Deck 8: Market and Government Failures
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/123
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Market and Government Failures
1
The price system will allocate resources efficiently except when
A) markets are perfectly competitive.
B) firms seek to maximize profit.
C) consumers pursue their own best interests.
D) market failures exist.
A) markets are perfectly competitive.
B) firms seek to maximize profit.
C) consumers pursue their own best interests.
D) market failures exist.
market failures exist.
2
When costs of producing a good spill over to third parties,
A) positive externalities result.
B) negative externalities result.
C) the price system will generate an efficient outcome on its own.
D) a government subsidy to the producer can correct the market failure.
A) positive externalities result.
B) negative externalities result.
C) the price system will generate an efficient outcome on its own.
D) a government subsidy to the producer can correct the market failure.
negative externalities result.
3
Which of the following is an example of a negative externality?
A) Having to pay a fine for a traffic violation
B) Pollution that results from consuming a good
C) Donating money to a charity
D) Improving city parks so that residents will be more inclined to use them
A) Having to pay a fine for a traffic violation
B) Pollution that results from consuming a good
C) Donating money to a charity
D) Improving city parks so that residents will be more inclined to use them
Pollution that results from consuming a good
4
Market failures arise when
A) people look out for their own best interests.
B) firms look out for their own best interests.
C) society seeks to operate at a point on the production possibilities curve.
D) there is a gap between the social and private costs of producing or consuming a good.
A) people look out for their own best interests.
B) firms look out for their own best interests.
C) society seeks to operate at a point on the production possibilities curve.
D) there is a gap between the social and private costs of producing or consuming a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Market failures arise when
A) society is not using its available resources in an optimal manner.
B) some consumers have different preferences than others.
C) the economy is operating at a point outside the production possibilities curve.
D) the private costs of an economic activity are the same as the social costs.
A) society is not using its available resources in an optimal manner.
B) some consumers have different preferences than others.
C) the economy is operating at a point outside the production possibilities curve.
D) the private costs of an economic activity are the same as the social costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When the city of London imposed a fee for the right to operate a vehicle in the designated congestion zone,
A) there was no change in driving habits.
B) the number of cars in the congestion zone increased.
C) the number of cars in the congestion zone decreased.
D) the average speed of cars in the congestion zone decreased.
A) there was no change in driving habits.
B) the number of cars in the congestion zone increased.
C) the number of cars in the congestion zone decreased.
D) the average speed of cars in the congestion zone decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Positive externalities create problems within a price system in the sense that
A) if consuming a good creates positive externalities, no one will want to consume it.
B) if producing a good creates positive externalities, no one will want to produce it.
C) if consuming or producing a good creates positive externalities, too many resources will be devoted to it.
D) if consuming or producing a good creates positive externalities, too few resources will be devoted to it.
A) if consuming a good creates positive externalities, no one will want to consume it.
B) if producing a good creates positive externalities, no one will want to produce it.
C) if consuming or producing a good creates positive externalities, too many resources will be devoted to it.
D) if consuming or producing a good creates positive externalities, too few resources will be devoted to it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is an incidence of market failure?
A) The firm producing the good is earning zero economic profit.
B) Consumers change their buying habits in response to a tax.
C) Firms change their production plans in response to a tax.
D) The price of a good exceeds the opportunity cost of producing it.
A) The firm producing the good is earning zero economic profit.
B) Consumers change their buying habits in response to a tax.
C) Firms change their production plans in response to a tax.
D) The price of a good exceeds the opportunity cost of producing it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A firm that produces chemical solvents creates some air pollution because of the emissions from its manufacturing facilities. A tax is imposed on the firm, equal to the amount of environmental damage caused by the emissions. What is the result?
A) The quantity of chemical solvents produced now will be the efficient amount.
B) Demand for the chemical solvents will increase.
C) Demand for the chemical solvents will decrease.
D) Consumers of the chemical solvents will be willing to pay the full amount of the tax, and so the quantity produced will be unaffected.
A) The quantity of chemical solvents produced now will be the efficient amount.
B) Demand for the chemical solvents will increase.
C) Demand for the chemical solvents will decrease.
D) Consumers of the chemical solvents will be willing to pay the full amount of the tax, and so the quantity produced will be unaffected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When does a subsidy to a business or a consumer result in a more efficient allocation of a resource?
