Deck 15: Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/306
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Monopoly
1
Which of the following are necessary characteristics of a monopoly? (i) The firm is the sole seller of its product.
(ii) The firm's product does not have close substitutes.
(iii) The firm generates a large economic profit.
(iv) The firm is located in a small geographic market.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(i) and (iii)
C)(ii) and (iv)
D)(i), (ii), and (iii)
(ii) The firm's product does not have close substitutes.
(iii) The firm generates a large economic profit.
(iv) The firm is located in a small geographic market.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(i) and (iii)
C)(ii) and (iv)
D)(i), (ii), and (iii)
A
2
Natural monopolies differ from other forms of monopoly because they
A)are not subject to barriers to entry.
B)are not regulated by government.
C)generally don't make a profit.
D)are generally not worried about competition eroding their monopoly position in the market.
A)are not subject to barriers to entry.
B)are not regulated by government.
C)generally don't make a profit.
D)are generally not worried about competition eroding their monopoly position in the market.
D
3
A monopoly's marginal cost will
A)be less than its average fixed cost.
B)be less than the price per unit of its product.
C)exceed its marginal revenue.
D)equal its average total cost.
A)be less than its average fixed cost.
B)be less than the price per unit of its product.
C)exceed its marginal revenue.
D)equal its average total cost.
B
4
Which of the following statements is (are)true of a monopoly? (i) A monopoly has the ability to set the price of its product at whatever level it desires.
(ii) A monopoly's total revenue will always increase when it increases the price of its product.
(iii) A monopoly can earn unlimited profits.
A)(i) only
B)(ii) only
C)(i) and (ii)
D)(ii) and (iii)
(ii) A monopoly's total revenue will always increase when it increases the price of its product.
(iii) A monopoly can earn unlimited profits.
A)(i) only
B)(ii) only
C)(i) and (ii)
D)(ii) and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Angelo is a wholesale meatball distributor.He sells his meatballs to all the finest Italian restaurants in town.Nobody can make meatballs like Angelo.As a result,his is the only business in town that sells meatballs to restaurants.Assuming that Angelo is maximizing his profit,which of the following statements is true?
A)Meatball prices will be less than marginal cost.
B)Meatball prices will equal marginal cost.
C)Meatball prices will exceed marginal cost.
D)Meatball prices will be a function of supply and demand and will therefore oscillate around marginal costs.
A)Meatball prices will be less than marginal cost.
B)Meatball prices will equal marginal cost.
C)Meatball prices will exceed marginal cost.
D)Meatball prices will be a function of supply and demand and will therefore oscillate around marginal costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An industry is a natural monopoly when (i) the government assists the firm in maintaining the monopoly.
(ii) a single firm owns a key resource.
(iii) a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market at a smaller cost than could two or more firms.
A)(ii) only
B)(iii) only
C)(i) and (ii)
D)(ii) and (iii)
(ii) a single firm owns a key resource.
(iii) a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market at a smaller cost than could two or more firms.
A)(ii) only
B)(iii) only
C)(i) and (ii)
D)(ii) and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The simplest way for a monopoly to arise is for a single firm to
A)decrease its price below its competitors' prices.
B)decrease production to increase demand for its product.
C)make pricing decisions jointly with other firms.
D)own a key resource.
A)decrease its price below its competitors' prices.
B)decrease production to increase demand for its product.
C)make pricing decisions jointly with other firms.
D)own a key resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Young Johnny inherited the only local cable TV company in town after his father passed away.The company is completely unregulated by the government and is therefore free to operate as it wishes.Assuming that Johnny understands the true power of his new monopoly,he is probably most excited about which of the following statements? (i) He will be able to set the price of cable TV service at whatever level he wishes.
(ii) The customers will be forced to purchase cable TV service at whatever price he wants to set.
(iii) He will be able to achieve any profit level that he desires.
A)(i) only
B)(ii) only
C)(i) and (iii)
D)All of the above are correct.
(ii) The customers will be forced to purchase cable TV service at whatever price he wants to set.
(iii) He will be able to achieve any profit level that he desires.
A)(i) only
B)(ii) only
C)(i) and (iii)
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is an example of a barrier to entry? (i) A key resource is owned by a single firm.
(ii) The costs of production make a single producer more efficient than a large number of producers.
(iii) The government has given the existing monopoly the exclusive right to produce the good.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(ii) and (iii)
C)(i) only
D)All of the above are examples of barriers to entry.
(ii) The costs of production make a single producer more efficient than a large number of producers.
(iii) The government has given the existing monopoly the exclusive right to produce the good.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(ii) and (iii)
C)(i) only
D)All of the above are examples of barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A fundamental source of monopoly market power arises from
A)perfectly elastic demand.
B)perfectly inelastic demand.
