Deck 4: Electricity and Magnetism Are Unified
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/334
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Electricity and Magnetism Are Unified
2
An iron atom's nucleus has 26 protons and 30 neutrons. A helium atom's nucleus has 2 protons and 2 neutrons. Solid iron is much denser than helium gas. How does the total positive charge in a gram of iron compare to that of a gram of helium?
A) Iron has more positive charge than helium per gram.
B) Iron has the same positive charge as helium per gram.
C) Iron has less positive charge than helium per gram.
D) There is not enough information to tell.
A) Iron has more positive charge than helium per gram.
B) Iron has the same positive charge as helium per gram.
C) Iron has less positive charge than helium per gram.
D) There is not enough information to tell.
Iron has less positive charge than helium per gram.
3
An "up" quark has a charge of times the electron's charge. A "strange" quark has a charge of times the electron's charge. What is the net charge of the quark triplet consisting of two up quarks and a strange quark? (This quark triplet is one of a family of three " particles.")
A)
B)
C)
D) zero
E)
F) -e
G) -(5/3)e
A)
B)
C)
D) zero
E)
F) -e
G) -(5/3)e
4
An electron a distance from a proton feels an electrostatic force of magnitude . Imagine that we move the electron so that it is a distance from a helium nucleus (which has two protons and two neutrons). The magnitude of the force on the electron now is , where is
A) 4
B) 2
C) 1
D)
E)
A) 4
B) 2
C) 1
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the situation shown below. Assume that the charges are point particles and that point is twice as far from the positive particle as it is from the negative particle. At which point might the electric field be zero? (If no labelled point seems exactly right, choose the closest.)
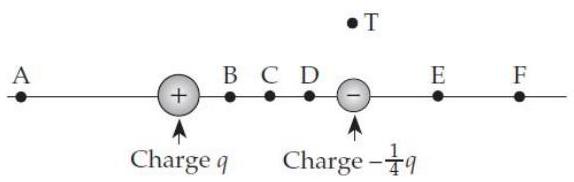
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
F) F
G) T

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
F) F
G) T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The electric field vector at a certain point in space points in the direction labelled BB in figure E1.9.
-We can consider a set of all chlorine atoms in a block of salt (sodium chloride) to be an "extended object."

-We can consider a set of all chlorine atoms in a block of salt (sodium chloride) to be an "extended object."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The electric field vector at a certain point in space points in the direction labelled BB in figure E1.9.

-A neutron?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

-A neutron?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The electric field vector at a certain point in space points in the direction labelled BB in figure E1.9.

-A helium nucleus?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

-A helium nucleus?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the direction of the electric field vector at point in the situation shown below? (Assume that the balls are actually point particles equidistant from .)
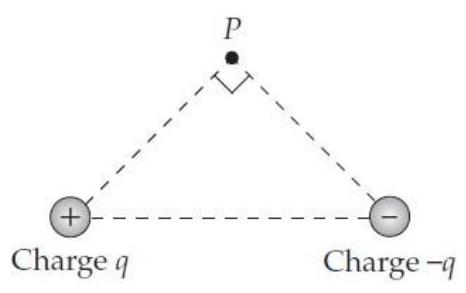
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I) CC
J) DD

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I) CC
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the direction of the electric field vector at point in the situation shown below? (Assume that the balls are actually point particles, they are equally spaced, and that the negative particles are equidistant from .)
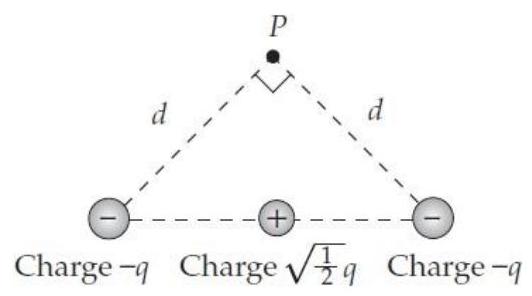
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the direction of the electric field vector at point in the situation shown below? (Assume that the balls are actually point particles with the same magnitudes of charge.)
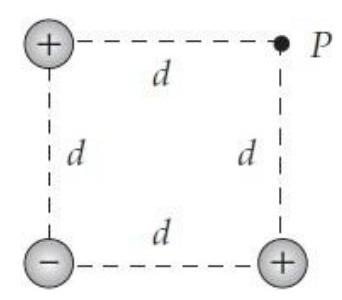
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I) CC
J) DD

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I) CC
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A point where the electric field created by two charged particles is zero must lie somewhere on the infinite line that goes through those particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
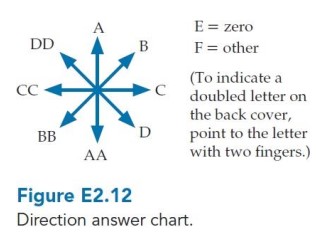
Imagine that we place a positively charged particle a distance from a neutral atom, as shown below. Choose your answers for parts through e from figure E2.12.
-
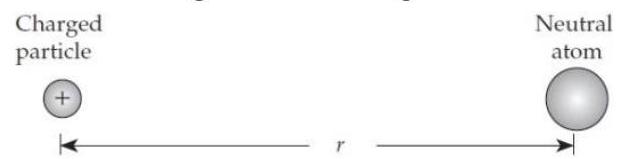
(a) The electric field of the charged particle causes the initially neutral atom to become charged. T or F?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I) CC
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14

Imagine that we place a positively charged particle a distance from a neutral atom, as shown below. Choose your answers for parts through e from figure E2.12.
-(b) What is the direction of the neutral atom's dipole moment after the charged particle is brought near?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15

Imagine that we place a positively charged particle a distance from a neutral atom, as shown below. Choose your answers for parts through e from figure E2.12.
-(c) What is the direction of the neutral atom's electric field at the location of the charged particle?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I) CC
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16

Imagine that we place a positively charged particle a distance from a neutral atom, as shown below. Choose your answers for parts through e from figure E2.12.
-(d) What is the direction of the force that the interaction between the particle and atom exerts on the particle?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

