be - $ x (u - u*) + ss..
B) B = Be + $ x (u - u*) +ss.
C) B = Be - $ x (u - u*) - ss.
D) B = Be - $ x (u*- u) - ss.
A) B = Be - $ x (u - u*) + ss..
B) B = Be + $ x (u - u*) +ss.
C) B = Be - $ x (u - u*) - ss.
D) B = Be - $ x (u*- u) - ss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If 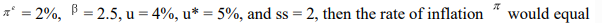
A) 6.5%.
B) 1.5%.
C) 2.5%.
D) -2.5%
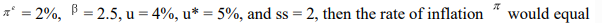
A) 6.5%.
B) 1.5%.
C) 2.5%.
D) -2.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The equation for the Phillips curve includes each of the following terms except
A) the expected inflation rate.
B) the unemployment rate.
C) the natural inflation rate.
D) a supply shock term.
A) the expected inflation rate.
B) the unemployment rate.
C) the natural inflation rate.
D) a supply shock term.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The equation for the Phillips curve includes each of the following terms except
A) the expected inflation rate.
B) the unemployment rate.
C) the natural rate of unemployment.
D) a demand shock term.
A) the expected inflation rate.
B) the unemployment rate.
C) the natural rate of unemployment.
D) a demand shock term.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The slope of the Phillips curve depends on
A) how sticky interest rates are.
B) how sticky the exchange rate is.
C) how sticky wages and prices are.
D) how sticky the inflation rate is.
A) how sticky interest rates are.
B) how sticky the exchange rate is.
C) how sticky wages and prices are.
D) how sticky the inflation rate is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The parameter 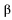 in the Phillips Curve equation tells us
in the Phillips Curve equation tells us
A) how sticky interest rates are.
B) how sticky the exchange rate is.
C) how sticky wages and prices are.
D) how sticky the inflation rate is.
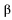 in the Phillips Curve equation tells us
in the Phillips Curve equation tells usA) how sticky interest rates are.
B) how sticky the exchange rate is.
C) how sticky wages and prices are.
D) how sticky the inflation rate is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The smaller the parameter 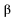 in the Phillips Curve is
in the Phillips Curve is
A) the stickier are wages and prices and the more vertical the Phillips Curve is.
B) the stickier are wages and prices and the more horizontal the Phillips Curve is.
C) the more flexible are wages and prices and the more vertical the Phillips Curve is.
D) the more flexible are wages and prices and the more horizontal the Phillips Curve is.
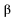 in the Phillips Curve is
in the Phillips Curve isA) the stickier are wages and prices and the more vertical the Phillips Curve is.
B) the stickier are wages and prices and the more horizontal the Phillips Curve is.
C) the more flexible are wages and prices and the more vertical the Phillips Curve is.
D) the more flexible are wages and prices and the more horizontal the Phillips Curve is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When inflation is higher than expected and production is higher than potential output
A) the unemployment rate will be lower than the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the unemployment rate will be higher than the natural rate of unemployment.
C) the interest rate will be higher than the natural interest rate.
D) the exchange rate will be higher than the natural exchange rate.
A) the unemployment rate will be lower than the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the unemployment rate will be higher than the natural rate of unemployment.
C) the interest rate will be higher than the natural interest rate.
D) the exchange rate will be higher than the natural exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When inflation is lower than expected and production is lower than potential output
A) the unemployment rate will be lower than the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the unemployment rate will be higher than the natural rate of unemployment.
C) the interest rate will be higher than the natural interest rate.
D) the exchange rate will be higher than the natural exchange rate.
A) the unemployment rate will be lower than the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the unemployment rate will be higher than the natural rate of unemployment.
C) the interest rate will be higher than the natural interest rate.
D) the exchange rate will be higher than the natural exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The stickier are wages and prices
A) the more vertical will be the Phillips curve.
B) the more vertical will be the LM curve.
C) the more horizontal will be the IS curve.
D) the more horizontal will be the Phillips curve.
A) the more vertical will be the Phillips curve.
B) the more vertical will be the LM curve.
C) the more horizontal will be the IS curve.
D) the more horizontal will be the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The less sticky are wages and prices
A) the more vertical will be the Phillips curve.
B) the more vertical will be the IS curve.
C) the more horizontal will be the LM curve.
