Deck 15: Appendix 15 A: Quick Stats Review
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/24
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Appendix 15 A: Quick Stats Review
1
The principle which guides the framing of a null hypothesis is:
A) one either rejects or accepts the null hypothesis on the basis of the evidence at hand
B) a null hypothesis may be rejected but can never be accepted
C) one must always reject the null hypothesis unless the evidence is convincingly (determined by the a level) to the contrary
D) one must always accept the null hypothesis unless the evidence is convincingly (determined by the a level) to the contrary
E) there is no guiding scientific principle and the analyst should frame them as he or she sees fit
A) one either rejects or accepts the null hypothesis on the basis of the evidence at hand
B) a null hypothesis may be rejected but can never be accepted
C) one must always reject the null hypothesis unless the evidence is convincingly (determined by the a level) to the contrary
D) one must always accept the null hypothesis unless the evidence is convincingly (determined by the a level) to the contrary
E) there is no guiding scientific principle and the analyst should frame them as he or she sees fit
a null hypothesis may be rejected but can never be accepted
2
An important philosophical point underlying statistical hypothesis testing is that a null hypothesis may be ____ but can never be____ .
A) accepted; rejected
B) incorrectly stated; rejected
C) rejected; accepted
D) unacceptable; rejected
E) rejected; unacceptable
A) accepted; rejected
B) incorrectly stated; rejected
C) rejected; accepted
D) unacceptable; rejected
E) rejected; unacceptable
rejected; accepted
3
A firm will follow a particular advertising strategy if the resultant expected sales are at least 20,000 units. The correct hypotheses for this decision rule are: .
A) Ho : 20,000
Ha : > 20,000
B) Ho : 20,000
Ha : < 20,000
C) Ho : > 20,000
Ha : < 20,000
D) Ha : = 20,000
Ho : = 20,000
E) Ho : < 20,000
Ha : < 20,000
A) Ho : 20,000
Ha : > 20,000
B) Ho : 20,000
Ha : < 20,000
C) Ho : > 20,000
Ha : < 20,000
D) Ha : = 20,000
Ho : = 20,000
E) Ho : < 20,000
Ha : < 20,000
Ho : 20,000
Ha : > 20,000
Ha : > 20,000
4
A product manager for an inexpensive shampoo product was concerned because of declining sales. The manager felt that in blind product testing there would be no difference or possibly even a preference by consumers for the inexpensive shampoo over the expensive brand name alternative. The product manager decides to test this hypothesis. If the inexpensive shampoo is given by I and the expensive shampoo by E, the correct hypotheses for this situation are
A) H0 : I = E, Ha : I > E.
B) H0 : I = .50, Ha : I .50.
C) H0 : I < .50, Ha : I .50.
D) H0 : I = E, Ha : I = E.
E) none of the above.
A) H0 : I = E, Ha : I > E.
B) H0 : I = .50, Ha : I .50.
C) H0 : I < .50, Ha : I .50.
D) H0 : I = E, Ha : I = E.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
(Use the following information for the next four questions.)
A large clothing manufacturer plans to introduce a new line of sports clothes for women if preliminary market research shows that at least 50% of the population are favorably impressed by the new line. Five hundred women were surveyed; 265 of the women were favorably impressed. The research manager wants to test the hypothesis at the .05 significance level. The z-value associated with this significance level is 1.645.
-What is the standard error of the proportion?
A) 0.0005
B) 0.0224
C) 0.0307
D) 0.0326
E) more information is needed
A large clothing manufacturer plans to introduce a new line of sports clothes for women if preliminary market research shows that at least 50% of the population are favorably impressed by the new line. Five hundred women were surveyed; 265 of the women were favorably impressed. The research manager wants to test the hypothesis at the .05 significance level. The z-value associated with this significance level is 1.645.
-What is the standard error of the proportion?
A) 0.0005
B) 0.0224
C) 0.0307
D) 0.0326
E) more information is needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
(Use the following information for the next four questions.)
