Deck 16: Data Analysis: Examination of Differences
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/14
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Data Analysis: Examination of Differences
1
Which of the following statistical distributions is completely determined by its degrees of freedom?
A) Chi-square
B) F-test
C) Kolmogorov-Smirnov
D) normal distribution
E) all nonparametric distributions
A) Chi-square
B) F-test
C) Kolmogorov-Smirnov
D) normal distribution
E) all nonparametric distributions
Chi-square
2
A market research manager wishes to verify that a set of nominal data follows an expected pattern. Which test is appropriate in this situation?
A) a t-test if there are less than 30 observations and a z-test if there are more than 30 observations
B) Kolmogorov-Smirnov test
C) Chi-square goodness-of-fit test
D) F-test
E) None of the above is appropriate.
A) a t-test if there are less than 30 observations and a z-test if there are more than 30 observations
B) Kolmogorov-Smirnov test
C) Chi-square goodness-of-fit test
D) F-test
E) None of the above is appropriate.
Chi-square goodness-of-fit test
3
In which of the following situations is the calculation of the z-statistic NOT appropriate for making inferences about a single mean?
A) The variable of interest is normally distributed in the population, is known, and n (number of observations) is large.
B) The variable of interest is normally distributed in the population, is known, and n is small.
C) The variable of interest is normally distributed in the population, is unknown, and n is small.
D) The variable of interest is not normally distributed in the population, is known, and n is large.
E) Calculation of the z-statistic is appropriate in each of these situations.
A) The variable of interest is normally distributed in the population, is known, and n (number of observations) is large.
B) The variable of interest is normally distributed in the population, is known, and n is small.
C) The variable of interest is normally distributed in the population, is unknown, and n is small.
D) The variable of interest is not normally distributed in the population, is known, and n is large.
E) Calculation of the z-statistic is appropriate in each of these situations.
The variable of interest is normally distributed in the population, is unknown, and n is small.
4
Which formula is appropriate for estimating the value of the z-statistic when the population variance 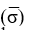 is known (where is the sample mean, µ represents the population mean, and is the standard error of the mean.
is known (where is the sample mean, µ represents the population mean, and is the standard error of the mean.
A)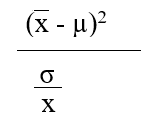
B)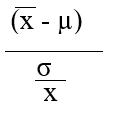
C)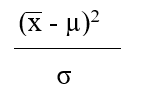
D)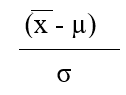
E)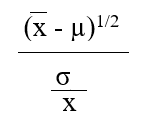
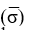 is known (where is the sample mean, µ represents the population mean, and is the standard error of the mean.
is known (where is the sample mean, µ represents the population mean, and is the standard error of the mean.A)
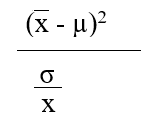
B)
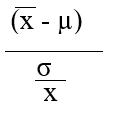
C)
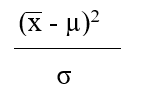
D)
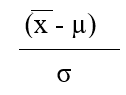
E)
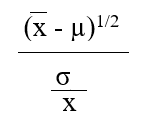

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements is FALSE? The t-test to test a hypothesis regarding the equity of two population means it
A) assumes the variable is normally distributed
B) is referred to a t-distribution which is completely determined by its degrees of freedom and which depends upon the number of observations in each sample
C) assumes the two samples are independent
D) applies when the variance of the variable in each population is known
E) THEORETICALLY applies for all size samples if the general conditions surrounding its use are satisfied
A) assumes the variable is normally distributed
B) is referred to a t-distribution which is completely determined by its degrees of freedom and which depends upon the number of observations in each sample
C) assumes the two samples are independent
D) applies when the variance of the variable in each population is known
E) THEORETICALLY applies for all size samples if the general conditions surrounding its use are satisfied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The z-statistic is appropriate if
A) the sample is chi-square distributed and the degrees of freedom is small.
B) the population mean is known.
C) the population variance is unknown.
D) the distribution of the characteristic is normal or the sample is very large such that the Central-Limit Theorem is operative.
E) both c and d above.
A) the sample is chi-square distributed and the degrees of freedom is small.
B) the population mean is known.
C) the population variance is unknown.
D) the distribution of the characteristic is normal or the sample is very large such that the Central-Limit Theorem is operative.
E) both c and d above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the following information to answer the next three questions.
? the population mean (µ) is hypothesized to be 200
? the sample mean ( ) is 220
? the sample size (n) is 25
? the unbiased sample standard ( ) is 15
-The estimated value of the standard error of the mean ( ) is
A) 0.6.
B) 0.9.
C) 1.6.
D) 2.6.
E) 3.0.
? the population mean (µ) is hypothesized to be 200
? the sample mean ( ) is 220
? the sample size (n) is 25
? the unbiased sample standard ( ) is 15
-The estimated value of the standard error of the mean ( ) is
A) 0.6.
B) 0.9.
C) 1.6.
D) 2.6.
E) 3.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the following information to answer the next three questions.
? the population mean (µ) is hypothesized to be 200
? the sample mean ( ) is 220
? the sample size (n) is 25
? the unbiased sample standard ( ) is 15
-The estimated value of the t-statistic is
A) 4.0.
B) 5.2.
C) 6.7.
D) 7.2.
E) 9.0.
? the population mean (µ) is hypothesized to be 200
? the sample mean ( ) is 220
? the sample size (n) is 25
? the unbiased sample standard ( ) is 15
-The estimated value of the t-statistic is
A) 4.0.
B) 5.2.
C) 6.7.
D) 7.2.
E) 9.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the following information to answer the next three questions.
