Deck 8: Groups and Teams
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/46
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Groups and Teams
1
A group is simply a collection of people doing the same thing.
False
2
Informal groups often have the potential to speed up the work flow.
True
3
If a company sponsored a local junior swimming team, that team is an example of a formal group since it is company sanctioned.
False
4
Disruptive behaviours in groups include social loafing and synergy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Groups can help organizations to foster creativity and make better decisions than individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Storming stage is the first stage of group formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Organizational culture and structure can affect group effectiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Emergent behaviours are what group members do in addition to, or in place of, what is formally asked of them by the organization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Teamwork happens naturally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Team building is a collaborative process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Norms are rules or standards about the behaviour that group members are expected to display.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Role ambiguity is the expectation that one has of others in the group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A quality circle is a small group of people who meet periodically to discuss well-defined tasks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Belbin argues that the most effective teams are heterogeneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
All self-managed teams require technical and interpersonal skills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A virtual team is one whose members work interdependently towards the achievement of a common goal across space and time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Self-managing teams operate with more layers of management than do traditional organizational structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Each of the following is a type of formal work group EXCEPT a(n):
A) project team
B) task force
C) command group
D) interest group
A) project team
B) task force
C) command group
D) interest group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The creation of a whole that is greater than the sum of its parts is known as:
A) status congruence
B) synergy
C) the Ringelmann effect
D) group effectiveness
A) status congruence
B) synergy
C) the Ringelmann effect
D) group effectiveness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When an individual contribution is less noticeable, there is greater risk for:
A) status incongruence
B) synergy
C) the Ringelmann effect/social loafing
D) group ineffectiveness
A) status incongruence
B) synergy
C) the Ringelmann effect/social loafing
D) group ineffectiveness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An effective group is one that:
A) shares a common sense of group purpose
B) simply achieves high levels of task performance
C) simply achieves high levels of human resource maintenance
D) achieves high levels of both task performance and human resource maintenance
A) shares a common sense of group purpose
B) simply achieves high levels of task performance
C) simply achieves high levels of human resource maintenance
D) achieves high levels of both task performance and human resource maintenance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A work group:
A) transforms resource inputs into resource outputs
B) provides members with the opportunity to become more broadly included in workplace affairs
C) fosters sub-goal optimisation
D) achieves high levels of task performance and human resource maintenance
A) transforms resource inputs into resource outputs
B) provides members with the opportunity to become more broadly included in workplace affairs
C) fosters sub-goal optimisation
D) achieves high levels of task performance and human resource maintenance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Each of the following is one of the four major categories of group input factors EXCEPT:
A) nature of the task
B) membership characteristics
C) group size
D) task performance
A) nature of the task
B) membership characteristics
C) group size
D) task performance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Groups whose members have similar backgrounds, interests, values and attitudes are called __________ groups.
A) homogeneous
B) heterogeneous
C) informal
D) interest
A) homogeneous
B) heterogeneous
C) informal
D) interest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Required behaviours are the:
A) contributions formally requested by the organization for continued employment
B) various tasks group members perform to reach group goals
C) activities that support group social and interpersonal relationships
D) internal operations of a group
A) contributions formally requested by the organization for continued employment
B) various tasks group members perform to reach group goals
C) activities that support group social and interpersonal relationships
D) internal operations of a group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Maintaining group cohesion by 'coming half-way' or admitting an error is an example of:
A) gatekeeping
B) compromising
C) following
D) setting standards
A) gatekeeping
B) compromising
C) following
D) setting standards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Collections of two or more people who interact with one another for a common purpose are which of the following?
A) teams
B) quality circles
C) groups
D) virtual teams
A) teams
B) quality circles
C) groups
D) virtual teams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Effective teams:
A) operate with scheduled dates for disbanding
B) are temporary
C) have a long-term working relationship
D) simply make recommendations
A) operate with scheduled dates for disbanding
B) are temporary
C) have a long-term working relationship
D) simply make recommendations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Each of the following is a step in the team-building process EXCEPT:
A) evaluation of results
B) action planning
C) data gathering and analysis
D) promoting individual competition
A) evaluation of results
B) action planning
C) data gathering and analysis
D) promoting individual competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements is NOT true of the continual improvement approach to team building?
