Deck 4: Engagement of Employees in the Workplace
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Engagement of Employees in the Workplace
1
The esteem needs are the highest level of needs in Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
False
2
Hygiene factors are dissatisfiers that are associated with aspects of a person's personal life.
False
3
Base salary is a motivator in Herzberg's theory.
False
4
Motivators are satisfiers that are associated with what people do in their work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The content motivation theories provide an understanding of the thought or cognitive processes that take place within the minds of people and that influence their behaviour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The work preferences of individuals high in need for achievement are likely to include individual responsibility and feedback on performance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
McClelland argues that the needs in his approach can be acquired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to equity theory, individuals compare their rewards and inputs at work to the rewards and inputs of others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Managers should recognise that an equity comparison will likely be made by their subordinates whenever especially visible rewards, such as pay, are being allocated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The general thrust of expectancy theory is that motivation is a product of Expectancy * Instrumentality * Valence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Extrinsic rewards are work outcomes that are received by the individual directly as a result of task performance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Empowerment is the process of handing over reward-granting power to low-level employees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Writers like Schaufeli argue that burnout constitutes the negative pole of employee well-being.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Nohria et al argue that there are 3 basic drives of motivation which determine employees behaviour at work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The organizational levers of motivation include the reward system, culture, job design and performance management and resource allocation processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Employee engagement can be defined as an individual's cognitive, emotional and behavioural state directed towards individual's outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An individual's willingness to perform is directly related to their:
A) needs, expectations, rewards
B) needs, expectations, values
C) expectations, values, effort
D) expectations, competencies, needs
A) needs, expectations, rewards
B) needs, expectations, values
C) expectations, values, effort
D) expectations, competencies, needs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Content motivation theories are represented by:
A) Maslow, Alderfer, Herzberg and McClelland
B) Maslow, Vroom, Alderfer and Herzberg
C) Alderfer, McClelland, Vroom and Adams
D) Alderfer, Maslow, Herzberg and Adams
A) Maslow, Alderfer, Herzberg and McClelland
B) Maslow, Vroom, Alderfer and Herzberg
C) Alderfer, McClelland, Vroom and Adams
D) Alderfer, Maslow, Herzberg and Adams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The need level immediately preceding self-actualisation in Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory is:
A) social
B) safety
C) esteem
D) security
A) social
B) safety
C) esteem
D) security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Maslow's theory:
A) applies equally to all people
B) is a content motivation theory
C) is more a theory of leadership than of motivation
D) is a process motivation theory
A) applies equally to all people
B) is a content motivation theory
C) is more a theory of leadership than of motivation
D) is a process motivation theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The need for love or affection or the sense of belongingness in one's relationships is known as:
A) self-actualisation
B) social
C) safety
D) security
A) self-actualisation
B) social
C) safety
D) security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
One of the needs in Alderfer's theory is called:
A) physiological
B) growth
C) self-actualisation
D) security
A) physiological
B) growth
C) self-actualisation
D) security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A theory of acquired needs was developed by:
A) Maslow
B) Alderfer
C) McClelland
D) Vroom
A) Maslow
B) Alderfer
C) McClelland
D) Vroom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Alderfer's modification of Maslow's theory puts the need levels into how many different categories?
A) Three
B) Four
C) Five
D) Six
A) Three
B) Four
C) Five
D) Six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The three acquired needs in McClelland's theory are:
A) achievement, affiliation, self-actualisation
B) achievement, affiliation, power
C) achievement, safety, power
D) achievement, affiliation, security
A) achievement, affiliation, self-actualisation
B) achievement, affiliation, power
C) achievement, safety, power
D) achievement, affiliation, security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The three needs in Alderfer's modification of Maslow's theory are existence, relatedness and:
A) growth
B) achievement
C) power
D) affiliation
A) growth
B) achievement
C) power
D) affiliation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Herzberg suggested that performance can be improved by:
A) emphasising instrumentality
B) stressing higher-order needs
C) adding satisfiers to people's jobs
D) adding hygienes to people's jobs
A) emphasising instrumentality
B) stressing higher-order needs
C) adding satisfiers to people's jobs
D) adding hygienes to people's jobs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
McClelland's need for achievement is characterised by a desire to:
A) solve problems
B) influence others' behaviour
C) be responsible for other people
D) emphasise higher-order needs
A) solve problems
B) influence others' behaviour
C) be responsible for other people
D) emphasise higher-order needs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In Alderfer's theory:
A) only one need can be activated at one time
B) more than one need can be activated at one time
C) activated needs become rewards
D) content and process theories are combined
A) only one need can be activated at one time
B) more than one need can be activated at one time
C) activated needs become rewards
D) content and process theories are combined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Herzberg's theory does not include:
A) satisfiers
B) hygiene factors
C) equity
D) job content factors
A) satisfiers
B) hygiene factors
C) equity
D) job content factors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Process theories:
A) are thought to be static and descriptive
B) lend insight into people's needs
C) are weakly linked with work efforts.
D) provide an understanding of the thoughts that influence behaviour
A) are thought to be static and descriptive
B) lend insight into people's needs
C) are weakly linked with work efforts.
D) provide an understanding of the thoughts that influence behaviour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Victor Vroom:
A) proposed a theory of hierarchy of needs
B) developed a well-known version of expectancy theory
C) refined Maslow's theory
D) refined equity theory
A) proposed a theory of hierarchy of needs
B) developed a well-known version of expectancy theory
C) refined Maslow's theory
D) refined equity theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The key terms in expectancy theory are:
A) expectancy, instrumentality, valence
B) instrumentality, equity, tension
C) valence, desirability, instrumentality
D) tension, valence, expectancy
A) expectancy, instrumentality, valence
B) instrumentality, equity, tension
C) valence, desirability, instrumentality
D) tension, valence, expectancy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The meaning of pay from an equity theory perspective is:
A) pay is an object of social comparison
B) pay is only one of many work valued rewards
C) pay is one of the extrinsic rewards that a manager may use
D) pay is one of the intrinsic rewards that a manager may use
A) pay is an object of social comparison
B) pay is only one of many work valued rewards
C) pay is one of the extrinsic rewards that a manager may use
D) pay is one of the intrinsic rewards that a manager may use