C)barriers to entry.
D)availability of "free" natural resources, such as water or air.
A)perfectly elastic demand.
B)perfectly inelastic demand.
C)barriers to entry.
D)availability of "free" natural resources, such as water or air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Allowing an inventor to have the exclusive rights to market her new invention will lead to (i) a product that is priced higher than it would be without the exclusive rights.
(ii) desirable behavior in the sense that inventors are encouraged to invent.
(iii) higher profits for the inventor.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(ii) and (iii)
C)(i) and (iii)
D)(i), (ii), and (iii)
(ii) desirable behavior in the sense that inventors are encouraged to invent.
(iii) higher profits for the inventor.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(ii) and (iii)
C)(i) and (iii)
D)(i), (ii), and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The defining characteristic of a natural monopoly is
A)constant marginal cost over the relevant range of output.
B)economies of scale over the relevant range of output.
C)constant returns to scale over the relevant range of output.
D)diseconomies of scale over the relevant range of output.
A)constant marginal cost over the relevant range of output.
B)economies of scale over the relevant range of output.
C)constant returns to scale over the relevant range of output.
D)diseconomies of scale over the relevant range of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Patent and copyright laws are major sources of
A)natural monopolies.
B)government-created monopolies.
C)resource monopolies.
D)antitrust regulation.
A)natural monopolies.
B)government-created monopolies.
C)resource monopolies.
D)antitrust regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)A competitive firm is a price maker and a monopoly is a price taker.
B)A competitive firm is a price taker and a monopoly is a price maker.
C)Both competitive firms and monopolies are price takers.
D)Both competitive firms and monopolies are price makers.
A)A competitive firm is a price maker and a monopoly is a price taker.
B)A competitive firm is a price taker and a monopoly is a price maker.
C)Both competitive firms and monopolies are price takers.
D)Both competitive firms and monopolies are price makers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A natural monopoly occurs when
A)the product is sold in its natural state (such as water or diamonds).
B)there are economies of scale over the relevant range of output.
C)the firm is characterized by a rising marginal cost curve.
D)production requires the use of free natural resources, such as water or air.
A)the product is sold in its natural state (such as water or diamonds).
B)there are economies of scale over the relevant range of output.
C)the firm is characterized by a rising marginal cost curve.
D)production requires the use of free natural resources, such as water or air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Because monopoly firms do not have to compete with other firms,the outcome in a market with a monopoly is often
A)not in the best interest of society.
B)one that fails to maximize total economic well-being.
C)inefficient.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)not in the best interest of society.
B)one that fails to maximize total economic well-being.
C)inefficient.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Encouraging firms to invest in research and development and individuals to engage in creative endeavors such as writing novels is one justification for
A)resource monopolies.
B)natural monopolies.
C)government-created monopolies.
D)breaking up monopolies into smaller firms.
A)resource monopolies.
B)natural monopolies.
C)government-created monopolies.
D)breaking up monopolies into smaller firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When a natural monopoly exists,it is
A)always cost effective for government-owned firms to produce the product.
B)never cost effective for one firm to produce the product.
C)always cost effective for two or more private firms to produce the product.
D)never cost effective for two or more private firms to produce the product.
A)always cost effective for government-owned firms to produce the product.
B)never cost effective for one firm to produce the product.
C)always cost effective for two or more private firms to produce the product.
D)never cost effective for two or more private firms to produce the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A government-created monopoly arises when
A)government spending in a certain industry gives rise to monopoly power.
B)the government exercises its market control by encouraging competition among sellers.
C)the government gives a firm the exclusive right to sell some good or service.
D)Both a and c are correct.
A)government spending in a certain industry gives rise to monopoly power.
B)the government exercises its market control by encouraging competition among sellers.
C)the government gives a firm the exclusive right to sell some good or service.
D)Both a and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When a firm's average total cost curve continually declines,the firm is a
A)government-created monopoly.
B)natural monopoly.
C)revenue monopoly.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)government-created monopoly.
B)natural monopoly.
C)revenue monopoly.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure 15-1
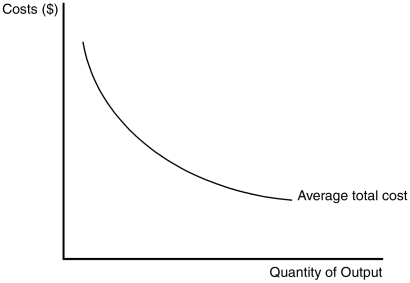
Refer to Figure 15-1.The shape of the average total cost curve reveals information about the nature of the barrier to entry that might exist in a monopoly market.Which of the following monopoly types best coincides with the figure?
A)Ownership of a key resource by a single firm
B)Natural monopoly
C)Government-created monopoly
D)A patent or copyright monopoly

