Deck 8: Productivity and Growth.
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/200
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Productivity and Growth.
1
The rules of the game refer to _____
A) any factor that facilitates production and exchange, such as tax laws and property rights.
B) a gradual but consistent change in the price level until a fair price is attained.
C) the set of election laws that ensure that all elections are fair.
D) the rules that a firm must follow in order to earn a profit.
E) the requirement that households must supply labor to firms.
A) any factor that facilitates production and exchange, such as tax laws and property rights.
B) a gradual but consistent change in the price level until a fair price is attained.
C) the set of election laws that ensure that all elections are fair.
D) the rules that a firm must follow in order to earn a profit.
E) the requirement that households must supply labor to firms.
any factor that facilitates production and exchange, such as tax laws and property rights.
2
Which of the following could cause the production possibilities frontier to shift to the right?
A) more government regulation that stunts economic growth
B) changes in the rules of the game that stunt economic growth
C) lower-quality resources
D) fewer productive resources
E) production of more capital goods and fewer consumer goods
A) more government regulation that stunts economic growth
B) changes in the rules of the game that stunt economic growth
C) lower-quality resources
D) fewer productive resources
E) production of more capital goods and fewer consumer goods
production of more capital goods and fewer consumer goods
3
Which of the following can expand the production possibilities frontier?
A) improved patent laws
B) legal reforms that increase transaction costs
C) reductions in the length of patent protection
D) stringent tax laws for R&D companies
E) the advent of a labor-deepening technology
A) improved patent laws
B) legal reforms that increase transaction costs
C) reductions in the length of patent protection
D) stringent tax laws for R&D companies
E) the advent of a labor-deepening technology
improved patent laws
4
Suppose the production possibilities frontier (PPF) of an economy has been plotted on a graph. If the horizontal axis of the graph measures the output of capital goods and the vertical axis measures the output of consumer goods, then a point inside the PPF represents _____
A) a larger quantity of capital goods than that represented by a point along the PPF.
B) an inefficient output combination of the two goods in the economy.
C) an unattainable output combination of the two goods in the economy.
D) an output combination of more consumer goods than capital goods.
E) a larger quantity of consumer goods than that represented by a point along the PPF.
A) a larger quantity of capital goods than that represented by a point along the PPF.
B) an inefficient output combination of the two goods in the economy.
C) an unattainable output combination of the two goods in the economy.
D) an output combination of more consumer goods than capital goods.
E) a larger quantity of consumer goods than that represented by a point along the PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Long-term growth in production can be explained by _____
A) improvements in the rules of the game that facilitate production and exchange.
B) a gradual but consistent rise in the price level.
C) a rapid and accelerating increase in the price level.
D) a trade surplus that leads to the accumulation of gold.
E) the peaks and troughs of economic fluctuations.
A) improvements in the rules of the game that facilitate production and exchange.
B) a gradual but consistent rise in the price level.
C) a rapid and accelerating increase in the price level.
D) a trade surplus that leads to the accumulation of gold.
E) the peaks and troughs of economic fluctuations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following factors can influence the production possibilities frontier in the future?
A) the amount of capital produced
B) a fall in the rate of inflation
C) a decrease in consumption in an economy
D) an increase in the tax rate
E) a legal reform that increases transaction costs
A) the amount of capital produced
B) a fall in the rate of inflation
C) a decrease in consumption in an economy
D) an increase in the tax rate
E) a legal reform that increases transaction costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is meant by the term standard of living?
A) increases in the amount of available resources
B) better technology
C) the availability of goods and services per capita
D) improvements in the "rules of the game"
E) improvements in the quality of labor
A) increases in the amount of available resources
B) better technology
C) the availability of goods and services per capita
D) improvements in the "rules of the game"
E) improvements in the quality of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A process that transforms resources into goods and services is known as _____
A) the production function.
B) capital deepening.
C) productivity.
D) production.
E) labor productivity.
A) the production function.
B) capital deepening.
C) productivity.
D) production.
E) labor productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The ratio of total output to a specific measure of input is known as _____
A) the production function.
B) capital deepening.
C) productivity.
D) production.
E) labor productivity.
A) the production function.
B) capital deepening.
C) productivity.
D) production.
E) labor productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The production possibilities frontier of an economy is based on the assumption that the _____
A) amount of consumer goods produced in the economy is constant during a given year.
B) quality of labor available in the economy is variable during a given year.
C) patent laws applicable in the economy are constant during a given year.
D) level of technology available in the economy is variable during a given year.
E) economy can produce either capital goods or consumer goods during a given year.
A) amount of consumer goods produced in the economy is constant during a given year.
B) quality of labor available in the economy is variable during a given year.