Imagine that we place a positively charged particle a distance from a neutral atom, as shown below. Choose your answers for parts through e from figure E2.12.
-(e) What is the direction of the force that the interaction between the particle and atom exerts on the atom?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The electric field created by a dipole at an arbitrary point in space around that dipole is always parallel to the dipole's dipole moment vector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The dipole moment of an electrically polarized atom always points in the same direction as the external field that has polarized it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Imagine that we place a dipole a distance from a neutral atom, as shown below.
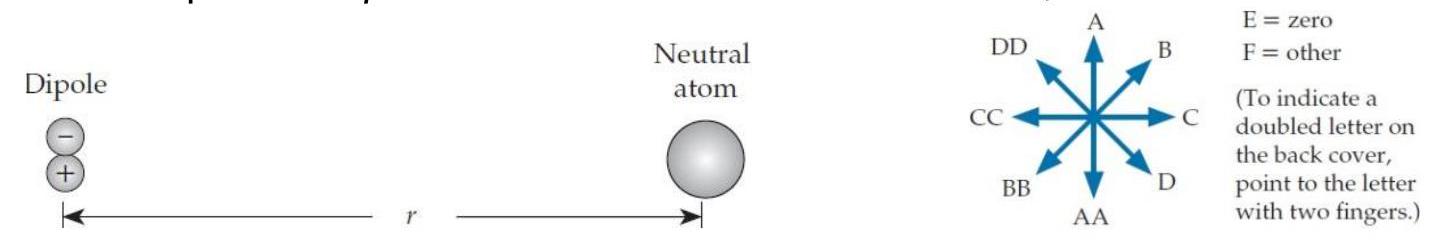
-(a) Will the dipole polarize the neutral atom? Choose E if not or specify the direction of the neutral atom's induced dipole moment from figure E2.12 if nonzero.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

-(a) Will the dipole polarize the neutral atom? Choose E if not or specify the direction of the neutral atom's induced dipole moment from figure E2.12 if nonzero.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Imagine that we place a dipole a distance from a neutral atom, as shown below.

-(b) Use figure E2.12 to specify the direction of the net force that the neutral atom exerts on the dipole. (Hint: Think of any dipole(s) as independent charged particles.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

-(b) Use figure E2.12 to specify the direction of the net force that the neutral atom exerts on the dipole. (Hint: Think of any dipole(s) as independent charged particles.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) Other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the electric field at any point inside a conductor is nonzero, the metal is not in static equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Imagine a neutral atom near an infinite charged plane. The neutral atom will be polarized by the plane's field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Imagine a spherical shell with a uniformly distributed negative charge, as shown below. What are the directions of the field vectors created by that shell at the two points shown?
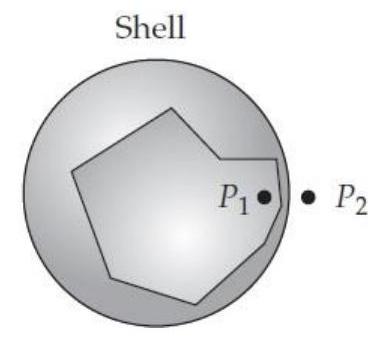
-(a) What is the direction at point just inside the shell?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

-(a) What is the direction at point just inside the shell?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Imagine a spherical shell with a uniformly distributed negative charge, as shown below. What are the directions of the field vectors created by that shell at the two points shown?

-(b) What is the direction at point just outside the shell?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

-(b) What is the direction at point just outside the shell?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Imagine that we place a spherical shell with a uniformly distributed positive charge and a particle with a negative charge as shown below. What are the directions of the total electric field vectors at the two points shown?

-(a) What is the direction at point at the shell's center?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

-(a) What is the direction at point at the shell's center?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Imagine that we place a spherical shell with a uniformly distributed positive charge and a particle with a negative charge as shown below. What are the directions of the total electric field vectors at the two points shown?

-(b) What is the direction at point ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

-(b) What is the direction at point ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) zero
F) other
G) AA
H) BB
I)
J) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider two concentric spherical shells, one with radius and one with radius . Both have the same uniformly distributed charge . Let . Which of the values below is closest to the magnitude of the electric field vector created by these shells at a point just barely inside the outer shell?
A) zero
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G) Other
A) zero
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G) Other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Consider a solid sphere with radius with a charge uniformly spread throughout its volume. The magnitude of the sphere's electric field is at a point on the sphere's surface and is at a point at a distance from the sphere's center. In the relationship , what is the value of ?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 4
E) 8
F) Other
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 4
E) 8
F) Other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The finite wire shown below has a uniformly distributed negative charge. Which of the arrows below is closest to the direction of the field vector that the wire produces at point ? (Point to a letter on the back cover with two fingers to specify a double-letter answer.)

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) AA
F) BB
G) CC
H) DD

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) AA
F) BB
G) CC
H) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The finite disk shown below has a uniformly distributed positive charge. Which of the arrows in figure E2.12 best indicates the direction of the electric field vector that the plate produces at the points specified?
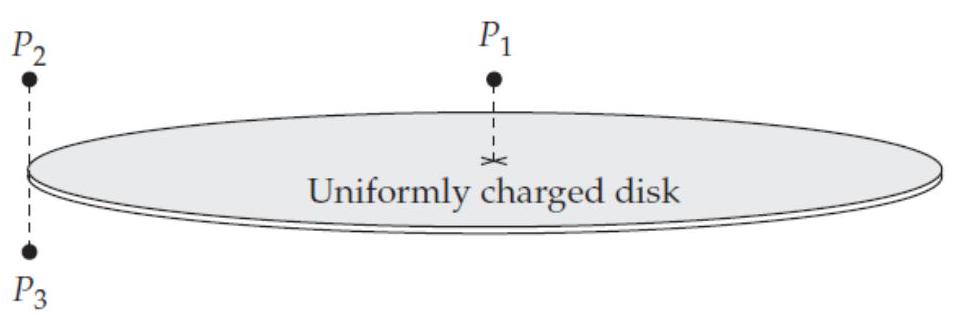
-(a) At point a small distance above the disk's center?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) AA
F) BB
G) CC
H) DD


-(a) At point a small distance above the disk's center?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) AA
F) BB
G) CC
H) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The finite disk shown below has a uniformly distributed positive charge. Which of the arrows in figure E2.12 best indicates the direction of the electric field vector that the plate produces at the points specified?


-(b) At point ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) AA
F) BB
G) CC
H) DD


-(b) At point ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) AA
F) BB
G) CC
H) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The finite disk shown below has a uniformly distributed positive charge. Which of the arrows in figure E2.12 best indicates the direction of the electric field vector that the plate produces at the points specified?


