Deck 10: The Structure and Function of DNA
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/46
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: The Structure and Function of DNA
1
Evidence for the spiral nature of DNA came from ______.
A) X-ray crystallography studies
B) studies of disease-causing bacteria
C) base rule studies
D) bacteriophage studies
A) X-ray crystallography studies
B) studies of disease-causing bacteria
C) base rule studies
D) bacteriophage studies
A
2
In a DNA double helix,adenine pairs with ______ and guanine pairs with ______.
A) cytosine... thymine
B) guanine... adenine
C) thymine... cytosine
D) uracil... cytosine
A) cytosine... thymine
B) guanine... adenine
C) thymine... cytosine
D) uracil... cytosine
C
3
How many amino acids are common to all living systems?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 100
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 100
B
4
The backbone of DNA consists of ______.
A) nitrogenous bases
B) a repeating sugar-nucleotide-sugar-nucleotide pattern
C) a repeating sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate pattern
D) paired nucleotides
A) nitrogenous bases
B) a repeating sugar-nucleotide-sugar-nucleotide pattern
C) a repeating sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate pattern
D) paired nucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If adenine makes up 20% of the bases in a DNA double helix,what percent of the bases are guanine?
A) 60%
B) 40%
C) 20%
D) 30%
A) 60%
B) 40%
C) 20%
D) 30%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following enzymes is responsible for RNA synthesis?
A) RNase
B) RNA helicase
C) RNA ligase
D) RNA polymerase
A) RNase
B) RNA helicase
C) RNA ligase
D) RNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
RNA contains the nitrogenous base ______ instead of ______,which is only found in DNA.
A) a deoxyribose sugar... a ribose sugar
B) uracil... thymine
C) uracil... guanine
D) thymine... uracil
A) a deoxyribose sugar... a ribose sugar
B) uracil... thymine
C) uracil... guanine
D) thymine... uracil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Thymine and cytosine differ from adenine and guanine in that
A) thymine and cytosine are single-ring structures, whereas adenine and guanine are double-ring structures.
B) thymine and cytosine are only found in DNA, whereas adenine and guanine are found in both DNA and RNA.
C) thymine and cytosine are only found in DNA, whereas adenine and guanine are only found in RNA.
D) thymine and cytosine are larger nitrogenous bases.
A) thymine and cytosine are single-ring structures, whereas adenine and guanine are double-ring structures.
B) thymine and cytosine are only found in DNA, whereas adenine and guanine are found in both DNA and RNA.
C) thymine and cytosine are only found in DNA, whereas adenine and guanine are only found in RNA.
D) thymine and cytosine are larger nitrogenous bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
After replication,______.
A) each new DNA double helix consists of two old strands
B) each new DNA double helix consists of one old strand and one new strand
C) each new DNA double helix consists of two new strands
D) one new DNA double helix consists of two old strands and the other new DNA double helix consists of two new strands
A) each new DNA double helix consists of two old strands
B) each new DNA double helix consists of one old strand and one new strand
C) each new DNA double helix consists of two new strands
D) one new DNA double helix consists of two old strands and the other new DNA double helix consists of two new strands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
DNA replication
A) is a slow process that results in virtually no errors.
B) requires DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase.
C) is a very fast process that results in numerous errors.
D) requires the cooperation of over a dozen enzymes and other proteins.
A) is a slow process that results in virtually no errors.
B) requires DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase.
C) is a very fast process that results in numerous errors.
D) requires the cooperation of over a dozen enzymes and other proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Transcription is the ______.
A) manufacture of a strand of RNA complementary to a strand of DNA
B) manufacture of two new DNA double helices that are identical to an old DNA double helix
C) modification of a strand of RNA prior to the manufacture of a protein
D) manufacture of a protein based on information carried by RNA
A) manufacture of a strand of RNA complementary to a strand of DNA
B) manufacture of two new DNA double helices that are identical to an old DNA double helix
C) modification of a strand of RNA prior to the manufacture of a protein
D) manufacture of a protein based on information carried by RNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If a strand of DNA has the sequence AAGCTC,transcription will result in a(n)______.
A) single RNA strand with the sequence TTCGAG
B) DNA double helix with the sequence AAGCTC for one strand and TTCGAG for the complementary strand
C) single RNA strand with the sequence UUCGAG
D) RNA double helix with the sequence UUCGAG for one strand and AAGCUC for the complimentary strand
A) single RNA strand with the sequence TTCGAG
B) DNA double helix with the sequence AAGCTC for one strand and TTCGAG for the complementary strand
C) single RNA strand with the sequence UUCGAG
D) RNA double helix with the sequence UUCGAG for one strand and AAGCUC for the complimentary strand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What type of chemical bond joins the bases of complementary DNA strands?
A) ionic
B) covalent
C) hydrophilic
D) hydrogen
A) ionic
B) covalent
C) hydrophilic
D) hydrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The shared genetic code of all life on Earth is evidence that ______.
A) the genetic code arose relatively late in the history of life on Earth
B) DNA replication is error-free
C) all life shares a common ancestry
D) bacterial cells arose earlier than eukaryotic cells
A) the genetic code arose relatively late in the history of life on Earth
B) DNA replication is error-free
C) all life shares a common ancestry
D) bacterial cells arose earlier than eukaryotic cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What name is given to the collection of traits exhibited by an organism?
A) holotype
B) genotype
C) phenotype
D) morphology
A) holotype
B) genotype
C) phenotype
D) morphology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The modern phrasing of Beadle and Tatum's hypothesis about relationships between genes and their products is "one gene-one ______."
A) enzyme
B) RNA
C) protein
D) polypeptide
A) enzyme
B) RNA
C) protein
D) polypeptide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If one strand of a DNA double helix has the sequence GTCCAT,what is the sequence of the other strand?
A) ACTTGC
B) TGAACG
C) CAGGTA
D) CAGGUA
A) ACTTGC
B) TGAACG
C) CAGGTA
D) CAGGUA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
DNA and RNA are polymers composed of ______ monomers.
A) nucleotide
B) carbohydrate
C) fatty acid
D) amino acid
A) nucleotide
B) carbohydrate
C) fatty acid
D) amino acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Who discovered the structure of DNA?
A) Pauling
B) Watson and Crick
C) Franklin
D) Hershey and Chase
A) Pauling
B) Watson and Crick
C) Franklin
D) Hershey and Chase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How many nucleotides make up a codon?
A) two
B) three
C) four
D) five
A) two
B) three
C) four
D) five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Peptide bonds form between ______.
A) amino acids
B) an mRNA codon and a tRNA anticodon
C) a tRNA and the amino acid it is carrying
D) an mRNA transcript and the small ribosomal subunit
A) amino acids
B) an mRNA codon and a tRNA anticodon
C) a tRNA and the amino acid it is carrying
D) an mRNA transcript and the small ribosomal subunit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)must use its own ______ to reproduce.
A) DNA polymerase
B) reverse transcriptase
C) RNA polymerase
D) tRNA
A) DNA polymerase
B) reverse transcriptase
C) RNA polymerase
D) tRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The expressed (coding)regions of eukaryotic genes are called ______.
A) caps
B) promoters
C) exons
D) introns
A) caps
B) promoters
C) exons
D) introns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Translation converts the information stored in ______ to ______.
A) DNA... RNA
B) RNA... a polypeptide
C) DNA... a polypeptide
D) RNA... DNA
A) DNA... RNA
B) RNA... a polypeptide
C) DNA... a polypeptide
D) RNA... DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The figure below shows the flow of genetic information in a eukaryotic cell.The transfer of information from DNA into an RNA molecule is known as ______. 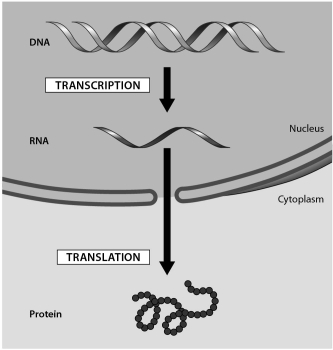
A) DNA replication
B) transcription
C) polypeptide
D) translation

