Deck 7: Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food
1
Through what structure(s)do plants obtain most of their water?
A) roots
B) interior cells
C) stomata
D) leaves
A) roots
B) interior cells
C) stomata
D) leaves
A
2
The shorter the wavelength of visible light,the ______.
A) less energy absorbed by photosynthetic pigments
B) redder the color
C) more photons it contains
D) greater the energy
A) less energy absorbed by photosynthetic pigments
B) redder the color
C) more photons it contains
D) greater the energy
D
3
The energy of wavelengths that appear ______ is least useful to photosynthesis.
A) red
B) green
C) blue
D) orange
A) red
B) green
C) blue
D) orange
B
4
Photosynthesis contributes to plant growth by _____.
A) taking in oxygen and making wood
B) taking in carbon dioxide and making sugars (carbohydrates)
C) synthesizing carbon dioxide and making cellulose
D) converting sugar to oxygen and water
A) taking in oxygen and making wood
B) taking in carbon dioxide and making sugars (carbohydrates)
C) synthesizing carbon dioxide and making cellulose
D) converting sugar to oxygen and water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The color that we see when looking at a pigmented object is ______.
A) the wavelengths that are absorbed by the pigment
B) the wavelengths that are reflected or transmitted by the pigmented object
C) the wavelengths that have been raised to an excited state by the pigmented object
D) the wavelengths that the pigmented object created after interacting with sunlight
A) the wavelengths that are absorbed by the pigment
B) the wavelengths that are reflected or transmitted by the pigmented object
C) the wavelengths that have been raised to an excited state by the pigmented object
D) the wavelengths that the pigmented object created after interacting with sunlight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What name is given to a discrete packet of light?
A) phaser
B) wavelength
C) photon
D) quantum
A) phaser
B) wavelength
C) photon
D) quantum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What are grana?
A) thick fluids inside chloroplasts
B) convolutions of the inner chloroplast membrane
C) stacks of membranous sacs
D) pigments found in chloroplasts
A) thick fluids inside chloroplasts
B) convolutions of the inner chloroplast membrane
C) stacks of membranous sacs
D) pigments found in chloroplasts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What name is given to the membranous sacs found within a chloroplast?
A) stroma
B) cristae
C) thylakoids
D) vesicles
A) stroma
B) cristae
C) thylakoids
D) vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Calvin cycle requires ______ and ______ from the light reactions in order to operate.
A) glucose... carbon dioxide
B) electrons... NADH
C) ATP... NADPH
D) RuBP... NADP+
A) glucose... carbon dioxide
B) electrons... NADH
C) ATP... NADPH
D) RuBP... NADP+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following equations best summarizes photosynthesis?
A) 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 6 O2 → C6H12O6
B) 6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
C) 6 CO2 + 6 O2 → C6H12O6 + 6 H2O
D) C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O
A) 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 6 O2 → C6H12O6
B) 6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
C) 6 CO2 + 6 O2 → C6H12O6 + 6 H2O
D) C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is responsible for the yellow-orange coloration of leaves in the fall?
A) RuBP
B) chlorophyll a
C) carotenoids
D) chlorophyll b
A) RuBP
B) chlorophyll a
C) carotenoids
D) chlorophyll b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is produced during the light reactions of photosynthesis?
A) O2
B) CO2
C) C6H12O6
D) ADP
A) O2
B) CO2
C) C6H12O6
D) ADP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is one reason why plants have accessory pigment molecules,like chlorophyll b and carotenoids?
A) to reflect more energy
B) to absorb energy in parts of the electromagnetic spectrum that chlorophyll a cannot
C) to give them different colors
D) because plants cannot make enough chlorophyll a for all of their energy needs
A) to reflect more energy
B) to absorb energy in parts of the electromagnetic spectrum that chlorophyll a cannot
C) to give them different colors
D) because plants cannot make enough chlorophyll a for all of their energy needs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Within the inner membrane of a chloroplast,interconnected sacs of membrane called ______ are suspended in a thick fluid called the ______.
A) chlorophyll... thylakoid
B) thylakoids... grana
C) thylakoids... stroma
D) grana... thylakoid
A) chlorophyll... thylakoid
B) thylakoids... grana
C) thylakoids... stroma
D) grana... thylakoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The products of the light reactions of photosynthesis are ______.
A) ATP and NADH
B) ATP and NADPH
C) RuBP and O2
D) ATP and NADP+
A) ATP and NADH
B) ATP and NADPH
C) RuBP and O2
D) ATP and NADP+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If a plant appears blue to us,what wavelength of light is being reflected?
A) blue
B) green
C) red
D) yellow
A) blue
B) green
C) red
D) yellow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In photosynthesis,redox reactions ultimately transfer electrons from ______ to ______.
A) O2... CO2
B) C6H12O6... O2
C) H2O... C6H12O6
D) H2O... CO2
A) O2... CO2
B) C6H12O6... O2
C) H2O... C6H12O6
D) H2O... CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is an autotroph?
A) human
B) mushroom
C) pine tree
D) fish
A) human
B) mushroom
C) pine tree
D) fish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If you provided your shade-tolerant plants with their preferred wavelength of light,but only minimal amounts of water,which of the following would you expect to occur?
A) increased plant growth
B) increased amounts of oxygen released by the plants
C) decreased amounts of ATP being produced by the plants
D) increased growth of the plants' leaves
A) increased plant growth
B) increased amounts of oxygen released by the plants
C) decreased amounts of ATP being produced by the plants
D) increased growth of the plants' leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the function of stomata?
A) water absorption
B) Calvin cycle
C) location of photosystems
D) gas exchange
A) water absorption
B) Calvin cycle
C) location of photosystems
D) gas exchange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Where are photosystems located?
A) chlorophyll
B) thylakoid membrane
C) cristae
D) stroma
A) chlorophyll
B) thylakoid membrane
C) cristae
D) stroma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
CAM plants conserve water by ______.
A) opening their stomata only at night
B) incorporating CO2 into RuBP
C) keeping their stomata closed at night
D) running the Calvin cycle at night
A) opening their stomata only at night
B) incorporating CO2 into RuBP
C) keeping their stomata closed at night
D) running the Calvin cycle at night

