Deck 10: The Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: The Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
1
Arrange the following entries in the order in which air contacts them as air is drawn into the body. a. trachea b. bronchiole c. pharynx
D) alveoli e. larynx
A) e, c, b, a, d
B) c, a, e, d, b
C) b, d, a, c, e
D) c, a, e, b, d
E) c, e, a, b, d
D) alveoli e. larynx
A) e, c, b, a, d
B) c, a, e, d, b
C) b, d, a, c, e
D) c, a, e, b, d
E) c, e, a, b, d
E
2
During exhalation, the pressure inside the lungs
A) initially is higher than atmospheric pressure, but drops as air leaves the body
B) must be maintained higher than atmospheric pressure
C) must be maintained lower than atmospheric pressure
D) gradually elevates as air enters the lungs
E) rapidly elevates
A) initially is higher than atmospheric pressure, but drops as air leaves the body
B) must be maintained higher than atmospheric pressure
C) must be maintained lower than atmospheric pressure
D) gradually elevates as air enters the lungs
E) rapidly elevates
A
3
Which one of the following muscles separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity?
A) intercostal
B) intracostal
C) cardiac
D) diaphragm
E) spleen
A) intercostal
B) intracostal
C) cardiac
D) diaphragm
E) spleen
D
4
During inspiration, intercostal muscles function to
A) flatten the diaphragm
B) pull the rib cage up and out, so that lung volume increases
C) constrict the lungs so that intrapulmonary pressure increases
D) separate the layers of pleural membranes
E) increase blood flow to lung tissue
A) flatten the diaphragm
B) pull the rib cage up and out, so that lung volume increases
C) constrict the lungs so that intrapulmonary pressure increases
D) separate the layers of pleural membranes
E) increase blood flow to lung tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A little girl was playing in the snow one day and found that she was wiping her nose quite often. The "runny nose" that she was experiencing due to the cold temperatures resulted from
A) an insufficient production of mucus
B) an inadequate supply of blood to the nasal epithelium
C) the slowed activity of nasal cilia
D) a buildup of tears in the nasal septum
E) the inability of the sinuses to drain
A) an insufficient production of mucus
B) an inadequate supply of blood to the nasal epithelium
C) the slowed activity of nasal cilia
D) a buildup of tears in the nasal septum
E) the inability of the sinuses to drain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How does external respiration differ from internal respiration?
A) External respiration is done only by some amphibians, which can exchange gases through their skin.
B) External respiration refers to gas exchange between inhaled air and blood, whereas internal respiration refers to gas exchange between the blood and tissue fluids.
C) External respiration involves gills, whereas internal respiration involves lungs.
D) Internal respiration refers to gas exchange between inhaled air and blood, whereas external respiration refers to gas exchange between the blood and tissue fluids.
E) External respiration refers to gas exchange, regardless of its location, whereas internal respiration refers to the cellular process that metabolizes glucose and results in the production of ATP.
A) External respiration is done only by some amphibians, which can exchange gases through their skin.
B) External respiration refers to gas exchange between inhaled air and blood, whereas internal respiration refers to gas exchange between the blood and tissue fluids.
C) External respiration involves gills, whereas internal respiration involves lungs.
D) Internal respiration refers to gas exchange between inhaled air and blood, whereas external respiration refers to gas exchange between the blood and tissue fluids.
E) External respiration refers to gas exchange, regardless of its location, whereas internal respiration refers to the cellular process that metabolizes glucose and results in the production of ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All of the following are involved in the process of breathing EXCEPT which one?
A) bones
B) respiratory system
C) circulatory system
D) skeletal muscles
E) nervous system
A) bones
B) respiratory system
C) circulatory system
D) skeletal muscles
E) nervous system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
During a cough, what is responsible for constricting the size of the trachea?
A) closure of the soft palate
B) cartilage
C) smooth muscle
D) epiglottis
E) skeletal muscle
A) closure of the soft palate
B) cartilage
C) smooth muscle
D) epiglottis
E) skeletal muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following structures is the location of gas exchange between the inhaled air and the blood?
A) trachea
B) bronchioles
C) alveoli
D) bronchi
E) pleura
A) trachea
B) bronchioles
C) alveoli
D) bronchi
E) pleura

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
All of the following are TRUE regarding the effect of smoking on the respiratory system EXCEPT which one?
A) The production of mucus increases in response to the presence of smoke.
B) Smoking destroys cilia lining the respiratory tract.