Refer to Figure 15-1.The shape of the average total cost curve reveals information about the nature of the barrier to entry that might exist in a monopoly market.Which of the following monopoly types best coincides with the figure?
A)Ownership of a key resource by a single firm
B)Natural monopoly
C)Government-created monopoly
D)A patent or copyright monopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Additional firms often do not try to compete with a natural monopoly because
A)they fear retaliation in the form of pricing wars from the natural monopolist.
B)they are unsure of the size of the market in general.
C)they know they cannot achieve the same low costs that the monopolist enjoys.
D)the natural monopoly doesn't make a huge profit.
A)they fear retaliation in the form of pricing wars from the natural monopolist.
B)they are unsure of the size of the market in general.
C)they know they cannot achieve the same low costs that the monopolist enjoys.
D)the natural monopoly doesn't make a huge profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Scenario 15-1
Consider a transportation corporation named C.R. Evans that has just completed the development of a new subway system in a medium-sized town in the Northwest. Currently, there are plenty of seats on the subway, and it is never crowded. Its capacity far exceeds the needs of the city. After just a few years of operation, the shareholders of C.R. Evans experienced incredible rates of return on their investment, due to the profitability of the corporation.
Refer to Scenario 15-1.Which of the following statements are most likely to be true? (i) New entrants to the market know they will earn a smaller piece of the market than C.R.Evans currently has.
(ii) C.R.Evans is most likely experiencing increasing average total cost.
(iii) C.R.Evans is a natural monopoly.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(ii) and (iii)
C)(i) and (iii)
D)(i), (ii), and (iii)
Consider a transportation corporation named C.R. Evans that has just completed the development of a new subway system in a medium-sized town in the Northwest. Currently, there are plenty of seats on the subway, and it is never crowded. Its capacity far exceeds the needs of the city. After just a few years of operation, the shareholders of C.R. Evans experienced incredible rates of return on their investment, due to the profitability of the corporation.
Refer to Scenario 15-1.Which of the following statements are most likely to be true? (i) New entrants to the market know they will earn a smaller piece of the market than C.R.Evans currently has.
(ii) C.R.Evans is most likely experiencing increasing average total cost.
(iii) C.R.Evans is a natural monopoly.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(ii) and (iii)
C)(i) and (iii)
D)(i), (ii), and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 15-1

