Deck 26: Controversies Over Stabilization Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Controversies Over Stabilization Policy
1
The predominant analytical framework for guiding economic policy during the 1940s,1950s,and early 1960s was
A) the classical model.
B) the monetarist view.
C) the Keynesian view.
D) the equation of exchange.
E) Say's law.
A) the classical model.
B) the monetarist view.
C) the Keynesian view.
D) the equation of exchange.
E) Say's law.
C
2
In the debate between the monetarists and the Keynesians over how best to achieve economic stability,the monetarists have tended to emphasize the role of
A) aggregate supply shifts.
B) economic dualism.
C) random events.
D) the federal budget.
E) the money supply.
A) aggregate supply shifts.
B) economic dualism.
C) random events.
D) the federal budget.
E) the money supply.
E
3
Supply-siders advocate influencing aggregate supply through the use of reductions in
A) spending.
B) income.
C) money.
D) tax rates.
E) foreign imports.
A) spending.
B) income.
C) money.
D) tax rates.
E) foreign imports.
D
4
Philosophically,the monetarists are most closely aligned with the views of
A) Karl Marx.
B) Keynes.
C) classical economists.
D) the Federal Reserve System.
E) Walter Heller.
A) Karl Marx.
B) Keynes.
C) classical economists.
D) the Federal Reserve System.
E) Walter Heller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The monetarist view gained adherents in the late 1960s because
A) of the obvious difficulty in using fiscal policy to restrain spending.
B) the 1968 surtax was effective in reducing inflation.
C) it was demonstrated empirically that MV = PQ.
D) at the time the U.S. economy was stagnant.
E) Keynesians and monetarists finally agreed on the line of causation between the money supply and GDP.
A) of the obvious difficulty in using fiscal policy to restrain spending.
B) the 1968 surtax was effective in reducing inflation.
C) it was demonstrated empirically that MV = PQ.
D) at the time the U.S. economy was stagnant.
E) Keynesians and monetarists finally agreed on the line of causation between the money supply and GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Until the Great Depression of the 1930s,the prevailing theory on the price level was the ________ theory.
A) rational expectations/supply
B) pendular
C) crude quantity
D) sunspot
E) Keynesian
A) rational expectations/supply
B) pendular
C) crude quantity
D) sunspot
E) Keynesian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When a central bank is required to provide enough information for markets and the public to understand and evaluate what the monetary authorities are doing,the central bank must have adopted a monetary policy framework known as
A) the cult of personality.
B) time inconsistency.
C) menu pricing.
D) functional finance.
E) inflation targeting.
A) the cult of personality.
B) time inconsistency.
C) menu pricing.
D) functional finance.
E) inflation targeting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In which of the following countries has the central bank NOT adopted the policy framework known as inflation targeting?
A) Australia
B) Canada
C) Sweden
D) the United Kingdom
E) the United States
A) Australia
B) Canada
C) Sweden
D) the United Kingdom
E) the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the debate between the monetarists and the Keynesians over how best to achieve economic stability,Keynesians have tended to emphasize the role of
A) aggregate supply shifts.
B) economic dualism.
C) random events.
D) the federal budget.
E) the money supply.
A) aggregate supply shifts.
B) economic dualism.
C) random events.
D) the federal budget.
E) the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Supply-side economics had its greatest influence on economic policy debate during the
A) 1920s.
B) 1930s.
C) 1940s and 1950s.
D) 1960s.
E) 1970s and 1980s.
A) 1920s.
B) 1930s.
C) 1940s and 1950s.
D) 1960s.
E) 1970s and 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The new classical macroeconomists conclude that
A) monetary and fiscal stabilization policies are most effective at countering supply-side shocks.
B) the short-run aggregate supply curve is unaffected by expected changes in the price level.
C) if firms and individuals formulate expectations rationally, they will frustrate activist government stabilization policy.
D) real output will increase as long as wage increases exceed price increases, thus stimulating aggregate demand.
E) firms and individuals can be counted on to make systematic errors in forecasting the future.
A) monetary and fiscal stabilization policies are most effective at countering supply-side shocks.
B) the short-run aggregate supply curve is unaffected by expected changes in the price level.
C) if firms and individuals formulate expectations rationally, they will frustrate activist government stabilization policy.
D) real output will increase as long as wage increases exceed price increases, thus stimulating aggregate demand.
E) firms and individuals can be counted on to make systematic errors in forecasting the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The phrase "You can't push on a string" is
A) a line from a 1930s song.
B) used to suggest that monetary policy can make money available but cannot ensure it will be spent.
C) an analogy used by monetarists to describe the ineffectiveness of fiscal policy.