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Herzberg's work:
A) has been fully approved by OB experts
B) led Maslow to develop his own theory
C) is a form of process motivation theory
D) is quite controversial
A) has been fully approved by OB experts
B) led Maslow to develop his own theory
C) is a form of process motivation theory
D) is quite controversial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Equity theory and expectancy theory:
A) are both content theories
B) are both extensions of Maslow
C) each involve need satisfaction
D) are both process theories
A) are both content theories
B) are both extensions of Maslow
C) each involve need satisfaction
D) are both process theories

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Extrinsic rewards:
A) tend to be large in magnitude
B) are similar to needs
C) are expensive to administer
D) are given to the individual by someone else
A) tend to be large in magnitude
B) are similar to needs
C) are expensive to administer
D) are given to the individual by someone else

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The integrated motivational model:
A) combines content and context motivation theories
B) combines content and process motivation theories
C) shows how rewards can lead to individual and group performance
D) shows how contingencies can lead to individual and group performance
A) combines content and context motivation theories
B) combines content and process motivation theories
C) shows how rewards can lead to individual and group performance
D) shows how contingencies can lead to individual and group performance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Empowerment is:
A) a means of achieving an upside-down pyramid organization
B) a means of giving middle managers more power to do their jobs properly
C) a means for managers to give employees greater responsibility to
Balance personal and organizational goals
D) an essential requirement in new workplaces
A) a means of achieving an upside-down pyramid organization
B) a means of giving middle managers more power to do their jobs properly
C) a means for managers to give employees greater responsibility to
Balance personal and organizational goals
D) an essential requirement in new workplaces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is NOT a strategy or technique for empowering employees?
A) provide emotional support
B) encourage job mastery
C) provide appropriate feedback
D) surrender all power
A) provide emotional support
B) encourage job mastery
C) provide appropriate feedback
D) surrender all power

