Deck 3: Important Bacterial Genera
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Important Bacterial Genera
1
A 21-year-old male college student who had complained of headache and feeling feverish the night before is brought this morning to the emergency department (ED) when his roommate was unable to rouse him. He had been well until yesterday. Vital signs include fever (39.8°C/103.1°F), tachycardia, and hypotension (BP 70/55). Remarkable on physical examination is petechial rash (purpuric in areas) and nuchal rigidity with positive Kernig and Brudzinski signs. CSF is cloudy with high protein and low glucose. Intracellular, red diplococci are seen on Gram stain. What is the most likely genus?
A) Staphylococcus
B) Streptococcus
C) Chlamydia
D) Mycobacterium
E) Neisseria
A) Staphylococcus
B) Streptococcus
C) Chlamydia
D) Mycobacterium
E) Neisseria
Neisseria
2
A 24-year-old female presents with dysuria, as well as urinary urgency and frequency. A urine dipstick test is positive for both leukocyte esterase and nitrites. What genus or family is noted for the production of nitrites?
A) Escherichia
B) Staphylococcus
C) Streptococcus
D) Vibrio
A) Escherichia
B) Staphylococcus
C) Streptococcus
D) Vibrio
Escherichia
3
What rapid test commonly used on Gramnegative rods rules out Enterobacteriaceae if positive?
A) Catalase
B) Coagulase
C) Oxidase
D) Chitinase
E) Urease
A) Catalase
B) Coagulase
C) Oxidase
D) Chitinase
E) Urease
Oxidase
4
A patient presents with rapid onset severe respiratory symptoms. Chest radiographs show a hemorrhagic lymphadenitis. The isolation of chains of fairly large, aerobic Gram-positive rods, some of which have started to sporulate from a patient with this resentation, should raise a major concern of which organism? (You should be able to answer this question from the genus alone, although a question might also mention that it was nonmotile.)
A) Actinomyces israelii
B) Bacillus anthracis
C) Campylobacter jejuni
D) Clostridium perfringens
E) Haemophilus influenzae
A) Actinomyces israelii
B) Bacillus anthracis
C) Campylobacter jejuni
D) Clostridium perfringens
E) Haemophilus influenzae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A patient undergoing chemotherapy develops a cough. Acid-fast stain of his sputum shows rods and slightly longer forms, with some branching; they vary in their acidfast reaction from one area of the slide to the next. The acid-fast stain was performed by n experienced medical technologist and, when redone, showed the same variation. The growth was done aerobically. What is the most likely agent?
A) Actinomyces
B) Chlamydophila
C) Mycobacterium avian-intracellulare (MAI or MAC)
D) Nocardia
A) Actinomyces
B) Chlamydophila
C) Mycobacterium avian-intracellulare (MAI or MAC)
D) Nocardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A female patient with a new genital lesion presents to your sexually transmitted disease clinic. She is homeless, has no health insurance, and is an intravenous drug user. You suspect syphilis. Which of these techniques would be most appropriate to emonstrate treponemes?
A) Immunological test such as the VDRL
B) Dark-field microscopy
C) Acid-fast stain
D) Gram stain
E) Electrophoresis
A) Immunological test such as the VDRL
B) Dark-field microscopy
C) Acid-fast stain
D) Gram stain
E) Electrophoresis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The CSF from a 2-week-old infant with meningitis shows rods with tumbling motility. These bacteria are found to be Gram-positive and do not form spores. What is the most likely agent?
A) Actinomyces
B) Bacillus
C) Clostridium
D) Corynebacterium
E) Listeria
A) Actinomyces
B) Bacillus
C) Clostridium
D) Corynebacterium
E) Listeria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Both a 53-year-old farmer and his 21-yearold son present in August with fever, myalgia, and malaise, which they came down with within a few hours of each other. The son had been home in southern Minnesota for only 3 weeks to help field train two new hunting dogs. You ask about potential tick bites, and the son did have one on him, which was quite engorged. Platelets and granulocytes are low in each man's blood. You ask one of your experienced techs to do a Giemsa stain on a thick blood smear. He calls, reporting clusters of cells resembling raspberries in granulocytes, even though nothing grows in any of the blood cultures. You realize that the blood cultures you set up will not grow and that you have two patients who have infections with a tick-borne obligate intracellular parasite of granulocytes. What genus does the organism belong to?