D) used by rational expectations theorists in their criticisms of supply-side economics.
E) a reference to the fact that Congress is in control of the government's purse strings and determines spending without regard to economic impact.
A) a line from a 1930s song.
B) used to suggest that monetary policy can make money available but cannot ensure it will be spent.
C) an analogy used by monetarists to describe the ineffectiveness of fiscal policy.
D) used by rational expectations theorists in their criticisms of supply-side economics.
E) a reference to the fact that Congress is in control of the government's purse strings and determines spending without regard to economic impact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to the new classical macroeconomists,the gap between actual and potential output is a result of
A) perfectly inflexible wages and prices.
B) a horizontal short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) the inability to accurately estimate depreciation when measuring national output.
D) anticipated changes in the money supply.
E) random forecasting errors.
A) perfectly inflexible wages and prices.
B) a horizontal short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) the inability to accurately estimate depreciation when measuring national output.
D) anticipated changes in the money supply.
E) random forecasting errors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A basic assumption of the new classical macroeconomists is that
A) fluctuations in aggregate demand are impossible in the short run.
B) MQ is identical to real GDP.
C) output is inversely related to the tax rate.
D) markets work efficiently.
E) most unemployment is involuntary.
A) fluctuations in aggregate demand are impossible in the short run.
B) MQ is identical to real GDP.
C) output is inversely related to the tax rate.
D) markets work efficiently.
E) most unemployment is involuntary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The monetarist views of economic stabilization policy gained significant support during the late
A) 1930s.
B) 1940s.
C) 1950s.
D) 1960s.
E) 1970s.
A) 1930s.
B) 1940s.
C) 1950s.
D) 1960s.
E) 1970s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The new classical macroeconomists stress that output fluctuations and unemployment
A) result from random errors and cannot be minimized by government stabilization policies.
B) require rational government actions to reduce the gap between actual and potential output.
C) will disappear if most large industries are nationalized.
D) are absent in a free market capitalist economy.
E) can be minimized if all sectors of the economy rationally expect high rates of inflation.
A) result from random errors and cannot be minimized by government stabilization policies.
B) require rational government actions to reduce the gap between actual and potential output.
C) will disappear if most large industries are nationalized.
D) are absent in a free market capitalist economy.
E) can be minimized if all sectors of the economy rationally expect high rates of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
According to the new classical macroeconomists,the only government policy changes that can have a substantial impact on output or employment are those that
A) are announced well in advance.
B) involve large budget deficits.
C) are discretionary, rather than adhering to a rule.
D) are unanticipated by businesses and households.
E) are designed to control wages and prices.
A) are announced well in advance.
B) involve large budget deficits.
C) are discretionary, rather than adhering to a rule.
D) are unanticipated by businesses and households.
E) are designed to control wages and prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When individuals and firms base their expectations on the best use of whatever information is available,they conform to the theory of ________ expectations.
A) great
B) passive
C) limited
D) systematic
E) rational
A) great
B) passive
C) limited
D) systematic
E) rational

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Monetary policy seems to be of little use during a depression because
A) even though money is made available, there is no way to ensure it will be spent.
B) increases in the money supply raise interest rates and choke off investment.
C) people do not save when incomes are low.
D) if more money is created, it goes to pay taxes.
E) increases in money lead to inflation.
A) even though money is made available, there is no way to ensure it will be spent.
B) increases in the money supply raise interest rates and choke off investment.
C) people do not save when incomes are low.
D) if more money is created, it goes to pay taxes.
E) increases in money lead to inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A contemporary economist closely associated with the hypothesis of rational expectations is
A) Milton Friedman.
B) John Muth.
C) John Maynard Keynes.
D) Franco Modigliani.
E) Paul Samuelson.
A) Milton Friedman.
B) John Muth.
C) John Maynard Keynes.
D) Franco Modigliani.
E) Paul Samuelson.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following would be excluded from a list of factors that shift the aggregate supply curve?
A) increases and decreases in the money supply
B) changes in the prices and availabilities of raw materials
C) technological advances
D) new products and processes
E) good or bad weather conditions
A) increases and decreases in the money supply
B) changes in the prices and availabilities of raw materials
C) technological advances
D) new products and processes
E) good or bad weather conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Proponents of real business cycle models argue that the correlation between changes in the money supply and changes in real GDP may reflect the fact that
A) the velocity of money is unpredictable.
B) the quantity of money demanded is relatively insensitive to changes in the interest rate.
C) as real output increases, the demand for money increases, leading to an increase in the money supply.
D) the free enterprise economy has strong self-regulating mechanisms promoting full employment.
E) the equation of exchange varies considerably over the course of the business cycle.