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is found in both cellular respiration and in the light reactions of photosynthesis?
A) citric acid cycle
B) glycolysis
C) Calvin cycle
D) electron transport chain
A) citric acid cycle
B) glycolysis
C) Calvin cycle
D) electron transport chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Refer to the accompanying figure.Which of the following is true regarding the behavior of a chlorophyll molecule as it absorbs a photon? 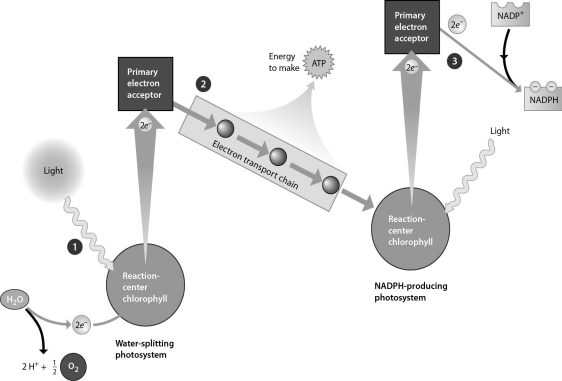
A) An electron goes from the excited state to the ground state.
B) Light is released.
C) The energy of a photon raises an electron to the excited state.
D) ATP is broken down.

A) An electron goes from the excited state to the ground state.
B) Light is released.
C) The energy of a photon raises an electron to the excited state.
D) ATP is broken down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The light reactions of photosynthesis take place ______.
A) in the stroma
B) on the cristae
C) in the thylakoid membrane
D) in the cytosol
A) in the stroma
B) on the cristae
C) in the thylakoid membrane
D) in the cytosol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What compound is found at the reaction center of a photosystem?
A) chlorophyll b
B) carotenoids
C) phycobilins
D) chlorophyll a
A) chlorophyll b
B) carotenoids
C) phycobilins
D) chlorophyll a