-(c) At point ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) AA
F) BB
G) CC
H) DD


-(c) At point ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) AA
F) BB
G) CC
H) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The units of the electric field are N/C. We can alternatively say the field has units of .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A single particle can have potential energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Even if we define the potential to be zero at infinity, the potential created by a charge distribution can be negative at another point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider a point midway between two identical charged particles. The potential at point is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Consider a point midway between two particles, one with charge and one with charge . The electric field vector at point is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider a point midway between two identical charged particles. The electric field vector at point is zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider a point midway between two identical charged particles. The electric field vector at point is zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In each of the situations shown below, the gray balls represent charged particles whose charges all have the same magnitude but whose signs may be different.
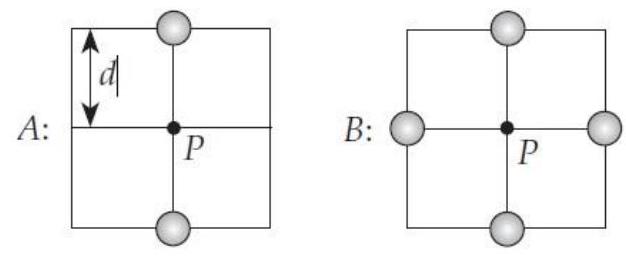
The potential at point has the same value in both cases (the reference position is infinity). In which case is the electric field magnitude larger at point ?
A) Case
B) Case
C) as the same nonzero value in both cases.
D) is zero in both cases.
E) The answer depends on information not specified.

The potential at point has the same value in both cases (the reference position is infinity). In which case is the electric field magnitude larger at point ?
A) Case
B) Case
C) as the same nonzero value in both cases.
D) is zero in both cases.
E) The answer depends on information not specified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Two particles whose charges have equal magnitudes but opposite signs are placed as shown. The reference point for zero potential is infinity.
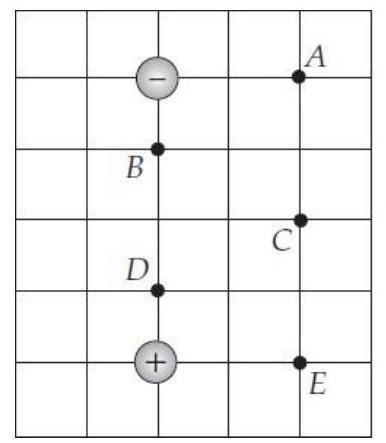
-(a) At which labeled point is the potential largest?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
. None of the labeled points

-(a) At which labeled point is the potential largest?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
. None of the labeled points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Two particles whose charges have equal magnitudes but opposite signs are placed as shown. The reference point for zero potential is infinity.

-(b) At which is the potential smallest?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
F) None of the labeled points

-(b) At which is the potential smallest?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
F) None of the labeled points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Two particles whose charges have equal magnitudes but opposite signs are placed as shown. The reference point for zero potential is infinity.

-(c) At which is the potential zero?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
F) None of the labeled points

-(c) At which is the potential zero?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
F) None of the labeled points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Two particles whose charges have equal magnitudes but opposite signs are placed as shown. The reference point for zero potential is infinity.

-(d) At which is the potential between zero and ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
F) None of the labeled points

-(d) At which is the potential between zero and ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
F) None of the labeled points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consider a region of space where the electric field is uniform with magnitude , as shown below.
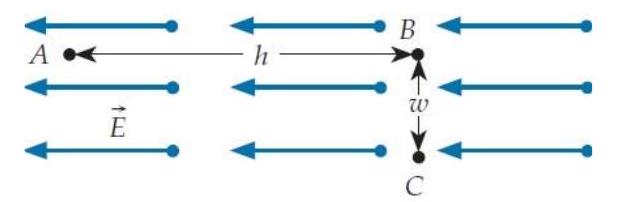
What is the value of the specified potential difference in each case?
(a) ?
(b) ?
(c) ?
Select your responses from the following choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
F.
T. zero

What is the value of the specified potential difference in each case?
(a) ?
(b) ?
(c) ?
Select your responses from the following choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
F.
T. zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider the electric field shown below:
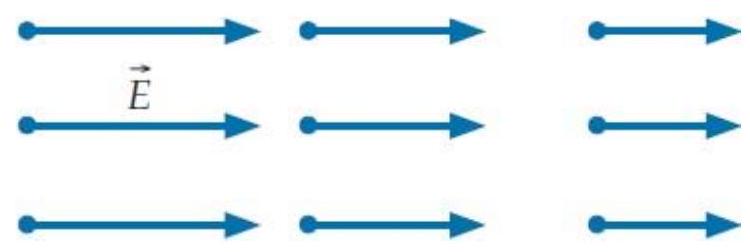
This is a physically possible static electric field (that is, we can calculate a well-defined potential difference between any two points in this field).

This is a physically possible static electric field (that is, we can calculate a well-defined potential difference between any two points in this field).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Consider the electric field shown below:
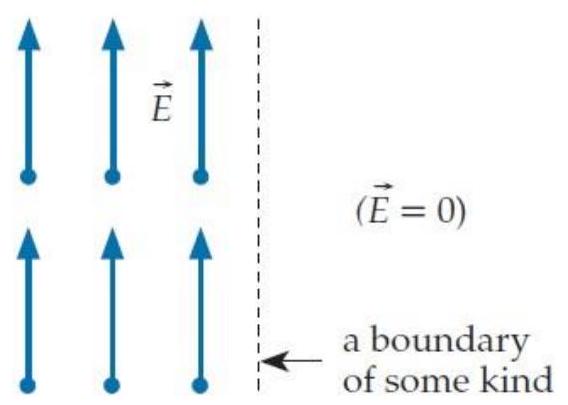
(This hypothetical field is uniform to the left of the boundary shown and zero to the right of that boundary.) This is a physically possible static electric field (that is, we can calculate a well-defined potential difference between any two points in this field).

(This hypothetical field is uniform to the left of the boundary shown and zero to the right of that boundary.) This is a physically possible static electric field (that is, we can calculate a well-defined potential difference between any two points in this field).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If (where is a constant) then is:
A)
B)
C)
D) 2azxly
E)
F) something else (specify)
A)
B)
C)
D) 2azxly
E)
F) something else (specify)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider the equipotential diagram shown below and to the left:
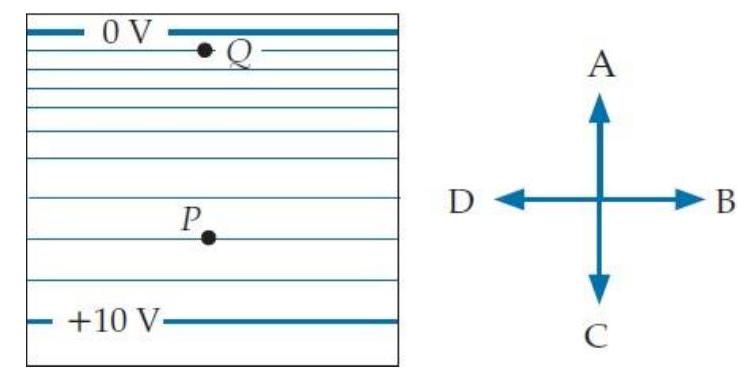
In what direction does the electric field at point point?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