C) patent laws applicable in the economy are constant during a given year.
D) level of technology available in the economy is variable during a given year.
E) economy can produce either capital goods or consumer goods during a given year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following best describes productivity?
A) Productivity is nominal GDP to a specific measure of output.
B) Productivity is real GDP to a specific measure of output.
C) Productivity is economic growth to a specific measure of output.
D) Productivity is the ratio of total output to a specific measure of input.
E) Productivity is the ratio of total input to a specific measure of output.
A) Productivity is nominal GDP to a specific measure of output.
B) Productivity is real GDP to a specific measure of output.
C) Productivity is economic growth to a specific measure of output.
D) Productivity is the ratio of total output to a specific measure of input.
E) Productivity is the ratio of total input to a specific measure of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Long-term growth in production can be explained by _____
A) an improvement in the quality of resources available.
B) the same level of technology and know-how.
C) a rapid and accelerating increase in the price level.
D) a trade surplus that leads to the accumulation of gold.
E) the peaks and troughs of economic fluctuations.
A) an improvement in the quality of resources available.
B) the same level of technology and know-how.
C) a rapid and accelerating increase in the price level.
D) a trade surplus that leads to the accumulation of gold.
E) the peaks and troughs of economic fluctuations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The production possibilities curve for capital and consumer goods is concave to the origin because _____
A) of decreasing opportunity costs of production.
B) resources are not perfectly adaptable to the production of both goods.
C) consumer goods and capital goods equally contribute to economic growth.
D) the level of technology along the frontier is assumed to vary.
E) of constant returns to scale.
A) of decreasing opportunity costs of production.
B) resources are not perfectly adaptable to the production of both goods.
C) consumer goods and capital goods equally contribute to economic growth.
D) the level of technology along the frontier is assumed to vary.
E) of constant returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose the production possibilities frontier (PPF) of an economy has been plotted on a graph. If the horizontal axis of the graph measures the output of capital goods and the vertical axis measures the output of consumer goods, then a point outside the PPF represents _____
A) a smaller quantity of consumer goods than that represented by a point inside the PPF.
B) an inefficient output combination of the two goods in the economy.
C) an unattainable output combination of the two goods in the economy.
D) an output combination of more consumer goods than capital goods.
E) a smaller quantity of capital goods than that represented by a point inside the PPF.
A) a smaller quantity of consumer goods than that represented by a point inside the PPF.
B) an inefficient output combination of the two goods in the economy.
C) an unattainable output combination of the two goods in the economy.
D) an output combination of more consumer goods than capital goods.
E) a smaller quantity of capital goods than that represented by a point inside the PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following does not contribute to an improved standard of living?
A) increases in the amount of available resources
B) better technology
C) higher prices for the necessities of life
D) improvements in the "rules of the game"
E) improvements in the quality of labor
A) increases in the amount of available resources
B) better technology
C) higher prices for the necessities of life
D) improvements in the "rules of the game"
E) improvements in the quality of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Long-term growth in production can be explained by _____
A) a rapid and accelerating increase in the price level.
B) a gradual but consistent rise in the price level.
C) better technology and know-how.
D) a trade surplus that leads to the accumulation of gold.
E) the peaks and troughs of economic fluctuations.
A) a rapid and accelerating increase in the price level.
B) a gradual but consistent rise in the price level.
C) better technology and know-how.
D) a trade surplus that leads to the accumulation of gold.
E) the peaks and troughs of economic fluctuations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is the single most important determinant of a nation's standard of living in the long run?
A) high economic growth rates
B) developing a market economy of conscious design
C) higher prices for the necessities of life
D) productivity of its resources
E) developing agricultural self-sufficiency
A) high economic growth rates
B) developing a market economy of conscious design
C) higher prices for the necessities of life
D) productivity of its resources
E) developing agricultural self-sufficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following does not contribute to an economy's standard of living in the long run?
A) increases in the amount and quality of resources, especially labor and capital
B) better technology and know-how
C) improvements in the rules of the game that facilitate production and exchange
D) a reliable and respected system of property rights, customs, and conventions that nurture productive activity
E) a reduction in productivity
A) increases in the amount and quality of resources, especially labor and capital
B) better technology and know-how
C) improvements in the rules of the game that facilitate production and exchange
D) a reliable and respected system of property rights, customs, and conventions that nurture productive activity
E) a reduction in productivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Productivity measures _____
A) how efficiently resources are turned into goods and services.
B) how efficiently goods and services are consumed by consumers.
C) the level of skills embodied in a unit of labor.
D) the ratio of inputs to a specific amount of output.
E) the availability of resources in an economy.
A) how efficiently resources are turned into goods and services.
