Deck 11: Keynesianism: the Macroeconomics of Wage and Price Rigidity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/98
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Keynesianism: the Macroeconomics of Wage and Price Rigidity
1
According to the efficiency wage model,during a recession,firms will not reduce real wages because
A)unions would go on strike, reducing profitability.
B)this would reduce worker effort and productivity.
C)the equilibrium real wage has increased.
D)legally, they can't.
A)unions would go on strike, reducing profitability.
B)this would reduce worker effort and productivity.
C)the equilibrium real wage has increased.
D)legally, they can't.
this would reduce worker effort and productivity.
2
The effort curve is
A)horizontal, because work effort is independent of the real wage.
B)negatively sloped, because of diminishing marginal returns to labor.
C)positively sloped, because of the law of increasing cost.
D)S-shaped, because a small increase in the real wage will increase work effort more at an intermediate wage than at a low wage or at a high wage.
A)horizontal, because work effort is independent of the real wage.
B)negatively sloped, because of diminishing marginal returns to labor.
C)positively sloped, because of the law of increasing cost.
D)S-shaped, because a small increase in the real wage will increase work effort more at an intermediate wage than at a low wage or at a high wage.
S-shaped, because a small increase in the real wage will increase work effort more at an intermediate wage than at a low wage or at a high wage.
3
In the efficiency wage model,an increase in productivity would
A)increase output but decrease the real wage.
B)decrease the real wage but have no effect on output.
C)increase output but have no effect on the real wage.
D)have no effect on either output or the real wage.
A)increase output but decrease the real wage.
B)decrease the real wage but have no effect on output.
C)increase output but have no effect on the real wage.
D)have no effect on either output or the real wage.
increase output but have no effect on the real wage.
4
According to the efficiency wage model,firms will pay the real wage that
A)maximizes workers' marginal productivity.
B)maximizes the marginal productivity of capital and the marginal productivity of labor together.
C)maximizes effort per dollar of real wage.
D)minimizes hiring and training costs to the firm.
A)maximizes workers' marginal productivity.
B)maximizes the marginal productivity of capital and the marginal productivity of labor together.
C)maximizes effort per dollar of real wage.
D)minimizes hiring and training costs to the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the Keynesian model with efficiency wages
A)the full-employment line is determined where the quantity of labor demanded equals the quantity of labor supplied.
B)the full-employment level is determined at the intersection of the labor demand curve and the efficiency wage line.
C)an increase in labor supply increases employment.
D)a decrease in labor supply shifts the FE line to the left.
A)the full-employment line is determined where the quantity of labor demanded equals the quantity of labor supplied.
B)the full-employment level is determined at the intersection of the labor demand curve and the efficiency wage line.
C)an increase in labor supply increases employment.
D)a decrease in labor supply shifts the FE line to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the Keynesian model,the full-employment level of output is the amount of output produced when
A)the quantity of labor demanded equals the quantity of labor supplied.
B)the market wage exceeds the efficiency wage.
C)labor is paid an efficiency wage, and the real wage equals the marginal product of labor.
D)the real wage exceeds the nominal wage.
A)the quantity of labor demanded equals the quantity of labor supplied.
B)the market wage exceeds the efficiency wage.
C)labor is paid an efficiency wage, and the real wage equals the marginal product of labor.
D)the real wage exceeds the nominal wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the efficiency wage model with the efficiency wage above the market-clearing wage,when employment is at its full-employment level
A)labor supply equals labor demand.
B)there is an excess supply of labor.
C)there is an excess demand for labor.
D)there could be either an excess demand for, or an excess supply of, labor.
A)labor supply equals labor demand.
B)there is an excess supply of labor.
C)there is an excess demand for labor.
D)there could be either an excess demand for, or an excess supply of, labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Real-wage rigidity in the Keynesian efficiency wage diagram of the labor market is depicted by
A)a vertical labor supply curve at the efficient level of employment,
B)a vertical labor demand curve at the efficient level of employment.
C)a horizontal line at the efficiency wage.
D)a steep, positively sloped labor supply curve depicting various efficiency wages at various employment levels.
A)a vertical labor supply curve at the efficient level of employment,
B)a vertical labor demand curve at the efficient level of employment.
C)a horizontal line at the efficiency wage.
D)a steep, positively sloped labor supply curve depicting various efficiency wages at various employment levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the efficiency wage model,an increase in productivity will cause
A)no change in the real wage.
B)an increase in the real wage.
C)a decrease in the real wage.