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
To work well, merit pay plans should:
A) be dependent on cost-of-living adjustments
B) be based on group incentives
C) make pay contingent on satisfaction
D) be based on accurate measure of individual performance
A) be dependent on cost-of-living adjustments
B) be based on group incentives
C) make pay contingent on satisfaction
D) be based on accurate measure of individual performance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
All of the following are examples of extrinsic work rewards EXCEPT:
A) use of a company car
B) stock options
C) piped-in music
D) sense of personal accomplishment from a job well done
A) use of a company car
B) stock options
C) piped-in music
D) sense of personal accomplishment from a job well done

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In a small manufacturing firm, a supervisor is concerned about motivating her subordinates. One of these, David, is a person whose instrumentality is low. David:
A) places little value on receiving merit pay raises
B) is not confident that performance will lead to reward
C) feels he/she cannot achieve the necessary performance level
D) is highly motivated
A) places little value on receiving merit pay raises
B) is not confident that performance will lead to reward
C) feels he/she cannot achieve the necessary performance level
D) is highly motivated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following situations is best explained by equity theory?
A) Liz is happy with her job because it is challenging.
B) Karen gets a good salary considering her needs.
C) Beth gets more money than Liz even though their jobs are essentially the same and both work equally hard.
D) Cindy likes the people she works with.
A) Liz is happy with her job because it is challenging.
B) Karen gets a good salary considering her needs.
C) Beth gets more money than Liz even though their jobs are essentially the same and both work equally hard.
D) Cindy likes the people she works with.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Wendy thinks that it is an excellent idea to have music playing in the background while her team carry out their duties. What kind of factor is being represented by Herzberg's theory?
A) a satisfier
B) a motivator
C) a hygiene factor
D) a job content factor
A) a satisfier
B) a motivator
C) a hygiene factor
D) a job content factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Wendy's team-members each receive a high base salary. Herzberg would consider this to be a:
A) motivator
B) hygiene factor
C) job content factor
D) something to raise satisfaction
A) motivator
B) hygiene factor
C) job content factor
D) something to raise satisfaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If you do not study for an examination because you do not think it will help your examination grade, that illustrates:
A) valence
B) instrumentality
C) expectancy
D) effort
A) valence
B) instrumentality
C) expectancy
D) effort

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Negative inequity is when an individual feels that he/she received a reward which is:
A) more than that of other people
B) equal to that of other people
C) not sufficient for his/her needs
D) less than others even though he/she worked as hard as others did
A) more than that of other people
B) equal to that of other people
C) not sufficient for his/her needs
D) less than others even though he/she worked as hard as others did

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Anne's team has just been given a contract to design a new series of travel brochures. Anne believes that she can influence her team's expectancies by:
A) selecting people with proper abilities
B) selecting people of the right gender
C) selecting people with high growth needs
D) offering group incentives
A) selecting people with proper abilities
B) selecting people of the right gender
C) selecting people with high growth needs
D) offering group incentives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
John's autocratic style upsets his subordinates, who often appear withdrawn and stressed. According to Maslow, what level of need does this demonstrate?
A) safety
B) self-actualisation
C) social
D) physiological
A) safety
B) self-actualisation
C) social
D) physiological

