Deck 27: Plant Tissues
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/96
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 27: Plant Tissues
1

Use the figure above to answer the following two questions.
The letter "B" in the accompanying figure represents ____.
A) sclerenchyma fibers
B) parenchyma
C) xylem
D) epidermis
E) phloem
B
2
Funds from carbon offsets, which are purchased by companies and individuals, are used for many purposes. What is one of these?
A) replanting deforested areas
B) burning large expanses of rainforests
C) decreasing plant density in existing forests
D) clear-cutting old growth forests
E) converting forests to cropland
A) replanting deforested areas
B) burning large expanses of rainforests
C) decreasing plant density in existing forests
D) clear-cutting old growth forests
E) converting forests to cropland
A
3

Use the figure above to answer the following two questions.
The letter "A" in the accompanying figure represents ____.
A) sclerenchyma fibers
B) parenchyma
C) xylem
D) epidermis
E) phloem
A
4
Chloroplast-containing parenchyma tissue is called ____.
A) sclerenchyma
B) collenchyma
C) meristem
D) mesophyll
E) periderm
A) sclerenchyma
B) collenchyma
C) meristem
D) mesophyll
E) periderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What are leaves specialized to do?
A) provide structural support
B) intercept sunlight for photosynthesis
C) absorb water
D) absorb minerals
E) distribute water and minerals
A) provide structural support
B) intercept sunlight for photosynthesis
C) absorb water
D) absorb minerals
E) distribute water and minerals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which cells are alive at maturity?
A) sieve elements
B) vessel members
C) tracheids
D) vessel members and tracheids
E) sieve elements and vessel members
A) sieve elements
B) vessel members
C) tracheids
D) vessel members and tracheids
E) sieve elements and vessel members

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
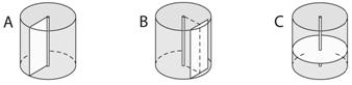
Use the figure above to answer the following two questions.
The letter "C" in the accompanying figure represents the ____ plane.
A) transverse
B) radial
C) tangential
D) elliptical
E) obtuse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
____ are short sections of underground stem encased by overlapping layers of thickened, modified leaves called scales.
A) Stolons
B) Rhizomes
C) Bulbs
D) Corms
E) Tubers
A) Stolons
B) Rhizomes
C) Bulbs
D) Corms
E) Tubers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
One way in which monocots and eudicots differ is in ____.
A) having the capacity to bear seeds
B) their types of tissues
C) their organ systems
D) their pattern of tissue organization
E) having vascular bundles
A) having the capacity to bear seeds
B) their types of tissues
C) their organ systems
D) their pattern of tissue organization
E) having vascular bundles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The complex polysaccharide that provides flexibility to the primary walls of collenchyma cells is called ____.
A) cellulose
B) lignin
C) fiber
D) pectin
E) cuticle
A) cellulose
B) lignin
C) fiber
D) pectin
E) cuticle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Complex tissues are tissues consisting of ____.
A) two or more cell types
B) only one cell type
C) only parenchyma cells
D) only collenchyma cells
E) only sclerenchyma cells
A) two or more cell types
B) only one cell type
C) only parenchyma cells
D) only collenchyma cells
E) only sclerenchyma cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which statement does not apply to carbon dioxide?
A) It is released in the burning of fossil fuels.
B) It contributes to ozone destruction.
C) It is absorbed by plants.
D) It contributes to global warming.
E) It is increasing in abundance in the atmosphere.
A) It is released in the burning of fossil fuels.
B) It contributes to ozone destruction.
C) It is absorbed by plants.
D) It contributes to global warming.
E) It is increasing in abundance in the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Regions of a stem that give rise to new shoots or roots are called ____.
A) ground tissue
B) dermal tissue
C) cortex cells
D) internodes
E) nodes
A) ground tissue
B) dermal tissue
C) cortex cells
D) internodes
E) nodes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What types of plants dominate the plant kingdom?
A) eudicots
B) monocots
C) trees
D) flowering plants
E) grasses
A) eudicots
B) monocots
C) trees
D) flowering plants
E) grasses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The vascular tissue that conducts water and mineral ions is called ____.
A) sieve elements
B) companion cells
C) sclerenchyma
D) xylem
E) phloem
A) sieve elements
B) companion cells
C) sclerenchyma
D) xylem
E) phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Most of the plant body is composed of ____.
A) dermal tissue
B) root tissue
C) ground tissue
D) vascular tissue
E) cork tissue
A) dermal tissue
B) root tissue
C) ground tissue
D) vascular tissue
E) cork tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which component distributes water and nutrients throughout the plant body?
A) ground tissue
B) vascular tissue
C) dermal tissue
D) root
E) shoot
A) ground tissue
B) vascular tissue
C) dermal tissue
D) root
E) shoot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What are the two organ systems of a vascular plant body?
A) shoots and roots
B) stems and leaves
C) stems and roots
D) leaves and roots
E) leaves and flowers
A) shoots and roots
B) stems and leaves
C) stems and roots
D) leaves and roots
E) leaves and flowers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Plants control the diffusion of water vapor and gases across the epidermis by means of ____.
A) xylem
B) phloem
C) periderm
D) companion cells
E) stomata
A) xylem
B) phloem
C) periderm
D) companion cells
E) stomata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