D)an increase in both the real wage and the level of employment.
A)no change in the real wage.
B)an increase in the real wage.
C)a decrease in the real wage.
D)an increase in both the real wage and the level of employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the efficiency wage model,if the real wage is higher than the market-clearing wage so that there is an excess supply of labor
A)firms will hire new workers at lower wages.
B)firms will replace high-paid workers with low-paid, formerly unemployed workers.
C)employers will not hire workers who are willing to work for a lower wage.
D)firms will demand a higher level of effort from existing employees.
A)firms will hire new workers at lower wages.
B)firms will replace high-paid workers with low-paid, formerly unemployed workers.
C)employers will not hire workers who are willing to work for a lower wage.
D)firms will demand a higher level of effort from existing employees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Assuming no change in the effort curve of employees,the efficiency wage model implies that
A)the real wage is rigid and equals the efficiency wage.
B)the real wage exceeds the marginal productivity of labor.
C)an increase in the marginal productivity of capital will increase the real wage.
D)the real wage is procyclical.
A)the real wage is rigid and equals the efficiency wage.
B)the real wage exceeds the marginal productivity of labor.
C)an increase in the marginal productivity of capital will increase the real wage.
D)the real wage is procyclical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the Keynesian model,the real wage is mildly procyclical because
A)demand for labor fluctuates with the demand for final goods.
B)firms take advantage of recessions to pay slightly lower wages, since there's excess labor supply.
C)workers' effort may depend on the unemployment rate and the real wage.
D)the supply of labor fluctuates with the business cycle.
A)demand for labor fluctuates with the demand for final goods.
B)firms take advantage of recessions to pay slightly lower wages, since there's excess labor supply.
C)workers' effort may depend on the unemployment rate and the real wage.
D)the supply of labor fluctuates with the business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A model in which workers won't be concerned about the possibility of being fired if they don't work hard,because their wage is so low,is called
A)a cost-benefit model.
B)a job-stress model.
C)a gift-exchange model.
D)a shirking model.
A)a cost-benefit model.
B)a job-stress model.
C)a gift-exchange model.
D)a shirking model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Keynesians are skeptical of the classical theory that recessions are periods of increased mismatch between workers and jobs because
A)help-wanted advertising falls during recessions.
B)help-wanted advertising rises during recessions.
C)workers spend a lot of time searching for work in recessions.
D)people are indifferent between being employed or not.
A)help-wanted advertising falls during recessions.
B)help-wanted advertising rises during recessions.
C)workers spend a lot of time searching for work in recessions.
D)people are indifferent between being employed or not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The efficiency wage model can be modified to allow real wages to vary over the business cycle by assuming that
A)workers' effort may depend on the unemployment rate and the real wage.
B)during a recession, labor supply will decrease, reducing the efficiency wage.
C)during a recession, productivity will fall, causing a reduction in the efficiency wage.
D)during a boom, labor demand will increase, causing the efficiency wage to rise.
A)workers' effort may depend on the unemployment rate and the real wage.
B)during a recession, labor supply will decrease, reducing the efficiency wage.
C)during a recession, productivity will fall, causing a reduction in the efficiency wage.
D)during a boom, labor demand will increase, causing the efficiency wage to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A firm faces the following relationship between the real wage it pays and the effort exerted by its workers. 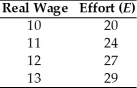
The marginal product of labor for this firm is given by MPN = E (100 - N)/9.How many workers will the firm employ?
A)96
B)92
C)88
D)80

The marginal product of labor for this firm is given by MPN = E (100 - N)/9.How many workers will the firm employ?
A)96
B)92
C)88
D)80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A firm faces the following relationship between the real wage it pays and the effort exerted by its workers. 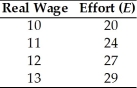
The marginal product of labor for this firm is given by MPN = E (100 - N)/9.The firm will choose to pay a wage such that the effort level is
A)20.
B)24.
C)27.
D)29.

The marginal product of labor for this firm is given by MPN = E (100 - N)/9.The firm will choose to pay a wage such that the effort level is
A)20.
B)24.
C)27.
D)29.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The existence of labor unions could contribute to real-wage rigidity,except that in the United States
A)labor unions are outlawed.
B)most workers aren't in unions.
C)unions are interested in benefits, not wages.
D)unions try to increase employment rather than negotiating over wages.
A)labor unions are outlawed.
B)most workers aren't in unions.
C)unions are interested in benefits, not wages.