C) Particles and debris from the smoke accumulate in the mucus of the airway and increase the risk for infections by pathogens.
D) Antimicrobial compounds found in the respiratory mucus of smokers decrease the likelihood of infection.
E) "Smoker's cough" results from the heavy coughing that is necessary to clear accumulated mucus or particles from the airway.
A) The production of mucus increases in response to the presence of smoke.
B) Smoking destroys cilia lining the respiratory tract.
C) Particles and debris from the smoke accumulate in the mucus of the airway and increase the risk for infections by pathogens.
D) Antimicrobial compounds found in the respiratory mucus of smokers decrease the likelihood of infection.
E) "Smoker's cough" results from the heavy coughing that is necessary to clear accumulated mucus or particles from the airway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following occurs as air is drawn through the nose?
A) Water is removed, and the air becomes drier.
B) Carbon dioxide is removed from the air and replaced with oxygen.
C) Air is mixed with odorants to produce smells.
D) Harmful allergens and other toxic materials such as cigarette smoke and asbestos are removed.
E) Air is warmed, filtered, and humidified.
A) Water is removed, and the air becomes drier.
B) Carbon dioxide is removed from the air and replaced with oxygen.
C) Air is mixed with odorants to produce smells.
D) Harmful allergens and other toxic materials such as cigarette smoke and asbestos are removed.
E) Air is warmed, filtered, and humidified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Air in the airways that does not participate in gas exchange is known as
A) expiratory reserve volume
B) tidal volume
C) inspiratory reserve volume
D) dead space volume
E) vital capacity
A) expiratory reserve volume
B) tidal volume
C) inspiratory reserve volume
D) dead space volume
E) vital capacity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
All of the following are part of an individual's vital capacity EXCEPT which one?
A) tidal volume
B) inspiratory reserve
C) expiratory reserve
D) residual volume
A) tidal volume
B) inspiratory reserve
C) expiratory reserve
D) residual volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
During puberty, the increased production of testosterone in males causes the rapid enlargement of which one of the following structures of the respiratory system?
A) pharynx
B) esophagus
C) larynx
D) bronchi
E) bronchioles
A) pharynx
B) esophagus
C) larynx
D) bronchi
E) bronchioles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
During the ingestion of food or liquid, which one of the following tips to block the opening to the trachea?
A) pharynx
B) bronchi
C) epiglottis
D) bronchioles
E) larynx
A) pharynx
B) bronchi
C) epiglottis
D) bronchioles
E) larynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which one of the following best explains why humans must constantly breathe in oxygen in order to stay alive?
A) Oxygen is an important source of energy for cells and is used to make glucose.
B) Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the process of cellular respiration, which results in the production of the ATPs required to fuel cell functions.
C) Oxygen must be available to cells in order for them to make the sugars necessary to supply energy for cell functions.
D) Oxygen is used to drive the anaerobic breakdown of sugars for the production of ATP.
E) Oxygen is converted to carbon dioxide, which is then used to drive the production of ADP.
A) Oxygen is an important source of energy for cells and is used to make glucose.
B) Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the process of cellular respiration, which results in the production of the ATPs required to fuel cell functions.
C) Oxygen must be available to cells in order for them to make the sugars necessary to supply energy for cell functions.
D) Oxygen is used to drive the anaerobic breakdown of sugars for the production of ATP.
