Deck 17: Data Analysis: Investigation of Association
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Data Analysis: Investigation of Association
1
The correlation coefficient is given by the following equation.
A)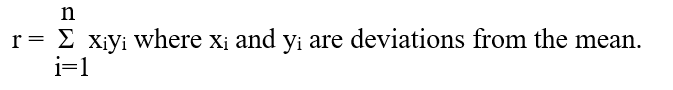
B)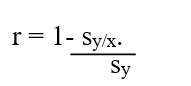
C)
D)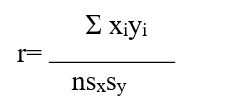
E) None of the above.
A)
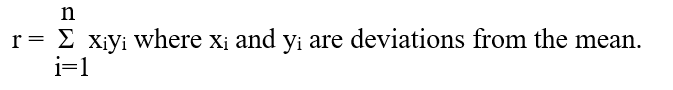
B)
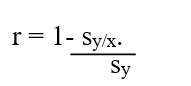
C)
D)
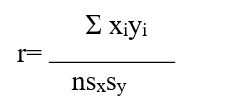
E) None of the above.
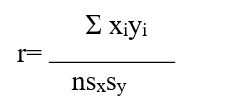
2
What assumption(s) of the error terms in a least squares solution of the linear regression model must be satisfied?
A) The mean of the disturbance term must equal one.
B) The variance of the disturbance term is independent of the values of the predictor variable.
C) The values of the error term are independent of one another.
D) all of the above.
E) Both b and c above must be satisfied.
A) The mean of the disturbance term must equal one.
B) The variance of the disturbance term is independent of the values of the predictor variable.
C) The values of the error term are independent of one another.
D) all of the above.
E) Both b and c above must be satisfied.
Both b and c above must be satisfied.
3
Which of the following is NOT an assumption made about the error term in least squares regression?
A) The mean or average value of the error term is zero.
B) The variance of the error term is constant across levels of the predictor variable.
C) The values of the error term are independent of the predictor variable.
D) The values of the error term are independent of one another.
E) All of the above are necessary assumptions underlying the least squares solution.
A) The mean or average value of the error term is zero.
B) The variance of the error term is constant across levels of the predictor variable.
C) The values of the error term are independent of the predictor variable.
D) The values of the error term are independent of one another.
E) All of the above are necessary assumptions underlying the least squares solution.
All of the above are necessary assumptions underlying the least squares solution.
4
For the linear equation y =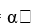 + ß1x1, if we do not reject the null hypothesis that ß1 = 01 we may
+ ß1x1, if we do not reject the null hypothesis that ß1 = 01 we may
A) conclude with absolute certainty that no relation exists between x1 and y.
B) have simply made a Type II error, and thus a relation between x and y may exist.
C) have simply chosen the wrong form of the model to investigate, as the relation between x1 and y may be nonlinear.
D) conclude that b and c above.
E) conclude that none of the above.
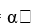 + ß1x1, if we do not reject the null hypothesis that ß1 = 01 we may
+ ß1x1, if we do not reject the null hypothesis that ß1 = 01 we mayA) conclude with absolute certainty that no relation exists between x1 and y.
B) have simply made a Type II error, and thus a relation between x and y may exist.
C) have simply chosen the wrong form of the model to investigate, as the relation between x1 and y may be nonlinear.
D) conclude that b and c above.
E) conclude that none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose the least squares solution to a regression analysis produced the following: Y2 = 20 - 39X
S2Y/X = 360
S2Y = 3600
R = .90
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) For every unit change in X there is a corresponding negative change in the average value of Y of 39 units.
B) 90 percent of the variation in Y is associated with variation in X.
C) The estimated average variance of the deviations of the errors about the regression line equals 360.
D) The average value of Y given x = 10 is -370.
E) They are all true.
S2Y/X = 360
S2Y = 3600
R = .90
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) For every unit change in X there is a corresponding negative change in the average value of Y of 39 units.
B) 90 percent of the variation in Y is associated with variation in X.
C) The estimated average variance of the deviations of the errors about the regression line equals 360.
D) The average value of Y given x = 10 is -370.
E) They are all true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An additional assumption made when discussing the correlation model that was not made in the regression model is
A) the observations come from a bivariate normal distribution.
B) the variance of the error term is dependent on the values of the predictor variable.
C) the variance of the disturbance term is constant.
D) the values of the error term are dependent on each other.
E) the Xi are fixed.
A) the observations come from a bivariate normal distribution.
B) the variance of the error term is dependent on the values of the predictor variable.
C) the variance of the disturbance term is constant.
D) the values of the error term are dependent on each other.
E) the Xi are fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If sß=3.57, and the least squares estimates of is 33.2, calculate the test statistic to determine if this value of could have been due to chance.
