Deck 37: Translation: Protein Synthesis and Modification
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/43
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 37: Translation: Protein Synthesis and Modification
1
During the process of protein synthesis the factor eEF-2 induces the hydrolysis of GTP. The energy of this hydrolysis is coupled to which of the following?
A) amino acid activation by attachment to a tRNA
B) correct alignment of the mRNA on the 40S ribosome
C) formation of the 80S initiation complex
D) formation of the peptide bond
E) translocation of the ribosome
A) amino acid activation by attachment to a tRNA
B) correct alignment of the mRNA on the 40S ribosome
C) formation of the 80S initiation complex
D) formation of the peptide bond
E) translocation of the ribosome
translocation of the ribosome
2
If the DNA shown was transcribed and then translated in a eukaryotic in vitro translation system, what would be the composition of the resultant peptide?
5′-CATTCCATAGCATGT-3′
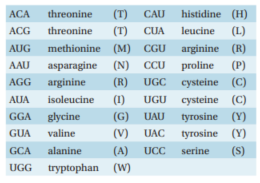
A) C-T-I-P-Y
B) H-S-I-A-C
C) M-L-W-N
D) T-C-Y-G-M
E) V-R-Y-R-T
5′-CATTCCATAGCATGT-3′

A) C-T-I-P-Y
B) H-S-I-A-C
C) M-L-W-N
D) T-C-Y-G-M
E) V-R-Y-R-T
M-L-W-N
3
Which of the following translation factors is responsible for engaging the cap structure of the mRNA?
A) eIF-2
B) eIF-2B
C) eIF-4E
D) eIF-4EBP (4EBP)
E) eIF-4G
A) eIF-2
B) eIF-2B
C) eIF-4E
D) eIF-4EBP (4EBP)
E) eIF-4G
eIF-4E
4
A hypothetical cell is exposed to a chemical agent that alters the structure of serine converting it to alanine but only when the serine is activated on an appropriate tRNA. What is the most likely outcome of this modification relative to protein synthesis?
A) protein synthesis ceases and the mRNA is degraded
B) the alanine is exchanged for serine by the appropriate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
C) the alanine is incorporated because there is no mechanism for the translational machinery to detect the change
D) the aminoacyl-tRNA is degraded and thus no effect is observable
E) translation is halted temporarily due to recognition of the abnormal aminoacyl-tRNA, while the alanine is removed and serine replaced
A) protein synthesis ceases and the mRNA is degraded
B) the alanine is exchanged for serine by the appropriate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
C) the alanine is incorporated because there is no mechanism for the translational machinery to detect the change
D) the aminoacyl-tRNA is degraded and thus no effect is observable
E) translation is halted temporarily due to recognition of the abnormal aminoacyl-tRNA, while the alanine is removed and serine replaced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The unfolded protein response is a stress response in the ER. This stress pathway results in a halt to global protein synthesis and the activation of translation of factors required to respond to the stress inducer. Which of the following proteins of translation is the primary target of the ER stress response?
A) eIF-2
B) eIF2B
C) eIF-4E
D) eEF-1α
E) eEF-2
A) eIF-2
B) eIF2B
C) eIF-4E
D) eEF-1α
E) eEF-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Growth factor effects on the rate of translation are, for the most part, the consequence of the phosphorylation of which of the following factors?
A) 4E-BP
B) eEF-2
C) eEF-1α
D) eIF-2
E) eIF-4A
A) 4E-BP
B) eEF-2
C) eEF-1α
D) eIF-2
E) eIF-4A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The immunosuppressant drug rapamycin exerts its function on processes of protein synthesis by interfering with the activity of mTOR. Which of the following translation factors is the protein that would normally be targeted for mTOR-mediated regulation in the absence of rapamycin?
A) eIF-2
B) eIF-2B
C) eIF-4A
D) eIF-4E
E) eIF-4G
A) eIF-2
B) eIF-2B
C) eIF-4A
D) eIF-4E
E) eIF-4G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements most closely reflects the actions of the translation factor eIF-4E?