Use the figure above to answer the following two questions.
The letter "A" in the accompanying figure represents the ____ plane.
A) transverse
B) radial
C) tangential
D) elliptical
E) obtuse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure 27.8A
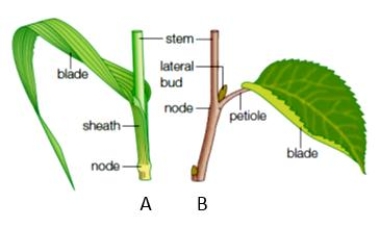
Figure "A" in the accompanying figure is a ____.
A) cotyledon
B) cladode
C) corm
D) eudicot leaf
E) monocot leaf

Figure "A" in the accompanying figure is a ____.
A) cotyledon
B) cladode
C) corm
D) eudicot leaf
E) monocot leaf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is periderm?
A) special epidermal cells that regulate gas exchange
B) outer layer of the vascular cylinder in a plant root
C) layers of cells just inside root endodermis
D) dermal tissue that replaces epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
E) tissue that consists of densely packed dead cells with thickened, waxy walls
A) special epidermal cells that regulate gas exchange
B) outer layer of the vascular cylinder in a plant root
C) layers of cells just inside root endodermis
D) dermal tissue that replaces epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
E) tissue that consists of densely packed dead cells with thickened, waxy walls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Roots that form on stems or leaves are called ____.
A) taproots
B) fibrous
C) adventitious
D) primary
E) secondary
A) taproots
B) fibrous
C) adventitious
D) primary
E) secondary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 27.13
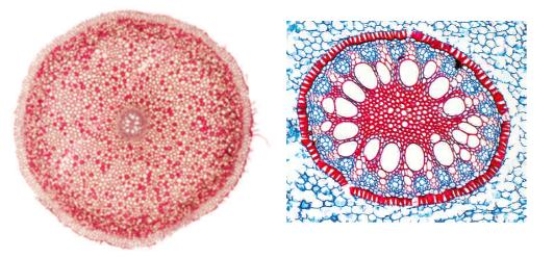
The accompanying figure shows a cross-section through the vascular cylinder of a(n) ____.
A) monocot stem
B) eudicot stem
C) monocot root
D) eudicot root
E) eudicot leaf vein

The accompanying figure shows a cross-section through the vascular cylinder of a(n) ____.
A) monocot stem
B) eudicot stem
C) monocot root
D) eudicot root
E) eudicot leaf vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A mass of ____ lies just below the surface of a terminal bud of an actively lengthening shoot.
A) ground tissue
B) dermal tissue
C) vascular tissue
D) apical meristem
E) cortex cells
A) ground tissue
B) dermal tissue
C) vascular tissue
D) apical meristem
E) cortex cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
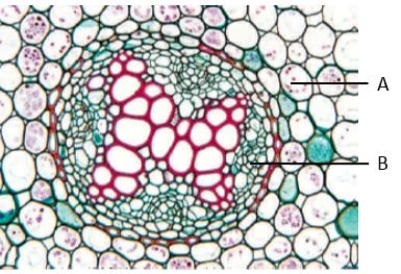
Use the figure above to answer the following two questions.
The letter "A" in the accompanying figure represents ____.
A) pericycle
B) endodermis
C) primary xylem
D) root cortex
E) primary phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Cylindrical layers of meristem that run lengthwise through shoots and roots, and allow for thickening, are called ____.
A) lateral meristems
B) apical meristems
C) ground meristem
D) Procambium
E) Protoderm
A) lateral meristems
B) apical meristems
C) ground meristem
D) Procambium
E) Protoderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Division and differentiation of ground meristem gives rise to ____.
A) ground tissue
B) vascular tissue
C) dermal tissue
D) protoderm
E) procambium
A) ground tissue
B) vascular tissue
C) dermal tissue
D) protoderm
E) procambium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 27.8A