A) F = 17.57
B) t = 0.108
C) F = 9.30
D) t = 17.57
E) t = 9.30
A) F = 17.57
B) t = 0.108
C) F = 9.30
D) t = 17.57
E) t = 9.30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is NOT a formula for computing the coefficient of determination?
A) = 1 -
B) =
C) = 1 -
D) =
E) All of the above are formulas for computing the coefficient of determination.
A) = 1 -
B) =
C) = 1 -
D) =
E) All of the above are formulas for computing the coefficient of determination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the symbol ßY1.23, the first primary subscript
A) is Y, which identifies the predictor variable.
B) is 1, which identifies the predictor variable, of which this ß-value is the coefficient.
C) is 2, which indicates another predictor variable in the regression equation.
D) is 3, which indicates another predictor variable in the regression equation.
E) is Y, which identifies the criterion variable.
A) is Y, which identifies the predictor variable.
B) is 1, which identifies the predictor variable, of which this ß-value is the coefficient.
C) is 2, which indicates another predictor variable in the regression equation.
D) is 3, which indicates another predictor variable in the regression equation.
E) is Y, which identifies the criterion variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Assuming the two predictors X1 and X2 are not correlated, the coefficients of partial regression, Y1.2 and Y2.1, can be interpreted as
A)the unit change in the criterion variable associated with an average change in the appropriate predictor variable while holding the other predictor variable constant.
B)the change in the criterion variable associated with an average change in the predictor variables.
C)the average change in the criterion variable associated with an average change in the appropriate predictor variable while holding the other predictor variable constant.
D)the average change in the criterion variable associated with a unit change in the appropriate predictor variable while holding the other predictor variable constant.
E)the average change in the criterion variable associated with a unit change in the appropriate predictor variable.
A)the unit change in the criterion variable associated with an average change in the appropriate predictor variable while holding the other predictor variable constant.
B)the change in the criterion variable associated with an average change in the predictor variables.
C)the average change in the criterion variable associated with an average change in the appropriate predictor variable while holding the other predictor variable constant.
D)the average change in the criterion variable associated with a unit change in the appropriate predictor variable while holding the other predictor variable constant.
E)the average change in the criterion variable associated with a unit change in the appropriate predictor variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements regarding multicollinearity is FALSE?
A) Multicollinearity is said to be present in a multiple regression problem when the predictor variables are correlated among themselves.
B) If the data are highly multicollinear, there will be a tendency to judge many of the predictor variables as not being related to the criterion variable when in fact they are.
C) The standard error of estimate of the least squares coefficients increases as the dependence among the predictor variables increases.
D) A multicollinear condition within a data set increases the efficiency of the estimates for the regression parameters.
E) Multicollinearity makes interpretation of the beta coefficients problematic.
A) Multicollinearity is said to be present in a multiple regression problem when the predictor variables are correlated among themselves.
B) If the data are highly multicollinear, there will be a tendency to judge many of the predictor variables as not being related to the criterion variable when in fact they are.
C) The standard error of estimate of the least squares coefficients increases as the dependence among the predictor variables increases.
D) A multicollinear condition within a data set increases the efficiency of the estimates for the regression parameters.
E) Multicollinearity makes interpretation of the beta coefficients problematic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The coefficient of partial determination r2Y2.1 = .86
A) suggests that 86 percent of the variation in Y is associated with variation in X2.
B) suggests that 86 percent of the variation in Y is explained by or is associated with variation in X1 and X2.
C) suggests that 86 percent of the variation in Y not associated with X2 is incrementally associated with X1.
D) suggests that 86 percent of the variation in Y not associated with X1 is incrementally associated with X2.
E) suggests that 86 percent of the variation in Y is associated with variation in X1.
A) suggests that 86 percent of the variation in Y is associated with variation in X2.
B) suggests that 86 percent of the variation in Y is explained by or is associated with variation in X1 and X2.
C) suggests that 86 percent of the variation in Y not associated with X2 is incrementally associated with X1.
D) suggests that 86 percent of the variation in Y not associated with X1 is incrementally associated with X2.
E) suggests that 86 percent of the variation in Y is associated with variation in X1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A t statistic has been calculated in order to test the significance of the estimate from a least squares analysis. The estimate was based on 50 observations. How many degrees of freedom are associated with this test?
A) 50
B) 48
C) 49
D) 47
E) none of the above
A) 50
B) 48
C) 49
D) 47
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14

A) An upper class person could be expected on the average to spend $38 per year more than a lower class person on the product.
B) A middle class person could be expected on the average to spend $16 more per year on the product than a lower class person.
C) A lower class person could be expected on the average to spend $5 per year on the product.