A) When the good being produced or consumed is not scarce
B) When the good being produced or consumed generates a negative externality
C) When the good being produced or consumed generates a positive externality
D) When the equilibrium price of the good is one that consumers don't like
A) When the good being produced or consumed is not scarce
B) When the good being produced or consumed generates a negative externality
C) When the good being produced or consumed generates a positive externality
D) When the equilibrium price of the good is one that consumers don't like

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose that an instance of market failure arises when a monopoly develops, and the monopoly charges a price higher than marginal cost. Which one of the following is TRUE?
A) The profit earned by the monopolist is a social benefit that will outweigh the cost of the market failure.
B) The appreciation consumers have from consuming the good will outweigh the cost of the market failure.
C) The price consumers pay for the good will exceed the opportunity cost to society of producing it.
D) A tax on the monopolist will eliminate the market failure, because she will cut back on the quantity produced.
A) The profit earned by the monopolist is a social benefit that will outweigh the cost of the market failure.
B) The appreciation consumers have from consuming the good will outweigh the cost of the market failure.
C) The price consumers pay for the good will exceed the opportunity cost to society of producing it.
D) A tax on the monopolist will eliminate the market failure, because she will cut back on the quantity produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If a corporation were forced to absorb the external cost arising from production of a good, this would likely cause the supply curve for the good to
A) become horizontal.
B) become vertical.
C) shift to the right.
D) shift to the left.
A) become horizontal.
B) become vertical.
C) shift to the right.
D) shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a method that the government could use to promote a positive externality?
A) Subsidize consumption of the good.
B) Regulate firms producing the good to limit their quantity of production.
C) Tax profits of firms producing the good.
D) All of the above are correct
A) Subsidize consumption of the good.
B) Regulate firms producing the good to limit their quantity of production.
C) Tax profits of firms producing the good.
D) All of the above are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An example of a negative externality created in the market system would be
A) poverty.
B) unemployment.
C) inflation.
D) pollution.
A) poverty.
B) unemployment.
C) inflation.
D) pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which one of the following is FALSE?
A) Market failure arises when consumers are unhappy with the choices available to them.
B) Negative externalities arise when costs are imposed on third parties.
C) Positive externalities arise when benefits accrue to third parties.
D) Public goods typically are not provided by the private sector.
A) Market failure arises when consumers are unhappy with the choices available to them.
B) Negative externalities arise when costs are imposed on third parties.
C) Positive externalities arise when benefits accrue to third parties.
D) Public goods typically are not provided by the private sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following best represents the concept of a public good?
A) Measures taken to combat air pollution
B) Automobile insurance
C) Safety features on cars
D) Automobile repair services
A) Measures taken to combat air pollution
B) Automobile insurance
C) Safety features on cars
D) Automobile repair services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following best represents the concept of a public good?
A) Copying and printing services
B) Tax preparation services
C) Baby-sitting services
D) Police protection
A) Copying and printing services
B) Tax preparation services
C) Baby-sitting services
D) Police protection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Why are public goods provided by the government, rather than by the private sector?
A) Because they are large-scale projects that require the kind of financing only governments can generate through the issuance of bonds.
B) Because it would be difficult for a private sector firm to make a profit providing a public good, as the consumers who benefit would not have to pay for it.
C) Because no one really benefits from public goods.
D) Because private sector firms do not have the foresight to plan for public goods.
A) Because they are large-scale projects that require the kind of financing only governments can generate through the issuance of bonds.
B) Because it would be difficult for a private sector firm to make a profit providing a public good, as the consumers who benefit would not have to pay for it.
C) Because no one really benefits from public goods.
D) Because private sector firms do not have the foresight to plan for public goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which one of the following characterizes public goods?
A) They are produced by oligopolies.
B) They generate negative externalities.
C) They are profitably provided by the public sector.
D) One additional consumer can enjoy the good without diminishing the benefit enjoyed by others.
A) They are produced by oligopolies.
B) They generate negative externalities.
C) They are profitably provided by the public sector.
D) One additional consumer can enjoy the good without diminishing the benefit enjoyed by others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which policy would correct a positive externality?
A) Regulation of the industry to restrict production.
B) Subsidize production or consumption of the good.
C) Tax production or consumption of the good.
D) Allow the firms producing the good to operate as a cartel.
A) Regulation of the industry to restrict production.
B) Subsidize production or consumption of the good.
C) Tax production or consumption of the good.
D) Allow the firms producing the good to operate as a cartel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following characterizes public goods?
A) The principle of rival consumption
B) The law of increasing marginal utility
C) Producers of the good cannot collect payment from all who benefit.
D) They will be overproduced by the private sector.
A) The principle of rival consumption
B) The law of increasing marginal utility
C) Producers of the good cannot collect payment from all who benefit.