B) how efficiently goods and services are consumed by consumers.
C) the level of skills embodied in a unit of labor.
D) the ratio of inputs to a specific amount of output.
E) the availability of resources in an economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Output per unit of labor is known as _____
A) the production function.
B) capital deepening.
C) productivity
D) production.
E) labor productivity.
A) the production function.
B) capital deepening.
C) productivity
D) production.
E) labor productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If Q is total real output, K is capital in use, and L is labor employed, then _____ is the formula to calculate the productivity of labor.
A) K/L
B) L/K
C) Q/L
D) Q/K
E) (Q + K)/L
A) K/L
B) L/K
C) Q/L
D) Q/K
E) (Q + K)/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following would increase labor productivity?
A) a labor-deepening production method
B) a decrease in the amount of capital per unit of labor
C) a lower unemployment rate
D) the recruitment of a new and young labor force
E) an increase in the education level of per unit of labor
A) a labor-deepening production method
B) a decrease in the amount of capital per unit of labor
C) a lower unemployment rate
D) the recruitment of a new and young labor force
E) an increase in the education level of per unit of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following does not contribute to labor productivity growth?
A) a steepening of the per-worker production function
B) an increase in the amount of capital per unit of labor
C) a growth in the labor force
D) an improvement in the quality of capital
E) an improvement in labor skills
A) a steepening of the per-worker production function
B) an increase in the amount of capital per unit of labor
C) a growth in the labor force
D) an improvement in the quality of capital
E) an improvement in labor skills

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In an iron and steel plant with 4 blast furnaces, 40 laborers produce 160 tons of pig iron every day. The labor productivity in the firm is equal to _____
A) 0.25 ton per worker.
B) 4 tons per worker.
C) 10 tons per worker.
D) 0.1 ton per worker.
E) 40 tons per worker
A) 0.25 ton per worker.
B) 4 tons per worker.
C) 10 tons per worker.
D) 0.1 ton per worker.
E) 40 tons per worker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is the correct formula to calculate productivity?
A) output + quantity of input
B) output ─ quantity of input
C) quantity of input ÷ output
D) output ÷ quantity of input
E) output × quantity of input
A) output + quantity of input
B) output ─ quantity of input
C) quantity of input ÷ output
D) output ÷ quantity of input
E) output × quantity of input

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If Q is total real output, K is capital in use, L is labor employed, an increase in the productivity of labor would imply a(n) _____
A) increase in K/L.
B) increase in L/K.
C) increase in Q/L.
D) decrease in Q/K.
E) decrease in (Q + K)/L.
A) increase in K/L.
B) increase in L/K.
C) increase in Q/L.
D) decrease in Q/K.
E) decrease in (Q + K)/L.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Ethan takes 7 hours to finish 3 assignments. Tyler takes 6 hours to finish 4 assignments. Who is more productive?
A) Tyler is more productive than Ethan but his output is less.
B) Ethan is more productive than Tyler but his output is less.
C) Ethan is more productive than Tyler and his output is more.
D) Tyler is more productive than Ethan and his output is more.
E) Neither Tyler nor Ethan are productive relative to one another.
A) Tyler is more productive than Ethan but his output is less.
B) Ethan is more productive than Tyler but his output is less.
C) Ethan is more productive than Tyler and his output is more.
D) Tyler is more productive than Ethan and his output is more.
E) Neither Tyler nor Ethan are productive relative to one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If Emma can create 2 websites in one day, what is her productivity?
A) 1 day
B) 2 websites per day
C) 1.5 websites per day
D) 0.5 websites per day
E) 2 days
A) 1 day
B) 2 websites per day
C) 1.5 websites per day
D) 0.5 websites per day
E) 2 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
_____ is the resource whose productivity is most commonly measured.
A) Labor
B) Capital
C) Land
D) Energy
E) Money supply
A) Labor
B) Capital
C) Land
D) Energy
E) Money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If Harper can create 3 websites in two days, what is her productivity?
A) 1 day
B) 2 websites per day
C) 1.5 websites per day
D) 0.5 websites per day
E) 2 days
A) 1 day
B) 2 websites per day
C) 1.5 websites per day
D) 0.5 websites per day
E) 2 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A website business employs 3 people. Emma can create 2 websites in one day. Harper can create 3 websites in two days. Lee can create 6 websites in three days. Who is the most productive?
A) Emma
B) Harper
C) Lee
D) Both Emma and Harper are more productive than Lee.
E) Both Emma and Lee are more productive than Harper.
A) Emma
B) Harper
C) Lee
D) Both Emma and Harper are more productive than Lee.