D) An upper class person could be expected on the average to spend $22 more per year on the product than a middle class person.
E) An upper class person could be expected on the average to spend $38 per year on the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If there are m category classifications, there needs to be _____ dummy variables in the regression equation.
A) m + 1
B) (m + 1)/2
C) m - 1
D) (m - 1)1/2
E) (m - 1)/2
A) m + 1
B) (m + 1)/2
C) m - 1
D) (m - 1)1/2
E) (m - 1)/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Political analysts believe that voters level of education has a significant impact on the approval ratings given to a particular politician. The hypothesis was tested using regression analysis. If the variable education had seven categories, how many dummy variables are necessary to include this variable in a regression equation?
A) 1
B) 7
C) 6
D) 8
E) none of the above
A) 1
B) 7
C) 6
D) 8
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The parameters of a model of the form = X1ß
A) can be estimated employing transformations and the simple linear regression model.
B) cannot be estimated employing transformations and the simple linear regression model.
C) requires the multiple regression model without transformations be employed to estimate them.
D) requires the multiple regression model with transformations be employed to estimate them.
E) cannot be estimated with regression analysis.
A) can be estimated employing transformations and the simple linear regression model.
B) cannot be estimated employing transformations and the simple linear regression model.
C) requires the multiple regression model without transformations be employed to estimate them.
D) requires the multiple regression model with transformations be employed to estimate them.
E) cannot be estimated with regression analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which linear regression model would be used to represent the relationship between a criterion variable y and a predictor variable having four categories?
A) y =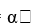 + ß1X1
+ ß1X1
B) y =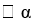 + ß1X1 + ß2X2
+ ß1X1 + ß2X2
C) y = 11eec98a_c51e_484e_b236_675ef5e75bfc_TB10464_11 + ß1X1 + ß2X2 + ß3X3
D) y = 11eec98a_c51e_484e_b236_675ef5e75bfc_TB10464_11 + ß1X1 + ß2X2 + ß3X3 + ß4X4
E) none of the above accurately captures the situation
A) y =
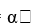 + ß1X1
+ ß1X1B) y =
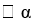 + ß1X1 + ß2X2
+ ß1X1 + ß2X2C) y = 11eec98a_c51e_484e_b236_675ef5e75bfc_TB10464_11 + ß1X1 + ß2X2 + ß3X3
D) y = 11eec98a_c51e_484e_b236_675ef5e75bfc_TB10464_11 + ß1X1 + ß2X2 + ß3X3 + ß4X4
E) none of the above accurately captures the situation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Exponential or logarithmic transformations to the predictor and criterion variables are useful for which of the following reasons?
A) Transformations allow regression analysis when the relationship between predictor and criterion is not additive.
B) Transformations allow regression analysis when the relationship between predictor and criterion is nonlinear.
C) Transformations allow regression analysis when the error terms are heteroscedastic.
D) None of the above are valid reasons for transforming predictor and criterion variables.
E) All of the above are valid reasons for transforming predictor and criterion variables.
A) Transformations allow regression analysis when the relationship between predictor and criterion is not additive.
B) Transformations allow regression analysis when the relationship between predictor and criterion is nonlinear.
C) Transformations allow regression analysis when the error terms are heteroscedastic.
D) None of the above are valid reasons for transforming predictor and criterion variables.
E) All of the above are valid reasons for transforming predictor and criterion variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Conjoint analysis
A) requires subjects to make judgments about stimuli that represent some predetermined combinations of attributes.
B) is like regression analysis with dummy variables.
C) relies on the ability of respondents to express their preferences for various combinations of attributes.
D) a and b.
E) a, b, and c.
-Conjoint analysis
A) requires subjects to make judgments about stimuli that represent some predetermined combinations of attributes.
B) is like regression analysis with dummy variables.
C) relies on the ability of respondents to express their preferences for various combinations of attributes.
D) a and b.
E) a, b, and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-The basic objective in conjoint analysis is to
A) determine the value systems people are using in making choices from combinations of attributes.
B) determine the perceived similarity of various objects.
C) determine the perceived similarity of various attributes.
D) measure the person's preference for specific objects.
E) none of the above.
-The basic objective in conjoint analysis is to
A) determine the value systems people are using in making choices from combinations of attributes.
B) determine the perceived similarity of various objects.
C) determine the perceived similarity of various attributes.
D) measure the person's preference for specific objects.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following statements about conjoint analysis is FALSE?
A) Subjects are asked to make judgments about stimuli that represent some predetermined combinations of attributes.
B) Respondents are asked to indicate their preference for each of the stimuli.
C) While the attributes that will be used to construct the stimuli will stem primarily from the purpose of the investigation, the analyst will have some discretion in this regard.
D) The attributes used to construct the stimuli should be actionable for the company.