A) DNA replication
B) transcription
C) polypeptide
D) translation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A mutation within a gene that will insert a premature stop codon in mRNA would ______.
A) result in a polypeptide that is one amino acid shorter than the one produced prior to the mutation
B) result in a shortened polypeptide chain
C) change the location at which transcription of the next gene begins
D) have the same effect as deleting a single nucleotide in the gene
A) result in a polypeptide that is one amino acid shorter than the one produced prior to the mutation
B) result in a shortened polypeptide chain
C) change the location at which transcription of the next gene begins
D) have the same effect as deleting a single nucleotide in the gene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The DNA codon AGT codes for an amino acid carried by a tRNA with the anticodon ______.
A) TCU
B) AGU
C) TCA
D) AGT
A) TCU
B) AGU
C) TCA
D) AGT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Where is translation accomplished?
A) lysosomes
B) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
C) ribosomes
D) nucleoli
A) lysosomes
B) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
C) ribosomes
D) nucleoli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The correct sequence of events occurring during transcription is ______.
A) splicing, capping, tailing
B) initiation, elongation, termination
C) tailing, capping, splicing
D) elongation, initiation, termination
A) splicing, capping, tailing
B) initiation, elongation, termination
C) tailing, capping, splicing
D) elongation, initiation, termination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the smallest number of nucleotides that must be added or subtracted to change the triplet grouping of the genetic message?
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Plant viruses ______.
A) often use RNA, rather than DNA, as their genetic material
B) benefit plants, rather than causing disease
C) cause diseases that can be easily cured
D) do not exist-viruses only attack animals
A) often use RNA, rather than DNA, as their genetic material
B) benefit plants, rather than causing disease
C) cause diseases that can be easily cured
D) do not exist-viruses only attack animals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What protects mRNA from attack by cellular enzymes?
A) RNA splicing
B) the removal of exons
C) the lack of RNA-digesting enzymes in the cytoplasm
D) a cap and tail
A) RNA splicing
B) the removal of exons
C) the lack of RNA-digesting enzymes in the cytoplasm
D) a cap and tail