A) the velocity of money is unpredictable.
B) the quantity of money demanded is relatively insensitive to changes in the interest rate.
C) as real output increases, the demand for money increases, leading to an increase in the money supply.
D) the free enterprise economy has strong self-regulating mechanisms promoting full employment.
E) the equation of exchange varies considerably over the course of the business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In real business cycle models,an unfavorable supply shock
A) leads to an increase in the price level and a decline in real GDP.
B) causes the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left.
C) increases total output.
D) increases aggregate demand because price levels rise.
E) leads to significant decreases in long-term involuntary unemployment.
A) leads to an increase in the price level and a decline in real GDP.
B) causes the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left.
C) increases total output.
D) increases aggregate demand because price levels rise.
E) leads to significant decreases in long-term involuntary unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The high rates of inflation in the late 1970s and early 1980s fell primarily because of
A) a severe recession brought on by a tight monetary policy.
B) an easy money policy tied to a large federal deficit.
C) price and wage controls.
D) incomes policies.
E) sharp increases in federal tax rates.
A) a severe recession brought on by a tight monetary policy.
B) an easy money policy tied to a large federal deficit.
C) price and wage controls.
D) incomes policies.
E) sharp increases in federal tax rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An unfavorable supply shock
A)shifts aggregate demand to the right.
B) shifts aggregate supply to the right.
C) shifts aggregate demand to the left.
D) shifts aggregate supply to the left.
E) has no effect on either aggregate supply or aggregate demand, only on the quantities supplied and demanded.
A)shifts aggregate demand to the right.
B) shifts aggregate supply to the right.
C) shifts aggregate demand to the left.
D) shifts aggregate supply to the left.
E) has no effect on either aggregate supply or aggregate demand, only on the quantities supplied and demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
One strategy consistent with the new classical macroeconomists' theories would have
A) fiscal policy focus on maintaining full employment regardless of the size of the resulting budget deficit.
B) monetary policy stick to an announced policy to keep the rate of inflation to some specified low figure.
C) the government emphasize policies of wage and price controls to achieve a targeted full-employment rate with stable prices.
D) monetary authorities impose a structure of variable tax rates that automatically adjusts to changes in the unemployment rate.
E) both fiscal and monetary policy coordinated in a way that ensures that both the Phillips curve and long-run aggregate supply curves are vertical.
A) fiscal policy focus on maintaining full employment regardless of the size of the resulting budget deficit.
B) monetary policy stick to an announced policy to keep the rate of inflation to some specified low figure.
C) the government emphasize policies of wage and price controls to achieve a targeted full-employment rate with stable prices.
D) monetary authorities impose a structure of variable tax rates that automatically adjusts to changes in the unemployment rate.
E) both fiscal and monetary policy coordinated in a way that ensures that both the Phillips curve and long-run aggregate supply curves are vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
New classical macroeconomists believe that the predominant factor causing fluctuations in aggregate demand is
A) increases in taxes.
B) instability in the investment function.
C) the weak self-regulating mechanisms of a free enterprise economy.
D) the unstable marginal propensity to consume.
E) erratic and unpredictable government policy.
A) increases in taxes.
B) instability in the investment function.
C) the weak self-regulating mechanisms of a free enterprise economy.
D) the unstable marginal propensity to consume.
E) erratic and unpredictable government policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the current debate over economic policy,the new classical macroeconomists argue that
A) the economy is at a full-employment equilibrium when money demand equals aggregate demand.
B) fiscal policy is effective in stabilizing the economy.
C) prices are upwardly flexible.
D) economic instability results primarily from the spending behavior of the private sector.
E) discretionary monetary and fiscal policies are ineffective in eliminating recessionary and inflationary gaps and may even promote instability.
A) the economy is at a full-employment equilibrium when money demand equals aggregate demand.
B) fiscal policy is effective in stabilizing the economy.
C) prices are upwardly flexible.
D) economic instability results primarily from the spending behavior of the private sector.
E) discretionary monetary and fiscal policies are ineffective in eliminating recessionary and inflationary gaps and may even promote instability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The view that business cycles are the natural (indeed efficient)response of the economy to changes in technology and the availability of resources is associated with the
A) new Keynesians.
B) traditional Keynesians.
C) monetarists.
D) adaptive demand siders.
E) real business cycle theorists.
A) new Keynesians.
B) traditional Keynesians.
C) monetarists.
D) adaptive demand siders.
E) real business cycle theorists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
According to real business cycle theory,supply shocks cause
A) changes in both the volume of transactions and the demand for money.
B) changes in the price level but no changes in the unemployment rate.