E) Subjects are asked to make judgments about existing objects.
-Which of the following statements about conjoint analysis is FALSE?
A) Subjects are asked to make judgments about stimuli that represent some predetermined combinations of attributes.
B) Respondents are asked to indicate their preference for each of the stimuli.
C) While the attributes that will be used to construct the stimuli will stem primarily from the purpose of the investigation, the analyst will have some discretion in this regard.
D) The attributes used to construct the stimuli should be actionable for the company.
E) Subjects are asked to make judgments about existing objects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following is FALSE?
A) An advantage of conjoint analysis over regression is that the dependent variable can also be a dummy variable.
B) In a conjoint analysis application, the basic aim is to determine the features of products that respondents most prefer.
C) Of primary concern to researchers employing conjoint analysis are the trade-offs consumers make when evaluating various combinations of product attributes.
D) Conjoint analysis depends on preference judgments that are ratings or rankings.
E) Conjoints are easily run via multiple regression.
-Which of the following is FALSE?
A) An advantage of conjoint analysis over regression is that the dependent variable can also be a dummy variable.
B) In a conjoint analysis application, the basic aim is to determine the features of products that respondents most prefer.
C) Of primary concern to researchers employing conjoint analysis are the trade-offs consumers make when evaluating various combinations of product attributes.
D) Conjoint analysis depends on preference judgments that are ratings or rankings.
E) Conjoints are easily run via multiple regression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Conjoint analysis
A) requires respondents to express how they are weighting particular attributes in forming their judgments for products.
B) uses actual products or brands as the typical stimuli.
C) gets its name from the fact that we can measure relative values of things considered jointly which might be unmeasurable taken one at a time.
D) a and b.
E) a, b, and c.
-Conjoint analysis
A) requires respondents to express how they are weighting particular attributes in forming their judgments for products.
B) uses actual products or brands as the typical stimuli.
C) gets its name from the fact that we can measure relative values of things considered jointly which might be unmeasurable taken one at a time.
D) a and b.
E) a, b, and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-In conjoint analysis, the stimuli represent
A) combinations of attitudes.
B) products for which perceptions of similarity will be recorded.
C) predetermined combinations of product attributes.
D) groupings of related products.
E) none of the above.
-In conjoint analysis, the stimuli represent
A) combinations of attitudes.
B) products for which perceptions of similarity will be recorded.
C) predetermined combinations of product attributes.
D) groupings of related products.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following is TRUE?
A) It is necessary to present all possible combinations of attribute levels to respondents in a conjoint analysis.
B) The attempt in a conjoint analysis solution is to assign values to the levels of each of the attributes so that the resulting values or utilities are as monotonic as possible with the input rank order judgments.
C) In a typical conjoint analysis, the utilities assigned to each attribute are combined by multiplying them to determine the total utility for each alternative.
D) a and b.
E) a, b, and c.
-Which of the following is TRUE?
A) It is necessary to present all possible combinations of attribute levels to respondents in a conjoint analysis.
B) The attempt in a conjoint analysis solution is to assign values to the levels of each of the attributes so that the resulting values or utilities are as monotonic as possible with the input rank order judgments.
C) In a typical conjoint analysis, the utilities assigned to each attribute are combined by multiplying them to determine the total utility for each alternative.
D) a and b.
E) a, b, and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following are NOT true of conjoint analysis?
A) Conjoint analysis does not require the respondent to provide self?reports regarding the importance of various product attributes.
B) Conjoint analysis attempts to determine individuals' utilities for various product attributes when determining choices.
C) Conjoint analysis provides essentially the same results as a multidimensional scaling analysis in a given situation.
D) Conjoint analysis is quite dependent on the availability of a computer.
E) All of the above are true of conjoint analysis.
-Which of the following are NOT true of conjoint analysis?
A) Conjoint analysis does not require the respondent to provide self?reports regarding the importance of various product attributes.
B) Conjoint analysis attempts to determine individuals' utilities for various product attributes when determining choices.
C) Conjoint analysis provides essentially the same results as a multidimensional scaling analysis in a given situation.
D) Conjoint analysis is quite dependent on the availability of a computer.
E) All of the above are true of conjoint analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following is TRUE?
A) The attributes used to construct the stimuli for a conjoint analysis are completely determined by the purpose of the investigation.
B) The attributes used to construct the stimuli for a conjoint analysis should be both actionable for the company and important to people.
C) In a typical conjoint analysis study, most of the attributes that could be used to construct stimuli will be used.
D) Our ability to generate good estimates of the utility of each attribute level depends upon the number of stimuli being relatively small versus the number of parameters that need to be estimated.
E) They are all false.
-Which of the following is TRUE?