D)unions try to increase employment rather than negotiating over wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The gift exchange motive suggests that
A)workers value benefits like health insurance more than job security.
B)workers prefer a nice work environment, even if they must accept lower wages.
C)workers who feel well treated will work harder and more efficiently.
D)workers will shirk if they are paid a low wage.
A)workers value benefits like health insurance more than job security.
B)workers prefer a nice work environment, even if they must accept lower wages.
C)workers who feel well treated will work harder and more efficiently.
D)workers will shirk if they are paid a low wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the efficiency wage model with the efficiency wage above the market-clearing wage,the level of employment depends on
A)the intersection of labor supply and labor demand.
B)the marginal productivity of capital and the marginal productivity of labor.
C)labor demand alone.
D)labor supply alone.
A)the intersection of labor supply and labor demand.
B)the marginal productivity of capital and the marginal productivity of labor.
C)labor demand alone.
D)labor supply alone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Because of price stickiness in the Keynesian model,a decline in investment demand will not cause the
A)LM curve to shift down and to the right in the short run.
B)LM curve to shift in the long run.
C)IS curve to shift down and to the left in the short run.
D)IS curve to shift in the long run.
A)LM curve to shift down and to the right in the short run.
B)LM curve to shift in the long run.
C)IS curve to shift down and to the left in the short run.
D)IS curve to shift in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the Keynesian model,firms are best characterized as
A)perfectly competitive.
B)irrational.
C)price takers.
D)monopolistically competitive.
A)perfectly competitive.
B)irrational.
C)price takers.
D)monopolistically competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In an economy where firms in most industries are monopolistically competitive firms,individual firms in each industry would produce ________ products and have a ________ share of industry output.
A)differentiated; large
B)differentiated; small
C)standardized; large
D)standardized; small
A)differentiated; large
B)differentiated; small
C)standardized; large
D)standardized; small

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the Keynesian model,a firm's high menu costs cause
A)real-wage rigidity.
B)full employment.
C)price stickiness.
D)efficiency wages.
A)real-wage rigidity.
B)full employment.
C)price stickiness.
D)efficiency wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Describe how each of the following changes would affect the equilibrium in the labor market in terms of the level of the real wage and quantity of employment in equilibrium:
(a)Increased immigration leads to higher labor supply at each real wage
(b)The effort curve makes a parallel shift upward
(c)Labor productivity increases (that is,the marginal product of labor increases at each level of employment).
(a)Increased immigration leads to higher labor supply at each real wage
(b)The effort curve makes a parallel shift upward
(c)Labor productivity increases (that is,the marginal product of labor increases at each level of employment).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In an economy where firms in most industries are purely competitive firms,individual firms in each industry would produce ________ products and have a ________ share of industry output.
A)differentiated; large
B)differentiated; small
C)standardized; large
D)standardized; small
A)differentiated; large
B)differentiated; small
C)standardized; large
D)standardized; small

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The cost to a firm of producing one more unit of output
A)usually exceeds the firm's price.
B)is significantly less than the firm's price for purely competitive firms operating in long-run equilibrium.
C)usually equals the firm's price for monopolistically competitive firms.
D)is the firm's marginal cost.
A)usually exceeds the firm's price.
B)is significantly less than the firm's price for purely competitive firms operating in long-run equilibrium.
C)usually equals the firm's price for monopolistically competitive firms.
D)is the firm's marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to the menu cost theory,firms will be slow in changing their prices because
A)if prices changed frequently, individuals would reduce their demand for that good because of uncertainty.
B)frequent price changes would be a sign of monopolistic behavior.
C)the cost of changing the price might exceed the additional revenue the price change would generate.
D)demand for their product would fall because consumers would purchase goods from firms that had not raised their prices.
A)if prices changed frequently, individuals would reduce their demand for that good because of uncertainty.
B)frequent price changes would be a sign of monopolistic behavior.
C)the cost of changing the price might exceed the additional revenue the price change would generate.
D)demand for their product would fall because consumers would purchase goods from firms that had not raised their prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to Nakamura and Steinsson's research,prices are ________ sticky than Bils and Klenow found because the latter failed to account for ________.
A)more; sales
B)more; taxes
C)less; taxes
D)less; sales
A)more; sales
B)more; taxes
C)less; taxes
D)less; sales

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When the demand for an imperfect competitor's product is greater than it planned,the firm will
A)increase the price of the product until supply equals demand.
B)meet the demand at its set price.
C)reduce the price until supply equals demand.
D)allow a shortage of the product to develop, without changing the product's price.