Refer to Figure 15-1.The shape of the average total cost curve in the figure suggests an opportunity for a profit-maximizing monopolist to take advantage of
A)economies of scale.
B)diseconomies of scale.
C)diminishing marginal product.
D)increasing marginal cost.

Refer to Figure 15-1.The shape of the average total cost curve in the figure suggests an opportunity for a profit-maximizing monopolist to take advantage of
A)economies of scale.
B)diseconomies of scale.
C)diminishing marginal product.
D)increasing marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Drug companies are allowed to be monopolists in the drugs they discover in order to
A)allow drug companies to charge a price that is equal to their marginal cost.
B)discourage new firms from entering the drug market.
C)encourage research.
D)allow the government to earn patent revenue.
A)allow drug companies to charge a price that is equal to their marginal cost.
B)discourage new firms from entering the drug market.
C)encourage research.
D)allow the government to earn patent revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A benefit to society of the patent and copyright laws is that those laws
A)help to keep prices down.
B)help to prevent a single firm from acquiring ownership of a key resource.
C)encourage creative activity.
D)discourage excessive amounts of output of certain products.
A)help to keep prices down.
B)help to prevent a single firm from acquiring ownership of a key resource.
C)encourage creative activity.
D)discourage excessive amounts of output of certain products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The laws governing patents and copyrights
A)can lead to monopolies.
B)are intended to serve private interests, not the public interest.
C)have costs, but no benefits.
D)eliminate the need for firms to engage in research and development.
A)can lead to monopolies.
B)are intended to serve private interests, not the public interest.
C)have costs, but no benefits.
D)eliminate the need for firms to engage in research and development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Figure 15-1