E) Both Emma and Lee are more productive than Harper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Surgeons earn more than janitors because _____
A) of the negative correlation between the level of education and productivity.
B) of the inverse relationship between wages and productivity.
C) the accumulation of human capital leads to an improvement in productivity.
D) of the negative relation between productivity and the amount of physical capital.
E) surgeons spend more time at work than janitors.
A) of the negative correlation between the level of education and productivity.
B) of the inverse relationship between wages and productivity.
C) the accumulation of human capital leads to an improvement in productivity.
D) of the negative relation between productivity and the amount of physical capital.
E) surgeons spend more time at work than janitors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If Lee can create 6 websites in three days, what is her productivity?
A) 1 day
B) 2 websites per day
C) 1.5 websites per day
D) 0.5 websites per day
E) 2 days
A) 1 day
B) 2 websites per day
C) 1.5 websites per day
D) 0.5 websites per day
E) 2 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Labor cost on average accounts for about _____ percent of the total cost of production.
A) 10
B) 30
C) 50
D) 70
E) 98
A) 10
B) 30
C) 50
D) 70
E) 98

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Tyler takes 6 hours to finish 4 assignments. What is his productivity per assignment?
A) 0.7 assignments per hour
B) 1.5 assignments per hour
C) 4 assignments per hour
D) 6 assignments per hour
E) His productivity cannot be determined from the information given.
A) 0.7 assignments per hour
B) 1.5 assignments per hour
C) 4 assignments per hour
D) 6 assignments per hour
E) His productivity cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A water bottle manufacturing plant uses a three-step procedure to produce each unit of bottle. The first step is casting, which needs 35 workers to operate the furnace. The second step is quenching, which needs 35 workers. At the third step, bottles are prepared for dispatch in the assembly line with the help of 70 workers. If the factory produces 14,000 bottles per day, then the productivity of labor in the factory is equal to _____
A) 200 bottles per worker.
B) 400 bottles per worker.
C) 100 bottles per worker.
D) 140 bottles per worker.
E) 220 bottles per worker.
A) 200 bottles per worker.
B) 400 bottles per worker.
C) 100 bottles per worker.
D) 140 bottles per worker.
E) 220 bottles per worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Productivity is defined as _____
A) the ratio of a specific measure of output to a specific measure of input.
B) the production of worthwhile goods and services.
C) the market value of goods, services, and resources produced per time period (e.g., per year).
D) average input divided by average output.
E) total input divided by average output.
A) the ratio of a specific measure of output to a specific measure of input.
B) the production of worthwhile goods and services.
C) the market value of goods, services, and resources produced per time period (e.g., per year).
D) average input divided by average output.
E) total input divided by average output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Joe runs a pizzeria at a busy place in a city. Around 125 customers visit every day, and they each buy 3 pizzas on average. Joe has employed 20 workers to make pizzas. The per-day productivity of workers in the pizzeria is equal to _____
A) 6.25 pizzas per worker.
B) 18.75 pizzas per worker.
C) 6.67 pizzas per worker.
D) 41.67 pizzas per worker.
E) 20.75 pizzas per worker.
A) 6.25 pizzas per worker.
B) 18.75 pizzas per worker.
C) 6.67 pizzas per worker.
D) 41.67 pizzas per worker.
E) 20.75 pizzas per worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Human capital represents _____
A) the equipment that labor uses on-the-job to improve labor productivity.
B) the ratio of capital to labor.
C) the education, skill, and training embodied in workers.
D) the technology developed by humans that is embodied in equipment.
E) the social institutions created by people, which promote the accumulation of equipment for production.
A) the equipment that labor uses on-the-job to improve labor productivity.
B) the ratio of capital to labor.
C) the education, skill, and training embodied in workers.
D) the technology developed by humans that is embodied in equipment.
E) the social institutions created by people, which promote the accumulation of equipment for production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Ethan takes 7 hours to finish 3 assignments. What is his productivity per assignment?
A) 0.4 assignments per hour.
B) 1.5 assignments per hour.
C) 2.3 assignments per hour.
D) 3 assignments per hour.
E) His productivity cannot be determined from the information given.
A) 0.4 assignments per hour.
B) 1.5 assignments per hour.
C) 2.3 assignments per hour.
D) 3 assignments per hour.
E) His productivity cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If a nation moves upward along its per-worker production function relating output per worker to capital per worker, then _____
A) labor productivity rises.
B) labor productivity falls.
C) the amount of capital decreases, other things constant.
D) labor input decreases.
E) the productivity of capital rises.
A) labor productivity rises.
B) labor productivity falls.
C) the amount of capital decreases, other things constant.
D) labor input decreases.