A)increase the price of the product until supply equals demand.
B)meet the demand at its set price.
C)reduce the price until supply equals demand.
D)allow a shortage of the product to develop, without changing the product's price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Why might firms pay an efficiency wage rather than a market-clearing wage?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The theory that firms will be slow to change their products' prices in response to changes in demand because there are costs to changing prices is called
A)transactions cost theory.
B)cost-benefit theory.
C)menu cost theory.
D)gift exchange theory.
A)transactions cost theory.
B)cost-benefit theory.
C)menu cost theory.
D)gift exchange theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If firms are price setters,a small decline in the demand for their outputs will cause them to
A)reduce price and reduce the level of output produced.
B)reduce output in the short run, but reduce price in the long run.
C)reduce price in the short run, but reduce output only in the long run.
D)increase price in the short run to offset the effect on profits of a decline in output.
A)reduce price and reduce the level of output produced.
B)reduce output in the short run, but reduce price in the long run.
C)reduce price in the short run, but reduce output only in the long run.
D)increase price in the short run to offset the effect on profits of a decline in output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In setting the price of its product,a monopolistic competitor sets the price equal to its marginal cost plus an amount called the
A)markup.
B)profit.
C)rent.
D)menu cost.
A)markup.
B)profit.
C)rent.
D)menu cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Firms that charge a price for their output in excess of marginal cost in the short run
A)are not maximizing profits.
B)cannot find buyers for their output.
C)are charging a markup.
D)will suffer huge losses.
A)are not maximizing profits.
B)cannot find buyers for their output.
C)are charging a markup.
D)will suffer huge losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the menu cost theory is true,then firms that change prices less frequently than other firms are likely to be in
A)more competitive industries.
B)service, rather than manufacturing, industries.
C)growing, rather than declining, industries.
D)less competitive industries.
A)more competitive industries.
B)service, rather than manufacturing, industries.
C)growing, rather than declining, industries.
D)less competitive industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A firm is a price taker if it
A)always sells its output at the industry-determined price.
B)takes consumer demand into consideration in setting its price.
C)takes its production costs into consideration in setting its price.
D)uses a pricing strategy to gain market share.
A)always sells its output at the industry-determined price.
B)takes consumer demand into consideration in setting its price.
C)takes its production costs into consideration in setting its price.
D)uses a pricing strategy to gain market share.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The effort of a firm's workers depends on their real wage according to the following schedule.
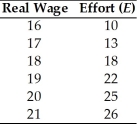
The marginal product of labor is MPN = E(400 - 4N)/30.
(a)What is the efficiency wage?
(b)How many workers will the firm hire?
(c)Suppose an adverse productivity shock reduces the marginal product of labor to MPN = E(360 - 4N)/30.How would your answers to parts (a)and (b)change?

The marginal product of labor is MPN = E(400 - 4N)/30.
(a)What is the efficiency wage?
(b)How many workers will the firm hire?
(c)Suppose an adverse productivity shock reduces the marginal product of labor to MPN = E(360 - 4N)/30.How would your answers to parts (a)and (b)change?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A model in which individual producers act as price setters,because there are only a few sellers and the product they sell is not standardized,is called
A)imperfect competition.
B)perfect competition.
C)monopoly.
D)monopsony.
A)imperfect competition.
B)perfect competition.
C)monopoly.
D)monopsony.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Describe the empirical research on the stickiness of prices.Given some doubt on how sticky prices are,why is it nevertheless useful for the Keynesian model to assume that prices are sticky,especially when analyzing monetary policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the Keynesian model in the long run,an increase in the money supply will cause
A)an increase in output and a decrease in the real interest rate.
B)a decrease in the real interest rate but no change in output.
C)an increase in the real interest rate and an increase in output.
D)no change in either the real interest rate or output.
A)an increase in output and a decrease in the real interest rate.
B)a decrease in the real interest rate but no change in output.
C)an increase in the real interest rate and an increase in output.
D)no change in either the real interest rate or output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Using the Keynesian model,the effect of a decrease in the effective tax rate on capital would be to cause ________ in the real interest rate and ________ in output in the short run.
A)a decrease; a decrease
B)a decrease; no change
C)an increase; an increase
D)no change; a decrease
A)a decrease; a decrease
B)a decrease; no change
C)an increase; an increase
D)no change; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the Keynesian model in the long run,an increase in the money supply will raise
A)the price level but not the level of output.
B)the level of output but not the price level.
C)both the level of output and the price level.