D) They will be overproduced by the private sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
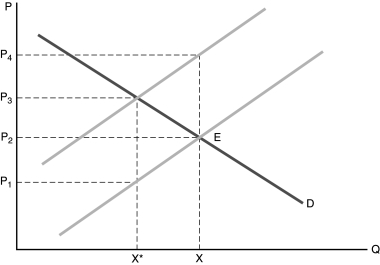 Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1-In Figure 8.1, market equilibrium occurs at X, but X* is the socially optimal quantity.
This indicates that
A) production of the good generates a negative externality.
B) production of the good generates a positive externality.
C) the good represented is a public good.
D) the industry producing the good is a monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
 Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1-In Figure 8.1, market equilibrium occurs at X, but X* is the socially optimal quantity. The government can achieve the optimal solution by
A) setting the price at P1.
B) establishing a tax equal to P3 - P1 per unit of the good sold.
C) establishing a tax equal to P3 - P2 per unit of the good sold.
D) setting the price at P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
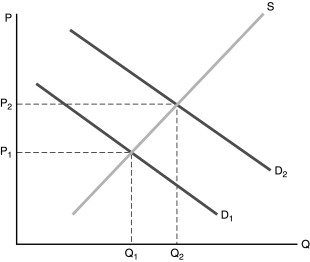 Figure 8.2
Figure 8.2-Refer to Figure 8.2. The market equilibrium is Q1. Point Q2 represents the optimal point of production. This indicates that
A) the good represented here is a public good.
B) regressive taxation of the product would result in the most efficient outcome.
C) consumption of the good generates a positive externality.
D) consumption of the good generates a negative externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
 Figure 8.2
Figure 8.2-Refer to Figure 8.2. The market equilibrium is Q1. Point Q2 represents the optimal point of production. To reach Q2,
A) production of the good could be taxed.
B) a subsidy could be given to consumers.
C) consumption of the good could be taxed.
D) the industry producing the good should operate as a cartel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Federal Trade Commission is charged with
A) protecting firms from aggressive consumers.
B) protecting firms from unscrupulous employees.
C) investigating unfair competitive practices.
D) determining which goods are public goods.
A) protecting firms from aggressive consumers.
B) protecting firms from unscrupulous employees.
C) investigating unfair competitive practices.
D) determining which goods are public goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An example of a public good is
A) software produced by Microsoft.
B) a car you rent.
C) the car you own.
D) a dam that provides flood control.
A) software produced by Microsoft.
B) a car you rent.
C) the car you own.
D) a dam that provides flood control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the spring I enjoy the fragrance coming from my neighbor's flowering trees. This is an
Example of
A) a negative externality.
B) a positive externality.
C) the need for antitrust legislation.
D) a noncompetitive market structure.
Example of
A) a negative externality.
B) a positive externality.
C) the need for antitrust legislation.
D) a noncompetitive market structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The difference between a private good and a public good is that
A) private goods are produced in competitive markets whereas public goods are produced in noncompetitive ones.
B) externalities are always created in the production process of private goods but not in the production of public goods.
C) the production of private goods requires a national market whereas public goods are produced locally.
D) the exclusion principle applies to private goods but not to public goods.
A) private goods are produced in competitive markets whereas public goods are produced in noncompetitive ones.
B) externalities are always created in the production process of private goods but not in the production of public goods.
C) the production of private goods requires a national market whereas public goods are produced locally.
D) the exclusion principle applies to private goods but not to public goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The percentage of additional income that must be paid in taxes is
A) the fair tax rate.
B) the equitable tax rate.
C) the average tax rate.
D) the marginal tax rate.
A) the fair tax rate.
B) the equitable tax rate.
C) the average tax rate.
D) the marginal tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The proportion of total income that must be paid in taxes is
A) the fair tax rate.
B) the equitable tax rate.
C) the average tax rate.
D) the marginal tax rate.
A) the fair tax rate.
B) the equitable tax rate.
C) the average tax rate.
D) the marginal tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Public goods generate market failure because
A) it is possible for consumers who benefit from the good to avoid paying for it.
B) they are produced by monopolies.
C) they generate negative externalities.
D) they generate positive externalities.
A) it is possible for consumers who benefit from the good to avoid paying for it.
B) they are produced by monopolies.
C) they generate negative externalities.
D) they generate positive externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A tax system is which the marginal tax rate falls as more income is earned is
A) progressive.
B) proportional.
C) regressive.
D) flat-rate.
A) progressive.
B) proportional.
C) regressive.
D) flat-rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A tax system is which the marginal tax rate increases as more income is earned is
A) progressive.