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Mad cow disease is caused by
A) a retrovirus similar to HIV.
B) an enveloped virus.
C) small circular RNA molecules called viroids.
D) infectious proteins called prions.
A) a retrovirus similar to HIV.
B) an enveloped virus.
C) small circular RNA molecules called viroids.
D) infectious proteins called prions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How can bacteriophage DNA be spread from cell to cell without causing cell death?
A) by altering the way a cell splices its RNA
B) via a lytic cycle
C) via a lysogenic cycle
D) by altering its DNA
A) by altering the way a cell splices its RNA
B) via a lytic cycle
C) via a lysogenic cycle
D) by altering its DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The RNA that is translated into a polypeptide is ______ RNA.
A) nuclear
B) ribosomal
C) transfer
D) messenger
A) nuclear
B) ribosomal
C) transfer
D) messenger

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
During translation,what is the correct order of events that occur as an amino acid is added?
A) codon recognition, peptide bond formation, translocation
B) translocation, codon recognition, termination
C) initiation, codon recognition, termination
D) peptide bond formation, translocation, codon recognition
A) codon recognition, peptide bond formation, translocation
B) translocation, codon recognition, termination
C) initiation, codon recognition, termination
D) peptide bond formation, translocation, codon recognition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The region of DNA where RNA synthesis begins is the ______.
A) start codon
B) promoter
C) initiator
D) processor
A) start codon
B) promoter
C) initiator
D) processor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A(n)______ is to bacteria as a ______ is to animal cells.
A) retrovirus... virus
B) phage... prophage
C) prophage... provirus
D) RNA virus... DNA virus
A) retrovirus... virus
B) phage... prophage
C) prophage... provirus
D) RNA virus... DNA virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The absence of a terminator in transcription will result in ______.
A) the creation of a virus
B) a strand of mRNA that lacks its cap and tail
C) the production of a longer RNA molecule
D) the production of a shorter RNA molecule
A) the creation of a virus
B) a strand of mRNA that lacks its cap and tail
C) the production of a longer RNA molecule
D) the production of a shorter RNA molecule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the ultimate source of all diversity?
A) natural selection
B) sexual recombination
C) meiosis
D) mutation
A) natural selection
B) sexual recombination
C) meiosis
D) mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Please read the following scenario to answer the following question(s).
While working with cultured mouse cells, a researcher unknowingly treated the cells with a mutagen that causes the deletion or insertion of individual nucleotides in DNA. Subsequently, she isolated and cultured a single cell from this group. She noticed that the progeny of this cell were not producing a certain protein and that this affected their survival.
The mutation that resulted from her accident was probably ______.
A) an amino acid substitution
B) one that changed the triplet grouping of the genetic message
C) an error in translation
D) a loss in regulation of gene expression
While working with cultured mouse cells, a researcher unknowingly treated the cells with a mutagen that causes the deletion or insertion of individual nucleotides in DNA. Subsequently, she isolated and cultured a single cell from this group. She noticed that the progeny of this cell were not producing a certain protein and that this affected their survival.
The mutation that resulted from her accident was probably ______.
A) an amino acid substitution
B) one that changed the triplet grouping of the genetic message
C) an error in translation
D) a loss in regulation of gene expression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Please read the following scenario to answer the following question(s).
If you were asked to study the pattern of bacterial growth (increase in numbers over time) during an infection, you would find that numbers of bacteria increase exponentially up to a certain point. Assume that you have been asked to interpret the growth of bacteriophages. You infect the host bacteria and measure the increase of phages over a defined period of time. You plot the results and get the graph shown here.
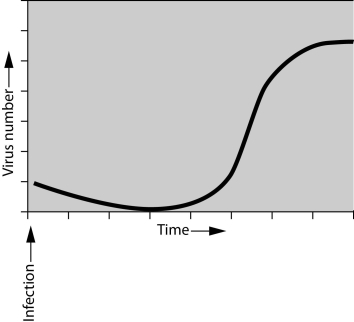
The first thing you notice is that there is no immediate increase in viruses following infection.This is because ______.
A) it takes the virus time to adapt to the host
B) although the virus has infected the host, it takes time to complete the lytic cycle
C) the host is immune to the virus
D) the virus is in a lysogenic cycle throughout the experiment
If you were asked to study the pattern of bacterial growth (increase in numbers over time) during an infection, you would find that numbers of bacteria increase exponentially up to a certain point. Assume that you have been asked to interpret the growth of bacteriophages. You infect the host bacteria and measure the increase of phages over a defined period of time. You plot the results and get the graph shown here.