Refer to Figure 15-1.Considering the relationship between average total cost and marginal cost,the marginal cost curve for this firm
A)must lie entirely above the average total cost curve.
B)must lie entirely below the average total cost curve.
C)must be upward sloping.
D)does not exist.

Refer to Figure 15-1.Considering the relationship between average total cost and marginal cost,the marginal cost curve for this firm
A)must lie entirely above the average total cost curve.
B)must lie entirely below the average total cost curve.
C)must be upward sloping.
D)does not exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The fundamental cause of monopoly is
A)incompetent management in competitive firms.
B)the zero-profit feature of long-run equilibrium in competitive markets.
C)advertising.
D)barriers to entry.
A)incompetent management in competitive firms.
B)the zero-profit feature of long-run equilibrium in competitive markets.
C)advertising.
D)barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When a firm has a natural monopoly,the firm's
A)marginal cost always exceeds its average total cost.
B)total cost curve is horizontal.
C)average total cost curve is downward sloping.
D)marginal cost curve must lie above the firm's average total cost curve.
A)marginal cost always exceeds its average total cost.
B)total cost curve is horizontal.
C)average total cost curve is downward sloping.
D)marginal cost curve must lie above the firm's average total cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Scenario 15-1
Consider a transportation corporation named C.R. Evans that has just completed the development of a new subway system in a medium-sized town in the Northwest. Currently, there are plenty of seats on the subway, and it is never crowded. Its capacity far exceeds the needs of the city. After just a few years of operation, the shareholders of C.R. Evans experienced incredible rates of return on their investment, due to the profitability of the corporation.
Refer to Scenario 15-1.C.R.Evans will continue to be a monopolist in the subway transportation industry only if
A)population growth leads to an overcrowding of the subway cars.
B)there are no new entrants to the market.
C)demand for transportation services decreases.
D)All of the above are correct.
Consider a transportation corporation named C.R. Evans that has just completed the development of a new subway system in a medium-sized town in the Northwest. Currently, there are plenty of seats on the subway, and it is never crowded. Its capacity far exceeds the needs of the city. After just a few years of operation, the shareholders of C.R. Evans experienced incredible rates of return on their investment, due to the profitability of the corporation.
Refer to Scenario 15-1.C.R.Evans will continue to be a monopolist in the subway transportation industry only if
A)population growth leads to an overcrowding of the subway cars.
B)there are no new entrants to the market.
C)demand for transportation services decreases.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A firm that is a natural monopoly
A)is not likely to be concerned about new entrants eroding its monopoly power.
B)is taking advantage of economies of scale.
C)would experience a higher average total cost if more firms entered the market.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)is not likely to be concerned about new entrants eroding its monopoly power.
B)is taking advantage of economies of scale.
C)would experience a higher average total cost if more firms entered the market.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose most people regard emeralds,rubies,and sapphires as close substitutes for diamonds.Then DeBeers,a large diamond company,has
A)less incentive to advertise than it would otherwise have.
B)less market power than it would otherwise have.
C)more control over the price of diamonds than it would otherwise have.
D)higher profits than it would otherwise have.
A)less incentive to advertise than it would otherwise have.
B)less market power than it would otherwise have.
C)more control over the price of diamonds than it would otherwise have.
D)higher profits than it would otherwise have.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Authors are allowed to be monopolists in the sale of their books in order to
A)encourage authors to write more and better books.
B)correct for the negative externalities that the internet and television impose.
C)satisfy literary advocacy groups that exercise their lobbying power.
D)promote a society in which people think for themselves and learn from whichever books they please.
A)encourage authors to write more and better books.
B)correct for the negative externalities that the internet and television impose.
C)satisfy literary advocacy groups that exercise their lobbying power.
D)promote a society in which people think for themselves and learn from whichever books they please.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements is true about patents and copyrights? (i) They both have benefits and costs.
(ii) They lead to higher prices.
(iii) They enhance the ability of monopolists to earn above-average profits.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(ii) and (iii)
C)(ii) only
D)(i), (ii), and (iii)
(ii) They lead to higher prices.
(iii) They enhance the ability of monopolists to earn above-average profits.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(ii) and (iii)
C)(ii) only
D)(i), (ii), and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When a single firm can supply a product to an entire market at a smaller cost than could two or more firms,the industry is called a
A)resource industry.
B)exclusive industry.
C)government monopoly.
D)natural monopoly.
A)resource industry.
B)exclusive industry.
C)government monopoly.
D)natural monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A natural monopoly arises when
A)there are constant returns to scale over the relevant range of output.
B)there are economies of scale over the relevant range of output.
C)one firm owns a key natural resource.
D)the government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce a particular good or service.
A)there are constant returns to scale over the relevant range of output.
B)there are economies of scale over the relevant range of output.
C)one firm owns a key natural resource.
D)the government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce a particular good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When an industry is a natural monopoly,
A)it is characterized by constant returns to scale.
B)it is characterized by diseconomies of scale.
C)a larger number of firms may lead to a lower average cost.
D)a larger number of firms will lead to a higher average cost.
A)it is characterized by constant returns to scale.
B)it is characterized by diseconomies of scale.
C)a larger number of firms may lead to a lower average cost.
D)a larger number of firms will lead to a higher average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following items is a primary source of barriers to entry?
A)The costs of production make a single firm more efficient than a large number of firms.
B)A single firm hires all the people who have the management skills that are important in the industry.
C)Contracts among firms prohibit them from competing with one another in the production and sale of certain products.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)The costs of production make a single firm more efficient than a large number of firms.
B)A single firm hires all the people who have the management skills that are important in the industry.
C)Contracts among firms prohibit them from competing with one another in the production and sale of certain products.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the distribution of water is a natural monopoly,then (i) multiple firms will each have to pay large fixed costs to develop their own network of pipes.
(ii) allowing for competition among different firms in the water-distribution industry is efficient.
(iii) a single firm can serve the market at the lowest possible average total cost.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(ii) and (iii)
C)(i) and (iii)
D)(iii) only
(ii) allowing for competition among different firms in the water-distribution industry is efficient.
(iii) a single firm can serve the market at the lowest possible average total cost.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(ii) and (iii)
C)(i) and (iii)
D)(iii) only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When a firm operates under conditions of monopoly,its price is
A)not constrained.
B)constrained by marginal cost.
C)constrained by demand.
D)constrained only by its social agenda.
A)not constrained.
B)constrained by marginal cost.
C)constrained by demand.
D)constrained only by its social agenda.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A firm that is the sole seller of a product without close substitutes is
A)perfectly competitive.
B)monopolistically competitive.
C)an oligopolist
D)a monopolist
A)perfectly competitive.
B)monopolistically competitive.
C)an oligopolist
D)a monopolist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If government officials break a natural monopoly up into several smaller firms,then
A)competition will force firms to attain economic profits rather than accounting profits.
B)competition will force firms to produce surplus output, which drives up price.
C)the average costs of production will increase.
D)the average costs of production will decrease.
A)competition will force firms to attain economic profits rather than accounting profits.
B)competition will force firms to produce surplus output, which drives up price.
C)the average costs of production will increase.
D)the average costs of production will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The key difference between a competitive firm and a monopoly firm is the ability to select
A)the level of competition in the market.
B)the level of production.
C)inputs in the production process.
D)the price of its output.
A)the level of competition in the market.
B)the level of production.
C)inputs in the production process.
D)the price of its output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For a profit-maximizing monopolist,
A)P > MR = MC.
B)P = MR = MC.
C)P > MR > MC.
D)MR < MC < P.
A)P > MR = MC.
B)P = MR = MC.
C)P > MR > MC.
D)MR < MC < P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Patents grant
A)permanent monopoly status to creators of scientific inventions.
B)permanent monopoly status to creators of any intellectual property.
C)temporary monopoly status to creators of scientific inventions.
D)temporary monopoly status to creators of any intellectual property.
A)permanent monopoly status to creators of scientific inventions.
B)permanent monopoly status to creators of any intellectual property.
C)temporary monopoly status to creators of scientific inventions.
D)temporary monopoly status to creators of any intellectual property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following would be most likely to have monopoly power?
A)A long-distance telephone service provider
B)A local cable TV provider
C)A large department store
D)A gas station
A)A long-distance telephone service provider
B)A local cable TV provider
C)A large department store
D)A gas station