E) Oxygen is converted to carbon dioxide, which is then used to drive the production of ADP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Ventilation refers to the process by which
A) gases are exchanged between the cells and the lungs
B) gases are exchanged between the air and the blood
C) air moves into and out of the lungs
D) gases are exchanged between the blood and the cells
E) ATPs are produced
A) gases are exchanged between the cells and the lungs
B) gases are exchanged between the air and the blood
C) air moves into and out of the lungs
D) gases are exchanged between the blood and the cells
E) ATPs are produced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Bronchioles differ from bronchi in that they
A) are wider in diameter
B) carry oxygenated air toward the alveoli
C) filter, warm, and humidify air
D) lack cartilage in their walls
E) are lined by a ciliated epithelium
A) are wider in diameter
B) carry oxygenated air toward the alveoli
C) filter, warm, and humidify air
D) lack cartilage in their walls
E) are lined by a ciliated epithelium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When air entering the respiratory tract leaves the pharynx, it next enters the
A) bronchioles
B) larynx
C) alveoli
D) bronchi
E) sinuses
A) bronchioles
B) larynx
C) alveoli
D) bronchi
E) sinuses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A small amount of fluid is contained in the pleural cavity to
A) promote the exchange of nutrients with both lungs
B) allow gas exchange between the lungs and the blood stream
C) allow white blood cells and macrophages access to foreign antigens entering the body through air
D) function as a lubricant as the lungs move during ventilation
E) serve as a shock absorber for the lungs during body movement
A) promote the exchange of nutrients with both lungs
B) allow gas exchange between the lungs and the blood stream
C) allow white blood cells and macrophages access to foreign antigens entering the body through air
D) function as a lubricant as the lungs move during ventilation
E) serve as a shock absorber for the lungs during body movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Oxygen moves from the lungs into the blood during internal respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Carbaminohemoglobin differs from hemoglobin in that carbaminohemoglobin
A) is found in blood plasma
B) binds carbon monoxide instead of carbon dioxide
C) is found in red blood cells
D) is bound to carbon dioxide
E) transports oxygen from the lungs to the cells
A) is found in blood plasma
B) binds carbon monoxide instead of carbon dioxide
C) is found in red blood cells
D) is bound to carbon dioxide
E) transports oxygen from the lungs to the cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Carbon dioxide is carried from the tissues to the lungs by a variety of mechanisms. Which of the following lists these mechanisms in order representing the mechanism that carries the most carbon dioxide to the mechanism that carries the smallest amount?
A) bicarbonate-carbaminohemoglobin-dissolved in plasma
B) bicarbonate-dissolved in plasma-carbaminohemoglobin
C) dissolved in plasma-bicarbonate-carbaminohemoglobin
D) carbaminohemoglobin-bicarbonate-dissolved in plasma
E) carbaminohemoglobin-dissolved in plasma-bicarbonate
A) bicarbonate-carbaminohemoglobin-dissolved in plasma
B) bicarbonate-dissolved in plasma-carbaminohemoglobin
C) dissolved in plasma-bicarbonate-carbaminohemoglobin
D) carbaminohemoglobin-bicarbonate-dissolved in plasma
E) carbaminohemoglobin-dissolved in plasma-bicarbonate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following disorders is described as follows: damage to motor nerves innervating skeletal muscle; skeletal muscles weaken; death usually results within five years of diagnosis?
A) amytrophic lateral sclerosis
B) pleurisy
C) cystic fibrosis
D) emphysema
E) botulism
A) amytrophic lateral sclerosis
B) pleurisy
C) cystic fibrosis
D) emphysema
E) botulism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The trachea is completely surrounded by rings of cartilage, resulting in an organ that is inflexible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In which one of the following situations is hemoglobin most likely to bind oxygen?
A) in a tissue with a low partial pressure of oxygen
B) in a tissue with a neutral pH
C) in a tissue with a high temperature
D) in a tissue with a low pH
E) in a metabolically active tissue (e.g., muscle)
A) in a tissue with a low partial pressure of oxygen
B) in a tissue with a neutral pH
C) in a tissue with a high temperature
D) in a tissue with a low pH
E) in a metabolically active tissue (e.g., muscle)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
External respiration is the process of
A) transporting gases in the blood stream to target cells
B) exchanging air in lungs with the surrounding environment
C) moving gases into or out of the blood stream within lung tissue
D) gas uptake by target cells
E) carbon dioxide release by cells into the bloodstream
A) transporting gases in the blood stream to target cells
B) exchanging air in lungs with the surrounding environment
C) moving gases into or out of the blood stream within lung tissue
D) gas uptake by target cells
E) carbon dioxide release by cells into the bloodstream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which one of the following is a symptom of botulism?
A) elevated stroke volume
B) paralysis of muscles used for breathing
C) cough yielding green phlegm
D) immune system attack of connective tissue
E) rash
A) elevated stroke volume
B) paralysis of muscles used for breathing
C) cough yielding green phlegm
D) immune system attack of connective tissue
E) rash

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in the body causes
A) a simultaneous increase in the amount of oxygen in the body
B) an increase in the pH of the blood
C) a decrease in the rate at which impulses are released from the respiratory center
D) slow, shallow breathing
E) a decrease in the pH of the cerebrospinal fluid
A) a simultaneous increase in the amount of oxygen in the body
B) an increase in the pH of the blood
C) a decrease in the rate at which impulses are released from the respiratory center
D) slow, shallow breathing
E) a decrease in the pH of the cerebrospinal fluid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The respiratory control center is located
A) in the pulmonary veins
B) in the pulmonary arteries
C) in the medulla oblongata
D) in the right lung
E) throughout the arteries
A) in the pulmonary veins
B) in the pulmonary arteries
C) in the medulla oblongata
D) in the right lung
E) throughout the arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
All of the following are involved in the regulation of the rate and depth of breathing EXCEPT which one?
