Deck 6: Organizational Structure and Design
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/62
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Organizational Structure and Design
1
Output goals define the types of business an organization is in.
True
2
System goals are goals concerned with how things run in the organization.
False
3
Rules that become ends in themselves are among the dysfunctions often associated with bureaucracy.
True
4
Organigraphs are exactly the same as organizational charts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The number of immediate subordinates that a manager supervises is referred to as the span of control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Line units and personnel in an organization provide specialised expertise and services to staff units and personnel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Staff personnel in organizations are groups that assist the line units by performing specialised services for the organization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Human resource managers in a bed linen production company would be line personnel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
One of the advantages of the functional structure is that it provides an excellent training ground for new managers, who must translate their academic training into organizational action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
One of the advantages of a matrix structure is that it helps provide a blending of technical and market emphasis in organizations operating in exceedingly complex environments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Mechanistic organizations stress rules, policies and procedures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Organic organizations tend to favour vertical specialisation and control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A divisionalised organization consolidates all divisions within an organization under a single, unitary design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Strategic alliances are announced cooperative arrangements or joint ventures between two independent companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Virtual organizations have certain aspects in common, like an actual physical space and boundary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Peripheral workers for the flexible ring and are thereby more easily outsourced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The process of choosing and implementing structural configuration is called:
A) planning
B) control
C) organizational design
D) staffing
A) planning
B) control
C) organizational design
D) staffing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The formal structures of organizations may be shown in a(n):
A) organization chart
B) horizontal diagram
C) matrix depiction
D) labour assignment chart
A) organization chart
B) horizontal diagram
C) matrix depiction
D) labour assignment chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The combination of resources knowledge and techniques that creates a product or service output is called:
A) the environment
B) technology
C) formalisation
D) organizational design
A) the environment
B) technology
C) formalisation
D) organizational design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The set of cultural, economic, educational and legal-political forces in a given geographical area is called the __________ of an organization.
A) environmental complexity
B) environmental interdependence
C) specific environment
D) general environment
A) environmental complexity
B) environmental interdependence
C) specific environment
D) general environment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In order to increase survival potential, organizations create:
A) process controls
B) matrix specialisations
C) systems goals
D) line and staff units
A) process controls
B) matrix specialisations
C) systems goals
D) line and staff units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Rules and procedures:
A) are written statements of organizational purpose
B) are flexible enough to accommodate unique conditions
C) allow for individual discretion without direct clearance from a higher-level authority
D) describe in detail how a task is to be performed
A) are written statements of organizational purpose
B) are flexible enough to accommodate unique conditions
C) allow for individual discretion without direct clearance from a higher-level authority
D) describe in detail how a task is to be performed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Control involves all of the following EXCEPT:
A) measuring results
B) taking corrective action
C) comparing results with goals
D) selecting manpower
A) measuring results
B) taking corrective action
C) comparing results with goals
D) selecting manpower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Common signs of too much control include all of the following EXCEPT:
A) too much confusing of documentation with action
B) too much focus on one goal to the exclusion of others
C) too many realistic expectations
D) too much rigidity and inflexibility
A) too much confusing of documentation with action
B) too much focus on one goal to the exclusion of others
C) too many realistic expectations
D) too much rigidity and inflexibility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The degree to which authority to make decisions is given to lower levels in an organization's hierarchy is referred to as:
A) bureaucracy
B) decentralisation
C) line units
D) empowerment
A) bureaucracy
B) decentralisation
C) line units
D) empowerment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A manager with a wide span of control is most likely to have:
A) many subordinates and high levels of authority
B) few subordinates and low levels of authority
C) many subordinates
D) few subordinates
A) many subordinates and high levels of authority
B) few subordinates and low levels of authority
C) many subordinates
D) few subordinates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Staff personnel:
A) directly link clients and/or suppliers to the organization
B) conduct the major business that directly affects the organization
C) work independently of line personnel
D) include such departments as public relations and accounting in a manufacturing firm
A) directly link clients and/or suppliers to the organization
B) conduct the major business that directly affects the organization
C) work independently of line personnel
D) include such departments as public relations and accounting in a manufacturing firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When action is needed quickly in a crisis situation, which design is typically most appropriate?
A) conglomerate
B) free form
C) organic
D) mechanistic
A) conglomerate
B) free form
C) organic
D) mechanistic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following characterises a mechanistic organization?
A) many rules and procedures
B) ambiguous division of labour
C) informal coordination and control
D) emphasis on coordination
A) many rules and procedures
B) ambiguous division of labour
C) informal coordination and control
D) emphasis on coordination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Departmentalisation for division does which of the following?
A) groups individuals and resources by product service, client, territory or legal entity
B) groups individuals and resources by skill knowledge and action
C) groups individuals and resources by the goals of an organization
D) provides written documentation of work rules, policies and procedures
A) groups individuals and resources by product service, client, territory or legal entity
B) groups individuals and resources by skill knowledge and action
C) groups individuals and resources by the goals of an organization
D) provides written documentation of work rules, policies and procedures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Grouping resources into departments by skill, knowledge and action is known as a __________ pattern.
A) functional
B) divisional
C) vertical
D) matrix
A) functional
B) divisional
C) vertical
D) matrix