E) the productivity of capital rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An increase in the amount of capital per worker is known as _____
A) the production function.
B) capital deepening.
C) productivity.
D) production.
E) labor productivity.
A) the production function.
B) capital deepening.
C) productivity.
D) production.
E) labor productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An increase in the amount of capital per worker will _____
A) increase labor productivity but not capital productivity.
B) increase capital productivity but not labor productivity.
C) increase both labor and capital productivity.
D) shift the per-worker production function upward.
E) increase total output but not the productivity levels of individual workers.
A) increase labor productivity but not capital productivity.
B) increase capital productivity but not labor productivity.
C) increase both labor and capital productivity.
D) shift the per-worker production function upward.
E) increase total output but not the productivity levels of individual workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Exhibit 8.2
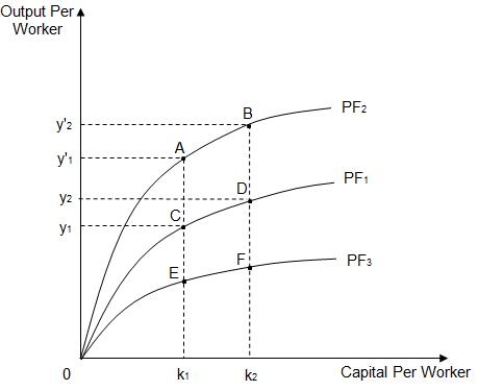
Refer to Exhibit 8.2 which shows three different per-worker production functions: PF₁, PF₂, and PF₃. If PF₁ is the initial per-worker production function, which of the following reflects the impact of an increase in the level of technology?
A) a movement from point D to point C
B) an upward shift from PF₁ to PF₂
C) a downward shift from PF₁ to PF₃
D) a movement from point C to point D
E) a movement from point D to point F

Refer to Exhibit 8.2 which shows three different per-worker production functions: PF₁, PF₂, and PF₃. If PF₁ is the initial per-worker production function, which of the following reflects the impact of an increase in the level of technology?
A) a movement from point D to point C
B) an upward shift from PF₁ to PF₂
C) a downward shift from PF₁ to PF₃
D) a movement from point C to point D
E) a movement from point D to point F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The slope of the per-worker production function diminishes as the amount of capital per worker increases. This is a reflection of the law of _____
A) increasing marginal returns.
B) diminishing marginal returns.
C) constant marginal returns.
D) first diminishing and then increasing marginal returns.
E) demand.
A) increasing marginal returns.
B) diminishing marginal returns.
C) constant marginal returns.
D) first diminishing and then increasing marginal returns.
E) demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following factors of production is likely to be most productive?
A) a certified doctor working in a well-equipped hospital
B) a medical student working as a volunteer in a rural health clinic
C) a trained nurse without access to the latest medical technology
D) a knowledgeable chemist without a degree in medical sciences
E) a specialist doctor working in a hospital with poor infrastructure
A) a certified doctor working in a well-equipped hospital
B) a medical student working as a volunteer in a rural health clinic
C) a trained nurse without access to the latest medical technology
D) a knowledgeable chemist without a degree in medical sciences
E) a specialist doctor working in a hospital with poor infrastructure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An improvement in the quality of capital would _____
A) rotate the per-worker production function upward.
B) make the per-worker production function flatter.
C) shift the per-worker production function downward.
D) rotate the per-worker production function downward.
E) have no effect on the per-worker production function.
A) rotate the per-worker production function upward.
B) make the per-worker production function flatter.
C) shift the per-worker production function downward.
D) rotate the per-worker production function downward.
E) have no effect on the per-worker production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The per-worker production function illustrates the fact that as the amount of capital per worker increases, output per worker _____
A) increases at an increasing rate.
B) increases and then decreases.
C) decreases but at an increasing rate.
D) decreases.
E) increases but at a decreasing rate.
A) increases at an increasing rate.
B) increases and then decreases.
C) decreases but at an increasing rate.
D) decreases.
E) increases but at a decreasing rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following factors pushes the per-worker production function of an economy downward?
A) a stable political environment
B) a high risk of terror attack
C) an increase in educated workforce in the country
D) an increase in road networks in the country
E) a law encouraging foreign investment
A) a stable political environment
B) a high risk of terror attack
C) an increase in educated workforce in the country
D) an increase in road networks in the country
E) a law encouraging foreign investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A point on the per-worker production function shows _____
A) the total output produced by the labor force of an industry on the vertical axis for each level of capital per worker on the horizontal axis.
B) the marginal output per worker on the vertical axis for each level of worker per unit of capital on the horizontal axis.
C) the marginal output per worker on the vertical axis for each level of capital per worker on the horizontal axis.