B) proportional.
C) regressive.
D) flat-rate.
A) progressive.
B) proportional.
C) regressive.
D) flat-rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A tax system in which everyone pays the same proportion of their income as tax is
A) progressive.
B) proportional.
C) regressive.
D) one of the above but we cannot tell without more information.
A) progressive.
B) proportional.
C) regressive.
D) one of the above but we cannot tell without more information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Why does the private sector typically fail to provide public goods?
A) Because public goods are consumed in the long run but must be paid for in the short run
B) Because production of public goods requires a capital investment beyond what a private firm can finance
C) Because private firms do not have a means of collecting payment from those who benefit from consumption of the good
D) Because the industries that produce public goods are not motivated by profit
A) Because public goods are consumed in the long run but must be paid for in the short run
B) Because production of public goods requires a capital investment beyond what a private firm can finance
C) Because private firms do not have a means of collecting payment from those who benefit from consumption of the good
D) Because the industries that produce public goods are not motivated by profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which one of the following is a public good?
A) House cleaning services
B) Landscaping services
C) National defense
D) A college education
A) House cleaning services
B) Landscaping services
C) National defense
D) A college education

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which one of the following is TRUE?
A) Public goods are a subset of private goods.
B) Private goods are subject to the principle of rival consumption.
C) Private goods are produced for a local market; public goods are produced for a national market.
D) Public goods are those that generate positive externalities.
A) Public goods are a subset of private goods.
B) Private goods are subject to the principle of rival consumption.
C) Private goods are produced for a local market; public goods are produced for a national market.
D) Public goods are those that generate positive externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which one of the following is TRUE?
A) Production of a public good involves no opportunity cost.
B) Production of a private good involves no opportunity cost.
C) Negative externalities can be corrected by taxing consumption or production of the good.
D) Positive externalities can be corrected by taxing consumption or production of the good.
A) Production of a public good involves no opportunity cost.
B) Production of a private good involves no opportunity cost.
C) Negative externalities can be corrected by taxing consumption or production of the good.
D) Positive externalities can be corrected by taxing consumption or production of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which one of the following is TRUE?
A) When the social benefits of consuming a good exceed the private benefit enjoyed by the consumer, positive externalities occur.
B) When the social benefits of consuming a good exceed the private benefit enjoyed by the consumer, negative externalities occur.
C) If the private sector fails to provide a public good, the government can correct the market failure by taxing firms that would be capable of providing the good.
D) Perfect competition results in market failure because it leads to an outcome in which the price of the good differs from its marginal cost.
A) When the social benefits of consuming a good exceed the private benefit enjoyed by the consumer, positive externalities occur.
B) When the social benefits of consuming a good exceed the private benefit enjoyed by the consumer, negative externalities occur.
C) If the private sector fails to provide a public good, the government can correct the market failure by taxing firms that would be capable of providing the good.
D) Perfect competition results in market failure because it leads to an outcome in which the price of the good differs from its marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An economic activity that results in too few or too many resources going to a specific economic activity is called
A) an inefficient market.
B) a market failure.
C) a laissez-faire market.
D) a unique market.
A) an inefficient market.
B) a market failure.
C) a laissez-faire market.
D) a unique market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose that a certain industry produces a product that results in negative external costs to society. This suggests that
A) resources are under-allocated to the industry.
B) the equilibrium market price of the product includes the external costs borne by society.
C) the costs borne by the firm are less than the true social costs of producing the good.
D) at the market price, quantity demanded is less than quantity supplied.
A) resources are under-allocated to the industry.
B) the equilibrium market price of the product includes the external costs borne by society.
C) the costs borne by the firm are less than the true social costs of producing the good.
D) at the market price, quantity demanded is less than quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If providing a service results in negative external costs, then
A) the market price is below the true opportunity cost of resources used to provide the service.
B) the market price is above the true opportunity cost of resources used to provide the service.
C) market forces will always correct the problem.
D) the market quantity is too low.
A) the market price is below the true opportunity cost of resources used to provide the service.
B) the market price is above the true opportunity cost of resources used to provide the service.
C) market forces will always correct the problem.
D) the market quantity is too low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is true of public goods?
A) They are produced by monopolies.
B) They are not subject to the principle of rival consumption.
C) They are produced without any opportunity cost.
D) They are produced in contestable markets.
A) They are produced by monopolies.
B) They are not subject to the principle of rival consumption.
C) They are produced without any opportunity cost.
D) They are produced in contestable markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Government can correct for negative externalities by
A) establishing a price ceiling for the good causing the externality.