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following does your text list as a disadvantage of functional structure?
A) Difficult to retrain new managers
B) Often yields confusing task assignments
C) Too much time and effort spent by management
D) Too little emphasis on technical affairs
A) Difficult to retrain new managers
B) Often yields confusing task assignments
C) Too much time and effort spent by management
D) Too little emphasis on technical affairs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The aerospace solution to the problem of a management structure placing emphasis both on technical development and on product development is called:
A) functional pattern of departmentalisation
B) departmentalisation by function
C) matrix organization
D) coordination organization
A) functional pattern of departmentalisation
B) departmentalisation by function
C) matrix organization
D) coordination organization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The unity of command principle is not achieved in which form of departmentalisation?
A) functional
B) divisionalisation by product
C) divisionalisation by customer
D) matrix
A) functional
B) divisionalisation by product
C) divisionalisation by customer
D) matrix

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Bureaucracy is the theory proposed by:
A) Weber
B) Thompson
C) Burns/Stalker
D) Woodward
A) Weber
B) Thompson
C) Burns/Stalker
D) Woodward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Possible problems of bureaucracy include which of the following?
A) Inflexibility
B) Underspecialisation
C) Rules specifying minimum requirements
D) Dominance by the leaders
A) Inflexibility
B) Underspecialisation
C) Rules specifying minimum requirements
D) Dominance by the leaders

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which design is appropriate for a huge corporation that produces many different products and services in many different industries?
A) conglomerate
B) quasi-autonomous
C) simple structure
D) machine bureaucracy
A) conglomerate
B) quasi-autonomous
C) simple structure
D) machine bureaucracy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The vertical emphasis of machine bureaucracy facilitates:
A) job satisfaction
B) control
C) higher profits
D) coordination across divisions
A) job satisfaction
B) control
C) higher profits
D) coordination across divisions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Mechanistic design is characterised by:
A) high job satisfaction
B) effective use of human resources
C) creative solutions to problems
D) inflexibility
A) high job satisfaction
B) effective use of human resources
C) creative solutions to problems
D) inflexibility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In which design are managers most likely to run their own businesses and compete against one another for resources?
A) adhocracy
B) simple
C) professional bureaucracy
D) divisionalised
A) adhocracy
B) simple
C) professional bureaucracy
D) divisionalised

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A greater need for flexibility in production has led to a(n) ________________ organization structure?
A) mechanistic
B) organic
C) core-ring
D) divisional
A) mechanistic
B) organic
C) core-ring
D) divisional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Harold Corporation is a firm dealing with food products, electronics and motor vehicles. This firm would be called:
A) a conglomerate
B) a strategic alliance
C) divisionalised
D) a bureaucracy
A) a conglomerate
B) a strategic alliance
C) divisionalised
D) a bureaucracy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Joe owns a gardening centre and employs six staff. This is an example of:
A) a matrix structure
B) a divisionalised structure
C) a simple structure
D) a functional structure
A) a matrix structure
B) a divisionalised structure
C) a simple structure
D) a functional structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Mel reports to two managers. This is an example of:
A) departmentalisation by function
B) departmentalisation by matrix
C) division of labour
D) span of control
A) departmentalisation by function
B) departmentalisation by matrix
C) division of labour
D) span of control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Sionne manages the production department in a company that makes golf balls. He has 44 subordinates. Which three attributes of organizations best describe this?
A) Functional departmentalisation, line personnel and narrow span of control
B) Product divisionalisation, line personnel and wide span of control
C) Functional departmentalisation, line personnel and wide span of control
D) Product divisionalisation, line personnel and wide span of control.
A) Functional departmentalisation, line personnel and narrow span of control
B) Product divisionalisation, line personnel and wide span of control
C) Functional departmentalisation, line personnel and wide span of control
D) Product divisionalisation, line personnel and wide span of control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
General Motors divided the company's operations into separate businesses for each model of automobile. This demonstrates:
A) a conglomerate
B) divisionalised design
C) a bureaucracy
D) a core-ring organization
A) a conglomerate
B) divisionalised design
C) a bureaucracy
D) a core-ring organization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Auditing the books of a company involves adherence to strict rules and policies. There is no room for flexibility in decision-making. This activity is best suited to which of the following structures?
A) matrix
B) divisional
C) core-ring
D) bureaucracy
A) matrix
B) divisional
C) core-ring
D) bureaucracy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
John's consultancy firm specialises in providing leadership and coaching for local businesses. This activity is best suited to which of the following structures?
A) bureaucracy
B) adhocracy
C) meritocracy
D) conglomerate
A) bureaucracy
B) adhocracy
C) meritocracy
D) conglomerate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The division of labour by grouping production staff and material resources deals with:
A) specialisation
B) co-ordination
C) divisionalisation
D) vertical specialisation
A) specialisation
B) co-ordination
C) divisionalisation
D) vertical specialisation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
David is team leader of a large production facility. His team consists of 46 staff. This is an example of:
A) a narrow span of control
B) a wide span of control
C) work specialisation
D) a vertical span of control
A) a narrow span of control
B) a wide span of control
C) work specialisation
D) a vertical span of control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Sue is the General Manager of Heap Manufacturing. She calls a meeting with Henry (head of manufacturing), Joe (manager of scheduling and planning), and Wendy (computer operations) to discuss rostering. The position titles suggest that:
A) Sue is line
B) Henry is staff
C) Joe is line
D) Wendy is line
A) Sue is line
B) Henry is staff
C) Joe is line
D) Wendy is line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Henry is second line manager to Fred, who is the subordinate of Jane. Who is the lowest ranking person in this organizational bureaucracy?
A) Fred
B) Henry
C) Jane
D) No one, they are all equal ranking
A) Fred
B) Henry
C) Jane
D) No one, they are all equal ranking