A) Group members frequently take responsibility for regularly engaging in the team-building process
B) It is typically held with the assistance of a consultant
C) Members occasionally hold self-managed retreats
D) The commitment of team members is to monitor group development and accomplishments continuously
A) Group members frequently take responsibility for regularly engaging in the team-building process
B) It is typically held with the assistance of a consultant
C) Members occasionally hold self-managed retreats
D) The commitment of team members is to monitor group development and accomplishments continuously

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A set of expectations for the behaviour of a person holding a particular office or position is known as a:
A) role
B) job description
C) psychological contract
D) norm
A) role
B) job description
C) psychological contract
D) norm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The degree to which members are attracted to, and motivated to remain a part of, a team is known as:
A) the basic rule of group dynamics
B) role negotiation
C) role expectations
D) cohesiveness
A) the basic rule of group dynamics
B) role negotiation
C) role expectations
D) cohesiveness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Rewarding individual results tends to:
A) increase cohesiveness
B) decrease cohesiveness
C) increase performance norms
D) decrease performance norms
A) increase cohesiveness
B) decrease cohesiveness
C) increase performance norms
D) decrease performance norms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Self-managing teams are:
A) small groups of people empowered to manage themselves
B) informal teams empowered to manage others
C) the same as a task force
D) exactly the same as autonomous work teams
A) small groups of people empowered to manage themselves
B) informal teams empowered to manage others
C) the same as a task force
D) exactly the same as autonomous work teams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Reports that reflect the activities of Hi-Spec's design team are due on the fifth working day of every month. As group leader, it is Te Huia's responsibility to make sure the report is completed and handed to his boss, though the whole group contributes. Preparing this report is a(n):
A) maintenance activity
B) emergent behaviour
C) required behaviour
D) example of work-flow interdependency
A) maintenance activity
B) emergent behaviour
C) required behaviour
D) example of work-flow interdependency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
You are a member of a quality circle that is able to deal effectively with complex tasks. Disagreements among members are handled creatively. It is likely that this quality circle is in the __________ stage of group development.
A) forming
B) adjourning
C) storming
D) performing
A) forming
B) adjourning
C) storming
D) performing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Sam is a member of a task force focusing on workplace safety. The leader and his colleagues both have different expectations from Sam. He is experiencing:
A) role conflict
B) role ambiguity
C) role negotiation
D) role shifting
A) role conflict
B) role ambiguity
C) role negotiation
D) role shifting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Explain the difference between formal and informal groups, and give an example of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Define a team and explain why it is different from the concept of a group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Explain the difference between role conflict and role ambiguity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Define cohesiveness and explain its relationship to team performance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Discuss the functions of formal and informal groups. How does each contribute to the organization?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Explain the open system concept as it pertains to group effectiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Compare and contrast employee involvement teams, quality circles and self-managing work teams. What effects might each have on the organization?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Discuss the role of the leader in effective team management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Visual Diagram Question
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-In relation to the following diagram:
a) Explain team cohesiveness.
b) Explain why you might want to increase or decrease team cohesiveness.
c) Will homogeneity always increase performance?
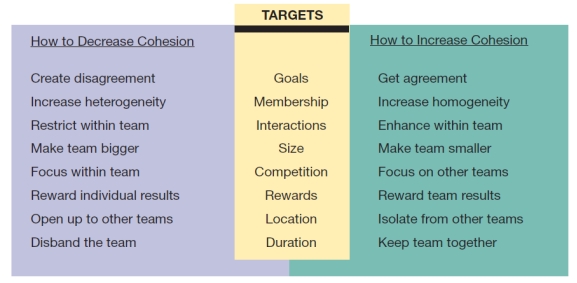
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-In relation to the following diagram:
a) Explain team cohesiveness.
b) Explain why you might want to increase or decrease team cohesiveness.
c) Will homogeneity always increase performance?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