A) carotid and aortic bodies
B) blood levels of CO₂
C) blood levels of O₂
D) bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli
E) medulla oblongata
A) carotid and aortic bodies
B) blood levels of CO₂
C) blood levels of O₂
D) bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli
E) medulla oblongata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Most of the carbon dioxide released by cells is transported in the venous supply in what form?
A) free carbon dioxide gas
B) oxyhemoglobin
C) soluble bicarbonate ion
D) bound to hemoglobin
E) carbon monoxide
A) free carbon dioxide gas
B) oxyhemoglobin
C) soluble bicarbonate ion
D) bound to hemoglobin
E) carbon monoxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A condition in which wheezing occurs with breathlessness and a persistent cough, and yields yellowish or greenish phlegm is
A) asthma
B) bronchitis
C) lung cancer
D) lupus
E) anemia
A) asthma
B) bronchitis
C) lung cancer
D) lupus
E) anemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
All of the following statements are TRUE regarding lung cancer EXCEPT which one?
A) Symptoms include chest pain, chronic cough, and wheezing.
B) One hundred percent of lung cancers are caused by smoking or exposure to cigarette smoke.
C) Lung cancer may be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation.
D) This type of cancer typically takes many years to develop.
E) Problems associated with lung cancer include inadequate exchange of gases in the alveoli and impairment of blood flow in the pulmonary blood vessels.
A) Symptoms include chest pain, chronic cough, and wheezing.
B) One hundred percent of lung cancers are caused by smoking or exposure to cigarette smoke.
C) Lung cancer may be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation.
D) This type of cancer typically takes many years to develop.
E) Problems associated with lung cancer include inadequate exchange of gases in the alveoli and impairment of blood flow in the pulmonary blood vessels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged with blood directly across the alveoli wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Surfactant is released to reduce surface tension in the alveoli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The rate and depth of normal breathing are determined by
A) oxygen levels in the blood
B) carbon dioxide levels in the blood
C) a pacemaker in the diaphragm
D) a pacemaker in the intercostal muscles
E) carbon monoxide levels in the blood
A) oxygen levels in the blood
B) carbon dioxide levels in the blood
C) a pacemaker in the diaphragm
D) a pacemaker in the intercostal muscles
E) carbon monoxide levels in the blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following results from the stimulation by nerve impulses generated in the respiratory center when they arrive at the muscles involved in inspiration?
A) contraction of the diaphragm
B) reduction in the efficiency of oxygen transport by the blood
C) increase in air pressure in the lungs
D) opening of the trachea
E) downward movement of the ribs
A) contraction of the diaphragm
B) reduction in the efficiency of oxygen transport by the blood
C) increase in air pressure in the lungs
D) opening of the trachea
E) downward movement of the ribs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Burning of carbon-based fuels can produce which one of the following, an odorless gas that competes with oxygen for binding to hemoglobin.
A) carbon tetrachloride
B) nitrogen
C) ozone
D) hydrogen
E) carbon monoxide
A) carbon tetrachloride
B) nitrogen
C) ozone
D) hydrogen
E) carbon monoxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Oxygen-rich blood flows through the heart
A) by entering the right atrium and continuing through the aortic arch
B) via the left atrium and ventricle before entering the systemic circuit
C) on the left side of the heart following returning from the lungs via the pulmonary arteries
D) right to left
E) only through the coronary arteries
A) by entering the right atrium and continuing through the aortic arch
B) via the left atrium and ventricle before entering the systemic circuit
C) on the left side of the heart following returning from the lungs via the pulmonary arteries
D) right to left
E) only through the coronary arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Longer vocal cords generate higher-pitched tones than longer ones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
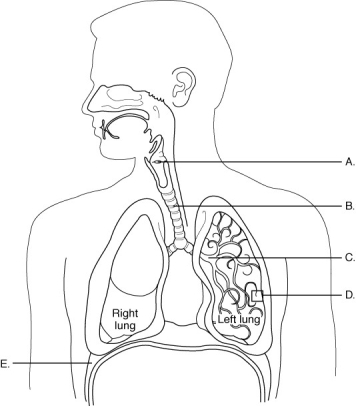
The figure above shows the components of the respiratory system. Match each labeled structure (A-E) to its description.