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In photosynthesis,an H+ ion gradient forms across the ______.
A) thylakoid membrane
B) outer chloroplast membrane
C) endomembrane
D) inner chloroplast membrane
A) thylakoid membrane
B) outer chloroplast membrane
C) endomembrane
D) inner chloroplast membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The Calvin cycle makes direct use of ______ to make ______.
A) light energy and CO2... sugar
B) CO2, ATP, and NADPH... sugar and O2
C) light energy, CO2, and water... sugar and O2
D) CO2, ATP, and NADPH... sugar
A) light energy and CO2... sugar
B) CO2, ATP, and NADPH... sugar and O2
C) light energy, CO2, and water... sugar and O2
D) CO2, ATP, and NADPH... sugar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Please refer to the following art to answer the following question(s).
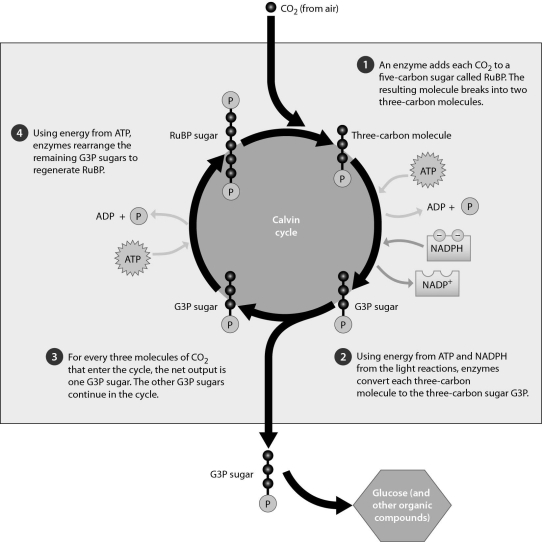
How many times must the Calvin cycle turn for the plant cell to be able to produce one molecule of glucose?
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) six

How many times must the Calvin cycle turn for the plant cell to be able to produce one molecule of glucose?
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
______ is the source of the oxygen gas released by a photosystem.
A) H2O
B) Chlorophyll a
C) CO2
D) C6H12O6
A) H2O
B) Chlorophyll a
C) CO2
D) C6H12O6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is the source of electrons for the light reactions?
A) C6H12O6
B) CO2
C) NADPH
D) H2O
A) C6H12O6
B) CO2
C) NADPH
D) H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Please refer to the following art to answer the following question(s).

The last stage of one complete turn of the Calvin cycle involves ______.
A) G3P production
B) oxidation of CO2
C) regeneration of RuBP
D) sugar production

The last stage of one complete turn of the Calvin cycle involves ______.
A) G3P production
B) oxidation of CO2
C) regeneration of RuBP
D) sugar production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Refer to the accompanying figure.Which of the following best describes the direct mechanism of ATP production during photosynthesis? 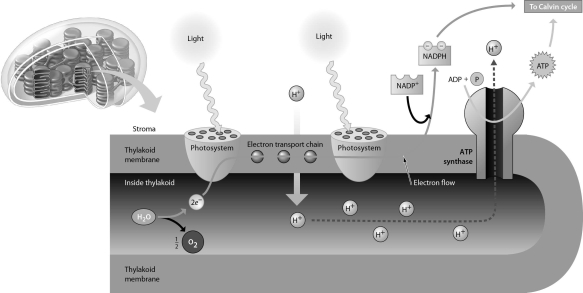
A) use of the energy generated as hydrogen ions (H+) move up a proton gradient; this energy is used to make ATP
B) use of the energy released as excited electrons are passed from one molecule to another in the electron transport system; the energy is converted to the chemical bond energy of ATP
C) use of the energy stored in excited electrons; as the electrons move from the excited state to the ground state, the energy released is converted to the energy stored in the third phosphate bond in ATP
D) use of the energy stored in hydrogen ion (H+) gradients; the potential energy of the proton gradient is released as the protons move down their gradient through special membrane protein channels; this energy is converted to chemical bond energy in the ATP molecule

A) use of the energy generated as hydrogen ions (H+) move up a proton gradient; this energy is used to make ATP
B) use of the energy released as excited electrons are passed from one molecule to another in the electron transport system; the energy is converted to the chemical bond energy of ATP
C) use of the energy stored in excited electrons; as the electrons move from the excited state to the ground state, the energy released is converted to the energy stored in the third phosphate bond in ATP
D) use of the energy stored in hydrogen ion (H+) gradients; the potential energy of the proton gradient is released as the protons move down their gradient through special membrane protein channels; this energy is converted to chemical bond energy in the ATP molecule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Please refer to the following art to answer the following question(s).