A) ATP-dependent unwinding of secondary structures in mRNAs
B) exchange of GTP for GDP bound to eIF-2
C) facilitation of the ternary complex (eIF-2/ GTP/mettRNA) binding to 40S ribosomal subunit
D) interaction with eIF-4G in order to bind to the cap structure of the mRNA
E) scaffold for the binding of eIF-4A
A) ATP-dependent unwinding of secondary structures in mRNAs
B) exchange of GTP for GDP bound to eIF-2
C) facilitation of the ternary complex (eIF-2/ GTP/mettRNA) binding to 40S ribosomal subunit
D) interaction with eIF-4G in order to bind to the cap structure of the mRNA
E) scaffold for the binding of eIF-4A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Reticulocytes control the rate of globin synthesis as a consequence of the level of heme in the cell. This prevents globin protein from being made when there are insufficient amounts of heme. Which of the following best explains the effects of heme on protein synthesis in these cells?
A) a heme-controlled phosphatase dephosphorylates cap-binding factor, which prevents recognition of globin mRNA by the ribosomes
B) a tRNA degrading enzyme is active in the absence of heme
C) heme normally activates peptidyltransferase in reticulocytes
D) RNA polymerase activity is decreased in reticulocytes by low heme
E) the initiation factor eIF-2 becomes phosphorylated, reducing its level of activity
A) a heme-controlled phosphatase dephosphorylates cap-binding factor, which prevents recognition of globin mRNA by the ribosomes
B) a tRNA degrading enzyme is active in the absence of heme
C) heme normally activates peptidyltransferase in reticulocytes
D) RNA polymerase activity is decreased in reticulocytes by low heme
E) the initiation factor eIF-2 becomes phosphorylated, reducing its level of activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following translation factors is the target of an interferon-mediated translational control mechanism?
A) eEF-1α
B) eEF-2
C) eIF-2
D) eIF-4A
E) eIF-4E
A) eEF-1α
B) eEF-2
C) eIF-2
D) eIF-4A
E) eIF-4E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
You are utilizing a cell culture system derived from a breast cancer tumor to examine the process of protein synthesis. You discover that these cells do not effectively generate the GTP-bound form of the translation initiation factor, eIF-2. Which of the following translation factors is most likely to be defective in these cells, thereby impairing the GDP for GTP exchange in eIF-2?
A) eIF-1
B) eIF-2B
C) eIF-4A
D) eIF-4E
E) eIF-4G
A) eIF-1
B) eIF-2B
C) eIF-4A
D) eIF-4E
E) eIF-4G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
You are utilizing a cell culture system derived from a breast cancer tumor to examine the process of protein synthesis. You discover that short peptides are present in the P-site of the ribosome whenever there is an aminoacyl-tRNA in the A-site, but it takes several hours for new aminoacyl-tRNAs to enter the ribosome. These results are most likely to be the result of a highly defective form of which of the following proteins?
A) eIF-2.
B) eIF-2
C) eEF-1α
D) eEF-1βγ
E) eEF-2
A) eIF-2.
B) eIF-2
C) eEF-1α
D) eEF-1βγ
E) eEF-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following translation factors contains a modified amino acid recognized by a toxin produced by Diphtheria?
A) eIF-2B
B) eIF-4F
C) eEF-1α
D) eEF-2
E) eRF
A) eIF-2B
B) eIF-4F
C) eEF-1α
D) eEF-2
E) eRF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A mutation that results in the loss of the formation of the iron response element (IRE) in the 5′-UTR of the ferritin mRNA will be expected to have what effect?
A) decreased translation of the mRNA in the presence of high iron
B) decreased translation of the mRNA when iron is low
C) increased translation of the mRNA in the presence of high iron
D) increased translation of the mRNA when iron is low
E) reduced stability of the mRNA
A) decreased translation of the mRNA in the presence of high iron
B) decreased translation of the mRNA when iron is low
C) increased translation of the mRNA in the presence of high iron
D) increased translation of the mRNA when iron is low
E) reduced stability of the mRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A decrease in the amount of heme within erythrocytes activates the heme-controlled inhibitor leading to phosphorylation of which factor?