A large clothing manufacturer plans to introduce a new line of sports clothes for women if preliminary market research shows that at least 50% of the population are favorably impressed by the new line. Five hundred women were surveyed; 265 of the women were favorably impressed. The research manager wants to test the hypothesis at the .05 significance level. The z-value associated with this significance level is 1.645.
-The calculated z-statistic for testing the hypothesis is:
A) 1.339
B) -1.339
C) 0.977
D) -0.977
E) more information is needed
A large clothing manufacturer plans to introduce a new line of sports clothes for women if preliminary market research shows that at least 50% of the population are favorably impressed by the new line. Five hundred women were surveyed; 265 of the women were favorably impressed. The research manager wants to test the hypothesis at the .05 significance level. The z-value associated with this significance level is 1.645.
-The calculated z-statistic for testing the hypothesis is:
A) 1.339
B) -1.339
C) 0.977
D) -0.977
E) more information is needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
(Use the following information for the next four questions.)
A large clothing manufacturer plans to introduce a new line of sports clothes for women if preliminary market research shows that at least 50% of the population are favorably impressed by the new line. Five hundred women were surveyed; 265 of the women were favorably impressed. The research manager wants to test the hypothesis at the .05 significance level. The z-value associated with this significance level is 1.645.
-How many women from a sample of 500 must be favorably impressed with the new line in order to reject the null hypothesis at the specified significance level?
A) 250
B) 251
C) 249
D) 269
E) 268
A large clothing manufacturer plans to introduce a new line of sports clothes for women if preliminary market research shows that at least 50% of the population are favorably impressed by the new line. Five hundred women were surveyed; 265 of the women were favorably impressed. The research manager wants to test the hypothesis at the .05 significance level. The z-value associated with this significance level is 1.645.
-How many women from a sample of 500 must be favorably impressed with the new line in order to reject the null hypothesis at the specified significance level?
A) 250
B) 251
C) 249
D) 269
E) 268

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The percentage of incorrect rejections of the null hypothesis which is expected to occur simply because of random variation in a large number of samples may be referred to as the .
A) b risk
B) 1-a risk
C) confidence level
D) 1-b risk
E) a risk
A) b risk
B) 1-a risk
C) confidence level
D) 1-b risk
E) a risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A researcher who rejects a null hypothesis when in fact it is true:
A) is committing a Type I error
B) is committing a Type II error
C) is committing neither a Type I nor Type II error
D) is typically sure that he has made an incorrect decision
E) none of the above
A) is committing a Type I error
B) is committing a Type II error
C) is committing neither a Type I nor Type II error
D) is typically sure that he has made an incorrect decision
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In an attempt to minimize error the researcher would like to keep a error as small as possible but he recognizes that an extremely low value of a error leads to .
A) low b error
B) the need for large samples
C) large opportunity losses
D) indeterminate b errors
E) large b errors
A) low b error
B) the need for large samples
C) large opportunity losses
D) indeterminate b errors
E) large b errors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The power of statistical test refers to the probability of and is measured by .
A) incorrectly rejecting a true null hypothesis; a
B) correctly accepting a correct null hypothesis; b
C) correctly accepting a correct null hypothesis; 1-b
D) correctly rejecting an incorrect null hypothesis; b
E) correctly rejecting an incorrect null hypothesis; 1-b
A) incorrectly rejecting a true null hypothesis; a
B) correctly accepting a correct null hypothesis; b
C) correctly accepting a correct null hypothesis; 1-b
D) correctly rejecting an incorrect null hypothesis; b
E) correctly rejecting an incorrect null hypothesis; 1-b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A p value of 0.01 means
A) the odds are only 1 in 100 of getting the results simply by chance.
B) there is only a 1% chance that the results are incorrect.
C) there is a probability of 1 in 100 that this result would occur if the null hypotheses were true.
D) all of the above are true.
E) none of the above are true.
A) the odds are only 1 in 100 of getting the results simply by chance.
B) there is only a 1% chance that the results are incorrect.
C) there is a probability of 1 in 100 that this result would occur if the null hypotheses were true.