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Mick reports to Sarah, but he is always finding ways to ingratiate himself. According to McClelland, Mick has a high need for:
A) achievement
B) power
C) affiliation
D) charisma
A) achievement
B) power
C) affiliation
D) charisma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Sarah likes to delegate authority and responsibility to Mick and in doing so to encourage Mick to become accountable for his own actions and to raise his self-efficacy. This is an example of:
A) achievement
B) power
C) self-determination
D) empowerment
A) achievement
B) power
C) self-determination
D) empowerment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
John demonstrates the capability (energy and vigour) at work, and willingness to work (involvement and dedication). According to Bakker, John is showing the signs of:
A) motivation
B) burnout
C) engagement
D) self-efficacy
A) motivation
B) burnout
C) engagement
D) self-efficacy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Julianne argues that pay is an object of social comparison. This mind set aligns with which of the following approaches:
A) reinforcement theory
B) expectancy theory
C) equity theory
D) None of the above
A) reinforcement theory
B) expectancy theory
C) equity theory
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Explain the relationship between job satisfaction and dissatisfaction in Herzberg's theory of motivation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Briefly explain two major adjustments made by Alderfer to Maslow's theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Explain the difference between hygiene and motivation factors in Herzberg's theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
List and give an example for each of the needs identified by Maslow's theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
McClelland has identified acquired needs in his motivation theory. List the three needs and explain how one of the needs might be acquired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Explain the concept of extrinsic rewards and give two examples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the key difference between the approaches taken by the content and process theories concerning their explanations of work motivation? Use various content and process theories to support your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose that you are a manager and find yourself with one group of subordinates who apparently seek higher-order need satisfactions at work, and another group that seems concerned only with lower-order needs. What would you do to motivate each group of subordinates? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain empowerment and discuss methods that managers might adopt to empower their employees. What potential benefits might emerge?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Visual Diagram Questions
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-Using the diagram below:
a) Explain how the issue of individual needs and expectancies relates to work motivation.
b) Describe the constraints which may restrict achieving these goals.
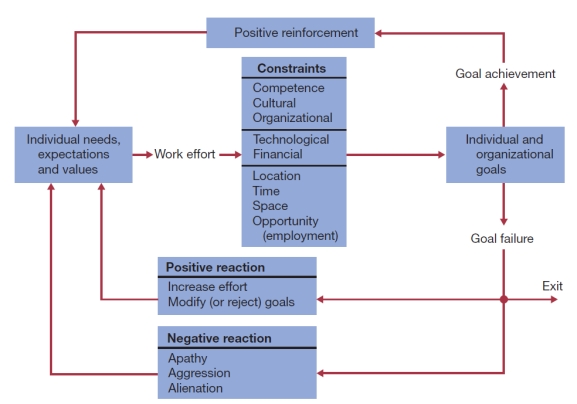
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-Using the diagram below:
a) Explain how the issue of individual needs and expectancies relates to work motivation.
b) Describe the constraints which may restrict achieving these goals.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Visual Diagram Questions
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-The diagram below identified the higher-order needs and lower-order needs.
a) Name the theory
b) Explain how this theory might be used to motivate individuals in a work-setting
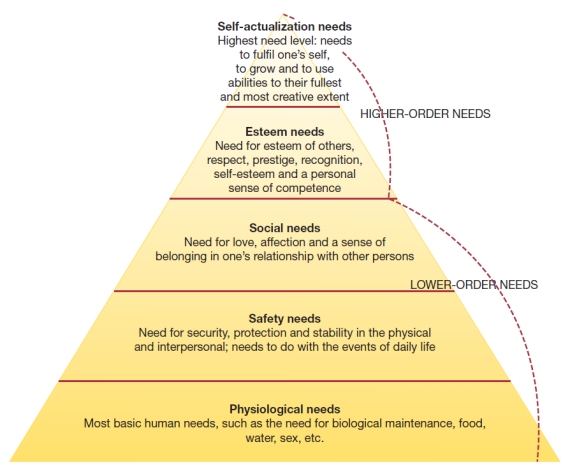
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-The diagram below identified the higher-order needs and lower-order needs.
a) Name the theory
b) Explain how this theory might be used to motivate individuals in a work-setting


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