C) no real changes in the economy, only changes in money, wages, and prices.
D) a shift in the aggregate demand curve but no change in the price level.
E) labor surpluses as firms attempt to increase output, holding wages constant.
A) changes in both the volume of transactions and the demand for money.
B) changes in the price level but no changes in the unemployment rate.
C) no real changes in the economy, only changes in money, wages, and prices.
D) a shift in the aggregate demand curve but no change in the price level.
E) labor surpluses as firms attempt to increase output, holding wages constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
With regard to the effectiveness of stabilization policies,the new classical macroeconomists conclude that
A) the price level is fixed, so government stabilization efforts are unnecessary.
B) only unexpected changes in the price level will induce changes in national output.
C) traditional demand-based stabilization policies work effectively if the money supply is fixed.
D) firms and individuals do not formulate expectations rationally, so government must step in.
E) money wage adjustments lag behind nominal adjustments, requiring the Fed to expand credit.
A) the price level is fixed, so government stabilization efforts are unnecessary.
B) only unexpected changes in the price level will induce changes in national output.
C) traditional demand-based stabilization policies work effectively if the money supply is fixed.
D) firms and individuals do not formulate expectations rationally, so government must step in.
E) money wage adjustments lag behind nominal adjustments, requiring the Fed to expand credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Critics of the new classical macroeconomics argue that
A) the necessary information for firms to formulate rational expectations is not generally available.
B) deviations from the natural rate of unemployment are too small and transitory to have resulted from purely unexpected events.
C) the theory neglects the slow and adaptive manner in which wages and prices adjust, thus extending the duration of a business cycle.
D) markets clear too rapidly and continuously for individuals and firms to plan effectively.
E) the natural rate of unemployment stated in the assumptions of the new classical macroeconomic theory is too high to be of much use to policy makers.
A) the necessary information for firms to formulate rational expectations is not generally available.
B) deviations from the natural rate of unemployment are too small and transitory to have resulted from purely unexpected events.
C) the theory neglects the slow and adaptive manner in which wages and prices adjust, thus extending the duration of a business cycle.
D) markets clear too rapidly and continuously for individuals and firms to plan effectively.
E) the natural rate of unemployment stated in the assumptions of the new classical macroeconomic theory is too high to be of much use to policy makers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
It is likely that involuntary unemployment would be reduced if wage rates were
A) rigid.
B) perfectly flexible.
C) indexed to upward movements in the price level but downwardly inflexible.
D) inversely related to labor productivity.
E) positively related to the unemployment rate.
A) rigid.
B) perfectly flexible.
C) indexed to upward movements in the price level but downwardly inflexible.
D) inversely related to labor productivity.
E) positively related to the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
According to real business cycle models
A) total real output does not change in response to changes in aggregate supply and demand; only price levels change.
B) aggregate supply is horizontal so that fluctuations in real GDP result from changes in aggregate demand.
C) changes in total real output vary inversely with changes in real GDP.
D) real output cannot grow faster than the real rate of interest.
E) real wages tend to fall when real GDP falls and rise when real GDP rises.
A) total real output does not change in response to changes in aggregate supply and demand; only price levels change.
B) aggregate supply is horizontal so that fluctuations in real GDP result from changes in aggregate demand.
C) changes in total real output vary inversely with changes in real GDP.
D) real output cannot grow faster than the real rate of interest.
E) real wages tend to fall when real GDP falls and rise when real GDP rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Both the new Keynesians and traditional Keynesians would disagree with which of the following ideas?
A) Prices and wages tend to adjust slowly in the short run.
B) Real GDP adjusts to changes in aggregate demand.
C) Discretionary monetary and fiscal policies are necessary to keep the economy stabilized.
D) Changes in business and consumer spending represent a substantial source of economic instability.
E) Markets clear continuously.
A) Prices and wages tend to adjust slowly in the short run.
B) Real GDP adjusts to changes in aggregate demand.
C) Discretionary monetary and fiscal policies are necessary to keep the economy stabilized.
D) Changes in business and consumer spending represent a substantial source of economic instability.
E) Markets clear continuously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Real business cycle theorists maintain that business fluctuations are due to
A) changes in the real money supply.
B) inflexible wages and prices.
C) increases and decreases in government spending.
D) shifts in the aggregate supply curve.
E) variability in household spending decisions on durable goods.
A) changes in the real money supply.
B) inflexible wages and prices.
C) increases and decreases in government spending.
D) shifts in the aggregate supply curve.
E) variability in household spending decisions on durable goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In real business cycle models,a favorable supply shock
A)pushes the aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) causes real GDP to rise.
C) lowers the income of firms and individuals.