What are leaf veins?
A) vascular bundles of leaves
B) photosynthetic cells of leaves
C) sclerenchyma cells of leaves
D) palisade mesophyll of leaves
E) spongy mesophyll of leaves

What are leaf veins?
A) vascular bundles of leaves
B) photosynthetic cells of leaves
C) sclerenchyma cells of leaves
D) palisade mesophyll of leaves
E) spongy mesophyll of leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure 27.2
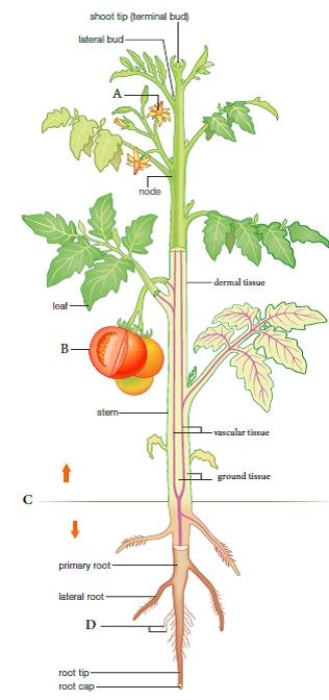
The plant parts ABOVE the line at "C" represent the __________.
A) ground tissue only
B) root system
C) shoot system
D) stalk
E) light-independent parts

The plant parts ABOVE the line at "C" represent the __________.
A) ground tissue only
B) root system
C) shoot system
D) stalk
E) light-independent parts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In most eudicots, the primary root that emerges from a seed thickens and grows longer to become a(n) ____.
A) taproot
B) fibrous root system
C) secondary root
D) adventitious root
E) lateral root
A) taproot
B) fibrous root system
C) secondary root
D) adventitious root
E) lateral root

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 27.13

In most eudicots, a short stalk called a ____ attaches the leaf to a stem.
A) vascular bundle
B) petiole
C) node
D) bundle sheath
E) stomata

In most eudicots, a short stalk called a ____ attaches the leaf to a stem.
A) vascular bundle
B) petiole
C) node
D) bundle sheath
E) stomata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Epidermal cells secrete a translucent, waxy ____ to slow water loss.
A) mesophyll
B) cuticle
C) pectin layer
D) lignin layer
E) trichome
A) mesophyll
B) cuticle
C) pectin layer
D) lignin layer
E) trichome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Primary growth in roots originates from ____.
A) dermal cells
B) vascular cells
C) apical meristems
D) lateral meristems
E) the pericycle
A) dermal cells
B) vascular cells
C) apical meristems
D) lateral meristems
E) the pericycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The outer boundary of a root's vascular cylinder is a layer of cells called ____.
A) pericycle
B) cortex
C) epidermis
D) stele
E) endodermis
A) pericycle
B) cortex
C) epidermis
D) stele
E) endodermis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which environment is most likely to produce trees without annual rings?
A) tropical rain forest
B) northern evergreen forest
C) areas with alternating wet and dry seasons
D) temperate-deciduous forests
E) none of these, because annual rings are characteristic of all trees
A) tropical rain forest
B) northern evergreen forest
C) areas with alternating wet and dry seasons
D) temperate-deciduous forests
E) none of these, because annual rings are characteristic of all trees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which structure gives rise to lateral roots?
A) endodermis
B) cortex
C) epidermis
D) pericycle
E) pith
A) endodermis
B) cortex
C) epidermis
D) pericycle
E) pith

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is wood?
A) secondary xylem that has accumulated outside a cylinder of vascular cambium
B) secondary xylem that has accumulated inside a cylinder of vascular cambium
C) primary xylem that has accumulated outside a cylinder of vascular cambium
D) primary xylem that has accumulated inside a cylinder of vascular cambium
E) vascular cambium cells
A) secondary xylem that has accumulated outside a cylinder of vascular cambium
B) secondary xylem that has accumulated inside a cylinder of vascular cambium
C) primary xylem that has accumulated outside a cylinder of vascular cambium
D) primary xylem that has accumulated inside a cylinder of vascular cambium
E) vascular cambium cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