? the population mean (µ) is hypothesized to be 200
? the sample mean ( ) is 220
? the sample size (n) is 25
? the unbiased sample standard ( ) is 15
-The two-tailed tabled value for the t-statistic with 24 degrees of freedom and alpha = 05 is 2.064. The 95 percent confidence interval is
A) 204.6 µ 230.7.
B) 213.8 µ 226.2.
C) 442.1 µ 448.6.
D) 511.2 µ 514.9.
E) none of the above.
? the population mean (µ) is hypothesized to be 200
? the sample mean ( ) is 220
? the sample size (n) is 25
? the unbiased sample standard ( ) is 15
-The two-tailed tabled value for the t-statistic with 24 degrees of freedom and alpha = 05 is 2.064. The 95 percent confidence interval is
A) 204.6 µ 230.7.
B) 213.8 µ 226.2.
C) 442.1 µ 448.6.
D) 511.2 µ 514.9.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
For large samples, use of the normal curve rather than the t distribution typically results in
A) larger confidence intervals.
B) significantly more computations on the part of the researcher.
C) no difference in the width of the confidence intervals.
D) smaller confidence intervals.
E) b and c above.
A) larger confidence intervals.
B) significantly more computations on the part of the researcher.
C) no difference in the width of the confidence intervals.
D) smaller confidence intervals.
E) b and c above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
(Use the following information for the next three questions.)
A researcher is interested in comparing the usage of bank debit cards by consumers in rural (r) and urban (u) areas. Each year for the past five years, she has surveyed 500 individuals (one half urban, one half rural) randomly selected from across the United States. She is specifically interested in any differences that may exist between the two groups with regard to usage. The results of the current study indicate that people in urban areas use bank debit cards 12 times per month on average ( u), while those in rural areas use bank cards 10 times per month on average ( r)
-Which of the following is the null hypothesis that the researcher should use in comparing the usage rates?
A)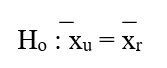
B)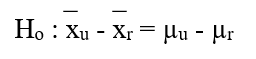
C)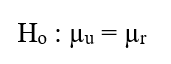
D)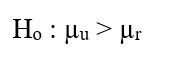
E)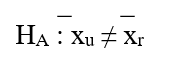
A researcher is interested in comparing the usage of bank debit cards by consumers in rural (r) and urban (u) areas. Each year for the past five years, she has surveyed 500 individuals (one half urban, one half rural) randomly selected from across the United States. She is specifically interested in any differences that may exist between the two groups with regard to usage. The results of the current study indicate that people in urban areas use bank debit cards 12 times per month on average ( u), while those in rural areas use bank cards 10 times per month on average ( r)
-Which of the following is the null hypothesis that the researcher should use in comparing the usage rates?
A)
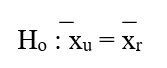
B)
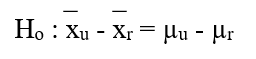
C)
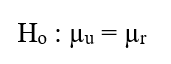
D)
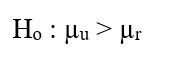
E)
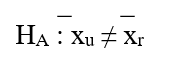

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
(Use the following information for the next three questions.)
A researcher is interested in comparing the usage of bank debit cards by consumers in rural (r) and urban (u) areas. Each year for the past five years, she has surveyed 500 individuals (one half urban, one half rural) randomly selected from across the United States. She is specifically interested in any differences that may exist between the two groups with regard to usage. The results of the current study indicate that people in urban areas use bank debit cards 12 times per month on average ( u), while those in rural areas use bank cards 10 times per month on average ( r)
-Given that the critical value that the test statistic is to be compared with is equal to 1.645 at a 90% significance level, which of the following statements are true?
A) The researcher should reject the null hypothesis at the 90% significance level.
B) The researcher might be able to reject the null hypothesis at the 95% level of significance.
C) The researcher cannot reject the null hypothesis at this significance level.
D) The researcher has provided evidence that people in urban areas use bank debit cards more than people in rural areas.
E) More information is needed before a decision about the null hypothesis can be made.
A researcher is interested in comparing the usage of bank debit cards by consumers in rural (r) and urban (u) areas. Each year for the past five years, she has surveyed 500 individuals (one half urban, one half rural) randomly selected from across the United States. She is specifically interested in any differences that may exist between the two groups with regard to usage. The results of the current study indicate that people in urban areas use bank debit cards 12 times per month on average ( u), while those in rural areas use bank cards 10 times per month on average ( r)
-Given that the critical value that the test statistic is to be compared with is equal to 1.645 at a 90% significance level, which of the following statements are true?
A) The researcher should reject the null hypothesis at the 90% significance level.
B) The researcher might be able to reject the null hypothesis at the 95% level of significance.
C) The researcher cannot reject the null hypothesis at this significance level.
D) The researcher has provided evidence that people in urban areas use bank debit cards more than people in rural areas.
E) More information is needed before a decision about the null hypothesis can be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If 85 women and 80 men are daily users of a deodorant product, the variance for the appropriate test is
A) 0.0029.
B) 0.0527.
C) 0.00128.
D) none of the above.
E) more information is necessary in order to calculate the variance for this example.
A) 0.0029.
B) 0.0527.
C) 0.00128.
D) none of the above.
E) more information is necessary in order to calculate the variance for this example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If 85 women and 80 men are daily users of a deodorant product, the calculated z statistic is
A) z=1.64.
B) z=1.96.
C) z=0.74.
D) z=0.93.
E) more information is necessary in order to calculate the z statistic for this example.
A) z=1.64.
B) z=1.96.
C) z=0.74.
D) z=0.93.
E) more information is necessary in order to calculate the z statistic for this example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