D) the more horizontal will be the Phillips curve.
A) the more vertical will be the Phillips curve.
B) the more vertical will be the IS curve.
C) the more horizontal will be the LM curve.
D) the more horizontal will be the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If wages and prices are completely flexible
A) the Phillips curve will be horizontal.
B) the IS curve will be vertical.
C) the LM curve will be horizontal.
D) the Phillips curve will be vertical.
A) the Phillips curve will be horizontal.
B) the IS curve will be vertical.
C) the LM curve will be horizontal.
D) the Phillips curve will be vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If wages and prices are completely fixed
A) the Phillips curve will be horizontal.
B) the IS curve will be vertical.
C) the LM curve will be horizontal.
D) the Phillips curve will be vertical.
A) the Phillips curve will be horizontal.
B) the IS curve will be vertical.
C) the LM curve will be horizontal.
D) the Phillips curve will be vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An increase in the natural rate of unemployment will
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A decrease in the natural rate of unemployment will
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An increase in the expected inflation rate will
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A decrease in the expected inflation rate will
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An adverse supply shock will
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A favorable supply shock will
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
A) result in a decrease in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.
B) shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) shift the Phillips curve to the left.
D) result in an increase in the inflation rate along the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The position of the Phillips curve depends on each of the following except
A) the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the expected rate of inflation.
C) the actual rate of inflation.
D) whether there are any current supply shocks affecting inflation.
A) the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the expected rate of inflation.
C) the actual rate of inflation.
D) whether there are any current supply shocks affecting inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Taylor rule is a description of how the central bank's targeted real interest depends on the gap
A) between the current inflation rate and the central bank's targeted inflation rate.
B) between the current unemployment rate and the central bank's targeted unemployment rate.
C) between the current inflation rate and the central bank's targeted unemployment rate.
D) between the current exchange rate and the central bank's targeted exchange rate.
A) between the current inflation rate and the central bank's targeted inflation rate.
B) between the current unemployment rate and the central bank's targeted unemployment rate.
C) between the current inflation rate and the central bank's targeted unemployment rate.
D) between the current exchange rate and the central bank's targeted exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The Taylor rule equation for the real interest rate is
A) r0 - rB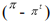
B) r0 + rB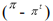
C) r0 + rB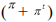
D) r0 - rB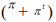
A) r0 - rB
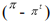
B) r0 + rB
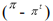
C) r0 + rB
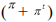
D) r0 - rB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The parameter rr in the Taylor rule equation tells how much the central bank changes
A) the money supply in reaction to a gap between the actual and target inflation rates.
B) the exchange rate in reaction to a gap between the actual and target inflation rates.
C) the real interest rate in reaction to a gap between the actual and target inflation rates.
D) the unemployment rate in reaction to a gap between the actual and target inflation rates.
A) the money supply in reaction to a gap between the actual and target inflation rates.
B) the exchange rate in reaction to a gap between the actual and target inflation rates.
C) the real interest rate in reaction to a gap between the actual and target inflation rates.
D) the unemployment rate in reaction to a gap between the actual and target inflation rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If inflation is above the central bank's targeted inflation rate, the central bank will_________ the real interest rate which will lead to a _________ real GDP.
A) raise; higher.
B) lower; higher
C) lower; lower
D) raise; lower
A) raise; higher.
B) lower; higher
C) lower; lower
D) raise; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If inflation is below the central bank's targeted inflation rate, the central bank will_________ the real interest rate which will lead to a _________ real GDP.
A) raise; higher.
B) lower; higher
C) lower; lower
D) raise; lower
A) raise; higher.
B) lower; higher
C) lower; lower
D) raise; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The monetary policy reaction function is
A) an upward-sloping relationship between the inflation rate and the money supply growth rate.
B) a downward-sloping relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate.
C) a downward-sloping relationship between the inflation rate and the total output growth rate.
D) an upward-sloping relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate.
A) an upward-sloping relationship between the inflation rate and the money supply growth rate.
B) a downward-sloping relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate.
C) a downward-sloping relationship between the inflation rate and the total output growth rate.
D) an upward-sloping relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Each of the following is a factor in the parameter 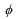 of the monetary reaction function except
of the monetary reaction function except
A) how much the central bank raises the real interest rate in response to a rise in inflation.