D)neither the level of output nor the price level.
A)the price level but not the level of output.
B)the level of output but not the price level.
C)both the level of output and the price level.
D)neither the level of output nor the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Using the Keynesian model,the effect of an increase in the effective tax rate on capital would be to cause ________ in the real interest rate and ________ in output in the short run.
A)a decrease; a decrease
B)a decrease; no change
C)an increase; an increase
D)no change; a decrease
A)a decrease; a decrease
B)a decrease; no change
C)an increase; an increase
D)no change; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Using the Keynesian model,the effect of a decrease in the effective tax rate on capital would be to cause ________ in the real interest rate and ________ in output in the long run.
A)an increase; no change
B)a decrease; no change
C)an increase; an increase
D)no change; a decrease
A)an increase; no change
B)a decrease; no change
C)an increase; an increase
D)no change; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the Keynesian model,which curve is vertical?
A)LRAS
B)SRAS
C)AD
D)NS
A)LRAS
B)SRAS
C)AD
D)NS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the Keynesian model in the short run,what is likely to happen to employment after each of the following shocks?
(a)An increase in taxes
(b)An increase in consumer spending generated by a reduced desire for saving
(c)An increase in the money supply
(a)An increase in taxes
(b)An increase in consumer spending generated by a reduced desire for saving
(c)An increase in the money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the Keynesian model,when the economy is not in long-run equilibrium,then the short-run equilibrium point is not on which curve?
A)SRAS
B)FE
C)IS
D)LM
A)SRAS
B)FE
C)IS
D)LM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the Keynesian model in the short run,a decrease in the money supply will cause
A)a decrease in output and an increase in the real interest rate.
B)an increase in the real interest rate but no change in output.
C)a decrease in the real interest rate and a decrease in output.
D)no change in either the real interest rate or output.
A)a decrease in output and an increase in the real interest rate.
B)an increase in the real interest rate but no change in output.
C)a decrease in the real interest rate and a decrease in output.
D)no change in either the real interest rate or output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the Keynesian model in the long run,a decrease in the money supply will cause ________ in the real interest rate and ________ in the price level.
A)an increase; an increase
B)a decrease; a decrease
C)no change; an increase
D)no change; a decrease
A)an increase; an increase
B)a decrease; a decrease
C)no change; an increase
D)no change; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the Keynesian model in the long run,a decrease in the money supply will cause
A)a decrease in output and an increase in the real interest rate.
B)an increase in the real interest rate but no change in output.
C)a decrease in the real interest rate and a decrease in output.
D)no change in either the real interest rate or output.
A)a decrease in output and an increase in the real interest rate.
B)an increase in the real interest rate but no change in output.
C)a decrease in the real interest rate and a decrease in output.
D)no change in either the real interest rate or output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the Keynesian model in the short run,the amount of employment is determined by the effective labor demand curve and the level of
A)prices.
B)output.
C)the real interest rate.
D)the supply of labor.
A)prices.
B)output.
C)the real interest rate.
D)the supply of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the Keynesian model in the short run,an increase in the money supply will cause
A)an increase in output and a decrease in the real interest rate.
B)a decrease in the real interest rate but no change in output.
C)an increase in the real interest rate and an increase in output.
D)no change in either the real interest rate or output.
A)an increase in output and a decrease in the real interest rate.
B)a decrease in the real interest rate but no change in output.
C)an increase in the real interest rate and an increase in output.
D)no change in either the real interest rate or output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the Keynesian model in the short run,a decrease in government purchases causes output to ________ and the real interest rate to ________.
A)fall; rise
B)fall; fall
C)rise; rise
D)rise; fall
A)fall; rise
B)fall; fall
C)rise; rise
D)rise; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
According to Keynesians,the primary reason money is not neutral is
A)rational expectations.
B)price stickiness.
C)reverse causation.
D)misperceptions over the aggregate price level.
A)rational expectations.
B)price stickiness.
C)reverse causation.
D)misperceptions over the aggregate price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the Keynesian model,money is
A)neutral in both the short run and the long run.
B)neutral in neither the short run nor the long run.
C)neutral in the short run, but not in the long run.
D)neutral in the long run, but not in the short run.
A)neutral in both the short run and the long run.
B)neutral in neither the short run nor the long run.
C)neutral in the short run, but not in the long run.
D)neutral in the long run, but not in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Using the Keynesian model,the effect of a government-imposed ceiling on interest rates paid on personal checking accounts that is lower than the current market interest rate would be to cause ________ in the real interest rate and ________ in output in the short run.