The first thing you notice is that there is no immediate increase in viruses following infection.This is because ______.
A) it takes the virus time to adapt to the host
B) although the virus has infected the host, it takes time to complete the lytic cycle
C) the host is immune to the virus
D) the virus is in a lysogenic cycle throughout the experiment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Please read the following scenario to answer the following question(s).
If you were asked to study the pattern of bacterial growth (increase in numbers over time) during an infection, you would find that numbers of bacteria increase exponentially up to a certain point. Assume that you have been asked to interpret the growth of bacteriophages. You infect the host bacteria and measure the increase of phages over a defined period of time. You plot the results and get the graph shown here.

Once viruses are detected,the number of viruses increases rapidly.This is because ______.
A) lysogeny produces large numbers of bacteriophages
B) DNA viruses reproduce more rapidly than RNA viruses
C) the host cell speeds the release process
D) the viruses lyse the hosts to release mature viruses all at once
If you were asked to study the pattern of bacterial growth (increase in numbers over time) during an infection, you would find that numbers of bacteria increase exponentially up to a certain point. Assume that you have been asked to interpret the growth of bacteriophages. You infect the host bacteria and measure the increase of phages over a defined period of time. You plot the results and get the graph shown here.

Once viruses are detected,the number of viruses increases rapidly.This is because ______.
A) lysogeny produces large numbers of bacteriophages
B) DNA viruses reproduce more rapidly than RNA viruses
C) the host cell speeds the release process
D) the viruses lyse the hosts to release mature viruses all at once

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Examine the genetic code table,shown below.The codon AGC codes for the amino acid ______. 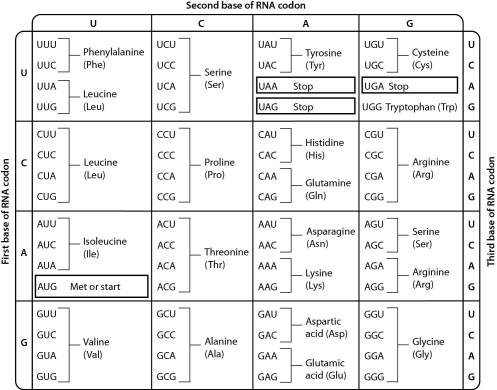
A) serine
B) arginine
C) threonine
D) alanine

A) serine
B) arginine
C) threonine
D) alanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Please read the following scenario to answer the following question(s).
While working with cultured mouse cells, a researcher unknowingly treated the cells with a mutagen that causes the deletion or insertion of individual nucleotides in DNA. Subsequently, she isolated and cultured a single cell from this group. She noticed that the progeny of this cell were not producing a certain protein and that this affected their survival.
The mutation would be most harmful to the cells if it resulted in ______.
A) a single nucleotide insertion near the start of the coding sequence
B) a single nucleotide deletion near the end of the coding sequence
C) a single nucleotide in the middle of an intron
D) deletion of a triplet near the middle of the gene
While working with cultured mouse cells, a researcher unknowingly treated the cells with a mutagen that causes the deletion or insertion of individual nucleotides in DNA. Subsequently, she isolated and cultured a single cell from this group. She noticed that the progeny of this cell were not producing a certain protein and that this affected their survival.
The mutation would be most harmful to the cells if it resulted in ______.
A) a single nucleotide insertion near the start of the coding sequence
B) a single nucleotide deletion near the end of the coding sequence
C) a single nucleotide in the middle of an intron
D) deletion of a triplet near the middle of the gene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consider the following figure.It indicates that a single amino acid substitution ______. 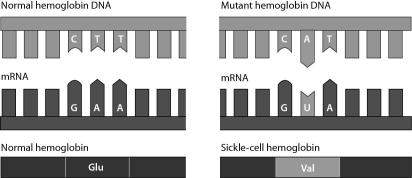
A) always involves adenine and uracil
B) may alter a protein so that it no longer functions properly
C) is a silent mutation
D) causes a nonsense mutation

A) always involves adenine and uracil
B) may alter a protein so that it no longer functions properly
C) is a silent mutation
D) causes a nonsense mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



