Deck 1: What Is Organizational Behaviour
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: What Is Organizational Behaviour
1
Organizational behaviour is the study of individuals and groups in profit-making organizations.
False
2
Organizational behaviour is the subject of psychology applied to the world of work.
False
3
Organizational behaviour is characterised by its emphasis on rigorous inquiry.
True
4
Hendrick's study of pilot error is an example of a positivist research study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Empowerment is the process of breaking work down into specialised tasks for individuals or groups to perform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The purpose of any organization is to make a profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Quality of work life refers to the overall quality of human experience in the workplace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Voice is the last resort when dealing with violations of the psychological contract and refers to voluntary termination of the relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Megatrends are deep underlying issues, linked to changes within societies which impact on the management of people at work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Globalisation is the process of wanting to work in another country and finding out about other cultures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Being culturally sensitive and adaptable is an important global management competency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Power distance is one of Hofstede's dimensions of culture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Work-life balance refers to workers who seek balance between their paid work and unpaid work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An example of a virtual organization is an office located in a high-rise building.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Ethical behaviour is behaviour that is morally accepted as good or right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Organizational behaviour is:
A) a commitment to continuous improvement
B) a relatively permanent change in behaviour that occurs as a result of work experiences
C) the study of individuals and groups in organizations
D) the attraction and continuation of a viable workforce
A) a commitment to continuous improvement
B) a relatively permanent change in behaviour that occurs as a result of work experiences
C) the study of individuals and groups in organizations
D) the attraction and continuation of a viable workforce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following provides insights which can help any organizational member deal with common workplace problems and opportunities?
A) Total quality management
B) Human resource maintenance
C) The contingency approach
D) Organizational behaviour
A) Total quality management
B) Human resource maintenance
C) The contingency approach
D) Organizational behaviour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Among the special characteristics of organizational behaviour are:
A) its stress on younger workers' behaviour
B) its emphasis on rigorous inquiry
C) its irrelevance to worker behaviour
D) its de-emphasis on an applied focus
A) its stress on younger workers' behaviour
B) its emphasis on rigorous inquiry
C) its irrelevance to worker behaviour
D) its de-emphasis on an applied focus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The contingency approach to organizational behaviour believes that:
A) women typically outperform men in management jobs
B) emotional intelligence is the most important attribute of a successful manager
C) behaviour may vary depending on circumstances and the people involved
D) the purpose of an organization is to gather information
A) women typically outperform men in management jobs
B) emotional intelligence is the most important attribute of a successful manager
C) behaviour may vary depending on circumstances and the people involved
D) the purpose of an organization is to gather information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Industrialisation which has been associated with the emergence of large work organizations occurred first in:
A) Northern Europe
B) South-East Asia
C) New Zealand
D) Latin America
A) Northern Europe
B) South-East Asia
C) New Zealand
D) Latin America

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Participant observation is a method of study in which:
A) People are surveyed on their views on work and their employing organization
B) The researcher develops a hypothesis to be tested in a controlled environment
C) The researcher becomes a member of the group they are studying
D) A group of people are asked about their attitudes towards specific issues
A) People are surveyed on their views on work and their employing organization
B) The researcher develops a hypothesis to be tested in a controlled environment
C) The researcher becomes a member of the group they are studying
D) A group of people are asked about their attitudes towards specific issues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The creation of a whole that is greater than the sum of its parts is known as:
A) synergy
B) performance effectiveness
C) performance efficiency
D) value-added management
A) synergy
B) performance effectiveness
C) performance efficiency
D) value-added management