A)a decrease; a decrease
B)a decrease; no change
C)a decrease; an increase
D)an increase; a decrease
A)a decrease; a decrease
B)a decrease; no change
C)a decrease; an increase
D)an increase; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the Keynesian model,an increase in government purchases affects output by
A)increasing labor supply, because workers feel effectively poorer.
B)increasing saving to pay for future taxes, lowering the real interest rate and shifting the IS curve to the left.
C)increasing the real interest rate due to crowding out, reducing aggregate demand.
D)increasing aggregate demand as national saving declines.
A)increasing labor supply, because workers feel effectively poorer.
B)increasing saving to pay for future taxes, lowering the real interest rate and shifting the IS curve to the left.
C)increasing the real interest rate due to crowding out, reducing aggregate demand.
D)increasing aggregate demand as national saving declines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The distinguishing feature that determines whether an analysis is classical or Keynesian is
A)the speed of price adjustment.
B)the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
C)the degree of monopoly power in the economy.
D)the assumption about the transmission mechanism of monetary policy.
A)the speed of price adjustment.
B)the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
C)the degree of monopoly power in the economy.
D)the assumption about the transmission mechanism of monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the Keynesian model,short-run equilibrium occurs
A)where the IS and LM curves intersect.
B)where the IS curve, LM curve, and FE lines intersect.
C)where the IS curve intersects the FE line.
D)where the LM curve intersects the FE line.
A)where the IS and LM curves intersect.
B)where the IS curve, LM curve, and FE lines intersect.
C)where the IS curve intersects the FE line.
D)where the LM curve intersects the FE line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The following equations describe a Keynesian model of the economy.
Cd = 500 + 0.5(Y - T)- 100r
Id = 350 - 100r
L = 0.5Y - 200i
πe = 0.05,G = T = 200,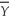 = 1850
= 1850
M = 3560
(a)Find the full-employment equilibrium values of the real interest rate,consumption,investment,and the price level.
(b)Suppose government purchases decline to 175,with no change in taxes.What happens to the real interest rate,output,consumption,and investment in the short run (in which the price level is fixed)? What happens in the long run to the real interest rate,consumption,investment,and the price level?
(c)Suppose instead that government purchases rise to 225,with no change in taxes,starting from the equilibrium in part (a).What happens to the real interest rate,output,consumption,and investment in the short run (in which the price level is fixed)? What happens in the long run to the real interest rate,consumption,investment,and the price level?
Cd = 500 + 0.5(Y - T)- 100r
Id = 350 - 100r
L = 0.5Y - 200i
πe = 0.05,G = T = 200,
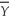 = 1850
= 1850M = 3560
(a)Find the full-employment equilibrium values of the real interest rate,consumption,investment,and the price level.
(b)Suppose government purchases decline to 175,with no change in taxes.What happens to the real interest rate,output,consumption,and investment in the short run (in which the price level is fixed)? What happens in the long run to the real interest rate,consumption,investment,and the price level?
(c)Suppose instead that government purchases rise to 225,with no change in taxes,starting from the equilibrium in part (a).What happens to the real interest rate,output,consumption,and investment in the short run (in which the price level is fixed)? What happens in the long run to the real interest rate,consumption,investment,and the price level?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the Keynesian model in the long run,an increase in taxes causes the price level to ________ and the real interest rate to ________.
A)fall; rise
B)fall; fall
C)rise; rise
D)rise; fall
A)fall; rise
B)fall; fall
C)rise; rise
D)rise; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A Keynesian economy is described by the following equations.
Cd = 250 + 0.5(Y - T)- 250r
Id = 250 - 250r
G = 300
T = 300
L = 0.5Y - 500r + πe
M = 3000
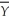 = 1250
= 1250
πe = 0
(a)Calculate the values of the real interest rate,the price level,consumption,and investment for the economy in general equilibrium.
(b)Now suppose government purchases increase to 350 with no change in taxes.What will be the real interest rate,the price level,output,consumption,and investment in the short run?
(c)What will be the real interest rate,the price level,output,consumption,and investment in the long run?
Cd = 250 + 0.5(Y - T)- 250r
Id = 250 - 250r
G = 300
T = 300
L = 0.5Y - 500r + πe
M = 3000
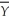 = 1250
= 1250πe = 0
(a)Calculate the values of the real interest rate,the price level,consumption,and investment for the economy in general equilibrium.
(b)Now suppose government purchases increase to 350 with no change in taxes.What will be the real interest rate,the price level,output,consumption,and investment in the short run?