In what direction does the electric field at point point?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Consider the equipotential diagram shown in problem E3T.12. In the expression , what is the approximate value of ?
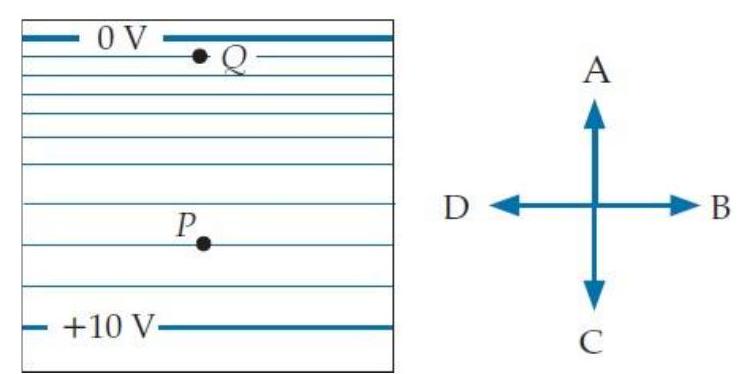
A) 8
B) 2
C) 0
D)
E)
F) Some other value (specify)

A) 8
B) 2
C) 0
D)
E)
F) Some other value (specify)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider the set of graphs shown in the column to the right. These graphs show plots of versus for fixed and in various electric fields. In comparisons, treat negative values as being smaller than positive values.
-(a) In which case is the value of largest at ?
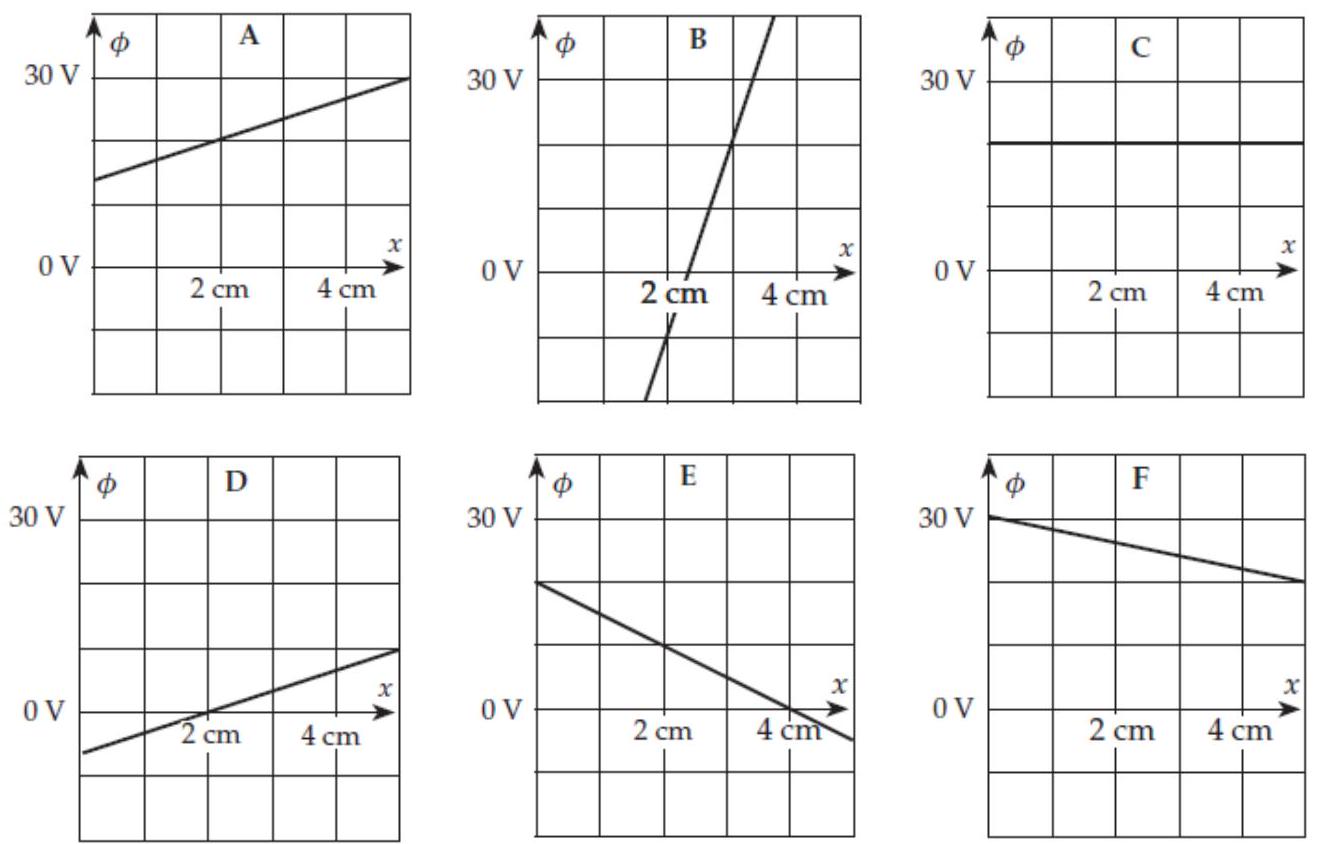
-(a) In which case is the value of largest at ?