D) the level of capital per worker on the vertical axis for respective average output per worker on the horizontal axis.
E) the average output per worker on the vertical axis for each level of capital per worker on the horizontal axis.
A) the total output produced by the labor force of an industry on the vertical axis for each level of capital per worker on the horizontal axis.
B) the marginal output per worker on the vertical axis for each level of worker per unit of capital on the horizontal axis.
C) the marginal output per worker on the vertical axis for each level of capital per worker on the horizontal axis.
D) the level of capital per worker on the vertical axis for respective average output per worker on the horizontal axis.
E) the average output per worker on the vertical axis for each level of capital per worker on the horizontal axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following implies a decline in labor productivity in an economy?
A) a high rate of growth of capital formation
B) an improvement in input quality
C) a decrease in the production of goods and services
D) an increase in the budget surplus in the economy
E) a decrease in the prices of goods and services
A) a high rate of growth of capital formation
B) an improvement in input quality
C) a decrease in the production of goods and services
D) an increase in the budget surplus in the economy
E) a decrease in the prices of goods and services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If an increase in capital per worker leads to increased output per worker, but by decreasing amounts as capital increases, the per-worker production function _____
A) is vertical.
B) has a decreasing slope.
C) has an increasing slope.
D) has a negative slope.
E) is horizontal.
A) is vertical.
B) has a decreasing slope.
C) has an increasing slope.
D) has a negative slope.
E) is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Capital deepening refers to _____
A) an increase in the amount of capital per worker.
B) an increase in the amount of workers per unit of capital.
C) a decrease in the amount of capital per unit of output.
D) an increase in the amount of output per unit of capital.
E) an increase in the productivity of capital.
A) an increase in the amount of capital per worker.
B) an increase in the amount of workers per unit of capital.
C) a decrease in the amount of capital per unit of output.
D) an increase in the amount of output per unit of capital.
E) an increase in the productivity of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Exhibit 8.2

Refer to Exhibit 8.2, which shows three different per-worker production functions: PF₁, PF₂, and PF₃. The diminishing slopes of the curves reflect _____
A) increasing returns to scale.
B) increasing marginal returns from capital.
C) diminishing marginal returns from capital.
D) decreasing returns to scale.
E) diminishing marginal returns from labor.

Refer to Exhibit 8.2, which shows three different per-worker production functions: PF₁, PF₂, and PF₃. The diminishing slopes of the curves reflect _____
A) increasing returns to scale.
B) increasing marginal returns from capital.
C) diminishing marginal returns from capital.
D) decreasing returns to scale.
E) diminishing marginal returns from labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The law of diminishing marginal returns states that as the quantity of capital per worker increases, other things constant, output per worker _____
A) increases at a constant rate.
B) increases at a decreasing rate.
C) increases at an increasing rate.
D) decreases.
E) remains constant.
A) increases at a constant rate.
B) increases at a decreasing rate.
C) increases at an increasing rate.
D) decreases.
E) remains constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is assumed to be constant along a per-worker production function?
A) output per worker
B) capital per worker
C) the level of technology
D) the amount of capital
E) the amount of output
A) output per worker
B) capital per worker
C) the level of technology
D) the amount of capital
E) the amount of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Exhibit 8.2

Refer to Exhibit 8.2, which shows three different per-worker production functions: PF₁, PF₂, and PF₃. If PF₁ is the initial per-worker production function for a farm, which of the following reflects an increase in the number of tractors per worker in the farm?
A) a movement from point D to point C
B) an upward shift from PF₁ to PF₂
C) a downward shift from PF₁ to PF₃
D) a movement from point C to point D
E) a movement from point D to point B

Refer to Exhibit 8.2, which shows three different per-worker production functions: PF₁, PF₂, and PF₃. If PF₁ is the initial per-worker production function for a farm, which of the following reflects an increase in the number of tractors per worker in the farm?
A) a movement from point D to point C
B) an upward shift from PF₁ to PF₂
C) a downward shift from PF₁ to PF₃
D) a movement from point C to point D
E) a movement from point D to point B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An increase in the quantity of capital per worker would _____
A) rotate the per-worker production function outward.
B) rotate the per-worker production function inward.
C) shift the per-worker production function downward.
D) shift the per-worker production function upward.
E) result in a rightward movement along the current per-worker production function.
A) rotate the per-worker production function outward.
B) rotate the per-worker production function inward.
C) shift the per-worker production function downward.
D) shift the per-worker production function upward.