B) allowing the market system to correct the problem.
C) taxing or regulating the firm at the source of the externality.
D) subsidizing consumption of the good causing the externality.
A) establishing a price ceiling for the good causing the externality.
B) allowing the market system to correct the problem.
C) taxing or regulating the firm at the source of the externality.
D) subsidizing consumption of the good causing the externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the production of a good results in external costs, an appropriate policy might be to
A) subsidize the production of the good.
B) tax the producer and thus shift the supply curve to the left.
C) tax the consumer's income and thus shift the demand curve to the left.
D) subsidize the consumer.
A) subsidize the production of the good.
B) tax the producer and thus shift the supply curve to the left.
C) tax the consumer's income and thus shift the demand curve to the left.
D) subsidize the consumer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A government subsidy is typically used
A) to correct a negative externality.
B) to provide a public good.
C) to compensate for the inconvenience imposed on firms subject to government regulation.
D) to encourage production or consumption of a good creating a positive externality.
A) to correct a negative externality.
B) to provide a public good.
C) to compensate for the inconvenience imposed on firms subject to government regulation.
D) to encourage production or consumption of a good creating a positive externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The theory of contestable markets asserts that
A) even industries with just a few firms can generate marginal-cost pricing if there are no barriers to the entry of new firms.
B) regulating monopolies and other noncompetitive markets is best done at the local level rather than at the national level.
C) market failure and government failure are the same thing.
D) market failure is best corrected by allowing the price system to operate without government interference.
A) even industries with just a few firms can generate marginal-cost pricing if there are no barriers to the entry of new firms.
B) regulating monopolies and other noncompetitive markets is best done at the local level rather than at the national level.
C) market failure and government failure are the same thing.
D) market failure is best corrected by allowing the price system to operate without government interference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The subsidization of medical care through insurance and government payments means that
A) health care is a public good.
B) health care providers will be monopolies.
C) health care will generate positive externalities.
D) the amount of resources going to health care will be above the socially optimal amount.
A) health care is a public good.
B) health care providers will be monopolies.
C) health care will generate positive externalities.
D) the amount of resources going to health care will be above the socially optimal amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Market _________ results when the outcome generated by supply and demand is not an optimal allocation of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Market failure occurs when the price consumers pay for a good differs from the _________ cost of producing it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
To the extent that there is market failure, the economy operates at a point _________ its production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A negative externality arises when production or consumption of a good imposes _________ on others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When production of a good generates negative externalities, the free market equilibrium quantity is _________ than the socially optimal amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When consumption of a good generates positive externalities, the free market equilibrium quantity is _________ than the socially optimal amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Subsidizing consumption of a good can lead to an efficient outcome when consumption generates _________ externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Taxing production of a good can lead to an efficient outcome when production generates _________ externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The intent of _________ regulation is to promote general social well-being across all industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The intent of _________ regulation is to affect prices, quantities, and profits in particular industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The primary piece of anti-monopoly legislation in the U.S. is the _________ Act.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Antitrust legislation seeks to address the instances of market failure arising from _________ power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Market failure arises in market structures that do not produce _________ _________ pricing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A _________ market is one in which there are no constraints on the entry or exit of new firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Rush hour congestion is a _________ externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Public goods are not subject to the principle of _________ consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Firms and individuals react to some government regulations with creative responses that create _________ effects, some of which are not in the best interests of society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
To enforce antitrust laws, the government must decide not only on the relevant product market, but also on the relevant _________ market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In a progressive taxation system, the marginal tax rates _________ as income increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In a _________ taxation system, an individual would pay a smaller proportion of his income in taxes as his income rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If production of a good generates negative externalities, how does the equilibrium quantity in a free market differ from the optimal quantity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If production of a good generates positive externalities, how does the equilibrium quantity in a free market differ from the optimal quantity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Why do economists characterize as market failure those instances where the price of a good differs from the true marginal cost of producing it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Why does monopoly result in market failure whereas perfect competition does not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If a tax system is designed so that the marginal and average tax rates are always equal, would that tax system be proportional, progressive, or regressive?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a tax system is designed so that the marginal tax rate is always greater than the average tax rate, would that tax system be proportional, progressive, or regressive?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If a tax system is designed so that the marginal tax rate is always less than the average tax rate, would that tax system be proportional, progressive, or regressive?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Why does a price system fail to provide public goods?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What conditions give rise to a contestable market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In what way does a subsidy to consumers correct a positive externality arising from consumption of a good?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In what way does a tax on producers correct a negative externality arising from production of a good?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



