Deck 21: Orthopedic Surgery
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Orthopedic Surgery
1
____________is inflammation and infection of the bone and bone marrow. It is a danger with any kind of orthopedic surgery.
Osteomyelitis
2
____________ bacteria are the most common causative organisms of bone infections.
Staphylococcus
3
A(n) __________ fracture is caused by disease.
pathological
4
A partial fracture in a pediatric patient would be termed a ________________ fracture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A complete fracture that penetrates the skin is a(n) ______________ or ________________ fracture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a fracture has more than two pieces, it usually occurs due to a direct crushing force and is called a _____________fracture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The patient slid off the roof, compressing the ends of the tibia into each other, creating a(n)_______________fracture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
As Susie fell when pushed, she fell on her outstretched hand, fracturing the distal radius, which is called a(n)______________ fracture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Match the description.
-Bunion
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Bunion
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Match the description.
-Hammer toe
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Hammer toe
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Match the description.
-Avascular necrosis
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Avascular necrosis
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Match the description.
-Genu valgum
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Genu valgum
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Match the description.
-Ganglion
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Ganglion
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Match the description.
-Subluxation
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Subluxation
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Match the description.
-Sprain
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Sprain
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Match the description.
-Hallux
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Hallux
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Match the description.
-Strain
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Strain
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Match the description.
-Avulsion
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Avulsion
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Match the description.
-Mice
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Mice
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Match the description.
-Coxa
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Coxa
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Match the description.
-Valgus
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Valgus
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Match the description.
-Varus
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Varus
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Match the description.
-Talipes
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles
-Talipes
A) Tendon sheath cyst
B) Tissue torn away from normal attachment(s)
C) Bony growth (exostosis) on medial aspect of first toe
D) Disruption of the blood supply due to trauma, disease, or medications
E) Also known as claw or mallet due to position of joints
F) Foot
G) Injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching
H) Hip
I) Partial dislocation of a joint
J) Turns inward toward midline (foot, toes, or hip)
K) Turns outward away from midline (laterally) (foot, toes, or hip)
L) Stretched or torn ligament
M) Great toe
N) Knees close to the midline, increasing the space between the ankles
O) Locking or pain in joint due to loose particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
As you set up the room for a closed reduction, you lay out the items to be used in order. Put the steps of a closed reduction in order:
-
-


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Cancellous screw
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Cancellous screw
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Cortical screw
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Cortical screw
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Lag screw
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Lag screw
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Cannulated screw
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Cannulated screw
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Kirschner (K-wire)
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Kirschner (K-wire)
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Steinman
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Steinman
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Rod or nail
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Rod or nail
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Orthopedic plates
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Orthopedic plates
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Stainless steel
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Stainless steel
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Artificial knee joint components
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Artificial knee joint components
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Artificial hip joint components
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Artificial hip joint components
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Stimulator
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Stimulator
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Polyester, braided nylon, polypropylene
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Polyester, braided nylon, polypropylene
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Match the type of implant with the description.
-Tap (tapping)
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-Tap (tapping)
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Match the type of implant with the description.
-PMMA (polymethylmethacrylate)
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.
-PMMA (polymethylmethacrylate)
A) Screw with hollow central shaft, usually inserted over a guide wire or pin.
B) Pin segments in larger diameters used for skeletal traction or as guide pin for screws.
C) Femoral/tibial and patellar components.
D) Bone cement to hold prosthesis in place.
E) Screw with closely spaced shallow threads for dense bone found in the diaphysis.
F) Wire segments with smaller diameter used for stabilization/ fixation or guide for screws.
G) Used with screws and bent to fit the bone to hold the fragments in place during healing.
H) Can be used to secure bone to bone, such as the sternum.
I) Low-level current treatment of nonunion or delayed union.
J) Screw with a wider thread and wider-spaced threads used in epiphyseal bone.
K) Used to attach tendon to bone (suture material).
L) Used to create the threads in the bone, typically cortical bone typically.
M) Screw that is partially threaded to compress bone between the screw head and the distal threads.
N) Placed in the intramedullary shaft for fractures of long bones-early ambulation.
O) Acetabular and femoral stem and head components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
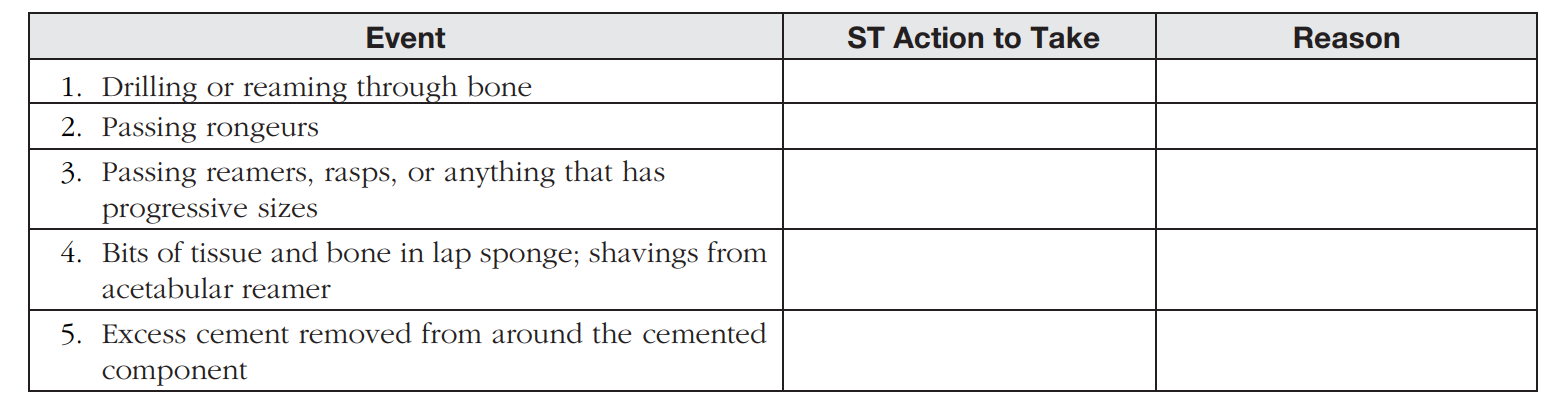
During the orthopedic procedure, there are duties for the surgical technologist. Identify the actions to take for each of these events.
-
-


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Describe what can happen if the metal alloys are mixed or scratches occur on the implant surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