B) the slope of the Phillips curve.
C) the slope of the IS curve.
D) the coefficient of Okun's law.
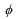 of the monetary reaction function except
of the monetary reaction function exceptA) how much the central bank raises the real interest rate in response to a rise in inflation.
B) the slope of the Phillips curve.
C) the slope of the IS curve.
D) the coefficient of Okun's law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The position of the monetary policy reaction function depends on
A) the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the value of the inflation rate when the central bank has set the real interest rate at the "normal" baseline value r0.
C) the value of the unemployment rate when the central bank has set the real interest rate at the "normal" baseline value r0.
D) the value of the total output growth rate when the central bank has set the real interest rate at the "normal" baseline value r0..
A) the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the value of the inflation rate when the central bank has set the real interest rate at the "normal" baseline value r0.
C) the value of the unemployment rate when the central bank has set the real interest rate at the "normal" baseline value r0.
D) the value of the total output growth rate when the central bank has set the real interest rate at the "normal" baseline value r0..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The position of the monetary policy reaction function depends on
A) the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of inflation.
C) the natural level of the interest rate.
D) the central bank's target value for inflation.
A) the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of inflation.
C) the natural level of the interest rate.
D) the central bank's target value for inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The parameter 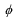 (which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following except
(which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following except
A) the term from Okun's law which tells us the change in the unemployment rate produced by a one percent change in real GDP relative to potential output.
B) the term which tells us how quickly the economy reacts to a supply shock.
C) the interest sensitivity of autonomous spending.
D) the multiplier.
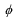 (which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following except
(which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following exceptA) the term from Okun's law which tells us the change in the unemployment rate produced by a one percent change in real GDP relative to potential output.
B) the term which tells us how quickly the economy reacts to a supply shock.
C) the interest sensitivity of autonomous spending.
D) the multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The parameter 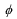 (which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following except
(which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following except
A) the term from Okun's law which tells us the change in the unemployment rate produced by a one percent change in real GDP relative to potential output.
B) the term which tells us the amount by which central bankers raise the real interest rate when inflation is one percent per year higher.
C) the interest sensitivity of government purchases.
D) the multiplier.
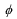 (which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following except
(which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following exceptA) the term from Okun's law which tells us the change in the unemployment rate produced by a one percent change in real GDP relative to potential output.
B) the term which tells us the amount by which central bankers raise the real interest rate when inflation is one percent per year higher.
C) the interest sensitivity of government purchases.
D) the multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The parameter 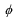 (which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following except
(which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following except
A) the term from Okun's law which tells us the change in the unemployment rate produced by a one percent change in real GDP relative to potential output.
B) the term which tells us the amount by which central bankers raise the real interest rate when inflation is one percent per year higher.
C) the interest sensitivity of autonomous spending.
D) the marginal propensity to export.
 (which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following except
(which governs the slope of the monetary policy reaction function) is determined by each of the following exceptA) the term from Okun's law which tells us the change in the unemployment rate produced by a one percent change in real GDP relative to potential output.
B) the term which tells us the amount by which central bankers raise the real interest rate when inflation is one percent per year higher.
C) the interest sensitivity of autonomous spending.
D) the marginal propensity to export.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Each of the following is one of the factors determining the economy's equilibrium inflation and unemployment rates except
A) the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of inflation.
C) whether there are any supply shocks affecting inflation.
D) the slope of the monetary policy reaction function.
A) the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of inflation.
C) whether there are any supply shocks affecting inflation.
D) the slope of the monetary policy reaction function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Each of the following is one of the factors determining the economy's equilibrium inflation and unemployment rates except
A) the slope of the Phillips curve.
B) the expected rate of inflation.
C) the natural real interest rate.
D) the slope of the monetary policy reaction function.
A) the slope of the Phillips curve.
B) the expected rate of inflation.
C) the natural real interest rate.
D) the slope of the monetary policy reaction function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Each of the following is one of the factors determining the economy's equilibrium inflation and unemployment rates except
A) the natural level of the interest rate.
B) the central bank's target level of inflation.
C) whether there are any supply shocks affecting inflation.
D) the slope of the monetary policy reaction function.
A) the natural level of the interest rate.
B) the central bank's target level of inflation.