(c)What will be the real interest rate,the price level,output,consumption,and investment in the long run?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Easy monetary policy and tight fiscal policy lead to
A)high real interest rates.
B)low real interest rates.
C)roughly unchanged real interest rates.
D)roughly unchanged real interest rates only when Ricardian equivalence holds; otherwise, low real interest rates.
A)high real interest rates.
B)low real interest rates.
C)roughly unchanged real interest rates.
D)roughly unchanged real interest rates only when Ricardian equivalence holds; otherwise, low real interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The Keynesian theory is consistent with the business cycle fact that inflation is
A)procyclical and leading.
B)procyclical and lagging.
C)countercyclical and leading.
D)countercyclical and lagging.
A)procyclical and leading.
B)procyclical and lagging.
C)countercyclical and leading.
D)countercyclical and lagging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Keynesians explain the procyclical behavior of average labor productivity by introducing the concept of
A)menu costs.
B)sticky prices.
C)labor hoarding.
D)sticky wages.
A)menu costs.
B)sticky prices.
C)labor hoarding.
D)sticky wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
(a)Draw a figure,using the Keynesian IS-LM framework,of an economy in recession.
(b)If the Fed's goal is to move output to its full-employment level,what should it do with monetary policy? What will happen to the real interest rate? What is the effect on the price level? Show the result in your diagram.
(c)Suppose the Fed decides to keep the money supply unchanged.How could the government use fiscal policy to move the economy to full employment? Show the result in your diagram.
(d)How does the real interest rate differ between parts (b)and (c)?
(b)If the Fed's goal is to move output to its full-employment level,what should it do with monetary policy? What will happen to the real interest rate? What is the effect on the price level? Show the result in your diagram.
(c)Suppose the Fed decides to keep the money supply unchanged.How could the government use fiscal policy to move the economy to full employment? Show the result in your diagram.
(d)How does the real interest rate differ between parts (b)and (c)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose the government decided to tighten monetary policy and decrease government expenditures.In the short run in the Keynesian model,the effect of these policies would be to ________ the real interest rate and ________ the level of output.
A)lower; decrease
B)lower; have an ambiguous effect on
C)have an ambiguous effect on; decrease
D)raise; decrease
A)lower; decrease
B)lower; have an ambiguous effect on
C)have an ambiguous effect on; decrease
D)raise; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
According to the Keynesian IS-LM model,what is the effect of each of the following on output,the real interest rate,employment,and the price level? Distinguish between the short run and the long run.
(a)Expected inflation decreases.
(b)Labor supply increases due to a change in demographics.
(c)The future marginal product of capital increases.
(a)Expected inflation decreases.
(b)Labor supply increases due to a change in demographics.
(c)The future marginal product of capital increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the Keynesian model,the difference between using monetary and fiscal policy to eliminate a recession is that
A)monetary policy will eliminate a recession quicker than fiscal policy will.
B)fiscal policy will eliminate a recession quicker than monetary policy will.
C)an expansionary monetary policy will leave the economy with a lower real interest rate than an expansionary fiscal policy.
D)an expansionary fiscal policy will leave the economy with a lower real interest rate than an expansionary monetary policy.
A)monetary policy will eliminate a recession quicker than fiscal policy will.
B)fiscal policy will eliminate a recession quicker than monetary policy will.
C)an expansionary monetary policy will leave the economy with a lower real interest rate than an expansionary fiscal policy.
D)an expansionary fiscal policy will leave the economy with a lower real interest rate than an expansionary monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose the government decided to ease monetary policy,then increase taxes.In the short run in the Keynesian model,the effect of these policies would be to ________ the real interest rate and ________ the level of output.
A)lower; increase
B)lower; decrease
C)lower; have an ambiguous effect on
D)have an ambiguous effect on; increase
A)lower; increase
B)lower; decrease
C)lower; have an ambiguous effect on
D)have an ambiguous effect on; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Keynesians believe that the most important shocks for affecting the business cycle are
A)productivity shocks.
B)aggregate supply shocks.
C)aggregate demand shocks.
D)government spending shocks.
A)productivity shocks.
B)aggregate supply shocks.
C)aggregate demand shocks.
D)government spending shocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The use of macroeconomic policies to smooth or moderate the business cycle is known as
A)aggregate demand management.
B)aggregate supply management.
C)automatic stabilization.
D)discretionary policy.
A)aggregate demand management.
B)aggregate supply management.