A) eIF-2
B) eIF-2B
C) eEF-4G
D) eEF-2
E) eIF-4E
A) eIF-2
B) eIF-2B
C) eEF-4G
D) eEF-2
E) eIF-4E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Some viruses, for example, poliovirus, contain a protease that cleaves one of the eukaryotic initiation factors allowing for cap-independent translational initiation of viral RNAs at internal ribosome entry site (IRES). Which of the following factors is the target of these viral proteases?
A) eIF-2
B) eIF-2B
C) eIF-4A
D) eIF-4E
E) eIF-4G
A) eIF-2
B) eIF-2B
C) eIF-4A
D) eIF-4E
E) eIF-4G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Control of the rate of translational initiation can be exerted at the level of the activity of the GTPbinding and hydrolyzing initiation factor, eIF-2. The efficiency with which eIF-2 recycles between the active GTP-bound form and the inactive GDPbound form is controlled by which of the following translation factors?
A) eIF-1
B) eIF-2B
C) eIF-4A
D) eIF-4E
E) eIF-4G
A) eIF-1
B) eIF-2B
C) eIF-4A
D) eIF-4E
E) eIF-4G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
You are studying the effects of a novel compound on the processes of protein synthesis using a cell culture system. You find that addition of your compound results in premature termination of protein synthesis. Analysis of the compound reveals that it has structural characteristics of an aminoacyltRNA. Which of the following protein-synthesis inhibitors is most similar to your test compound?
A) erythromycin
B) puromycin
C) ricin
D) streptomycin
E) tetracyclin
A) erythromycin
B) puromycin
C) ricin
D) streptomycin
E) tetracyclin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
You are examining the mutational changes that occurred in a breast cancer cell line. You discover that there is a mutation in the gene encoding selenoprotein translation factor B (SelB). Which of the following is most likely defective in these cells as a result of this mutation?
A) decreased bile acid synthesis
B) decreased glycogen synthesis
C) decreased reactive oxygen species generation by pancreatic mitochondria
D) increased fatty acid incorporation into triglycerides
E) increased rate of erythrocyte lysis
A) decreased bile acid synthesis
B) decreased glycogen synthesis
C) decreased reactive oxygen species generation by pancreatic mitochondria
D) increased fatty acid incorporation into triglycerides
E) increased rate of erythrocyte lysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
You are studying the function of a protein isolated from a lung tumor cell line and comparing it to the same protein from normal tissue. You find that the protein derived from the cancer cells does not carry out its correct function as a result of improper folding of the protein. Which of the following, involved in the prevention of aggregation and improper folding of newly synthesized proteins, is most likely to be defective in the lung cancer cells?
A) chaperones
B) lysozymes
C) mitochondrial precursor proteins
D) ribosomal-binding proteins
E) zymogens
A) chaperones
B) lysozymes
C) mitochondrial precursor proteins
D) ribosomal-binding proteins
E) zymogens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The RNA codon for methionine is 5′-AUG-3′. Which of the following is the anticodon in the correct methionyl-tRNA?
A) 5′-CAT-3′
B) 5′-CAU-3′
C) 5′-GAU-3′
D) 5′-TAC-3′
E) 5′-UAC-3′
A) 5′-CAT-3′
B) 5′-CAU-3′
C) 5′-GAU-3′
D) 5′-TAC-3′
E) 5′-UAC-3′

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Reading of the genetic code is dependent on recognition of a codon on which of the following?
A) DNA by an amino acid
B) DNA by an mRNA
C) mRNA by an amino acid
D) mRNA by an aminoacyl-tRNA
E) tRNA by an amino acid
A) DNA by an amino acid
B) DNA by an mRNA
C) mRNA by an amino acid
D) mRNA by an aminoacyl-tRNA
E) tRNA by an amino acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is a function of codons in eukaryotic cells?