A) The attributes used to construct the stimuli for a conjoint analysis are completely determined by the purpose of the investigation.
B) The attributes used to construct the stimuli for a conjoint analysis should be both actionable for the company and important to people.
C) In a typical conjoint analysis study, most of the attributes that could be used to construct stimuli will be used.
D) Our ability to generate good estimates of the utility of each attribute level depends upon the number of stimuli being relatively small versus the number of parameters that need to be estimated.
E) They are all false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-The computer output of a conjoint analysis provides which of the following?
A) the respondent's preference for each object or brand.
B) the respondent's perception of each object or brand.
C) the respondent's utility for each attribute or product feature.
D) the mapping of perceptions and preferences.
E) none of the above.
-The computer output of a conjoint analysis provides which of the following?
A) the respondent's preference for each object or brand.
B) the respondent's perception of each object or brand.
C) the respondent's utility for each attribute or product feature.
D) the mapping of perceptions and preferences.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following statements about conjoint analysis is TRUE?
A) The typical stimuli are actual products or brands.
B) Respondents are asked to make judgments about the relative similarity of objects.
C) The attributes used for the stimuli should be important to people.
D) Most of the attributes that could be used will be used.
E) All the above statements are false.
-Which of the following statements about conjoint analysis is TRUE?
A) The typical stimuli are actual products or brands.
B) Respondents are asked to make judgments about the relative similarity of objects.
C) The attributes used for the stimuli should be important to people.
D) Most of the attributes that could be used will be used.
E) All the above statements are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following regarding conjoint analysis is FALSE?
A) The utilities or part?worth functions for a single subject can be determined.
B) The utilities can be used to determine the relative importance of each of the attributes.
C) The importance of any attribute is determined by the spread in utilities between the highest and lowest rated levels of the attribute.
D) A subject's preferences for any attribute must be monotonic for the procedure to work.
E) The importance of an attribute to an individual can depend on the levels of the attribute used when securing judgments.
-Which of the following regarding conjoint analysis is FALSE?
A) The utilities or part?worth functions for a single subject can be determined.
B) The utilities can be used to determine the relative importance of each of the attributes.
C) The importance of any attribute is determined by the spread in utilities between the highest and lowest rated levels of the attribute.
D) A subject's preferences for any attribute must be monotonic for the procedure to work.
E) The importance of an attribute to an individual can depend on the levels of the attribute used when securing judgments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Conjoint analysis seems to have great potential at the_____ stage of the product development process.
A) idea generation
B) business analysis
C) concept evaluation
D) test marketing
E) none of the above
-Conjoint analysis seems to have great potential at the_____ stage of the product development process.
A) idea generation
B) business analysis
C) concept evaluation
D) test marketing
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following methods should not be used for determining attributes to be used in conjoint analysis?
A) managerial judgment
B) focus groups
C) analysis of insight?stimulating examples
D) depth interviews
E) All of the above methods can be used.
-Which of the following methods should not be used for determining attributes to be used in conjoint analysis?
A) managerial judgment
B) focus groups
C) analysis of insight?stimulating examples
D) depth interviews
E) All of the above methods can be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following is FALSE?
A) A linear preference model for a conjoint analysis study implies that subjects always prefer more or less of the attribute.
B) The utilities of the various levels of an attribute used for conjoint analysis can be used to infer the importance of an attribute to a subject.
C) An important trade-off occurs for respondents between easier judgments but more of them when using the full profile approach to presenting attribute combinations in a conjoint analysis.
D) It is generally recommended that the ranges for the various attributes in a conjoint analysis study be made somewhat larger than what is normally found.
E) a and c.
-Which of the following is FALSE?
A) A linear preference model for a conjoint analysis study implies that subjects always prefer more or less of the attribute.
B) The utilities of the various levels of an attribute used for conjoint analysis can be used to infer the importance of an attribute to a subject.
C) An important trade-off occurs for respondents between easier judgments but more of them when using the full profile approach to presenting attribute combinations in a conjoint analysis.
D) It is generally recommended that the ranges for the various attributes in a conjoint analysis study be made somewhat larger than what is normally found.
E) a and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-The actual average number of attributes used in a typical conjoint analysis study is
A) 2.
B) 3.
C) 4.
D) 5.
E) more than 5.
-The actual average number of attributes used in a typical conjoint analysis study is
A) 2.
B) 3.
C) 4.
D) 5.
E) more than 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following statements regarding the use of rating scale versus rank order judgments in conjoint analysis is FALSE?
A) The rating scale method is currently more popular.
B) A fundamental premise underlying the rank order method is that it makes the judgment task as close as possible to a consumer's behavior while actually shopping.
C) Rating scale data are easier to analyze.
D) When the rating method is used, subjects are asked to make relative judgments with respect to their preference for one alternative versus another.