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A monopolist's average revenue is always
A)equal to marginal revenue.
B)greater than the price of its product.
C)equal to the price of its product.
D)less than the price of its product.
A)equal to marginal revenue.
B)greater than the price of its product.
C)equal to the price of its product.
D)less than the price of its product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In order to sell more of its product,a monopolist must
A)sell to the government.
B)sell in international markets.
C)lower its price.
D)use its market power to force up the price of complementary products.
A)sell to the government.
B)sell in international markets.
C)lower its price.
D)use its market power to force up the price of complementary products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A profit-maximizing monopolist will produce the level of output at which
A)average revenue is equal to average total cost.
B)average revenue is equal to marginal cost.
C)marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
D)total revenue is equal to opportunity cost.
A)average revenue is equal to average total cost.
B)average revenue is equal to marginal cost.
C)marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
D)total revenue is equal to opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Most markets are not monopolies in the real world because
A)firms usually face downward-sloping demand curves.
B)supply curves slope upward.
C)price is usually set equal to marginal cost by firms.
D)there are reasonable substitutes for most goods.
A)firms usually face downward-sloping demand curves.
B)supply curves slope upward.
C)price is usually set equal to marginal cost by firms.
D)there are reasonable substitutes for most goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Because a monopolist is the sole producer in its market,it can necessarily alter the price of its good (i) without affecting the quantity sold.
(ii) without affecting its average total cost.
(iii) by adjusting the quantity it supplies to the market.
A)(ii) only
B)(iii) only
C)(i) and (ii)
D)(ii) and (iii)
(ii) without affecting its average total cost.
(iii) by adjusting the quantity it supplies to the market.
A)(ii) only
B)(iii) only
C)(i) and (ii)
D)(ii) and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
For a monopolist,marginal revenue is
A)positive when the demand effect is greater than the supply effect.
B)positive when the monopoly effect is greater than the competitive effect.
C)negative when the price effect is greater than the output effect.
D)negative when the output effect is greater than the price effect.
A)positive when the demand effect is greater than the supply effect.
B)positive when the monopoly effect is greater than the competitive effect.
C)negative when the price effect is greater than the output effect.
D)negative when the output effect is greater than the price effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Sizable economic profits can persist over time under monopoly if the monopolist
A)produces that output where average total cost is at a maximum.
B)is protected by barriers to entry.
C)operates as a price taker rather than a price maker.
D)realizes revenues that exceed variable costs.
A)produces that output where average total cost is at a maximum.
B)is protected by barriers to entry.
C)operates as a price taker rather than a price maker.
D)realizes revenues that exceed variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Economists assume that monopolists behave as
A)cost minimizers.
B)profit maximizers.
C)price maximizers.
D)maximizers of social welfare.
A)cost minimizers.
B)profit maximizers.
C)price maximizers.
D)maximizers of social welfare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The market demand curve for a monopolist is typically
A)unitary elastic at the point of profit maximization.
B)downward sloping.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.
A)unitary elastic at the point of profit maximization.
B)downward sloping.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a profit-maximizing monopolist faces a downward-sloping market demand curve,its
A)average revenue is less than the price of the product.
B)average revenue is less than marginal revenue.
C)marginal revenue is less than the price of the product.
D)marginal revenue is greater than the price of the product.
A)average revenue is less than the price of the product.
B)average revenue is less than marginal revenue.
C)marginal revenue is less than the price of the product.
D)marginal revenue is greater than the price of the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is not a reason for the existence of a monopoly?
A)Sole ownership of a key resource
B)Patents
C)Copyrights
D)Diseconomies of scale
A)Sole ownership of a key resource
B)Patents
C)Copyrights
D)Diseconomies of scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A natural monopolist's ability to price its product is
A)constrained by the market demand curve.
B)constrained by market supply.
C)not affected by market demand.
D)enhanced by regulatory control of the government.
A)constrained by the market demand curve.
B)constrained by market supply.
C)not affected by market demand.
D)enhanced by regulatory control of the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When a monopolist increases the number of units it sells,there are two effects on revenue.They are the
A)demand effect and the supply effect.
B)competition effect and the cost effect.
C)competitive effect and the monopoly effect.
D)output effect and the price effect.
A)demand effect and the supply effect.
B)competition effect and the cost effect.
C)competitive effect and the monopoly effect.
D)output effect and the price effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When a monopolist increases the amount of output that it produces and sells,its average revenue
A)increases and its marginal revenue increases.
B)increases and its marginal revenue decreases.
C)decreases and its marginal revenue increases.
D)decreases and its marginal revenue decreases.
A)increases and its marginal revenue increases.
B)increases and its marginal revenue decreases.
C)decreases and its marginal revenue increases.
D)decreases and its marginal revenue decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Marginal revenue for a monopolist is computed as
A)average revenue divided by quantity sold.
B)average revenue times quantity divided by price.
C)total revenue divided by quantity sold.
D)change in total revenue per one unit increase in quantity sold.
A)average revenue divided by quantity sold.
B)average revenue times quantity divided by price.
C)total revenue divided by quantity sold.
D)change in total revenue per one unit increase in quantity sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Figure 15-2
The figure below illustrates the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm.
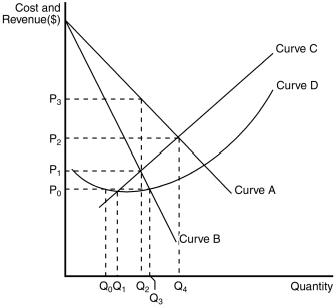
Refer to Figure 15-2.The marginal cost curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)a.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.
The figure below illustrates the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm.