A) initiation of gene expression
B) recognition of complementary sequences in mRNA
C) recognition of specific mRNA sequences
D) specification of individual amino acids
E) used for directing the cap-binding complex to an mRNA
A) initiation of gene expression
B) recognition of complementary sequences in mRNA
C) recognition of specific mRNA sequences
D) specification of individual amino acids
E) used for directing the cap-binding complex to an mRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
You are studying the process of protein synthesis and the effects of mutations introduced into tRNA genes. You alter the sequences of the anticodon of a tRNA from CAU into GUU. As a consequence of this change, which of the following, regarding the steps of translation, is most likely to occur?
A) increased translation rate
B) premature termination
C) shift of the reading frame
D) substitution of 1 amino acid
E) no effect
A) increased translation rate
B) premature termination
C) shift of the reading frame
D) substitution of 1 amino acid
E) no effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following best describes what happens when an 80S ribosome completes synthesis of a protein?
A) the entire ribosome is degraded by proteases and nucleases
B) the protein components of the ribosome are degraded by the proteasome, but the rRNAs are recycled
C) the ribosome dissociates into 60S and 40S subunits, which are then available for another round of protein synthesis
D) the 80S ribosome stays intact and is available for initiating another round of protein synthesis
E) the RNA components of the ribosome are degraded by nucleases, but the proteins are recycled
A) the entire ribosome is degraded by proteases and nucleases
B) the protein components of the ribosome are degraded by the proteasome, but the rRNAs are recycled
C) the ribosome dissociates into 60S and 40S subunits, which are then available for another round of protein synthesis
D) the 80S ribosome stays intact and is available for initiating another round of protein synthesis
E) the RNA components of the ribosome are degraded by nucleases, but the proteins are recycled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
During the process of protein synthesis the elongating peptide is transferred to the incoming aminoacyltRNA by a peptidyltransferase activity. Which of the following components of the translational machinery is most likely to possess this enzymatic activity?
A) peptidase
B) ribosomal protein L11
C) ribosomal protein S16
D) 5S rRNA
E) 28S rRNA
F) tRNA nucleotidyltransferase
A) peptidase
B) ribosomal protein L11
C) ribosomal protein S16
D) 5S rRNA
E) 28S rRNA
F) tRNA nucleotidyltransferase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following describes the direction of translation of mRNAs and synthesis of protein on ribosomes?
A) Translation : 5′ → 3′
Synthesis: C-terminus → N-terminus
B) Translation: 3′ → 5′
Synthesis: C-terminus → N-terminus
C) Translation : 5′ →3′
Synthesis: N-terminus → C-terminus
D) Translation: 3′ → 5′
Synthesis: N-terminus → C-terminus
A) Translation : 5′ → 3′
Synthesis: C-terminus → N-terminus
B) Translation: 3′ → 5′
Synthesis: C-terminus → N-terminus
C) Translation : 5′ →3′
Synthesis: N-terminus → C-terminus
D) Translation: 3′ → 5′
Synthesis: N-terminus → C-terminus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
You are studying the processes of protein synthesis via the use of a cell-free system and synthetic RNAs. You have introduced the following RNA to this system:
5′-AUAUAAUGACUAAAUAU-3′
Table of codons
Aaa lysine
Aau asparagine
ACu threonine
Aua isoleucine
AuG methionine
Uau tyrosine
Cau leucine
Using the above indicated codons, which of the following is the most likely sequence of the peptide synthesized in this system?
A) isoleucine, methionine, threonine, lysine, tyrosine
B) methionine, isoleucine, asparagine
C) methione, threonine, leucine, threonine
D) methionine, threonine, lysine, tyrosine
5′-AUAUAAUGACUAAAUAU-3′
Table of codons
Aaa lysine
Aau asparagine
ACu threonine
Aua isoleucine
AuG methionine
Uau tyrosine
Cau leucine
Using the above indicated codons, which of the following is the most likely sequence of the peptide synthesized in this system?