E) a and d.
-Which of the following statements regarding the use of rating scale versus rank order judgments in conjoint analysis is FALSE?
A) The rating scale method is currently more popular.
B) A fundamental premise underlying the rank order method is that it makes the judgment task as close as possible to a consumer's behavior while actually shopping.
C) Rating scale data are easier to analyze.
D) When the rating method is used, subjects are asked to make relative judgments with respect to their preference for one alternative versus another.
E) a and d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following statements about conjoint analysis is FALSE?
A) The use of a linear preference model implies that subjects always prefer more or less of the attribute.
B) If the analyst suspects that subjects might prefer an intermediate level of an attribute, the analyst should attempt to fit their preferences using a part?worth model.
C) The ranges of the various attributes should be somewhat narrower than what is normally found so as to increase the believability of the task.
D) The number of stimuli should be relatively large versus the number of parameters to be estimated.
E) With the paired-comparison data collection method, respondents can be asked to simply choose which alternative in each pair they prefer.
-Which of the following statements about conjoint analysis is FALSE?
A) The use of a linear preference model implies that subjects always prefer more or less of the attribute.
B) If the analyst suspects that subjects might prefer an intermediate level of an attribute, the analyst should attempt to fit their preferences using a part?worth model.
C) The ranges of the various attributes should be somewhat narrower than what is normally found so as to increase the believability of the task.
D) The number of stimuli should be relatively large versus the number of parameters to be estimated.
E) With the paired-comparison data collection method, respondents can be asked to simply choose which alternative in each pair they prefer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following is typically not used with the full profile approach of presenting stimuli in conjoint analysis?
A) paragraph description
B) verbal description
C) prototype evaluation
D) pictorial representation
E) all of the above are typically used
-Which of the following is typically not used with the full profile approach of presenting stimuli in conjoint analysis?
A) paragraph description
B) verbal description
C) prototype evaluation
D) pictorial representation
E) all of the above are typically used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following statements regarding conjoint analysis is FALSE?
A) The technique is restricted to product evaluations.
B) The utilities assigned each attribute level are typically added to determine the total utility for each alternative.
C) The pairwise procedure treats two attributes at a time but considers all possible pairs.
D) It is typically easier for subjects to supply pairwise judgments than full profile judgments.
E) Subjects typically need to make more judgments with the pairwise approach than the full profile approach.
-Which of the following statements regarding conjoint analysis is FALSE?
A) The technique is restricted to product evaluations.
B) The utilities assigned each attribute level are typically added to determine the total utility for each alternative.
C) The pairwise procedure treats two attributes at a time but considers all possible pairs.
D) It is typically easier for subjects to supply pairwise judgments than full profile judgments.
E) Subjects typically need to make more judgments with the pairwise approach than the full profile approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-In which of the following applications would conjoint analysis not be useful?
A) the design of a new type of motorcycle
B) the determination of an appropriate price for a new electric fan
C) the determination of a market segment, or "niche," for very high quality electronic equipment
D) the selection of advertising media for a new product introduction
E) conjoint analysis is useful in each of these situations
-In which of the following applications would conjoint analysis not be useful?
A) the design of a new type of motorcycle
B) the determination of an appropriate price for a new electric fan
C) the determination of a market segment, or "niche," for very high quality electronic equipment
D) the selection of advertising media for a new product introduction
E) conjoint analysis is useful in each of these situations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following is TRUE?
A) The pairwise procedure in conjoint analysis considers all attributes at the same time but only allows each attribute to be set at two or a pair of levels.
B) An individual typically needs to make more judgments when the full profile method of data collection is used in conjoint analysis than when the pairwise method is used.
C) The use of rating scales in lieu of rank order judgments to measure preference in conjoint analysis has been increasing in popularity.
D) When the rating method is used in conjoint analysis, subjects are asked to make relative judgments with respect to their preference for one alternative versus another.
E) They are all false.
-Which of the following is TRUE?
A) The pairwise procedure in conjoint analysis considers all attributes at the same time but only allows each attribute to be set at two or a pair of levels.
B) An individual typically needs to make more judgments when the full profile method of data collection is used in conjoint analysis than when the pairwise method is used.
C) The use of rating scales in lieu of rank order judgments to measure preference in conjoint analysis has been increasing in popularity.
D) When the rating method is used in conjoint analysis, subjects are asked to make relative judgments with respect to their preference for one alternative versus another.
E) They are all false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The following questions focus on Conjoint Measurement:
-Which of the following is NOT a reason for the increasing popularity of the paired comparison approach to determining attribute combinations in a conjoint analysis?
A) The paired comparison approach works well with computer?interactive interviewing procedures.
B) The paired comparison approach allows the researcher to check respondents' consistency in their judgment of alternatives.