C) whether there are any supply shocks affecting inflation.
D) the slope of the monetary policy reaction function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Each of the following is one of the factors determining the economy's equilibrium inflation and unemployment rates except
A) the level of unemployment when the interest rate is at what the central bank thinks of as its long-run average rate.
B) the expected rate of inflation.
C) the slope of the monetary policy reaction function.
D) the natural level of output.
A) the level of unemployment when the interest rate is at what the central bank thinks of as its long-run average rate.
B) the expected rate of inflation.
C) the slope of the monetary policy reaction function.
D) the natural level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Unemployment cannot be reduced below its natural rate
A) without increasing interest rates.
B) without accelerating inflation.
C) without increasing government purchases.
D) without increasing the exchange rate.
A) without increasing interest rates.
B) without accelerating inflation.
C) without increasing government purchases.
D) without increasing the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Each of the following is a factor influencing the natural rate of unemployment except
A) expectations of the future natural rate of unemployment.
B) the relative age and educational distribution of the labor force.
C) the rate of productivity growth.
D) the type of institutions that characterize the labor market.
A) expectations of the future natural rate of unemployment.
B) the relative age and educational distribution of the labor force.
C) the rate of productivity growth.
D) the type of institutions that characterize the labor market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Each of the following is a factor influencing the natural rate of unemployment except
A) the relative age and educational distribution of the labor force.
B) the rate of money supply growth.
C) the past level of the unemployment rate.
D) the type of institutions that characterize the labor market.
A) the relative age and educational distribution of the labor force.
B) the rate of money supply growth.
C) the past level of the unemployment rate.
D) the type of institutions that characterize the labor market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Demography is a factor affecting the natural rate of unemployment because
A) where unemployment is located is important.
B) teenagers have a lower rate of unemployment than adults, so an economy with a lot of teenagers will have a lower natural rate.
C) the experience, skill, and education levels of the labor force will affect the natural rate.
D) gender, racial, and ethnic groups tend to have the same rates of unemployment.
A) where unemployment is located is important.
B) teenagers have a lower rate of unemployment than adults, so an economy with a lot of teenagers will have a lower natural rate.
C) the experience, skill, and education levels of the labor force will affect the natural rate.
D) gender, racial, and ethnic groups tend to have the same rates of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Productivity growth is a factor affecting the natural rate of unemployment because
A) increases in productivity results in higher unemployment.
B) a slowdown in productivity growth is not always immediately accompanied by a slowdown in real . wage growth, so unemployment rises.
C) a slowdown in productivity growth means that more workers are need, so the unemployment decreases.
D) productivity growth results in lower wages.
A) increases in productivity results in higher unemployment.
B) a slowdown in productivity growth is not always immediately accompanied by a slowdown in real . wage growth, so unemployment rises.
C) a slowdown in productivity growth means that more workers are need, so the unemployment decreases.
D) productivity growth results in lower wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Static expectations of inflation prevail when people
A) ignore the fact that inflation can change.
B) assume that future inflation will be like recent past inflation.
C) get really charged about inflation.
D) use all the information they have as best they can.
A) ignore the fact that inflation can change.
B) assume that future inflation will be like recent past inflation.
C) get really charged about inflation.
D) use all the information they have as best they can.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Adaptive expectations of inflation prevail when people
A) ignore the fact that inflation can change.
B) assume that future inflation will be like recent past inflation.
C) assume that inflation will adapt to current conditions.
D) use all the information they have as best they can.
A) ignore the fact that inflation can change.
B) assume that future inflation will be like recent past inflation.
C) assume that inflation will adapt to current conditions.
D) use all the information they have as best they can.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Rational expectations of inflation prevail when people
A) ignore the fact that inflation can change.
B) assume that future inflation will be like recent past inflation.
C) feel that inflation is rational.
D) use all the information they have as best they can.
A) ignore the fact that inflation can change.
B) assume that future inflation will be like recent past inflation.
C) feel that inflation is rational.
D) use all the information they have as best they can.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If inflation increases under conditions of static expectations of inflation,
A) the Phillips curve will shift to the right, further exacerbating the inflation problem.
B) the Phillips curve will shift to the left, improving the inflation-unemployment situation.
C) the Phillips curve will remain in place and unemployment will decrease.