D) all of the above are true.
E) none of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The probability beta (ß) is
A) the probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis.
B) the probability of retaining a correct null hypothesis.
C) equal to one minus the confidence level.
D) equal to the power of the test.
E) none of the above.
A) the probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis.
B) the probability of retaining a correct null hypothesis.
C) equal to one minus the confidence level.
D) equal to the power of the test.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The power of a statistical test can be increased by___sample size,____the level of significance or using___tests of significance.
A) decreasing; decreasing; one-tailed
B) increasing; decreasing; one-tailed
C) increasing; reducing; two-tailed
D) decreasing; reducing; two-tailed
E) increasing; increasing; one-tailed
A) decreasing; decreasing; one-tailed
B) increasing; decreasing; one-tailed
C) increasing; reducing; two-tailed
D) decreasing; reducing; two-tailed
E) increasing; increasing; one-tailed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The sample proportion is theoretically____distributed but when the sample size is large enough____may be used and the____may be appropriate.
A) normally; the binomial approximation; runs test
B) binomially; the normal approximation; chi-square
C) normally; the binomial approximation; t-test
D) cumulatively; the normal approximation; z-test
E) binomially; the normal approximation; z-test
A) normally; the binomial approximation; runs test
B) binomially; the normal approximation; chi-square
C) normally; the binomial approximation; t-test
D) cumulatively; the normal approximation; z-test
E) binomially; the normal approximation; z-test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is TRUE?
A) a error and b error are completely complementary in that a + b always equals one.
B) A Type I or error occurs when a false null hypothesis is not rejected.
C) A Type II or ß error occurs when a true null hypothesis is rejected.
D) When it is said that the difference between two numbers (e.g., two means) is significant at the 5 percent level, it means there is only a 5% chance that the difference is the wrong amount.
E) All of the above statements are false.
A) a error and b error are completely complementary in that a + b always equals one.
B) A Type I or error occurs when a false null hypothesis is not rejected.
C) A Type II or ß error occurs when a true null hypothesis is rejected.
D) When it is said that the difference between two numbers (e.g., two means) is significant at the 5 percent level, it means there is only a 5% chance that the difference is the wrong amount.
E) All of the above statements are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
You wish to test the hypothesis that female college students spend more on wearing apparel than male college students. Which of the following is INCORRECT?
A) The null and alternate hypotheses are:
Ho : mF mM
HA : mF > mM
B) If you concluded that female students spend more than male students when in fact there is no difference between the two groups, you would be committing a Type II error.
C) The probability of concluding that females spend more than male students when in fact this is the case, is called the power of the test.
D) If in testing the above hypothesis, we insist on reducing the probability of making the Type I error, ceteris paribus the probability of Type II error will increase.
E) If we conclude that females spend less than males when in fact that is the case, we have made a correct decision.
A) The null and alternate hypotheses are:
Ho : mF mM
HA : mF > mM
B) If you concluded that female students spend more than male students when in fact there is no difference between the two groups, you would be committing a Type II error.
C) The probability of concluding that females spend more than male students when in fact this is the case, is called the power of the test.
D) If in testing the above hypothesis, we insist on reducing the probability of making the Type I error, ceteris paribus the probability of Type II error will increase.
E) If we conclude that females spend less than males when in fact that is the case, we have made a correct decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a test of consumers preference of two popular air freshners, the following hypotheses were stated:
H0: Proportion Preferring Brand A = 0.50
Ha: Proportion Preferring Brand A 0.50
Of 200 people tested, 49% preferred Brand A. At =0.05, which of the following is correct?
A) The null hypothesis is accepted.
B) The null hypothesis is rejected.
C) Based on the evidence available, no support for the alternative hypothesis is found.
D) Based on the evidence available, the alternative hypothesis is supported.
E) More information is required to test these hypotheses.
H0: Proportion Preferring Brand A = 0.50
Ha: Proportion Preferring Brand A 0.50
Of 200 people tested, 49% preferred Brand A. At =0.05, which of the following is correct?
A) The null hypothesis is accepted.