D) increases the price level.
E) pushes the aggregate supply curve to the left.
A)pushes the aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) causes real GDP to rise.
C) lowers the income of firms and individuals.
D) increases the price level.
E) pushes the aggregate supply curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A favorable supply shock
A)pushes the aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) shifts aggregate supply to the right.
Shifts aggregate supply to the left
C) shifts aggregate demand to the left.
D)shifts aggregate demand to the right.
E) has no effect on either the aggregate supply or aggregate demand, only on the quantities supplied and demanded.
A)pushes the aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) shifts aggregate supply to the right.
Shifts aggregate supply to the left
C) shifts aggregate demand to the left.
D)shifts aggregate demand to the right.
E) has no effect on either the aggregate supply or aggregate demand, only on the quantities supplied and demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
That wage and price rigidities cause changes in aggregate demand to lead to changes in real output is a concept associated with
A) classical economists.
B) new classical macroeconomists.
C) real business cycle theorists.
D) new and traditional Keynesians.
E) supply-side economists.
A) classical economists.
B) new classical macroeconomists.
C) real business cycle theorists.
D) new and traditional Keynesians.
E) supply-side economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Critics of real business cycle models argue that
A) the model works only under conditions of inflexible wages and prices.
B) its proponents fail to identify supply shock events that could be used to explain most of the actual booms and recessions.
C) the theory places too much emphasis on fluctuations in the money supply and its velocity of circulation.
D) only the Great Depression of the 1930s fits the real business cycle theory closely.
E) its assumption of a vertical long-run aggregate demand curve does not conform to either sound economic theory or empirical evidence.
A) the model works only under conditions of inflexible wages and prices.
B) its proponents fail to identify supply shock events that could be used to explain most of the actual booms and recessions.
C) the theory places too much emphasis on fluctuations in the money supply and its velocity of circulation.
D) only the Great Depression of the 1930s fits the real business cycle theory closely.
E) its assumption of a vertical long-run aggregate demand curve does not conform to either sound economic theory or empirical evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The belief that the self-regulating capabilities of a market economy are insufficient to ensure a stable,full-employment equilibrium is associated with
A) monetarists.
B) Keynesians.
C) supply siders.
D) rational expectations theorists.
E) new classical macroeconomists.
A) monetarists.
B) Keynesians.
C) supply siders.
D) rational expectations theorists.
E) new classical macroeconomists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Both the new Keynesians and the new classical economists have
A) agreed that changes in the price level are unrelated to changes in the money supply.
B) concluded that the U.S. business cycle is dead.
C) advocated the elimination of the Federal Reserve System.
D) adopted the theory of rational expectations.
E) seen their theories become so divergent since the 1960s that they are useless to policy makers.
A) agreed that changes in the price level are unrelated to changes in the money supply.
B) concluded that the U.S. business cycle is dead.
C) advocated the elimination of the Federal Reserve System.
D) adopted the theory of rational expectations.
E) seen their theories become so divergent since the 1960s that they are useless to policy makers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
One explanation for why product prices adjust slowly is that
A) most markets are perfectly competitive.
B) businesses incur menu costs when they change prices.
C) markets clear continuously, making price adjustments difficult.
D) if wages adjust rapidly, prices take a while to catch up.
E) most markets are subject to government price control laws.
A) most markets are perfectly competitive.
B) businesses incur menu costs when they change prices.
C) markets clear continuously, making price adjustments difficult.
D) if wages adjust rapidly, prices take a while to catch up.
E) most markets are subject to government price control laws.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The basic distinction between a rigid policy rule and a feedback policy rule is that a rigid policy rule
A) specifies completely the behavior of the variable influenced by the rule; a feedback rule allows that variable to change.
B) requires congressional action; a feedback rule is governed by the Fed.
C) targets the money supply; a feedback rule is used when controlling interest rates.
D) is advocated by the new Keynesians; traditional Keynesians favor a feedback policy rule.
E) is used when targeting the full-employment level of real GDP; a feedback rule is used when targeting the full-employment level of nominal GDP.
A) specifies completely the behavior of the variable influenced by the rule; a feedback rule allows that variable to change.
B) requires congressional action; a feedback rule is governed by the Fed.
C) targets the money supply; a feedback rule is used when controlling interest rates.
D) is advocated by the new Keynesians; traditional Keynesians favor a feedback policy rule.
E) is used when targeting the full-employment level of real GDP; a feedback rule is used when targeting the full-employment level of nominal GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The effectiveness of a market economy's self-regulating mechanisms in stabilizing the economy is most closely associated with
A) new Keynesians.
B) Marxists.
C) traditional Keynesians.