A) isoleucine, methionine, threonine, lysine, tyrosine
B) methionine, isoleucine, asparagine
C) methione, threonine, leucine, threonine
D) methionine, threonine, lysine, tyrosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
You are a visiting physician treating patients at a clinic in Bangladesh. Your current patient is a 5-year-old girl complaining of a fever and sore throat for the past week. Physical examination shows a gray-white membrane on the tonsils and the pharyngeal wall. A swab of the membranes is taken and an infectious agent is characterized. Your studies of a toxin purified from this infectious agent demonstrate that it markedly inhibits protein synthesis. Which of the following is most likely to be the mechanism by which this toxin exerts its activity?
A) inhibition of GTP binding to aminoacyl-tRNA
B) inhibition of release of factor binding to the translational complex
C) inhibition of transcript initiation
D) inhibition of the translocation step in protein
Chain elongation
E) premature termination of the translated protein
A) inhibition of GTP binding to aminoacyl-tRNA
B) inhibition of release of factor binding to the translational complex
C) inhibition of transcript initiation
D) inhibition of the translocation step in protein
Chain elongation
E) premature termination of the translated protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following occurs to mRNA molecules during protein synthesis?
A) amplification in the cytoplasm to code for new proteins
B) conversion to DNA by reverse transcriptase
C) synthesis from individual ribonucleotides
D) transcription in a 3′ → 5′ direction
E) translation in a 5′ → 3′ direction
A) amplification in the cytoplasm to code for new proteins
B) conversion to DNA by reverse transcriptase
C) synthesis from individual ribonucleotides
D) transcription in a 3′ → 5′ direction
E) translation in a 5′ → 3′ direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
At which of the following sites on a eukaryotic mRNA is translation most likely to begin?
A) at the cap
B) at the 3′-end of the mRNA
C) at the 5′-end of the mRNA
D) first AUG codon
E) within 5 nucleotides of the Shine-Delgarno sequence
A) at the cap
B) at the 3′-end of the mRNA
C) at the 5′-end of the mRNA
D) first AUG codon
E) within 5 nucleotides of the Shine-Delgarno sequence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following proteins or complexes involved in protein synthesis exhibits peptidyltransferase activity?
A) elongating peptide
B) elongation factor 2 (eEF-2)
C) mRNA
D) ribosome
E) tRNA
A) elongating peptide
B) elongation factor 2 (eEF-2)
C) mRNA
D) ribosome
E) tRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The synthesis of all proteins in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells begins with which of the following amino acids?
A) alanine
B) glycine
C) leucine
D) methionine
E) tryptophan
A) alanine
B) glycine
C) leucine
D) methionine
E) tryptophan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
You are studying the effects of chemical treatment of components of the translational machinery. You discover that one chemical in particular results in the conversion of the cysteine attached to a tRNA to alanine. Which of the following would best describe the results of this chemical-induced insertion of alanine into the resultant polypeptide?
A) it would not occur due to altered structure
B) it would occur randomly
C) it would occur where alanine is normally present
D) it would occur where cysteine is normally present
A) it would not occur due to altered structure
B) it would occur randomly
C) it would occur where alanine is normally present
D) it would occur where cysteine is normally present

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
You are studying the process of protein synthesis in cultures of hepatocytes. During an experiment, you
Observe that translation of certain mRNAs continues until a termination codon reside in the A-site of the ribosome. The liberation of the polypeptide chain at this point involves the eukaryotic releasing factor and hydrolysis of which of the following?
A) ATP
B) CTP
C) GTP
D) TTP
E) UTP
Observe that translation of certain mRNAs continues until a termination codon reside in the A-site of the ribosome. The liberation of the polypeptide chain at this point involves the eukaryotic releasing factor and hydrolysis of which of the following?
A) ATP
B) CTP
C) GTP
D) TTP
E) UTP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following determines the sequence of a polypeptide synthesized by the polyribosome complex?
A) aminoacyl-tRNA
B) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
C) elongation factor 1 (eEF-1)
D) mRNA
E) peptidyltransferase
A) aminoacyl-tRNA
B) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
C) elongation factor 1 (eEF-1)
D) mRNA
E) peptidyltransferase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
You are studying the effects of insulin addition to cultures of eukaryotic cells at the level of protein synthesis. Your results demonstrate that addition of insulin stimulates protein synthesis concomitant with the phosphorylation of protein S6 of the 40S ribosomal subunit of the ribosome. Which of the following steps in protein synthesis is most likely stimulated when S6 is phosphorylated in this system?