C)automatic stabilization.
D)discretionary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The idea that firms retain some workers in a recession,whom they would otherwise lay off,to avoid the costs of hiring and training,is called
A)the gift exchange motive.
B)worker pooling.
C)labor hoarding.
D)union busting.
A)the gift exchange motive.
B)worker pooling.
C)labor hoarding.
D)union busting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose the economy's production function is Y = A(300N - N2).The marginal product of labor is MPN = A(300 - 2N).Suppose that A = 10.The supply of labor is NS = 0.05w + 0.005G.
(a)If G is 26,000,what are the real wage,employment,and output?
(b)If G rises to 26,400,what are the real wage,employment,and output?
(c)If G falls to 25,600,what are the real wage,employment,and output?
(d)In cases (b)and (c),what is the government purchases multiplier; that is,what is the change in output divided by the change in government purchases?
(a)If G is 26,000,what are the real wage,employment,and output?
(b)If G rises to 26,400,what are the real wage,employment,and output?
(c)If G falls to 25,600,what are the real wage,employment,and output?
(d)In cases (b)and (c),what is the government purchases multiplier; that is,what is the change in output divided by the change in government purchases?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
(a)Draw a figure,using the Keynesian IS-LM framework,of an economy in recession.
(b)Now suppose the IS curve shifts up and to the right far enough that if the real interest rate is unchanged,output will increase beyond full employment.If the Fed's goal is to move output to its full-employment level,what must happen to the real interest rate? What is the effect on the price level?
(c)Suppose,before the Fed can act,that the government announces a restrictive fiscal policy,shifting the IS curve down and to the left relative to its position in part (b)What is the Fed likely to do (relative to what it would do if fiscal policy wasn't restrictive)if its goal is to target full-employment output? What happens to the real interest rate relative to what it is in part (b)?
(b)Now suppose the IS curve shifts up and to the right far enough that if the real interest rate is unchanged,output will increase beyond full employment.If the Fed's goal is to move output to its full-employment level,what must happen to the real interest rate? What is the effect on the price level?
(c)Suppose,before the Fed can act,that the government announces a restrictive fiscal policy,shifting the IS curve down and to the left relative to its position in part (b)What is the Fed likely to do (relative to what it would do if fiscal policy wasn't restrictive)if its goal is to target full-employment output? What happens to the real interest rate relative to what it is in part (b)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The 1980s were characterized by ________ monetary policy and ________ fiscal policy.
A)tight; easy
B)tight; tight
C)easy; easy
D)easy; tight
A)tight; easy
B)tight; tight
C)easy; easy
D)easy; tight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A monopolistically competitive firm prices its product using the markup pricing formula P = 1.25MC,where MC is the marginal cost of producing an additional unit.Suppose the demand for the firm's product is given by Q = 2000 - 0.1P,so the revenue from selling Q units of the product is PQ = 2000P - 0.1P2.
(a)If the marginal cost of producing each unit of the product is $10,000,calculate the price of the product,the quantity produced,and the firm's revenues,costs,and profits.
(b)Now suppose the marginal cost rises to $11,000.The firm can keep the price of the product unchanged,or it can change the product's price at a total cost of $700,000.Calculate the price,quantity,revenues,costs,and profits as in part (a)both for changing the price and leaving the price unchanged.Should the firm change the price of its product?
(a)If the marginal cost of producing each unit of the product is $10,000,calculate the price of the product,the quantity produced,and the firm's revenues,costs,and profits.
(b)Now suppose the marginal cost rises to $11,000.The firm can keep the price of the product unchanged,or it can change the product's price at a total cost of $700,000.Calculate the price,quantity,revenues,costs,and profits as in part (a)both for changing the price and leaving the price unchanged.Should the firm change the price of its product?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
According to the Keynesian IS-LM model,what is the effect of each of the following on output,the real interest rate,employment,and the price level? Distinguish between the short run and the long run.
(a)Expected inflation rises.
(b)Wealth increases.
(c)Labor supply decreases due to a change in demographics.
(d)The future marginal product of capital decreases.
(a)Expected inflation rises.
(b)Wealth increases.
(c)Labor supply decreases due to a change in demographics.
(d)The future marginal product of capital decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
According to Keynesians,the primary source of business cycle fluctuations is
A)aggregate demand shocks.
B)productivity shocks.
C)oil price shocks.
D)consumer confidence shocks.
A)aggregate demand shocks.
B)productivity shocks.
C)oil price shocks.
D)consumer confidence shocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