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An effective manager is one who:
A) believes in saving money and time at every opportunity
B) helps others to plan ahead and control their outputs
C) focuses on task performance and human resource performance
D) follows rules and regulations to the letter
A) believes in saving money and time at every opportunity
B) helps others to plan ahead and control their outputs
C) focuses on task performance and human resource performance
D) follows rules and regulations to the letter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What specifies what the individual and the organization expect to give to and receive from each other in the course of their working relationship?
A) exchange theory
B) contribution/inducement theory
C) the offer of employment
D) the psychological contract
A) exchange theory
B) contribution/inducement theory
C) the offer of employment
D) the psychological contract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is not a course of action associated with violation of the psychological contract?
A) Discussing issues of concern with a manager or other appropriate colleague
B) Remaining silent while hoping that unfavourable circumstances will improve
C) Counterproductive behaviour including slowing work and destroying relationships
D) Beginning our day by checking emails even while travelling abroad
A) Discussing issues of concern with a manager or other appropriate colleague
B) Remaining silent while hoping that unfavourable circumstances will improve
C) Counterproductive behaviour including slowing work and destroying relationships
D) Beginning our day by checking emails even while travelling abroad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following has not been cited as a disadvantage of email communication at work?
A) lack of supportive non-verbal communication
B) ability to communicate easily across world time-zones
C) messages are not easy to withdraw
D) reduction in a person's ability to establish rapport
A) lack of supportive non-verbal communication
B) ability to communicate easily across world time-zones
C) messages are not easy to withdraw
D) reduction in a person's ability to establish rapport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Globalisation is the process of:
A) understanding international business strategy
B) becoming more international in scope, influence or application
C) moving across borders to do business
D) acquiring global management skills and competencies
A) understanding international business strategy
B) becoming more international in scope, influence or application
C) moving across borders to do business
D) acquiring global management skills and competencies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The presence of demographic differences among members of a given workforce is known specifically as:
A) cultural diversity
B) workforce diversity
C) the global workplace
D) internationalism
A) cultural diversity
B) workforce diversity
C) the global workplace
D) internationalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the UK National Health Service what proportion of nurses are 'recent migrants'?
A) More than 5%
B) More than 10%
C) More than 30%
D) More than 90%
A) More than 5%
B) More than 10%
C) More than 30%
D) More than 90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of these statements is correct (based on research findings)?
A) In Scandinavian countries employees prefer participative management styles
B) In Scandinavian countries employees prefer autocratic management styles
C) In Scandinavian countries employees prefer negligent management styles
D) In Scandinavian countries employees prefer macho management styles
A) In Scandinavian countries employees prefer participative management styles
B) In Scandinavian countries employees prefer autocratic management styles
C) In Scandinavian countries employees prefer negligent management styles
D) In Scandinavian countries employees prefer macho management styles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which one of the following is not a trend in workplace diversity?
A) More women are entering the workforce
B) There is a smaller pool of younger workers
C) Workforce mobility is increasing
D) The size of the workforce is growing more slowly than in the past
A) More women are entering the workforce
B) There is a smaller pool of younger workers
C) Workforce mobility is increasing
D) The size of the workforce is growing more slowly than in the past

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In Hofstede's classification of culture, Singapore is depicted as exhibiting:
A) low power distance
B) high individualism
C) low uncertainty avoidance
D) low masculinity
A) low power distance
B) high individualism
C) low uncertainty avoidance
D) low masculinity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements regarding generations X and Y is not true?
A) they expect to have one job throughout their working lives
B) they bring high levels of technical competence to the workplace
C) they are less focussed on pay and security than earlier generations
D) they are increasingly concerned with quality of life issues
A) they expect to have one job throughout their working lives
B) they bring high levels of technical competence to the workplace
C) they are less focussed on pay and security than earlier generations
D) they are increasingly concerned with quality of life issues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is not an advantage of a family-friendly workplace?
A) increased ability to recruit quality staff
B) improved staff morale and performance
C) increased parochialism
D) reduced absenteeism - employees can work knowing their children are safe
A) increased ability to recruit quality staff
B) improved staff morale and performance
C) increased parochialism
D) reduced absenteeism - employees can work knowing their children are safe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The European country offering the most paid paternity leave is:
A) Poland
B) Spain
C) UK
D) Norway
A) Poland
B) Spain
C) UK
D) Norway