Use the figure above to answer the following two questions.
The letter "B" in the accompanying figure represents ____.
A) pericycle
B) endodermis
C) xylem
D) root cortex
E) phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Runners are modified stems that resemble roots and are also known as ____.
A) stolons
B) rhizomes
C) bulbs
D) corms
E) Tubers
A) stolons
B) rhizomes
C) bulbs
D) corms
E) Tubers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Choose the one most appropriate answer for each.
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
companion cells
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
companion cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Choose the one most appropriate answer for each.
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
vascular bundles
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
vascular bundles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
endodermis
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
endodermis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
parenchyma
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
parenchyma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
epidermis
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
epidermis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
phloem
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Choose the one most appropriate answer for each.
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
vascular cylinder
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
vascular cylinder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
collenchyma
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
collenchyma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
stomata
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
stomata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
xylem
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
xylem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Choose the one most appropriate answer for each.
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
sclereids
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
sclereids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Choose the one most appropriate answer for each.
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
sieve elements
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
sieve elements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
mesophyll
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
mesophyll

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Choose the one most appropriate answer for each.
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
spongy mesophyll
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
spongy mesophyll

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Choose the one most appropriate answer for each.
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
cork cambium
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
cork cambium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Choose the one most appropriate answer for each.
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
tracheids
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
tracheids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Choose the one most appropriate answer for each.
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
meristems
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
meristems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
sclerenchyma
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
sclerenchyma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Choose the one most appropriate answer for each.
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
palisade mesophyll
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
palisade mesophyll

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Choose the one most appropriate answer for each.
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
pericycle
a.gives rise to periderm
b.transfer sugars into sieve elements
c.vascular tissue in the root
d.living cells that conduct sugars and other organic solutes
e.a layer of specialized parenchyma one or two cells thick, just inside the endodermis
f.clusters of strands containing xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium
g.the principle xylem cells of pines, cypress, and other conifers
h.cells with thick secondary walls impregnated with lignin that are especially abundant in some fruits and seeds
i.the principal photosynthetic region of a leaf
j.regions of undifferentiated cells that can divide rapidly
k.bottom layer of parenchyma in a leaf with large air spaces between the cells
pericycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Classification. Answer the following questions in reference to the five plant tissues listed below.
a.parenchyma
b.collenchyma
c.sclerenchyma
d.xylem
e.phloem
tissue involved with storage of proteins, water, oils, and starch
a.parenchyma
b.collenchyma
c.sclerenchyma
d.xylem
e.phloem
tissue involved with storage of proteins, water, oils, and starch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
pith
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
pith

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Classification. Respond to the following statements in reference to the four source tissues of plant roots listed below.
a.primary meristems
b.ground meristem
c.pericycle
d.vascular cambium
This tissue gives rise to ground meristem.
a.primary meristems
b.ground meristem
c.pericycle
d.vascular cambium
This tissue gives rise to ground meristem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Classification. Respond to the following statements in reference to the five plant tissues listed below.
a.protoderm
b.ground meristem
c.procambium
d.vascular cambium
e.cork cambium
This tissue gives rise to the xylem and phloem of an older tree.
a.protoderm
b.ground meristem
c.procambium
d.vascular cambium
e.cork cambium
This tissue gives rise to the xylem and phloem of an older tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Classification. Respond to the following statements in reference to the five plant tissues listed below.
a.protoderm
b.ground meristem
c.procambium
d.vascular cambium
e.cork cambium
This tissue gives rise to periderm.
a.protoderm
b.ground meristem
c.procambium
d.vascular cambium
e.cork cambium
This tissue gives rise to periderm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Classification. Respond to the following statements in reference to the four source tissues of plant roots listed below.
a.primary meristems
b.ground meristem
c.pericycle
d.vascular cambium
This tissue gives rise to protoderm and procambium.
a.primary meristems
b.ground meristem
c.pericycle
d.vascular cambium
This tissue gives rise to protoderm and procambium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Classification. Answer the following questions in reference to the five plant tissues listed below.
a.parenchyma
b.collenchyma
c.sclerenchyma
d.xylem
e.phloem
tissue containing cells with pectin on their primary walls
a.parenchyma
b.collenchyma
c.sclerenchyma
d.xylem
e.phloem
tissue containing cells with pectin on their primary walls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Classification. Answer the following questions in reference to the five plant tissues listed below.
a.parenchyma
b.collenchyma
c.sclerenchyma
d.xylem
e.phloem
part of ground tissue, sometimes containing lignin that strengthens the adult plant
a.parenchyma
b.collenchyma
c.sclerenchyma
d.xylem
e.phloem
part of ground tissue, sometimes containing lignin that strengthens the adult plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Classification. Respond to the following statements in reference to the four source tissues of plant roots listed below.
a.primary meristems
b.ground meristem
c.pericycle
d.vascular cambium
This tissue gives rise to the root cortex.
a.primary meristems
b.ground meristem
c.pericycle
d.vascular cambium
This tissue gives rise to the root cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Classification. Respond to the following statements in reference to the four source tissues of plant roots listed below.
a.primary meristems
b.ground meristem
c.pericycle
d.vascular cambium
This tissue gives rise to lateral roots.
a.primary meristems
b.ground meristem
c.pericycle
d.vascular cambium
This tissue gives rise to lateral roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Classification. Answer the following questions in reference to the five plant tissues listed below.
a.parenchyma
b.collenchyma
c.sclerenchyma
d.xylem
e.phloem
vascular tissue that conducts and distributes food to plant cells
a.parenchyma
b.collenchyma
c.sclerenchyma
d.xylem
e.phloem
vascular tissue that conducts and distributes food to plant cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Labeling. The following statements refer to the figure below showing the general body plan of a plant. Figure 27.2
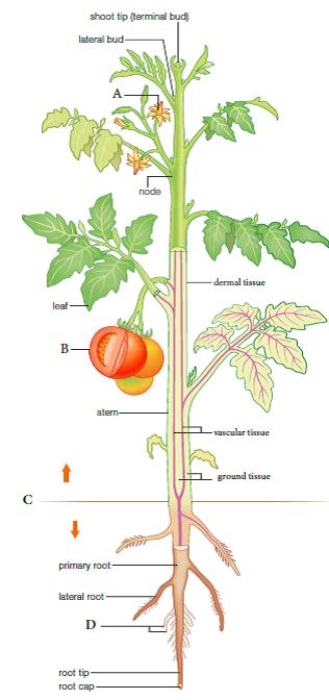
The absorption of water and minerals occurs at the structure labeled __________.