A) aminoacyl-tRNA binding to the A-site of the ribosome
B) initiation
C) peptide bond formation
D) termination
E) translocation
A) aminoacyl-tRNA binding to the A-site of the ribosome
B) initiation
C) peptide bond formation
D) termination
E) translocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
During the development of B cells there is switch from the synthesis of membrane-bound immunoglobulin to a secreted form of immunoglobulin. This change occurs because the mRNA population encodes a protein missing which of the following sequence motifs?
A) anchor sequence
B) glycosylation sites
C) leucine zipper
D) signal sequence
E) zinc-binding domain
A) anchor sequence
B) glycosylation sites
C) leucine zipper
D) signal sequence
E) zinc-binding domain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
You are studying the translation of mRNAs derived from human erythrocytes in cell-free system derived from the E coli bacterium. You find the human globin mRNA is translated with extremely low efficiency in this system. Which of the following is the best explanation for these findings?
A) absence of methylated nucleotides
B) absence of more than 1 open-reading frame
C) absence of a Shine-Delgarno sequence
D) presence of intron
E) presence of a poly(a) tail
A) absence of methylated nucleotides
B) absence of more than 1 open-reading frame
C) absence of a Shine-Delgarno sequence
D) presence of intron
E) presence of a poly(a) tail

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Many proteins contain a specialized stretch of amino acids that are recognized by a protein complex called the signal recognition particle. Which of the following best describes the function of this complex during the synthesis of secretory proteins?
A) anchors the ribosome to the Golgi membrane
B) enhances the rate of protein synthesis
C) interact with the amino terminus of the nascent polypeptide
D) interacts with glycosyltransferases within the endoplasmic reticulum
E) promotes the binding of specific mRNAs to ribosomes
A) anchors the ribosome to the Golgi membrane
B) enhances the rate of protein synthesis
C) interact with the amino terminus of the nascent polypeptide
D) interacts with glycosyltransferases within the endoplasmic reticulum
E) promotes the binding of specific mRNAs to ribosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Translocation of newly synthesized protein from the ribosome into the lipid bilayer of a membrane occurs most frequently at the level of which of the following?
A) cis Golgi membrane
B) nucleolus
C) plasma membrane
D) rough endoplasmic reticulum
E) secretory vesicles
A) cis Golgi membrane
B) nucleolus
C) plasma membrane
D) rough endoplasmic reticulum
E) secretory vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
You are studying the effects of a novel drug on the process of protein synthesis in a cell culture system. You discover that addition of the drug causes failure of ribosomes to attach to membranes of the ER. Which of the following is the most likely shortterm consequence in the treated cells?
A) general decrease in translation of all proteins
B) increase in biogenesis of lysosomes
C) increase in exocytosis
D) no short-term consequences
E) selective decrease in secretion of glycoproteins
A) general decrease in translation of all proteins
B) increase in biogenesis of lysosomes
C) increase in exocytosis
D) no short-term consequences
E) selective decrease in secretion of glycoproteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Ribosomal RNAs are synthesized and processed within the nucleolus. Which of the following molecular mechanisms best describes the method by which a newly assembled 60S ribosomal subunit is made available to the translational machinery in the cytoplasm?
A) disassembled at the nuclear pore and reassembled in the cytoplasm
B) transported by transcytosis
C) transported out of the nucleus by active transport through the nuclear envelope
D) transported out of the nucleus by passive diffusion through the nuclear envelope
E) transported out of the nucleus through a nuclear pore complex
A) disassembled at the nuclear pore and reassembled in the cytoplasm
B) transported by transcytosis
C) transported out of the nucleus by active transport through the nuclear envelope
D) transported out of the nucleus by passive diffusion through the nuclear envelope
E) transported out of the nucleus through a nuclear pore complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