E) result in a rightward movement along the current per-worker production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Exhibit 8.1
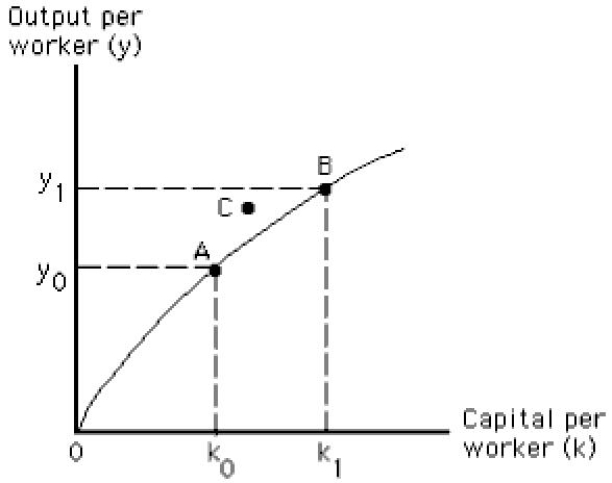
Refer to Exhibit 8.1. The movement from point A to point B in the figure illustrates the effect of _____
A) an increase in the capital stock relative to the workforce.
B) an increase in the labor productivity growth rate.
C) an increase in labor productivity because of higher quality capital.
D) a decrease in labor productivity.
E) a decrease in the capital stock.

Refer to Exhibit 8.1. The movement from point A to point B in the figure illustrates the effect of _____
A) an increase in the capital stock relative to the workforce.
B) an increase in the labor productivity growth rate.
C) an increase in labor productivity because of higher quality capital.
D) a decrease in labor productivity.
E) a decrease in the capital stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A decrease in the capital-labor ratio would result in _____
A) higher labor productivity because labor does more work.
B) lower labor productivity because labor is working with relatively less capital.
C) higher labor productivity because labor is producing less capital and more of other goods.
D) lower labor productivity because more capital is available.
E) higher labor productivity because more capital is available.
A) higher labor productivity because labor does more work.
B) lower labor productivity because labor is working with relatively less capital.
C) higher labor productivity because labor is producing less capital and more of other goods.
D) lower labor productivity because more capital is available.
E) higher labor productivity because more capital is available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is most likely to increase productivity growth, as measured using GDP statistics?
A) reduced capital formation
B) decreased human capital
C) increased research and development
D) increased government regulation
E) higher price of a raw material
A) reduced capital formation
B) decreased human capital
C) increased research and development
D) increased government regulation
E) higher price of a raw material

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following would increase labor productivity?
A) a decrease in the amount of capital per unit of labor
B) a change in technology that improves the quality of capital
C) a decrease in the unemployment rate
D) an increase in the number of inexperienced workers entering the labor force
E) a decrease in the quality of capital
A) a decrease in the amount of capital per unit of labor
B) a change in technology that improves the quality of capital
C) a decrease in the unemployment rate
D) an increase in the number of inexperienced workers entering the labor force
E) a decrease in the quality of capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An economy's standard of living grows over the long run because of _____
A) better protection of domestic industries from foreign competition.
B) centralized planning and decision making.
C) technological improvements.
D) stringent foreign trade policies.
E) a high-growth rate of population.
A) better protection of domestic industries from foreign competition.
B) centralized planning and decision making.
C) technological improvements.
D) stringent foreign trade policies.
E) a high-growth rate of population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why are poor countries poor?
A) because they have more human capital
B) because they have more physical capital
C) because they experience high labor productivity
D) because they experience low labor productivity
E) because they experience bad weather
A) because they have more human capital
B) because they have more physical capital
C) because they experience high labor productivity
D) because they experience low labor productivity
E) because they experience bad weather

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
According to Nobel Laureate Simon Kuznets, the greatest increase in output and economic growth comes from changes in the _____
A) quantity of loanable funds.
B) quantity of natural resources (land).
C) quantity of labor.
D) quality of resources.
E) quantity of capital.
A) quantity of loanable funds.
B) quantity of natural resources (land).
C) quantity of labor.
D) quality of resources.
E) quantity of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is not included in the rules of the game?
A) the laws, customs, conventions, and other institutional elements associated with trade
B) property rights
C) the stock of natural resources
D) a stable political environment
E) a stable legal system
A) the laws, customs, conventions, and other institutional elements associated with trade
B) property rights
C) the stock of natural resources
D) a stable political environment
E) a stable legal system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
_____ is/are an important determinant of its standard of living in the long run.
A) A nation's net exports
B) The productivity of a nation's resources
C) A nation's population growth rate
D) The deficit in a nation's capital account
E) The deficit in a nation's current account
A) A nation's net exports
B) The productivity of a nation's resources
C) A nation's population growth rate
D) The deficit in a nation's capital account
E) The deficit in a nation's current account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Developing countries make up about _____ of the world's population.