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consider the set of graphs shown in the column to the right. These graphs show plots of versus for fixed and in various electric fields. In comparisons, treat negative values as being smaller than positive values.
-(b) In which case is the value of smallest at ?
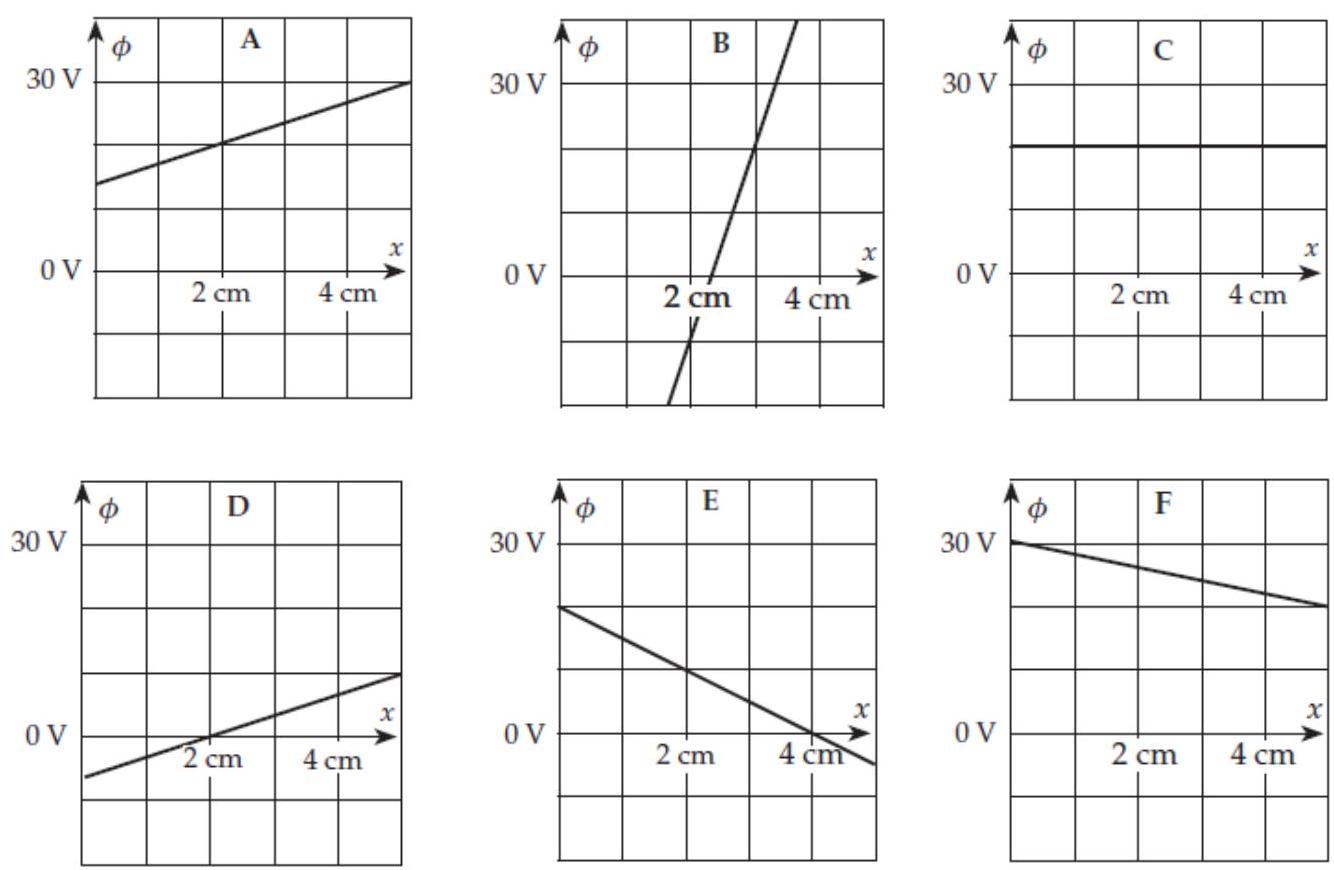
-(b) In which case is the value of smallest at ?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Consider the set of graphs shown in the column to the right. These graphs show plots of versus for fixed and in various electric fields. In comparisons, treat negative values as being smaller than positive values.
-(c) In which case is the value of the same at as it is in case ?
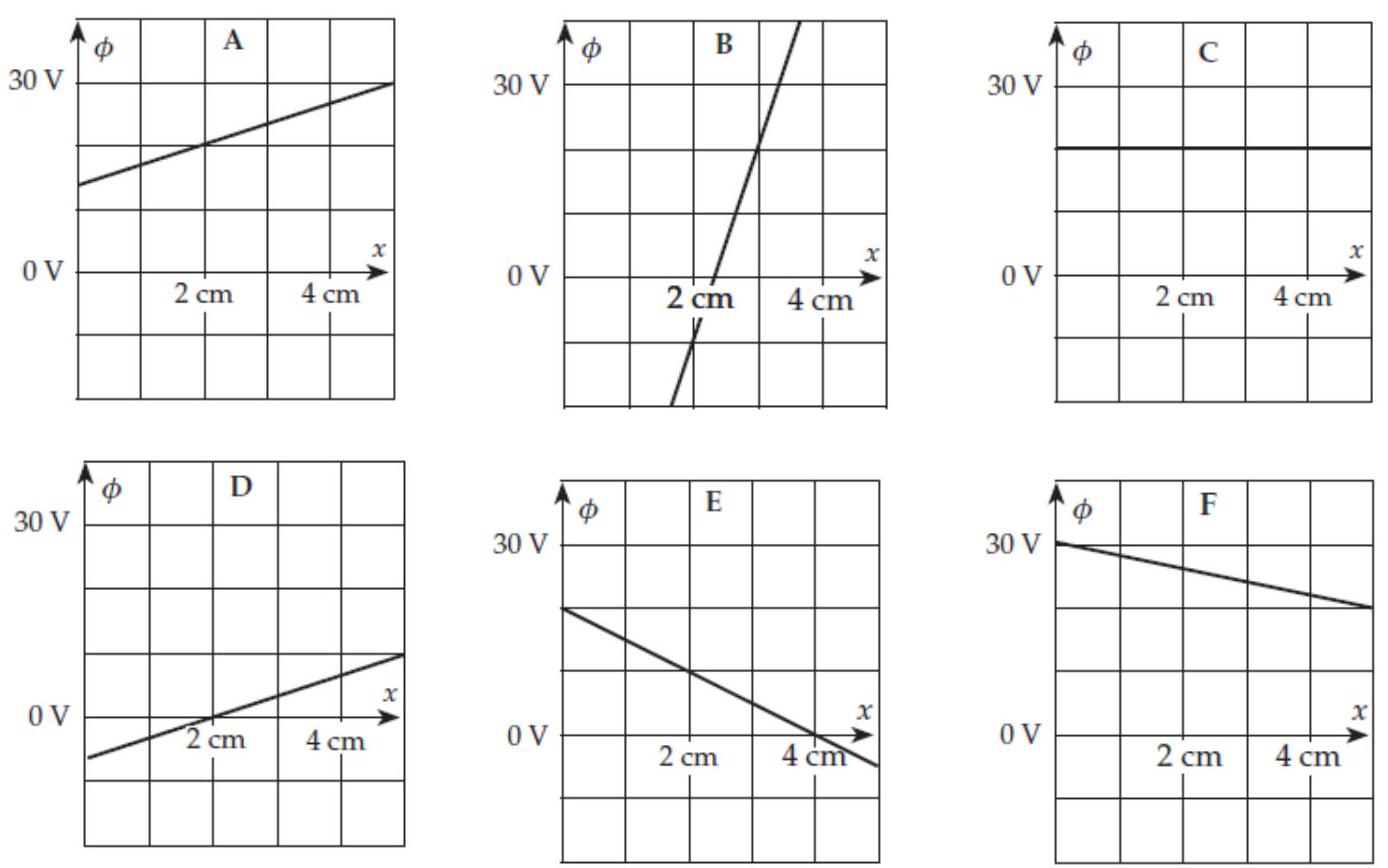
-(c) In which case is the value of the same at as it is in case ?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Consider the set of graphs shown in the column to the right. These graphs show plots of versus for fixed and in various electric fields. In comparisons, treat negative values as being smaller than positive values.