D) socialists.
E) new classical macroeconomists.
A) new Keynesians.
B) Marxists.
C) traditional Keynesians.
D) socialists.
E) new classical macroeconomists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Ampere Electronics estimates that it costs $50,000 to change its catalogs,price lists,and billing system when it changes prices.Under which of the following situations would a price increase be clearly profitable?
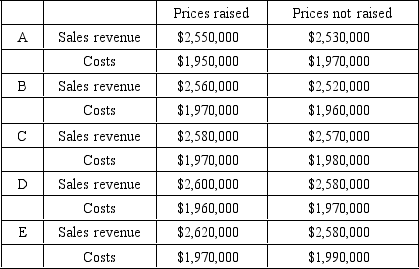
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Opponents of policy activism argue that even if intended private spending is NOT stable,economic stability nonetheless occurs because of
A) large government budget deficit spending.
B) the willingness of banks to hold excess reserves.
C) offsetting fluctuations in the velocity of circulation.
D) flexible wages and prices.
E) the acceleration effect.
A) large government budget deficit spending.
B) the willingness of banks to hold excess reserves.
C) offsetting fluctuations in the velocity of circulation.
D) flexible wages and prices.
E) the acceleration effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following theories might the new Keynesians use to explain wage rigidity?
A) permanent income hypothesis
B) labor theory of value
C) law of diminishing returns
D) implicit contract theory
E) quantity theory of money
A) permanent income hypothesis
B) labor theory of value
C) law of diminishing returns
D) implicit contract theory
E) quantity theory of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Some argue that according to implicit contract theory,unemployment is really voluntary since
A) workers enter freely into these agreements, recognizing that they are accepting the risk of unemployment.
B) firms agree not to lay off anyone if the economy should turn down.
C) under such contracts wages are tied to a firm's profits, minimizing involuntary unemployment.
D) the importance of seniority in hiring practices is minimized.
E) under such contracts wage rates are tied directly to the market demand and supply conditions.
A) workers enter freely into these agreements, recognizing that they are accepting the risk of unemployment.
B) firms agree not to lay off anyone if the economy should turn down.
C) under such contracts wages are tied to a firm's profits, minimizing involuntary unemployment.
D) the importance of seniority in hiring practices is minimized.
E) under such contracts wage rates are tied directly to the market demand and supply conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Proponents of policy activism argue that the time period required for wages and prices to adjust during a severe recession would be
A) intolerably long and entail great human cost.
B) quite short and promote a quick recovery.
C) unimportant given the relative stability of the components of private spending.
D) shortened by balancing the federal budget.
E) dependent on the ratio of nominal to real GDP.
A) intolerably long and entail great human cost.
B) quite short and promote a quick recovery.
C) unimportant given the relative stability of the components of private spending.
D) shortened by balancing the federal budget.
E) dependent on the ratio of nominal to real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The notion that workers are more inclined to shun risk and accept stable wages with layoffs based on seniority is an important element in
A) the theory of deferred payments.
B) new classical macroeconomic theory.
C) profit-sharing plans.
D) the "efficient insider" hypothesis.
E) implicit contract theory.
A) the theory of deferred payments.
B) new classical macroeconomic theory.
C) profit-sharing plans.
D) the "efficient insider" hypothesis.
E) implicit contract theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If menu costs associated with a price increase are $15,000,under which of the following situations will it pay the firm to raise prices?
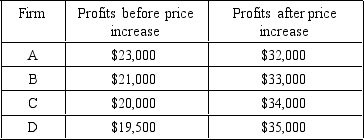
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) It should raise prices in all of these situations.

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) It should raise prices in all of these situations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The next question is based on the following table:
Wage Increases in First, Second, and Third Years of Union Contracts, United States, 1997-2003
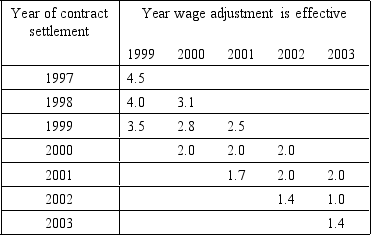
What can be said on the basis of the union contract settlement data shown?
A) Unions are becoming much more powerful in their ability to negotiate wage increases.
B) Price levels in the country are rising rapidly.
C) The most recently negotiated wage increase for a given year is below the average increase prevailing under continuing contracts for that year.
D) Wage rates adjust immediately throughout the economy in response to changing labor market conditions.
E) Labor markets are tight, so firms are increasing employment.
Wage Increases in First, Second, and Third Years of Union Contracts, United States, 1997-2003

What can be said on the basis of the union contract settlement data shown?