A) 10 percent
B) 18 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 50 percent
E) 84 percent
A) 10 percent
B) 18 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 50 percent
E) 84 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is likely to cause a decrease in labor productivity?
A) an increase in student achievement scores
B) a service sector that is growing slower than the growth rate of GDP
C) an increased spending on research and development
D) a decrease in capital formation
E) a low federal budget deficit
A) an increase in student achievement scores
B) a service sector that is growing slower than the growth rate of GDP
C) an increased spending on research and development
D) a decrease in capital formation
E) a low federal budget deficit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
_____ is a resource whose quality is most often enhanced by technological change.
A) Capital
B) Land
C) Labor
D) Entrepreneurship
E) Credit
A) Capital
B) Land
C) Labor
D) Entrepreneurship
E) Credit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is included in social capital?
A) a neighborhood crime watch
B) a successful entrepreneur
C) accumulated knowledge, skill, and experience
D) a college degree
E) specialized software
A) a neighborhood crime watch
B) a successful entrepreneur
C) accumulated knowledge, skill, and experience
D) a college degree
E) specialized software

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
According to Simon Kuznets, how much of the increase in economic growth can be attributed to changes in the quantities of labor and capital?
A) all of the increase in economic growth
B) one-third of the increase in economic growth
C) half of the increase in economic growth
D) one-tenth of the increase in economic growth
E) nine-tenths of the increase in economic growth
A) all of the increase in economic growth
B) one-third of the increase in economic growth
C) half of the increase in economic growth
D) one-tenth of the increase in economic growth
E) nine-tenths of the increase in economic growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Compared to the world's poorest countries, per capita output in the United States is _____
A) about 10 times more.
B) about 25 times more.
C) about 75 times more.
D) about 90 times more.
E) almost double.
A) about 10 times more.
B) about 25 times more.
C) about 75 times more.
D) about 90 times more.
E) almost double.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is true of an improvement in technology?
A) An improvement in technology shifts the per-worker production function upward.
B) An improvement in technology shifts the per-worker production function downward.
C) An improvement in technology increases the concavity of the production possibilities frontier.
D) An improvement in technology decreases the concavity of the production possibilities frontier.
E) An improvement in technology increases the quantity of input in the production process.
A) An improvement in technology shifts the per-worker production function upward.
B) An improvement in technology shifts the per-worker production function downward.
C) An improvement in technology increases the concavity of the production possibilities frontier.
D) An improvement in technology decreases the concavity of the production possibilities frontier.
E) An improvement in technology increases the quantity of input in the production process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Industrial market countries, or developed countries, make up about _____ of the world's population.
A) 10 percent
B) 16 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 50 percent
E) 84 percent
A) 10 percent
B) 16 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 50 percent
E) 84 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
According to Simon Kuznets, how much of the increase in economic growth can be attributed to changes in the qualities of labor and capital?
A) all of the increase in economic growth
B) one-third of the increase in economic growth
C) half of the increase in economic growth
D) one-tenth of the increase in economic growth
E) nine-tenths of the increase in economic growth
A) all of the increase in economic growth
B) one-third of the increase in economic growth
C) half of the increase in economic growth
D) one-tenth of the increase in economic growth
E) nine-tenths of the increase in economic growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
According to Simon Kuznets, which of the following is likely to induce economic growth in the automobile industry of a country?
A) an increase in the amount of labor used in the industry
B) a government subsidy for automobile production
C) an increase in the import of spare parts for the engines
D) an increase in the number of paint bays per factory
E) the replacement of manual assembly lines with robots
A) an increase in the amount of labor used in the industry
B) a government subsidy for automobile production
C) an increase in the import of spare parts for the engines
D) an increase in the number of paint bays per factory
E) the replacement of manual assembly lines with robots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following is included in physical capital?
A) roads and bridges
B) a university graduate in physics
C) an astrophysicist
D) a high school diploma or college degree
E) a successful entrepreneur
A) roads and bridges
B) a university graduate in physics
C) an astrophysicist
D) a high school diploma or college degree
E) a successful entrepreneur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
According to Simon Kuznets, _____
A) the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quantity of labor.
B) the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quantity of capital.
C) the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quality of inputs.
D) government regulations increase labor productivity.
E) government regulations decrease labor productivity.
A) the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quantity of labor.
B) the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quantity of capital.
C) the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quality of inputs.
D) government regulations increase labor productivity.
E) government regulations decrease labor productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What percentage of the world's output do industrial market countries produce?
A) 10 percent
B) 18 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 50 percent
E) 84 percent
A) 10 percent
B) 18 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 50 percent
E) 84 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