-(d) In which case is the at ?
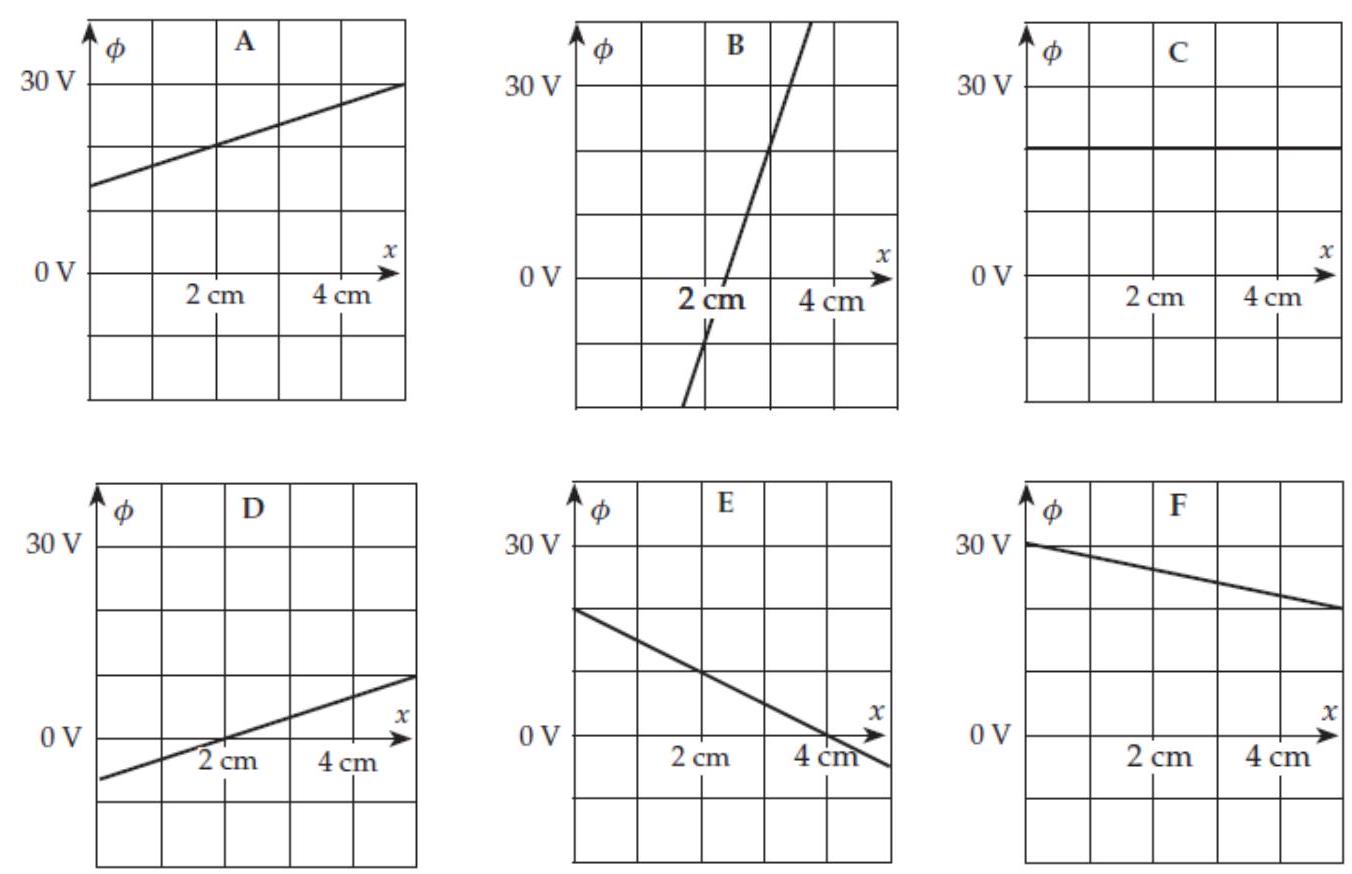
-(d) In which case is the at ?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Consider the situation shown below. Object is a metal sphere with zero net charge, and objects and are particles with charges and , respectively. Point is at the sphere's center. Answer each question below by choosing one of the arrows to the right of the picture or by choosing answer . (If you are using the letters on the back cover to display your answer, you can indicate the double-letter choices by pointing to a letter with two fingers.)
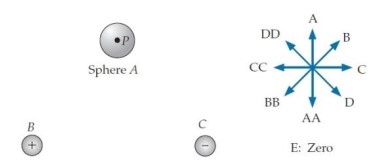
-(a) Which arrow best indicates the direction of the electric field at point created by particle ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) AA
G) BB
H) CC
I) DD