The absorption of water and minerals occurs at the structure labeled __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Classification. Answer the following questions in reference to the five plant tissues listed below.
a.parenchyma
b.collenchyma
c.sclerenchyma
d.xylem
e.phloem
vascular tissue that conducts water and mineral ions throughout a plant
a.parenchyma
b.collenchyma
c.sclerenchyma
d.xylem
e.phloem
vascular tissue that conducts water and mineral ions throughout a plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
periderm
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
periderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
procambium
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
procambium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Match all applicable letters with the most appropriate term.
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
vascular cambium
a.tissue that supports rapidly growing pant parts
b.cells that die when mature, but their thick cell walls remain to lend sturdiness to the plant
c.replaces the epidermis on the surfaces of older stems and roots
d.ground tissue located inside the ring of vascular bundles in a eudicot stem
e.cells that regulate the diffusion of water vapor and other gases into and out of the plant
f.outermost layer of a young plant
g.comprised of sieve elements and their associated companion cells
h.ground tissue is primarily composed of this type of cell
i.gives rise to xylem and phloem during secondary growth
j.layer of cells that form the outer boundary of the vascular cylinder
k.gives rise to vascular tissue during primary growth
l.consists of two types of cells: vessel elements and tracheids
m.parenchyma cells that contain chloroplasts
vascular cambium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Classification. Respond to the following statements in reference to the five plant tissues listed below.
a.protoderm
b.ground meristem
c.procambium
d.vascular cambium
e.cork cambium
This tissue gives rise to primary vascular tissue.
a.protoderm
b.ground meristem
c.procambium
d.vascular cambium
e.cork cambium
This tissue gives rise to primary vascular tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Classification. Respond to the following statements in reference to the four source tissues of plant roots listed below.
a.primary meristems
b.ground meristem
c.pericycle
d.vascular cambium
This tissue gives rise to secondary phloem and xylem.
a.primary meristems
b.ground meristem
c.pericycle
d.vascular cambium
This tissue gives rise to secondary phloem and xylem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Classification. Respond to the following statements in reference to the five plant tissues listed below.
a.protoderm
b.ground meristem
c.procambium
d.vascular cambium
e.cork cambium
This tissue gives rise to primary tissue forming xylem and phloem.
a.protoderm
b.ground meristem
c.procambium
d.vascular cambium
e.cork cambium
This tissue gives rise to primary tissue forming xylem and phloem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Classification. Respond to the following statements in reference to the five plant tissues listed below.
a.protoderm
b.ground meristem
c.procambium
d.vascular cambium
e.cork cambium
This tissue gives rise to the protective covering that forms the bark of a tree.
a.protoderm
b.ground meristem
c.procambium
d.vascular cambium
e.cork cambium
This tissue gives rise to the protective covering that forms the bark of a tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