B) The null hypothesis is rejected.
C) Based on the evidence available, no support for the alternative hypothesis is found.
D) Based on the evidence available, the alternative hypothesis is supported.
E) More information is required to test these hypotheses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the previous example, how large of a sample size would be required in order for the 49% preferring Brand A to be significantly different from the hypothesized proportion?
A) 200 people
B) 4,800 people
C) 9,600 people
D) 50,500 people.
E) cannot be determined with the information provided in the example.
A) 200 people
B) 4,800 people
C) 9,600 people
D) 50,500 people.
E) cannot be determined with the information provided in the example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is typically, but which should not be necessarily, of greater concern to a researcher with regard to a test of a Hypothesis?
A)the power of the test
B)the rejection of a true null hypothesis
C)the failure to reject a false null hypothesis
D)committing a Type II error
E)none of the above
A)the power of the test
B)the rejection of a true null hypothesis
C)the failure to reject a false null hypothesis
D)committing a Type II error
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A one-tailed test to test the null hypothesis Ho : m mC where C is some specific constant, could be carried out by comparing the calculated z value with the area under the curve (in the graph below) designated by___ . 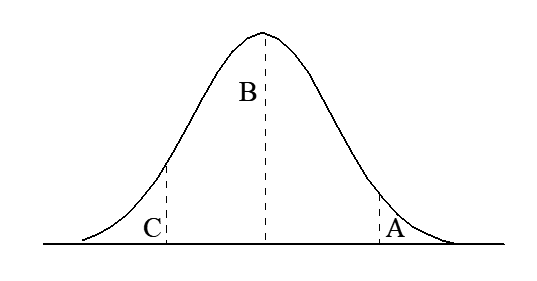
A) C
B) B
C) A
D) AB
E) None of the above

A) C
B) B
C) A
D) AB
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a two-tailed test to test the null hypothesis H0: = c the p value would be designated by
A) one minus the area between B and C
B) the area between A and C
C) the area to the left of C
D) twice the area to the left of C
E) none of the above
A) one minus the area between B and C
B) the area between A and C
C) the area to the left of C
D) twice the area to the left of C
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
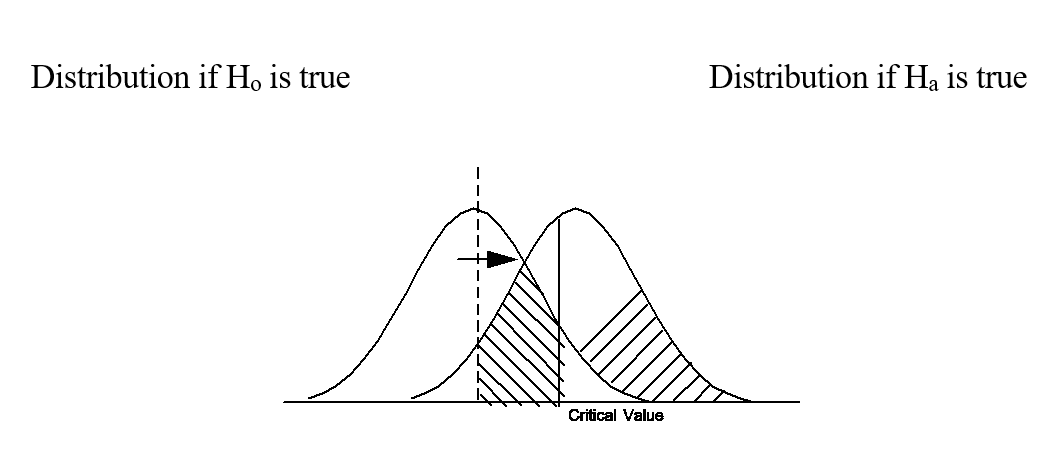
-In the above diagram which area depicts the probability of making a Type II error?
A) BC
B) BA
C) A
D) B
E) BD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24

-In the above diagram which area shows the probability of making a Type I error?
A) BC
B) BA
C) A
D) B
E) BD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