-(a) Which arrow best indicates the direction of the electric field at point created by particle ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) AA
G) BB
H) CC
I) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Consider the situation shown below. Object is a metal sphere with zero net charge, and objects and are particles with charges and , respectively. Point is at the sphere's center. Answer each question below by choosing one of the arrows to the right of the picture or by choosing answer . (If you are using the letters on the back cover to display your answer, you can indicate the double-letter choices by pointing to a letter with two fingers.)

-(b) Which arrow best indicates the direction of the electric field at point created by particle ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) AA
G) BB
H) CC
I) DD

-(b) Which arrow best indicates the direction of the electric field at point created by particle ?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) AA
G) BB
H) CC
I) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider the situation shown below. Object is a metal sphere with zero net charge, and objects and are particles with charges and , respectively. Point is at the sphere's center. Answer each question below by choosing one of the arrows to the right of the picture or by choosing answer . (If you are using the letters on the back cover to display your answer, you can indicate the double-letter choices by pointing to a letter with two fingers.)

-(c) Which arrow best indicates the direction of the electric field at point created by the charge distribution on the sphere's surface?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) AA
G) BB
H) CC
I) DD

-(c) Which arrow best indicates the direction of the electric field at point created by the charge distribution on the sphere's surface?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) AA
G) BB
H) CC
I) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Consider the situation shown below. Object is a metal sphere with zero net charge, and objects and are particles with charges and , respectively. Point is at the sphere's center. Answer each question below by choosing one of the arrows to the right of the picture or by choosing answer . (If you are using the letters on the back cover to display your answer, you can indicate the double-letter choices by pointing to a letter with two fingers.)

-(d) Which arrow best indicates the position (relative to ) of the greatest concentration of positive charge on the sphere's surface?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) AA
G) BB
H) CC
I) DD

-(d) Which arrow best indicates the position (relative to ) of the greatest concentration of positive charge on the sphere's surface?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) Zero
F) AA
G) BB
H) CC
I) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider the situation below. Object is a metal sphere with zero net charge, and objects and are particles with the same negative charge. Which choice shown to the right best indicates the direction of the electric field at point ? (If you are using the letters on the back cover to indicate your answer, you can indicate the double-letter choices by pointing to a letter with two fingers.)
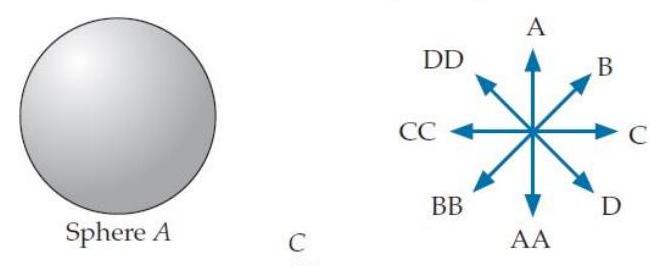
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E: Zero
E) Zero
F) AA
G) BB
H) CC
I) DD

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E: Zero
E) Zero
F) AA
G) BB
H) CC
I) DD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Momentum is not conserved in an inelastic collision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Imagine a neutral atom near an infinite charged plane. Will the atom be attracted to the plate (A), repelled by it (B) or experience no force from it (C)?
(A) A
(B) B
(C)
(A) A
(B) B
(C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A closed metal can (in static equilibrium) will perfectly shield a point in its interior from the static field of any external charged particle(s).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Every fundamental charged particle has an antiparticle such that when the particle and antiparticle collide, they
annihilate each other to create two (uncharged) photons. What does conservation of charge imply about how a
particle's charge compares to that of its antiparticle? The particle's and antiparticle's charges
A. must be identical in sign and magnitude.
B. must have opposite signs and the same magnitude.
C. must have opposite signs, maybe different magnitudes.
D. must each be zero.
E. are not constrained at all by charge conservation.
annihilate each other to create two (uncharged) photons. What does conservation of charge imply about how a
particle's charge compares to that of its antiparticle? The particle's and antiparticle's charges
A. must be identical in sign and magnitude.
B. must have opposite signs and the same magnitude.
C. must have opposite signs, maybe different magnitudes.
D. must each be zero.
E. are not constrained at all by charge conservation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Because of electrostatic polarization, a sufficiently charged rubber balloon will attract a neutral horizontal insulating plate strongly enough so that the balloon sticks firmly to the plate's bottom. If the horizontal plate is a conductor instead of an insulator, the charged balloon will
A) stick only if the plate is connected to the earth.
B) stick only if the plate is insulated from the earth.
C) stick in either case.
D) not stick at all.
E) repel the plate.
A) stick only if the plate is connected to the earth.
B) stick only if the plate is insulated from the earth.
C) stick in either case.
D) not stick at all.
E) repel the plate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Imagine that we have two identical metal spheres on insulating stands that we give the same negative charge. If we slowly bring the spheres closer and closer together, the charge per unit area on each sphere will at the point nearest the other sphere
A) become increasingly negative.
B) become less negative.
C) remain constant.
A) become increasingly negative.
B) become less negative.
C) remain constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Two metal spheres on insulating stands have the same positive charge . If we reduce the distance between the spheres' centers by a factor of two, the magnitude of the repulsive force between the spheres increases by
A) a bit less than a factor of two.
B) exactly a factor of two.
C) a bit more than a factor of two.
D) a bit less than a factor of four.
E) exactly a factor of four.
F) a bit more than a factor of four.
A) a bit less than a factor of two.
B) exactly a factor of two.
C) a bit more than a factor of two.
D) a bit less than a factor of four.
E) exactly a factor of four.
F) a bit more than a factor of four.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose we suspend a negatively charged ball like a pendulum inside a hollow but completely enclosing metal box. Assume that the ball hangs a few inches from the box's left vertical face. Imagine that we now bring a very strong positively charged object to a point just to the left of the box's left face, so that it is only a few inches away from the suspended ball (though the box's left face is between them). The ball will be deflected
A) strongly toward the external object.
B) strongly away from the external object.
C) weakly toward the external object.
D) weakly away from the external object.
E) not the least little bit.
A) strongly toward the external object.
B) strongly away from the external object.
C) weakly toward the external object.
D) weakly away from the external object.
E) not the least little bit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose the two plates of a parallel-plate capacitor have fixed charges and . If we double the gap between the plates, the:
-(a) potential difference between the plates,
A) quadruples.
B) doubles.
C) remains the same.
D) is reduced by a factor of two.
E) is reduced by a factor of four.
F) some other result (specify).
-(a) potential difference between the plates,
A) quadruples.
B) doubles.
C) remains the same.
D) is reduced by a factor of two.
E) is reduced by a factor of four.
F) some other result (specify).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose the two plates of a parallel-plate capacitor have fixed charges and . If we double the gap between the plates, the:
-(b) the capacitor's capacitance,
A) quadruples.
B) doubles.
C) remains the same.
D) is reduced by a factor of two.
E) is reduced by a factor of four.
F) some other result (specify).
-(b) the capacitor's capacitance,
A) quadruples.
B) doubles.
C) remains the same.
D) is reduced by a factor of two.
E) is reduced by a factor of four.
F) some other result (specify).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose the two plates of a parallel-plate capacitor have fixed charges and . If we double the gap between the plates, the:
-(c) the energy stored in the capacitor
A) quadruples.
B) doubles.
C) remains the same.
D) is reduced by a factor of two.
E) is reduced by a factor of four.
F) some other result (specify).
-(c) the energy stored in the capacitor
A) quadruples.
B) doubles.
C) remains the same.
D) is reduced by a factor of two.
E) is reduced by a factor of four.
F) some other result (specify).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Assume that the Drude model accurately describes a certain metal. If we increase the metal's temperature, its conductivity
A) should increase.
B) should decrease.
C) should remain the same.
D) changes in a way that depends on the specific metal.
A) should increase.
B) should decrease.
C) should remain the same.
D) changes in a way that depends on the specific metal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If each copper atom in a wire were to contribute two conduction electrons instead of just one, its conductivity would
A) increase by a factor of 4 .
B) increase by a factor of 2.
C) remain the same.
D) decrease by a factor of 2 .
E) decrease by a factor of 4 .
A) increase by a factor of 4 .
B) increase by a factor of 2.
C) remain the same.
D) decrease by a factor of 2 .
E) decrease by a factor of 4 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Two wires have a nearly equal electron number density. Assume that the electric field in each wire points directly along the wire, that electric fields in the two wires have the same magnitude, but that the conductivity in wire is twice that in wire . This means that the drift velocity in wire is times that in wire , where is
A) 4 .
B) 2.
C) 1 .
D) .
E) .
F) Impossible to determine from the given information.
A) 4 .
B) 2.
C) 1 .
D) .
E) .
F) Impossible to determine from the given information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Why do you think air is such a poor conductor com-pared to a metal (at normal field strengths)?
A) Air is much less dense than a metal.
B) Electrons can travel much farther in a metal before col-liding with an atom than they can in air.
C) Air molecules are much bigger than metal atoms.
D) Electrons move much more slowly in air.
E) Air normally has very few free charge carriers.
A) Air is much less dense than a metal.
B) Electrons can travel much farther in a metal before col-liding with an atom than they can in air.
C) Air molecules are much bigger than metal atoms.
D) Electrons move much more slowly in air.
E) Air normally has very few free charge carriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Imagine that at a certain place in a river, water moves horizontally to the left. Consider an oriented sur-face facing upward. The flux of water velocity through this surface is
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) zero.
D) Impossible to determine from the given information.
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) zero.
D) Impossible to determine from the given information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Imagine that at a certain place in a river, water moves horizontally to the left. Consider an oriented sur-face that faces in a direction that is upward of right. The flux of water velocity through this surface is
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) zero.
D) Impossible to determine from the given information.
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) zero.
D) Impossible to determine from the given information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Consider two vector fields and . At every point in space, points vertically upward, while points radially away from some central point. But a fixed constant everywhere. Assume that we calculate the flux of and through hemispherical surfaces having the same size and orientation, as shown below. Assume that the tile vectors on each surface point outward. Also assume that in the right-hand case, the central point from which the field radiates is at the center of the flat plane at the bottom of the hemisphere. Do not assume that these fields necessarily represent particle flows.
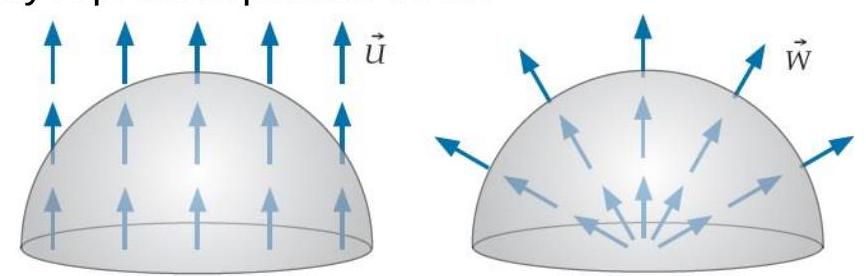
How do the fluxes of these fields through the two identical hemispherical surfaces compare?
A. Field has the larger flux.
B. Field has the larger flux.
C. Both fields have the same flux.
D. The result depends on the surface's radius.
E. We need more information to compare the fluxes.