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Ethical behaviour is:
A) that which is accepted as morally 'good' or 'right'.
B) that which results in more profits for the company
C) that which avoids loss for the company
D) that which motivates employees
A) that which is accepted as morally 'good' or 'right'.
B) that which results in more profits for the company
C) that which avoids loss for the company
D) that which motivates employees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Siobhan operates a catering business from home. She perceives that although she is working very hard she is getting a great sense of satisfaction from her work
Siobhan's psychological contract appears to be:
A) unfair and unhealthy
B) fair and balanced
C) violated
D) driven by money
Siobhan's psychological contract appears to be:
A) unfair and unhealthy
B) fair and balanced
C) violated
D) driven by money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Tina's products are in such demand that she now needs to employ additional workers. She has been told that a key concept when managing others is emotional intelligence. Siobhan's has asked you to provide a working definition of emotional intelligence. Is it?
A) The view that people are primarily motivated by money
B) A commitment to fostering diversity among a workforce
C) A form of social intelligence allowing us to shape our emotions and those of others
D) An acknowledgement of the benefits of teleworking
A) The view that people are primarily motivated by money
B) A commitment to fostering diversity among a workforce
C) A form of social intelligence allowing us to shape our emotions and those of others
D) An acknowledgement of the benefits of teleworking

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Aidan is the manager of a discount store. Following requests from the community and his customers, he has decided to implement an in-store recycling programme. He sent out a memo announcing the new programme and detailing how it would work.
This is an example of his adopting which of Mintzberg's roles?
A) entrepreneur
B) figurehead
C) disseminator
D) resource allocator
This is an example of his adopting which of Mintzberg's roles?
A) entrepreneur
B) figurehead
C) disseminator
D) resource allocator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Shilpa often works overtime for no pay as she is committed to ensuring her customers' satisfaction. Her manager has grown to expect this behaviour from Shilpa.
Shilpa's behaviour can be categorised under the _____________ component of the psychological contract.
A) contributions
B) inducements
C) organizational commitment
D) job satisfaction
Shilpa's behaviour can be categorised under the _____________ component of the psychological contract.
A) contributions
B) inducements
C) organizational commitment
D) job satisfaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Harriet has been sent to Sweden to work on a project. She is pleasantly surprised to find that her new boss appreciates the goodwill that she brings with her, and they work cooperatively to increase their client base. According to Hofstede, this could be an example of Sweden's:
A) high masculinity
B) low masculinity
C) high power-distance
D) high uncertainty avoidance
A) high masculinity
B) low masculinity
C) high power-distance
D) high uncertainty avoidance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A United Kingdom based Information Technology company has arranged for the bulk of its call-centre activity to be located in the Philippines. This is an example of:
A) outsourcing
B) a virtual organization
C) immigration
D) IT transfer
A) outsourcing
B) a virtual organization
C) immigration
D) IT transfer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Mark has just been accepted as an IT consultant for MLF Solutions. He has not been assigned an office desk and will work partly from home and partly while travelling to and from client meetings. This pattern of work is known as:
A) globalisation
B) casualisation
C) teleworking
D) diversity
A) globalisation
B) casualisation
C) teleworking
D) diversity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the difference between the following two manager concerns: task performance and human resource performance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Briefly define the positivist tradition within organizational behaviour .Use examples to enhance your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
There are several pressures for employee rights in the workplace. List and briefly explain two of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Explain the concept of workforce diversity and briefly indicate two predominant trends that are taking place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Explain the psychological contract and its main components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Identify and explain the three special characteristics of organizational behaviour.
Organizational behaviour is the study of individuals and groups in organizations. Special characteristics are:
Organizational behaviour is the study of individuals and groups in organizations. Special characteristics are:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Managers face considerable challenges in the new workplace. Discuss the reasons for some of the challenges and the qualities and behaviours required of managers to work effectively within this environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Discuss the importance of ethical behaviour in workplaces and ways in which unethical behaviour might be avoided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Visual Diagram Question
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-What does the following diagram illustrate? Explain how it might work for a graduate recruit who has started her first management job in a large multinational organization.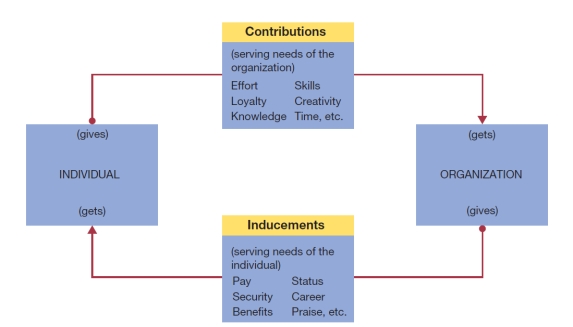
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-What does the following diagram illustrate? Explain how it might work for a graduate recruit who has started her first management job in a large multinational organization.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