A) Unions are becoming much more powerful in their ability to negotiate wage increases.
B) Price levels in the country are rising rapidly.
C) The most recently negotiated wage increase for a given year is below the average increase prevailing under continuing contracts for that year.
D) Wage rates adjust immediately throughout the economy in response to changing labor market conditions.
E) Labor markets are tight, so firms are increasing employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A(n)________ policy rule allows the behavior of the variable governed by the policy rule to change based on future circumstances.
A) effective
B) domestic
C) feedback
D) managerial
E) golden
A) effective
B) domestic
C) feedback
D) managerial
E) golden

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In employer-employee relationships,informal understandings NOT found in writing are called
A) illegal.
B) sidebars.
C) cartels.
D) constitutional.
E) implicit contracts.
A) illegal.
B) sidebars.
C) cartels.
D) constitutional.
E) implicit contracts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Costs incurred by a firm when it changes its prices are called ________ costs.
A) opportunity
B) fixed
C) menu
D) variable
E) advertising
A) opportunity
B) fixed
C) menu
D) variable
E) advertising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
One explanation for why wages adjust slowly and with a substantial lag to changes in aggregate demand is
A) the presence of formal multiyear labor contracts in unionized industries.
B) the widespread practice of profit-sharing plans as part of most employee compensation packages.
C) that such changes have little or no impact on rates of unemployment because the short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) that labor markets clear readily without changes in wage rates.
E) a belief by most workers that real wages are unaffected by changes in the price level.
A) the presence of formal multiyear labor contracts in unionized industries.
B) the widespread practice of profit-sharing plans as part of most employee compensation packages.
C) that such changes have little or no impact on rates of unemployment because the short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) that labor markets clear readily without changes in wage rates.
E) a belief by most workers that real wages are unaffected by changes in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Workers and firms prefer to enter into long-term contracts because
A) workers assume the rate of inflation is going to increase whereas employers believe it is likely to fall.
B) wage negotiations are costly to each side in terms of both time and money.
C) such contracts allow enough time for all labor markets to clear.
D) seniority is more easily acquired by both employers and employees under such agreements.
E) wages, profits, and employment are less affected by changes in aggregate demand under these conditions.
A) workers assume the rate of inflation is going to increase whereas employers believe it is likely to fall.
B) wage negotiations are costly to each side in terms of both time and money.
C) such contracts allow enough time for all labor markets to clear.
D) seniority is more easily acquired by both employers and employees under such agreements.
E) wages, profits, and employment are less affected by changes in aggregate demand under these conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Multiyear labor contracts slow the rate of adjustment of wages because
A) people get used to the size of their paychecks and are reluctant to change them up or down.
B) they are negotiated in real, not nominal, terms.
C) firms set their prices in terms of wages and are not able to change them when labor costs vary frequently.
D) such contracts are not all negotiated, and thus up for renewal on the same cycle, causing the economic impact of older contracts to linger.
E) new labor contracts normally specify wage rates equal to the current national average wage rate.
A) people get used to the size of their paychecks and are reluctant to change them up or down.
B) they are negotiated in real, not nominal, terms.
C) firms set their prices in terms of wages and are not able to change them when labor costs vary frequently.
D) such contracts are not all negotiated, and thus up for renewal on the same cycle, causing the economic impact of older contracts to linger.
E) new labor contracts normally specify wage rates equal to the current national average wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In labor-management relationships,what are implicit contracts?
A) contracts imposed by outside arbitration panels
B) informal unwritten understandings between labor and management
C) agreements between management and union leaders that are kept secret from the rank and file members
D) contracts that do not specify a wage rate but ensure that workers get the current going rate
E) documents that spell out in detail the intent and meaning of the provisions in the formal contract
A) contracts imposed by outside arbitration panels
B) informal unwritten understandings between labor and management
C) agreements between management and union leaders that are kept secret from the rank and file members
D) contracts that do not specify a wage rate but ensure that workers get the current going rate
E) documents that spell out in detail the intent and meaning of the provisions in the formal contract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
One of the points made by economist Richard Gill in the video is that over the period from 1950 to 1980,Keynesian stabilization policies
A) had little impact on nominal GDP but did contribute to systematic increases in the price level.
B) increased the likelihood of severe recessions while keeping prices stable.
C) stabilized the fluctuations in real GDP but contributed to inflationary expectations.
D) encouraged people to save rather than to borrow for spending on things such as art, land, and housing.
E) had little impact on the real economy because wages and prices were flexible and markets cleared.
A) had little impact on nominal GDP but did contribute to systematic increases in the price level.
B) increased the likelihood of severe recessions while keeping prices stable.