C) The paired comparison approach, although a more difficult task for respondents than the full profile approach, is considerably more thorough.
D) All of the above are reasons.
E) b and c only are NOT reasons
-Which of the following is NOT a reason for the increasing popularity of the paired comparison approach to determining attribute combinations in a conjoint analysis?
A) The paired comparison approach works well with computer?interactive interviewing procedures.
B) The paired comparison approach allows the researcher to check respondents' consistency in their judgment of alternatives.
C) The paired comparison approach, although a more difficult task for respondents than the full profile approach, is considerably more thorough.
D) All of the above are reasons.
E) b and c only are NOT reasons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the following information to answer the next 5 questions:
A marketing research team collected preferences from consumers in the MidWest who rated the likelihood that they would go on each of the 16 possible week long spa packages created by combining the factors: San Diego, CA or Phoenix, AZ; $1499 or $2599; golf green fees included or not; and daily massages included or not. (The factors were scored: 0=San Diego, 1=Phoenix; 0=$1499, 1=$2599; 0=golf not included, 1= golf included; 0 = massage not included, 1= massage included. The likelihood scale ranged from 0 to 100, with 100 meaning greater preference.) When the marketing research team conducted the conjoint analysis, they obtained the following beta weights (after averaging across the sample):
likelihood = -.85 destination -.15 price +.70 golf +.50 massage
-What feature dominates the consumers' preferences?
A)destination
B)price
C)golf
D)massage
E)golf with price, or destination
A marketing research team collected preferences from consumers in the MidWest who rated the likelihood that they would go on each of the 16 possible week long spa packages created by combining the factors: San Diego, CA or Phoenix, AZ; $1499 or $2599; golf green fees included or not; and daily massages included or not. (The factors were scored: 0=San Diego, 1=Phoenix; 0=$1499, 1=$2599; 0=golf not included, 1= golf included; 0 = massage not included, 1= massage included. The likelihood scale ranged from 0 to 100, with 100 meaning greater preference.) When the marketing research team conducted the conjoint analysis, they obtained the following beta weights (after averaging across the sample):
likelihood = -.85 destination -.15 price +.70 golf +.50 massage
-What feature dominates the consumers' preferences?
A)destination
B)price
C)golf
D)massage
E)golf with price, or destination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Use the following information to answer the next 5 questions:
A marketing research team collected preferences from consumers in the MidWest who rated the likelihood that they would go on each of the 16 possible week long spa packages created by combining the factors: San Diego, CA or Phoenix, AZ; $1499 or $2599; golf green fees included or not; and daily massages included or not. (The factors were scored: 0=San Diego, 1=Phoenix; 0=$1499, 1=$2599; 0=golf not included, 1= golf included; 0 = massage not included, 1= massage included. The likelihood scale ranged from 0 to 100, with 100 meaning greater preference.) When the marketing research team conducted the conjoint analysis, they obtained the following beta weights (after averaging across the sample):
likelihood = -.85 destination -.15 price +.70 golf +.50 massage
-Which location do the consumers tend to prefer?
A)San Diego
B)Phoenix
C)Tucson (it's in between)
D)Cancun would do better because it is closer to the MidWest
E)indeterminate, more analytical details are required to make that specification
A marketing research team collected preferences from consumers in the MidWest who rated the likelihood that they would go on each of the 16 possible week long spa packages created by combining the factors: San Diego, CA or Phoenix, AZ; $1499 or $2599; golf green fees included or not; and daily massages included or not. (The factors were scored: 0=San Diego, 1=Phoenix; 0=$1499, 1=$2599; 0=golf not included, 1= golf included; 0 = massage not included, 1= massage included. The likelihood scale ranged from 0 to 100, with 100 meaning greater preference.) When the marketing research team conducted the conjoint analysis, they obtained the following beta weights (after averaging across the sample):
likelihood = -.85 destination -.15 price +.70 golf +.50 massage
-Which location do the consumers tend to prefer?
A)San Diego
B)Phoenix
C)Tucson (it's in between)
D)Cancun would do better because it is closer to the MidWest
E)indeterminate, more analytical details are required to make that specification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the following information to answer the next 5 questions:
A marketing research team collected preferences from consumers in the MidWest who rated the likelihood that they would go on each of the 16 possible week long spa packages created by combining the factors: San Diego, CA or Phoenix, AZ; $1499 or $2599; golf green fees included or not; and daily massages included or not. (The factors were scored: 0=San Diego, 1=Phoenix; 0=$1499, 1=$2599; 0=golf not included, 1= golf included; 0 = massage not included, 1= massage included. The likelihood scale ranged from 0 to 100, with 100 meaning greater preference.) When the marketing research team conducted the conjoint analysis, they obtained the following beta weights (after averaging across the sample):
likelihood = -.85 destination -.15 price +.70 golf +.50 massage
-Which location do consumers prefer?