How do the fluxes of these fields through the two identical hemispherical surfaces compare?
A. Field has the larger flux.
B. Field has the larger flux.
C. Both fields have the same flux.
D. The result depends on the surface's radius.
E. We need more information to compare the fluxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the segment of cylindrical metal wire shown below. Note that the drift speed of electrons is increasing in the wire as we move to the right.
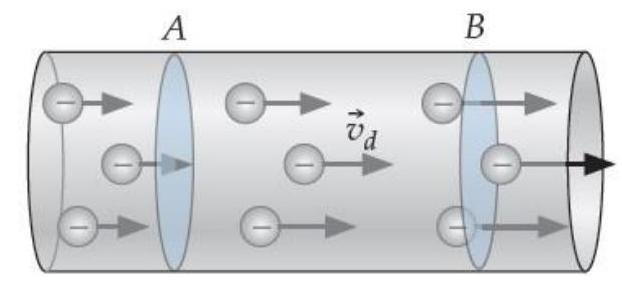
Assume that charge cannot move off the wire. The total charge between the two cross-sectional areas and is
A) Increasing.
B) Decreasing.
C) Remaining the same.

Assume that charge cannot move off the wire. The total charge between the two cross-sectional areas and is
A) Increasing.
B) Decreasing.
C) Remaining the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Consider the segment of cylindrical metal wire shown below. Assume that the drift speed of electrons is everywhere the same in the segment.
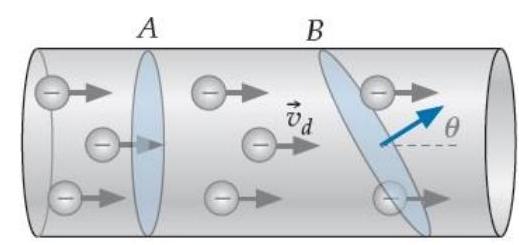
Note that area is tilted so that its nose vector makes an angle of with the drift velocity direction but still spans the wire's entire cross section. How do the current density fluxes through areas and compare?
A) The flux through is greater than the flux through .
B) The flux through is greater than the flux through .
C) The fluxes through and are the same.

Note that area is tilted so that its nose vector makes an angle of with the drift velocity direction but still spans the wire's entire cross section. How do the current density fluxes through areas and compare?
A) The flux through is greater than the flux through .
B) The flux through is greater than the flux through .
C) The fluxes through and are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
81
Suppose that at a given point in a given piece of metal, the drift velocities of electrons are oriented leftward. The direction of the conventional current in this metal
A) is leftward.
B) is rightward.
C) is zero.
D) depends on the type of metal.
A) is leftward.
B) is rightward.
C) is zero.
D) depends on the type of metal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 334 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