C) stabilized the fluctuations in real GDP but contributed to inflationary expectations.
D) encouraged people to save rather than to borrow for spending on things such as art, land, and housing.
E) had little impact on the real economy because wages and prices were flexible and markets cleared.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The view that the cause of economic stabilization is best served by adherence to a rigid monetary rule is associated with
A) Milton Friedman.
B) new Keynesians.
C) Franco Modigliani.
D) policy activists.
E) eclectic subversives.
A) Milton Friedman.
B) new Keynesians.
C) Franco Modigliani.
D) policy activists.
E) eclectic subversives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
According to the Stabilization Policy video,one problem with discretionary fiscal stimulus is that
A) as you expand the economy, spending on foreign goods increases, thus reducing its impact on domestic output and employment.
B) consumers and businesses do not expect the policies to work, so they are unprepared to take advantage of the opportunities created.
C) it works only when monetary authorities reduce the money supply to counter inflation.
D) the employment created is primarily in government agencies and not in the private sector.
E) it leads to stabilization in the long run while allowing existing economic hardship to persist indefinitely.
A) as you expand the economy, spending on foreign goods increases, thus reducing its impact on domestic output and employment.
B) consumers and businesses do not expect the policies to work, so they are unprepared to take advantage of the opportunities created.
C) it works only when monetary authorities reduce the money supply to counter inflation.
D) the employment created is primarily in government agencies and not in the private sector.
E) it leads to stabilization in the long run while allowing existing economic hardship to persist indefinitely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Those who argue that discretionary fiscal and monetary policies are "time inconsistent" advocate instead
A) fine-tuning.
B) policy activism.
C) governmental duplicity.
D) credible policies.
E) ongoing flexibility.
A) fine-tuning.
B) policy activism.
C) governmental duplicity.
D) credible policies.
E) ongoing flexibility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the listed policy rules tends to be supported by the new classical macroeconomists?
A) feedback
B) golden
C) marginal
D) discretionary
E) rigid
A) feedback
B) golden
C) marginal
D) discretionary
E) rigid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The notion that discretionary fiscal and monetary policies are subject to strong incentives to change them in an attempt to achieve short-term gains is called
A) the separation of powers.
B) policy transitivity.
C) systematic inefficiency.
D) rational expectancy.
E) time inconsistency.
A) the separation of powers.
B) policy transitivity.
C) systematic inefficiency.
D) rational expectancy.
E) time inconsistency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Economists' views and analyses of the economy are most clearly influenced by their political beliefs when
A) gathering data.
B) formulating theory.
C) testing hypotheses.
D) making policy recommendations.
E) engaging in positive economics.
A) gathering data.
B) formulating theory.
C) testing hypotheses.
D) making policy recommendations.
E) engaging in positive economics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Fine-tuning the economy
A) is made difficult because of the problem of forecasting the many destabilizing events that regularly occur.
B) has rendered business fluctuations obsolete.
C) became more effective since econometric models were replaced by the leading indicators.
D) has increased the likelihood of recurring depressions.
E) is now possible, but we lack the will to accomplish it.
A) is made difficult because of the problem of forecasting the many destabilizing events that regularly occur.
B) has rendered business fluctuations obsolete.
C) became more effective since econometric models were replaced by the leading indicators.
D) has increased the likelihood of recurring depressions.
E) is now possible, but we lack the will to accomplish it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Among the structural changes that have made recessions less severe in recent years is the
A) willingness of the federal government to balance the budget each and every year.
B) fact that firms on average now hold much larger inventories, which serve as buffers to unexpected shocks.
C) fact that the service sector now dominates the U.S. economy, and the demand for services is typically more stable than that for goods.
D) decision by the Fed to adhere to a strict money growth rate rule.
E) rapid growth in productivity in basic manufacturing industries such as steel and chemicals.
A) willingness of the federal government to balance the budget each and every year.
B) fact that firms on average now hold much larger inventories, which serve as buffers to unexpected shocks.
C) fact that the service sector now dominates the U.S. economy, and the demand for services is typically more stable than that for goods.
D) decision by the Fed to adhere to a strict money growth rate rule.
E) rapid growth in productivity in basic manufacturing industries such as steel and chemicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The notion that the appropriate monetary policy at all times is one that requires the Federal Reserve to expand the money supply at a steady rate of 4 to 5 percent per year is an example of
A) the rules of the game.
B) the rule of reason.
C) a rule of thumb.
D) a rigid policy rule.
E) a feedback policy rule.
A) the rules of the game.
B) the rule of reason.
C) a rule of thumb.
D) a rigid policy rule.
E) a feedback policy rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