A) San Diego, by a lot
B) Phoenix, by a lot
C) San Diego, marginally
D) Phoenix, marginally
E) San Diego, only if they can golf
A marketing research team collected preferences from consumers in the MidWest who rated the likelihood that they would go on each of the 16 possible week long spa packages created by combining the factors: San Diego, CA or Phoenix, AZ; $1499 or $2599; golf green fees included or not; and daily massages included or not. (The factors were scored: 0=San Diego, 1=Phoenix; 0=$1499, 1=$2599; 0=golf not included, 1= golf included; 0 = massage not included, 1= massage included. The likelihood scale ranged from 0 to 100, with 100 meaning greater preference.) When the marketing research team conducted the conjoint analysis, they obtained the following beta weights (after averaging across the sample):
likelihood = -.85 destination -.15 price +.70 golf +.50 massage
-Which location do consumers prefer?
A) San Diego, by a lot
B) Phoenix, by a lot
C) San Diego, marginally
D) Phoenix, marginally
E) San Diego, only if they can golf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the following information to answer the next 5 questions:
A marketing research team collected preferences from consumers in the MidWest who rated the likelihood that they would go on each of the 16 possible week long spa packages created by combining the factors: San Diego, CA or Phoenix, AZ; $1499 or $2599; golf green fees included or not; and daily massages included or not. (The factors were scored: 0=San Diego, 1=Phoenix; 0=$1499, 1=$2599; 0=golf not included, 1= golf included; 0 = massage not included, 1= massage included. The likelihood scale ranged from 0 to 100, with 100 meaning greater preference.) When the marketing research team conducted the conjoint analysis, they obtained the following beta weights (after averaging across the sample):
likelihood = -.85 destination -.15 price +.70 golf +.50 massage
-Which price do the consumers prefer?
A) 15% discount
B) $1499
C) $2599
D) it depends on the segmentation structure
E) cheaper is always better
A marketing research team collected preferences from consumers in the MidWest who rated the likelihood that they would go on each of the 16 possible week long spa packages created by combining the factors: San Diego, CA or Phoenix, AZ; $1499 or $2599; golf green fees included or not; and daily massages included or not. (The factors were scored: 0=San Diego, 1=Phoenix; 0=$1499, 1=$2599; 0=golf not included, 1= golf included; 0 = massage not included, 1= massage included. The likelihood scale ranged from 0 to 100, with 100 meaning greater preference.) When the marketing research team conducted the conjoint analysis, they obtained the following beta weights (after averaging across the sample):
likelihood = -.85 destination -.15 price +.70 golf +.50 massage
-Which price do the consumers prefer?
A) 15% discount
B) $1499
C) $2599
D) it depends on the segmentation structure
E) cheaper is always better

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the following information to answer the next 5 questions:
A marketing research team collected preferences from consumers in the MidWest who rated the likelihood that they would go on each of the 16 possible week long spa packages created by combining the factors: San Diego, CA or Phoenix, AZ; $1499 or $2599; golf green fees included or not; and daily massages included or not. (The factors were scored: 0=San Diego, 1=Phoenix; 0=$1499, 1=$2599; 0=golf not included, 1= golf included; 0 = massage not included, 1= massage included. The likelihood scale ranged from 0 to 100, with 100 meaning greater preference.) When the marketing research team conducted the conjoint analysis, they obtained the following beta weights (after averaging across the sample):
likelihood = -.85 destination -.15 price +.70 golf +.50 massage
-What would it mean if b2 were not significant?
A) destination wouldn't matter
B) consumers are price insensitive
C) the respondents weren't golfers
D) the respondents don't care for spas
E) the golf course could be exchanged for a spa
A marketing research team collected preferences from consumers in the MidWest who rated the likelihood that they would go on each of the 16 possible week long spa packages created by combining the factors: San Diego, CA or Phoenix, AZ; $1499 or $2599; golf green fees included or not; and daily massages included or not. (The factors were scored: 0=San Diego, 1=Phoenix; 0=$1499, 1=$2599; 0=golf not included, 1= golf included; 0 = massage not included, 1= massage included. The likelihood scale ranged from 0 to 100, with 100 meaning greater preference.) When the marketing research team conducted the conjoint analysis, they obtained the following beta weights (after averaging across the sample):
likelihood = -.85 destination -.15 price +.70 golf +.50 massage
-What would it mean if b2 were not significant?
A) destination wouldn't matter
B) consumers are price insensitive
C) the respondents weren't golfers
D) the respondents don't care for spas
E) the golf course could be exchanged for a spa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