Refer to Figure 15-2.The marginal cost curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)a.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Competitive firms have
A)downward-sloping demand curves and they can sell as much output as they desire at the market price.
B)downward-sloping demand curves and they can sell only a limited quantity of output at each price.
C)horizontal demand curves and they can sell as much output as they desire at the market price.
D)horizontal demand curves and they can sell only a limited quantity of output at each price.
A)downward-sloping demand curves and they can sell as much output as they desire at the market price.
B)downward-sloping demand curves and they can sell only a limited quantity of output at each price.
C)horizontal demand curves and they can sell as much output as they desire at the market price.
D)horizontal demand curves and they can sell only a limited quantity of output at each price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Table 15-1
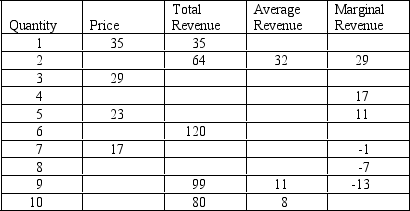
Refer to Table 15-1.What is the marginal revenue for the monopolist for the sixth unit sold?
A)3
B)5
C)11
D)17

Refer to Table 15-1.What is the marginal revenue for the monopolist for the sixth unit sold?
A)3
B)5
C)11
D)17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements is true? (i) When a competitive firm sells an additional unit of output,its revenue increases by an amount less than the price.
(ii) When a monopoly firm sells an additional unit of output,its revenue increases by an amount less than the price.
(iii) Average revenue is the same as price for both competitive and monopoly firms.
A)(ii) only
B)(iii) only
C)(i) and (ii)
D)(ii) and (iii)
(ii) When a monopoly firm sells an additional unit of output,its revenue increases by an amount less than the price.
(iii) Average revenue is the same as price for both competitive and monopoly firms.
A)(ii) only
B)(iii) only
C)(i) and (ii)
D)(ii) and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Figure 15-2
The figure below illustrates the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm.

Refer to Figure 15-2.The average total cost curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)a.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.
The figure below illustrates the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm.