This structure is also known as the "windpipe."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
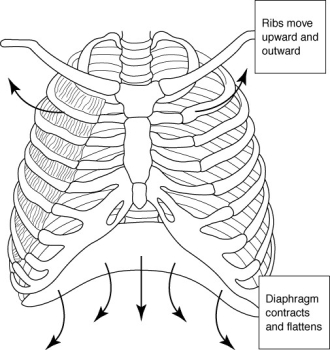
The figure above depicts expiration.

The figure above depicts expiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The respiratory system functions to ________ with the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Hemoglobin binds more tightly to carbon monoxide than to oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in the body results in a decrease in the pH of the cerebrospinal fluid, which results in an increase in breathing rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47

The figure above shows the components of the respiratory system. Match each labeled structure (A-E) to its description.
Site of the vocal cords; the glottis is the opening to this structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Deoxygenated blood is transported to the pulmonary capillaries of the lungs by the pulmonary veins; oxygenated blood is transported away from the pulmonary capillaries by the pulmonary arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

The figure above shows the components of the respiratory system. Match each labeled structure (A-E) to its description.
Contraction of this structure causes it to flatten out, increasing lung volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Antibiotics are the preferred treatment for colds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The rate and depth of normal breathing are controlled by the need to get rid of CO₂.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Hemoglobin in red blood cells can bind both oxygen and carbon dioxide, but not at the same time since it uses the same binding site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53

The figure above shows the components of the respiratory system. Match each labeled structure (A-E) to its description.
Site of external respiration; walls consist of one layer of squamous epithelial cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54

The figure above shows the components of the respiratory system. Match each labeled structure (A-E) to its description.
Large airways that enter each lung and then branch into smaller and smaller airways; walls contain connective tissue, smooth muscles, and cartilage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
There is substantial evidence that children who live with smokers are at an increased risk for asthma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Lung diseases, such as emphysema, can be diagnosed by measuring lung volumes and the rates at which these volumes change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Lung capacity is typically measured with the use of a spirometer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Sound results from the ________ of the vocal cords as air passes through the larynx.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Air spaces in the skull called the ________ drain into the nasal cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
During the cough reflex, the trachea ________ slightly to increase the velocity of air movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The muscles involved in respiration include the ________ muscles located between the ribs and the ________ located between the thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The concentration of ________ is monitored by the aortic and carotid bodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The lower pharynx serves as a passageway for both the ________ and ________ systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The amount of air that enters and leaves the lungs with each breath is the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the figure above, ________ must be released over the inner surface of the sac-like structures to reduce surface tension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Intrapulmonary pressure must be reduced prior to the process of ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
During a normal breathing cycle, pressure changes are essential to the exchange of gases with the environment. Describe what type of pressure changes must occur during ventilation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The pleural cavity, which is located between the pleural membranes, contains small amounts of ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
It is impossible to talk while swallowing because the ________ blocks the opening to the lower respiratory tract, routing food to the esophagus instead of the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The exchange of gases in the lungs occurs between the alveoli and the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The anatomical design of the paired lungs makes them easy to distinguish; the right lung has ________ lobes, whereas the left side has ________ lobes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The concentration of ________ in the blood is monitored indirectly by monitoring the pH of the cerebrospinal fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
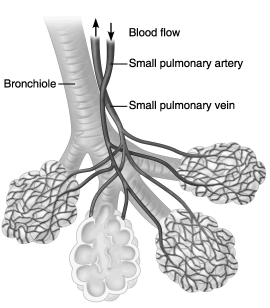
At the end of every ________ is a cluster of ________, where gas exchange takes place.

At the end of every ________ is a cluster of ________, where gas exchange takes place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The basic pattern of inhalation and exhalation is controlled by a region at the base of the brain called the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Oxygen and carbon dioxide both have the ability to bind to hemoglobin, which would seem to be an unfavorable situation for the body, particularly in terms of cellular respiration. What features does the human body use to favor oxygen and not carbon dioxide binding to hemoglobin?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Tobacco smoke contains chemicals that ________ the production of mucus and ________ the activity of cilia in the respiratory system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The structure nicknamed the "Adam's apple" is associated with the ________, part of the respiratory passageway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
During intense physical exercise, human cells and tissues increase their need for oxygen to provide the ATP necessary for work. Why does heart rate have to increase to meet the need for oxygen?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