D) the monetary policy reaction function will shift to the right.
A) the Phillips curve will shift to the right, further exacerbating the inflation problem.
B) the Phillips curve will shift to the left, improving the inflation-unemployment situation.
C) the Phillips curve will remain in place and unemployment will decrease.
D) the monetary policy reaction function will shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If inflation increases and last year's inflation is expected to be this year's inflation,
A) the Phillips curve will shift to the right, further exacerbating the inflation problem.
B) the Phillips curve will shift to the left, improving the inflation-unemployment situation.
C) the Phillips curve will remain in place and unemployment will decrease.
D) the monetary policy reaction function will shift to the right.
A) the Phillips curve will shift to the right, further exacerbating the inflation problem.
B) the Phillips curve will shift to the left, improving the inflation-unemployment situation.
C) the Phillips curve will remain in place and unemployment will decrease.
D) the monetary policy reaction function will shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Under conditions of rational expectations of inflation,
A) the Phillips curve will eventually shift to the right if the economy is expending and inflation is increasing.
B) the Phillips curve will shift to the left if the economy is expanding and inflation is increasing.
C) the Phillips curve will remain in place and unemployment will decrease if the economy is expanding
And inflation is increasing.
D) the Phillips curve will shift as rapidly as, or faster than, changes in economic policy that affect the level of aggregate demand.
A) the Phillips curve will eventually shift to the right if the economy is expending and inflation is increasing.
B) the Phillips curve will shift to the left if the economy is expanding and inflation is increasing.
C) the Phillips curve will remain in place and unemployment will decrease if the economy is expanding
And inflation is increasing.
D) the Phillips curve will shift as rapidly as, or faster than, changes in economic policy that affect the level of aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Under conditions of rational expectations of inflation,
A) the only way that government policy can affect the level of unemployment is if the policy is known in advance.
B) the only way that government policy can affect the level of unemployment is if the policy comes as a surprise.
C) the Phillips curve remains in place and unemployment will change in response to government policy changes.
D) the only way that government policy can affect the level of unemployment is if the policy is anticipated by workers, managers, savers, and investors.
A) the only way that government policy can affect the level of unemployment is if the policy is known in advance.
B) the only way that government policy can affect the level of unemployment is if the policy comes as a surprise.
C) the Phillips curve remains in place and unemployment will change in response to government policy changes.
D) the only way that government policy can affect the level of unemployment is if the policy is anticipated by workers, managers, savers, and investors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
On a graph with the inflation and unemployment rates as the axes, an expansionary fiscal policy will
A) initially shift the monetary policy reaction curve to the right.
B) initially shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) initially shift the monetary policy reaction curve to the left.
D) initially shift the Phillips curve to the left.
A) initially shift the monetary policy reaction curve to the right.
B) initially shift the Phillips curve to the right.
C) initially shift the monetary policy reaction curve to the left.
D) initially shift the Phillips curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
On a graph with the inflation and unemployment rates as the axes, if an expansionary fiscal policy results in a decrease in unemployment with no shift of the Phillips curve,
A) inflation expectations must be static.
B) inflation expectations must be adaptive.
C) inflation expectations must be dynamic.
D) inflation expectations must be rational.
A) inflation expectations must be static.
B) inflation expectations must be adaptive.
C) inflation expectations must be dynamic.
D) inflation expectations must be rational.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
On a graph with the inflation and unemployment rates as the axes, if an expansionary fiscal policy results in a decrease in unemployment with a rightward shift of the Phillips curve,
A) inflation expectations must be static.
B) inflation expectations must be adaptive.
C) inflation expectations must be dynamic.
D) inflation expectations must be rational.
A) inflation expectations must be static.
B) inflation expectations must be adaptive.
C) inflation expectations must be dynamic.
D) inflation expectations must be rational.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
On a graph with the inflation and unemployment rates as the axes, if an expansionary fiscal policy results in no decrease in unemployment,
A) inflation expectations must be static.
B) inflation expectations must be adaptive.
C) inflation expectations must be dynamic.
D) inflation expectations must be rational.
A) inflation expectations must be static.
B) inflation expectations must be adaptive.
C) inflation expectations must be dynamic.