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A Strategic Business Unit (SBU) would direct responsibility for its own:
A) Financial budgets
B) Trade Union Policy
C) Branding
D) Corporate Communication Strategy
A) Financial budgets
B) Trade Union Policy
C) Branding
D) Corporate Communication Strategy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Explain the difference between output goals and system goals.
Output goals are the goals that define the organization's type of business, e.g. to increase market share by 10% per annum.
Output goals are the goals that define the organization's type of business, e.g. to increase market share by 10% per annum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Define and illustrate the concept of an organizational chart and compare it with the idea of an organigraph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What is meant by the concept of decentralisation in an organization's structure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Explain unity of command and span of control and how they relate to each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Compare and contrast the major advantages and disadvantages of functional departmentalisation with the major advantages and disadvantages of divisional departmentalisation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Bureaucracies are often criticised; however, the concept is not a single or simple one. Describe the term, the different forms that bureaucracies might take, and the potential advantages and disadvantages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Contemporary organizations are often required to be flexible. Discuss new forms of organizational design that enable more flexible response to environmental and other influences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Visual Diagram Questions
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-The following diagram shows a matrix form of horizontal specialisation.
a) Explain in words (and using marks on the diagram if you wish) the functional and project areas of the structure.
b) Discuss the behavioural implications of such a structure for an individual.
c) Discuss the general advantages and disadvantages of such a structure.
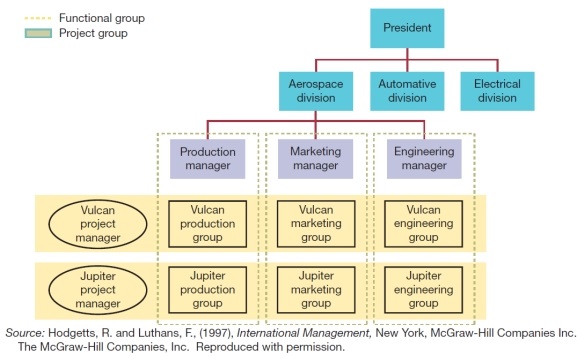
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-The following diagram shows a matrix form of horizontal specialisation.
a) Explain in words (and using marks on the diagram if you wish) the functional and project areas of the structure.
b) Discuss the behavioural implications of such a structure for an individual.
c) Discuss the general advantages and disadvantages of such a structure.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Visual Diagram Questions
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-Using the diagram below:
a) Compare the three designs.
b) Describe the staffing in each.
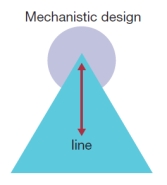
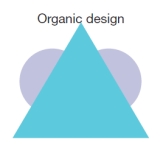
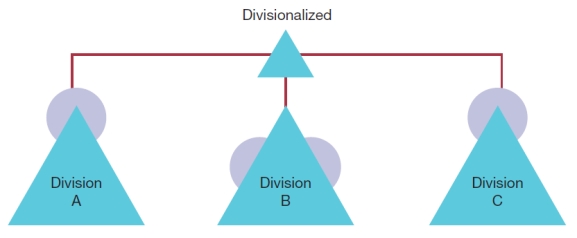
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-Using the diagram below:
a) Compare the three designs.
b) Describe the staffing in each.




Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