Refer to Figure 15-2.The average total cost curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)a.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Marginal revenue can become negative for
A)both competitive and monopoly firms.
B)competitive firms, but not for monopoly firms.
C)monopoly firms, but not for competitive firms.
D)neither competitive nor monopoly firms.
A)both competitive and monopoly firms.
B)competitive firms, but not for monopoly firms.
C)monopoly firms, but not for competitive firms.
D)neither competitive nor monopoly firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Because many good substitutes exist for a competitive firm's product,the demand curve that it faces is
A)unit-elastic.
B)perfectly inelastic.
C)perfectly elastic.
D)inelastic only over a certain region.
A)unit-elastic.
B)perfectly inelastic.
C)perfectly elastic.
D)inelastic only over a certain region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When a monopolist decreases the price of its good,consumers
A)continue to buy the same amount.
B)buy more.
C)buy less.
D)may buy more or less, depending on the price elasticity of demand.
A)continue to buy the same amount.
B)buy more.
C)buy less.
D)may buy more or less, depending on the price elasticity of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Monopoly firms have
A)downward-sloping demand curves and they can sell as much output as they desire at the market price.
B)downward-sloping demand curves and they can sell only a limited quantity of output at each price.
C)horizontal demand curves and they can sell as much output as they desire at the market price.
D)horizontal demand curves and they can sell only a limited quantity of output at each price.
A)downward-sloping demand curves and they can sell as much output as they desire at the market price.
B)downward-sloping demand curves and they can sell only a limited quantity of output at each price.
C)horizontal demand curves and they can sell as much output as they desire at the market price.
D)horizontal demand curves and they can sell only a limited quantity of output at each price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Figure 15-2
The figure below illustrates the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm.

Refer to Figure 15-2.The marginal revenue curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)a.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.
The figure below illustrates the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm.

Refer to Figure 15-2.The marginal revenue curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)a.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For a monopoly firm,which of the following equalities is always true?
A)price = marginal revenue
B)price = average revenue
C)price = total revenue
D)marginal revenue = marginal cost
A)price = marginal revenue
B)price = average revenue
C)price = total revenue
D)marginal revenue = marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Table 15-1

Refer to Table 15-1.If the monopolist sells 8 units of its product,how much total revenue will it receive from the sale?
A)14
B)40
C)112
D)164

Refer to Table 15-1.If the monopolist sells 8 units of its product,how much total revenue will it receive from the sale?
A)14
B)40
C)112
D)164

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Figure 15-2
The figure below illustrates the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm.

Refer to Figure 15-2.The demand curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)a.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.
The figure below illustrates the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm.

Refer to Figure 15-2.The demand curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)a.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Table 15-1

Refer to Table 15-1.When 4 units of output are produced and sold,what is average revenue?
A)17
B)21
C)23
D)26

Refer to Table 15-1.When 4 units of output are produced and sold,what is average revenue?
A)17
B)21
C)23
D)26

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The marginal revenue curve for a monopoly firm starts at the same point on the vertical axis as the (i) average revenue curve.
(ii) marginal cost curve.
(iii) demand curve.
A)(i) only
B)(i) and (ii)
C)(i) and (iii)
D)(iii) only
(ii) marginal cost curve.
(iii) demand curve.
A)(i) only
B)(i) and (ii)
C)(i) and (iii)
D)(iii) only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When a monopolist increases the amount of output that it produces and sells,the price of its output
A)stays the same.
B)increases.
C)decreases.
D)may increase or decrease depending on the price elasticity of demand.
A)stays the same.
B)increases.
C)decreases.
D)may increase or decrease depending on the price elasticity of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Table 15-1

Refer to Table 15-1.Assume this monopolist's marginal cost is constant at $12.What quantity of output (Q)will it produce and what price (P)will it charge?
A)Q = 4, P = $29
B)Q = 4, P = $26
C)Q = 5, P = $23
D)Q = 7, P = $17

Refer to Table 15-1.Assume this monopolist's marginal cost is constant at $12.What quantity of output (Q)will it produce and what price (P)will it charge?
A)Q = 4, P = $29
B)Q = 4, P = $26
C)Q = 5, P = $23
D)Q = 7, P = $17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Table 15-1

Refer to Table 15-1.If the monopolist wants to maximize its revenue,how many units of its product should it sell?
A)4
B)5
C)6
D)8

Refer to Table 15-1.If the monopolist wants to maximize its revenue,how many units of its product should it sell?
A)4
B)5
C)6
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 306 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