D) inflation expectations must be rational.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The reason that expansionary policy cannot reduce unemployment when inflation expectations are rational is that
A) the Phillips curve shifts far enough to the right to completely offset the unemployment effect of the leftward shift of the monetary policy reaction function.
B) the monetary policy reaction function does not shift to the left if inflation expectations are rational.
C) the Phillips curve shifts far enough to the left to completely offset the unemployment effect of the . rightward shift of the monetary policy reaction function.
D) the LM curve shifts far enough to the right to offset the effect of the leftward shift of the IS curve.
A) the Phillips curve shifts far enough to the right to completely offset the unemployment effect of the leftward shift of the monetary policy reaction function.
B) the monetary policy reaction function does not shift to the left if inflation expectations are rational.
C) the Phillips curve shifts far enough to the left to completely offset the unemployment effect of the . rightward shift of the monetary policy reaction function.
D) the LM curve shifts far enough to the right to offset the effect of the leftward shift of the IS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If inflation expectations are rationally formed,
A) the Phillips curve is essentially horizontal.
B) the monetary policy reaction function is essentially horizontal.
C) the Phillips curve is essentially vertical.
D) the monetary policy reaction function is essential vertical.
A) the Phillips curve is essentially horizontal.
B) the monetary policy reaction function is essentially horizontal.
C) the Phillips curve is essentially vertical.
D) the monetary policy reaction function is essential vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If inflation is low and stable,
A) inflation expectations are probably rational.
B) inflation expectations are probably static.
C) inflation expectations are probably adaptive.
D) inflation expectations are probably dynamic.
A) inflation expectations are probably rational.
B) inflation expectations are probably static.
C) inflation expectations are probably adaptive.
D) inflation expectations are probably dynamic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If inflation is moderate and fluctuates,
A) inflation expectations are probably rational.
B) inflation expectations are probably static.
C) inflation expectations are probably adaptive.
D) inflation expectations are probably dynamic.
A) inflation expectations are probably rational.
B) inflation expectations are probably static.
C) inflation expectations are probably adaptive.
D) inflation expectations are probably dynamic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When shifts in inflation are clearly related to changes in monetary policy, swift to occur, and large enough to seriously affect profitability,
A) inflation expectations are probably rational.
B) inflation expectations are probably static.
C) inflation expectations are probably adaptive.
D) inflation expectations are probably dynamic.
A) inflation expectations are probably rational.
B) inflation expectations are probably static.
C) inflation expectations are probably adaptive.
D) inflation expectations are probably dynamic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If inflation expectations are rational,
A) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the fixed-price model; that is, the output and employment levels change, not prices.
B) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the flexible-price model; that is, prices adjust to keep the economy at its potential output level.
C) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is a combination of output and price adjustments in the short-run and eventual price adjustments in the long-run..
D) there can never be a change in output and employment.
A) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the fixed-price model; that is, the output and employment levels change, not prices.
B) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the flexible-price model; that is, prices adjust to keep the economy at its potential output level.
C) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is a combination of output and price adjustments in the short-run and eventual price adjustments in the long-run..
D) there can never be a change in output and employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If inflation expectations are adaptive,
A) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the fixed-price model; that is, the output and employment levels change, not prices.
B) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the flexible-price model; that is, prices adjust to keep the economy at its potential output level.
C) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is a combination of output and price adjustments in the short-run and eventual price adjustments in the long-run..
D) there can never be a change in output and employment.
A) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the fixed-price model; that is, the output and employment levels change, not prices.
B) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the flexible-price model; that is, prices adjust to keep the economy at its potential output level.
C) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is a combination of output and price adjustments in the short-run and eventual price adjustments in the long-run..
D) there can never be a change in output and employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If inflation expectations are static,
A) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the fixed-price model; that is, the output and employment levels change, not prices.
B) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the flexible-price model; that is, prices adjust to keep the economy at its potential output level.
C) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is a combination of output and price adjustments in the short-run and eventual price adjustments in the long-run..
D) there can never be a change in output and employment.
A) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the fixed-price model; that is, the output and employment levels change, not prices.
B) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is the same as in the flexible-price model; that is, prices adjust to keep the economy at its potential output level.
C) the economy's reaction to a demand-side shock is a combination of output and price adjustments in the short-run and eventual price adjustments in the long-run..
D) there can never be a change in output and employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