A) Anaplasma (formerly Ehrlichia)
B) Borrelia
C) Chlamydia
D) Haemophilus
E) Mycoplasma
A) Anaplasma (formerly Ehrlichia)
B) Borrelia
C) Chlamydia
D) Haemophilus
E) Mycoplasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A full-term 6-day-old neonate is brought in with a purulent conjunctivitis which the parents noticed earlier today. On Gram stain of the purulent exudate, no bacteria are seen. Which of the following bacteria is most likely the cause of the conjunctivitis?
A) Chlamydia trachomatis
B) Escherichia coli
C) Listeria monocytogenes
D) Neisseria gonorrhoeae
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae
A) Chlamydia trachomatis
B) Escherichia coli
C) Listeria monocytogenes
D) Neisseria gonorrhoeae
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An 83-year-old who still lives in her own home has developed pneumonia following influenza. The Gram stain of her sputa is shown. What is the most likely agent? 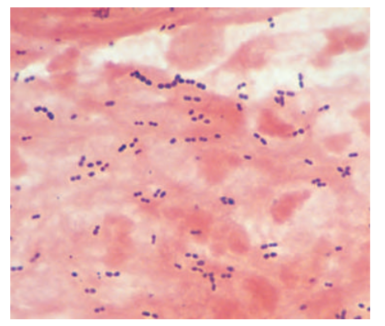
A) Chlamydophila pneumoniae
B) Influenza virus
C) Klebsiella pneumoniae
D) Mycoplasma pneumoniae
E) Staphylococcus aureus
F) Streptococcus pneumoniae

A) Chlamydophila pneumoniae
B) Influenza virus
C) Klebsiella pneumoniae
D) Mycoplasma pneumoniae
E) Staphylococcus aureus
F) Streptococcus pneumoniae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The reagent used to distinguish staphylococci from streptococci is
A) Hydrogen peroxide
B) Fibronectin
C) Fibrinogen
D) Oxidase
A) Hydrogen peroxide
B) Fibronectin
C) Fibrinogen
D) Oxidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A 14-month-old boy is brought in by his parents with fever, fussiness and lethargy, and apparent headache. On examination, the neck is stiff. His parents have not allowed his routine childhood vaccines. Very short Gramnegative rods are seen in the CSF, so antibiotics are immediately started. The organism grows on chocolate agar but not blood agar. No one else in the family is ill. What is the most likely causative agent?
A) Escherichia coli
B) Haemophilus influenzae type b
C) Klebsiella pneumoniae
D) Neisseria meningitidis
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae
A) Escherichia coli
B) Haemophilus influenzae type b
C) Klebsiella pneumoniae
D) Neisseria meningitidis
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A healthy 7-year-old boy who has not traveled outside the United States is brought in by his parents in June with signs of meningitis. No bacteria are seen in the Gram stain of the CSF, and no bacterial capsule material is present as determined by a series of latex particle agglutination tests standard to the diagnosis of meningitis. The CSF glucose level is slightly low, protein is near normal, and white cell count is less than 500 cells/microL, mainly lymphocytes. What is the most likely causative agent?
A) Chlamydophila pneumoniae
B) Enterovirus
C) Mycoplasma pneumoniae
D) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
E) Treponema pallidum
A) Chlamydophila pneumoniae
B) Enterovirus
C) Mycoplasma pneumoniae
D) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
E) Treponema pallidum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In any case, a clue indicating that the causative organism is an obligate intracellular pathogen transmitted by an arthropod bite should lead you to which of the following groups of organisms?
A) Chlamydiae
B) Enterobacteriaceae
C) Rickettsias including Anaplasma and Ehrlichia
D) Spirochetes including Borrelia burgdorferi
A) Chlamydiae
B) Enterobacteriaceae
C) Rickettsias including Anaplasma and Ehrlichia
D) Spirochetes including Borrelia burgdorferi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the main difference between fluorochrome staining (e.g., auraminerhodamine screening for Mycobacterium tuberculosis) and indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) staining?
A) Fluorochromes are more specific and used just for Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
B) IFAs are less specific since they use antibody to a different species' antibody (i.e., rabbit antibody to human antibody).
C) Fluorochrome staining is less sensitive than comparable staining with light microscopy.
D) IFA's specificity is dependent on the primary antibody used; fluorochromes lack the antibody specificity.
A) Fluorochromes are more specific and used just for Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
B) IFAs are less specific since they use antibody to a different species' antibody (i.e., rabbit antibody to human antibody).
C) Fluorochrome staining is less sensitive than comparable staining with light microscopy.
D) IFA's specificity is dependent on the primary antibody used; fluorochromes lack the antibody specificity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