One of the compounds that is a direct output of the Calvin cycle is ______.
A) C6H12O6
B) NADPH
C) G3P
D) ATP

One of the compounds that is a direct output of the Calvin cycle is ______.
A) C6H12O6
B) NADPH
C) G3P
D) ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the accompanying figure.Plant cells that contain the organelle responsible for photosynthesis are concentrated in cells of the ______. 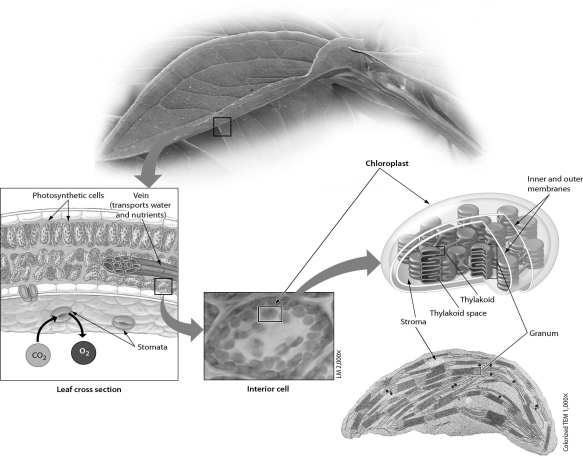
A) roots
B) leaves
C) stomata
D) grana

A) roots
B) leaves
C) stomata
D) grana

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When a molecule absorbs a photon,one of its electrons is raised to the ______ state.
A) energetic
B) quantum
C) higher
D) excited
A) energetic
B) quantum
C) higher
D) excited

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Please refer to the following art to answer the following question(s).

The first step of the Calvin cycle is the incorporation of ______ into ______.
A) O2... G3P
B) RuBP... O2
C) CO2... RuBP
D) G3P... RuBP

The first step of the Calvin cycle is the incorporation of ______ into ______.
A) O2... G3P
B) RuBP... O2
C) CO2... RuBP
D) G3P... RuBP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is a way that a molecule releases energy gained by absorption of a photon?
A) heat
B) fluorescence
C) light
D) all of the above
A) heat
B) fluorescence
C) light
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Please refer to the following art to answer the following question(s).

If an herbicide blocked the Calvin cycle before the generation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P),which of the following statements would be true?
A) The plant would still be able to make sugar, just a lot less.
B) No oxygen would be released by the plant.
C) No sugar would be made by the plant.
D) Only RuBP would be recycled.

If an herbicide blocked the Calvin cycle before the generation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P),which of the following statements would be true?
A) The plant would still be able to make sugar, just a lot less.
B) No oxygen would be released by the plant.
C) No sugar would be made by the plant.
D) Only RuBP would be recycled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
C4 plants conserve water by ______.
A) shuttling CO2 from the Calvin cycle to the water-splitting photosystem
B) keeping their stomata closed when the weather is hot and dry
C) growing very deep roots
D) running the Calvin cycle at night
A) shuttling CO2 from the Calvin cycle to the water-splitting photosystem
B) keeping their stomata closed when the weather is hot and dry
C) growing very deep roots
D) running the Calvin cycle at night

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Please use the following information to answer the following question(s).
You work for a company selling tropical rain forest plants commonly found in the understory of the forest. These plants are shade tolerant and can be grown indoors because they require low light. Your employer wants you to find out what is the best type of light to maximize growth of these understory plants. Using a full spectrum of natural light would cause these plants to die because they are a shade-tolerant plant species.
From your biology class, you recall that the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis involve pigment molecules that absorb light of specific wavelengths. You also remember the experiments done by the German biologist Theodor Engelmann, in which he separated light using a prism into different wavelengths and then determined which wavelengths were best for promoting photosynthesis in the algae species he was examining. Your goal is to determine which wavelengths (colors) of light are best for promoting photosynthesis to enhance growth in your species of plant. To achieve this, you grew your plants under different wavelengths of light and measured their growth rates. The wavelengths were measured in nanometers (nm), and the growth rate was measured in millimeters per day (mm/day). The data you collected are as follows:
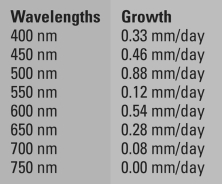
Make a bar graph plotting growth rates on the y-axis and wavelengths of light on the x-axis. Referring to your graph, answer the following question(s):
Why do some plant species require shaded conditions while other plant species require bright sunlight?
A) Different species of plants have different pigment molecules that utilize different wavelengths of light.
B) Different species of plants have leaves that are shaped differently.
C) Some species of plants are able to produce sugar without ever having been exposed to sunlight.
D) Some species of plants are consumers and do not need sunlight.
You work for a company selling tropical rain forest plants commonly found in the understory of the forest. These plants are shade tolerant and can be grown indoors because they require low light. Your employer wants you to find out what is the best type of light to maximize growth of these understory plants. Using a full spectrum of natural light would cause these plants to die because they are a shade-tolerant plant species.
From your biology class, you recall that the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis involve pigment molecules that absorb light of specific wavelengths. You also remember the experiments done by the German biologist Theodor Engelmann, in which he separated light using a prism into different wavelengths and then determined which wavelengths were best for promoting photosynthesis in the algae species he was examining. Your goal is to determine which wavelengths (colors) of light are best for promoting photosynthesis to enhance growth in your species of plant. To achieve this, you grew your plants under different wavelengths of light and measured their growth rates. The wavelengths were measured in nanometers (nm), and the growth rate was measured in millimeters per day (mm/day). The data you collected are as follows:

Make a bar graph plotting growth rates on the y-axis and wavelengths of light on the x-axis. Referring to your graph, answer the following question(s):
Why do some plant species require shaded conditions while other plant species require bright sunlight?
A) Different species of plants have different pigment molecules that utilize different wavelengths of light.
B) Different species of plants have leaves that are shaped differently.
C) Some species of plants are able to produce sugar without ever having been exposed to sunlight.
D) Some species of plants are consumers and do not need sunlight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Please use the following information to answer the following question(s).
You work for a company selling tropical rain forest plants commonly found in the understory of the forest. These plants are shade tolerant and can be grown indoors because they require low light. Your employer wants you to find out what is the best type of light to maximize growth of these understory plants. Using a full spectrum of natural light would cause these plants to die because they are a shade-tolerant plant species.
From your biology class, you recall that the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis involve pigment molecules that absorb light of specific wavelengths. You also remember the experiments done by the German biologist Theodor Engelmann, in which he separated light using a prism into different wavelengths and then determined which wavelengths were best for promoting photosynthesis in the algae species he was examining. Your goal is to determine which wavelengths (colors) of light are best for promoting photosynthesis to enhance growth in your species of plant. To achieve this, you grew your plants under different wavelengths of light and measured their growth rates. The wavelengths were measured in nanometers (nm), and the growth rate was measured in millimeters per day (mm/day). The data you collected are as follows:

Make a bar graph plotting growth rates on the y-axis and wavelengths of light on the x-axis. Referring to your graph, answer the following question(s):
Of the following,which wavelength is least useful to your plants?
A) 650 nm
B) 450 nm
C) 550 nm
D) 400 nm
You work for a company selling tropical rain forest plants commonly found in the understory of the forest. These plants are shade tolerant and can be grown indoors because they require low light. Your employer wants you to find out what is the best type of light to maximize growth of these understory plants. Using a full spectrum of natural light would cause these plants to die because they are a shade-tolerant plant species.
From your biology class, you recall that the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis involve pigment molecules that absorb light of specific wavelengths. You also remember the experiments done by the German biologist Theodor Engelmann, in which he separated light using a prism into different wavelengths and then determined which wavelengths were best for promoting photosynthesis in the algae species he was examining. Your goal is to determine which wavelengths (colors) of light are best for promoting photosynthesis to enhance growth in your species of plant. To achieve this, you grew your plants under different wavelengths of light and measured their growth rates. The wavelengths were measured in nanometers (nm), and the growth rate was measured in millimeters per day (mm/day). The data you collected are as follows:

Make a bar graph plotting growth rates on the y-axis and wavelengths of light on the x-axis. Referring to your graph, answer the following question(s):
Of the following,which wavelength is least useful to your plants?
A) 650 nm
B) 450 nm
C) 550 nm
D) 400 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Please use the following information to answer the following question(s).
You work for a company selling tropical rain forest plants commonly found in the understory of the forest. These plants are shade tolerant and can be grown indoors because they require low light. Your employer wants you to find out what is the best type of light to maximize growth of these understory plants. Using a full spectrum of natural light would cause these plants to die because they are a shade-tolerant plant species.
From your biology class, you recall that the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis involve pigment molecules that absorb light of specific wavelengths. You also remember the experiments done by the German biologist Theodor Engelmann, in which he separated light using a prism into different wavelengths and then determined which wavelengths were best for promoting photosynthesis in the algae species he was examining. Your goal is to determine which wavelengths (colors) of light are best for promoting photosynthesis to enhance growth in your species of plant. To achieve this, you grew your plants under different wavelengths of light and measured their growth rates. The wavelengths were measured in nanometers (nm), and the growth rate was measured in millimeters per day (mm/day). The data you collected are as follows:

Make a bar graph plotting growth rates on the y-axis and wavelengths of light on the x-axis. Referring to your graph, answer the following question(s):
Which wavelength of light is the least useful to your plant's growth?
A) 750 nm
B) 650 nm
C) 550 nm
D) 500 nm
You work for a company selling tropical rain forest plants commonly found in the understory of the forest. These plants are shade tolerant and can be grown indoors because they require low light. Your employer wants you to find out what is the best type of light to maximize growth of these understory plants. Using a full spectrum of natural light would cause these plants to die because they are a shade-tolerant plant species.
From your biology class, you recall that the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis involve pigment molecules that absorb light of specific wavelengths. You also remember the experiments done by the German biologist Theodor Engelmann, in which he separated light using a prism into different wavelengths and then determined which wavelengths were best for promoting photosynthesis in the algae species he was examining. Your goal is to determine which wavelengths (colors) of light are best for promoting photosynthesis to enhance growth in your species of plant. To achieve this, you grew your plants under different wavelengths of light and measured their growth rates. The wavelengths were measured in nanometers (nm), and the growth rate was measured in millimeters per day (mm/day). The data you collected are as follows:

Make a bar graph plotting growth rates on the y-axis and wavelengths of light on the x-axis. Referring to your graph, answer the following question(s):
Which wavelength of light is the least useful to your plant's growth?
A) 750 nm
B) 650 nm
C) 550 nm
D) 500 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Please use the following information to answer the following question(s).
You work for a company selling tropical rain forest plants commonly found in the understory of the forest. These plants are shade tolerant and can be grown indoors because they require low light. Your employer wants you to find out what is the best type of light to maximize growth of these understory plants. Using a full spectrum of natural light would cause these plants to die because they are a shade-tolerant plant species.
From your biology class, you recall that the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis involve pigment molecules that absorb light of specific wavelengths. You also remember the experiments done by the German biologist Theodor Engelmann, in which he separated light using a prism into different wavelengths and then determined which wavelengths were best for promoting photosynthesis in the algae species he was examining. Your goal is to determine which wavelengths (colors) of light are best for promoting photosynthesis to enhance growth in your species of plant. To achieve this, you grew your plants under different wavelengths of light and measured their growth rates. The wavelengths were measured in nanometers (nm), and the growth rate was measured in millimeters per day (mm/day). The data you collected are as follows:

Make a bar graph plotting growth rates on the y-axis and wavelengths of light on the x-axis. Referring to your graph, answer the following question(s):
Which wavelength is best for your plants' growth?
A) 650 nm
B) 550 nm
C) 500 nm
D) 400 nm
You work for a company selling tropical rain forest plants commonly found in the understory of the forest. These plants are shade tolerant and can be grown indoors because they require low light. Your employer wants you to find out what is the best type of light to maximize growth of these understory plants. Using a full spectrum of natural light would cause these plants to die because they are a shade-tolerant plant species.
From your biology class, you recall that the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis involve pigment molecules that absorb light of specific wavelengths. You also remember the experiments done by the German biologist Theodor Engelmann, in which he separated light using a prism into different wavelengths and then determined which wavelengths were best for promoting photosynthesis in the algae species he was examining. Your goal is to determine which wavelengths (colors) of light are best for promoting photosynthesis to enhance growth in your species of plant. To achieve this, you grew your plants under different wavelengths of light and measured their growth rates. The wavelengths were measured in nanometers (nm), and the growth rate was measured in millimeters per day (mm/day). The data you collected are as follows:

Make a bar graph plotting growth rates on the y-axis and wavelengths of light on the x-axis. Referring to your graph, answer the following question(s):
Which wavelength is best for your plants' growth?
A) 650 nm
B) 550 nm
C) 500 nm
D) 400 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



